Abstract
1. In cats under Dial anaesthesia, Ca2+ was injected inside lumbosacral motoneurones, by passing currents between CaCl2- and KCl-containing barrels of compound micropipettes.
2. There was a reduction in excitability and a fall in membrane resistance, both rapid in onset and quickly reversible.
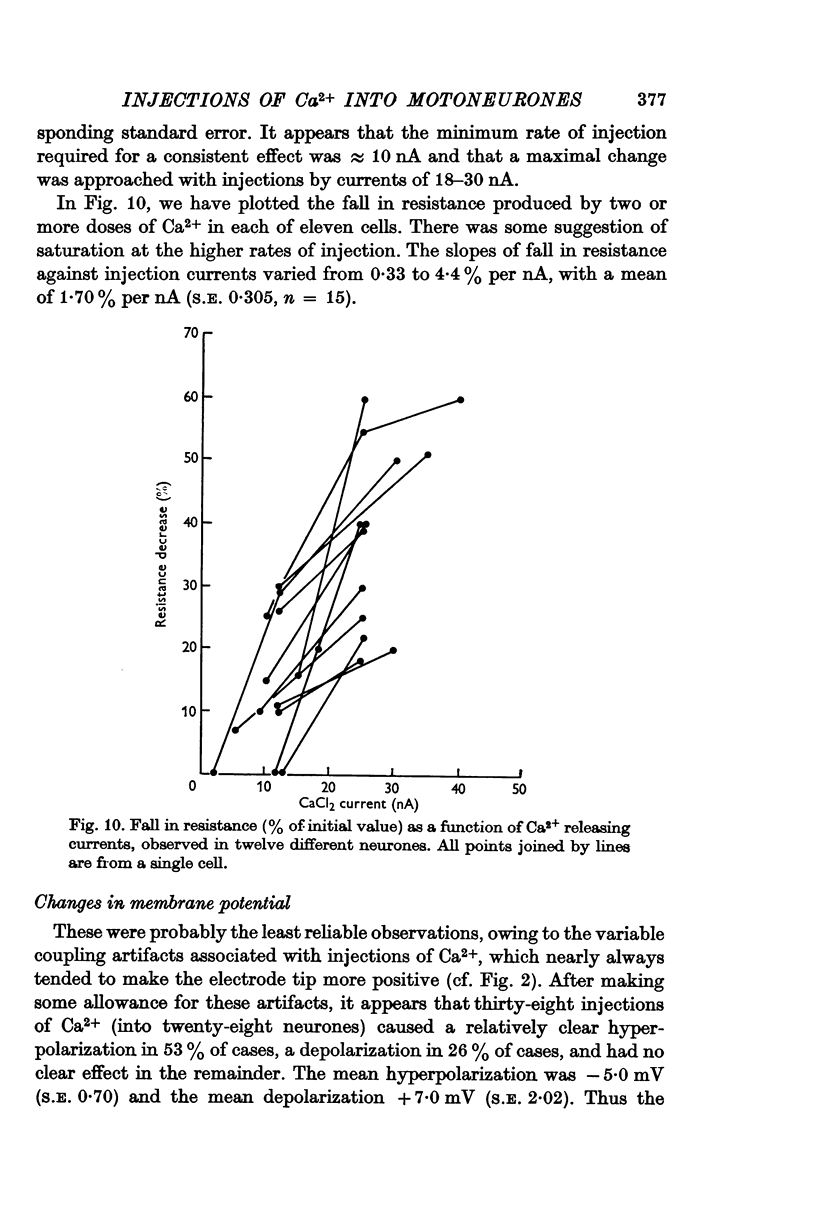
3. The minimum effective injection current was ≈ 10 nA, and the effect reached a maximum with currents of ≈ 30 nA. The mean slope of resistance change against injection current was -1·7%/nA (S.E. 0·35).
4. The most common change in membrane potential was a hyperpolarization; but in nearly half the cases, there was no clear change or a small depolarization. A reversal level for the effect of Ca2+ could be measured in five cells: on the average, it was 10 mV more negative than the resting potential.
5. Observations on i.p.s.p.s showed that Ca2+ probably does not alter gCl: it was concluded that the fall in membrane resistance caused by intracellular Ca2+ is mainly due to an increase in gK.
6. These results confirm previous suggestions that a steep transmembrane gradient of Ca2+ is essential for the maintenance of a low membrane conductivity, and that a rise in internal free Ca2+ — whether due to influx or release from internal stores — may play an important role in regulating neuronal activity.
Full text
PDF


























Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARAKI T., OTANI T. Response of single motoneurons to direct stimulation in toad's spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1955 Sep;18(5):472–485. doi: 10.1152/jn.1955.18.5.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames A., 3rd, Higashi K., Nesbett F. B. Relation of potassium concentration in choroidplexus fluid to that in plasma. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(3):506–515. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER P. F., HODGKIN A. L., SHAW T. I. Replacement of the axoplasm of giant nerve fibres with artificial solutions. J Physiol. 1962 Nov;164:330–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp007025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Hodgkin A. L., Ridgway E. B. Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):709–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B. THE ENERGY-LINKED REACTION OF CALCIUM WITH MITOCHONDRIA. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2729–2748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E., Rossi C. S. Calcium transport in mitochondria. Adv Cytopharmacol. 1971 May;1:209–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK K., FUORTES M. G. Stimulation of spinal motoneurones with intracellular electrodes. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):451–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfraind J. M., Kawamura H., Krnjević K., Pumain R. Actions of dinitrophenol and some other metabolic inhibitors on cortical neurones. J Physiol. 1971 May;215(1):199–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfraind J. M., Krnjević K., Pumain R. Unexpected features of the action of dinitrophenol on cortical neurones. Nature. 1970 Nov 7;228(5271):562–564. doi: 10.1038/228562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of calcium on the axoplasm of giant nerve fibers. J Exp Biol. 1949 Oct;26(3):292-4, pl. doi: 10.1242/jeb.26.3.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Experiments on the injection of substances into squid giant axons by means of a microsyringe. J Physiol. 1956 Mar 28;131(3):592–616. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Movements of labelled calcium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):253–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., LEWIS P. R. The intracellular calcium contents of some invertebrate nerves. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):399–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G., Somjen G. G. Effects of micro-iontophoretic administration of magnesium and calcium on neurones in the central nervous system of cats. J Neurobiol. 1969;1(2):181–195. doi: 10.1002/neu.480010206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROBERTS N. R., LEINER K. Y., WU M. L., FARR A. L., ALBERS R. W. The quantitative histochemistry of brain. III. Ammon's horn. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):39–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehninger A. L., Carafoli E., Rossi C. S. Energy-linked ion movements in mitochondrial systems. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:259–320. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehninger A. L. Mitochondria and calcium ion transport. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(2):129–138. doi: 10.1042/bj1190129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L. Effect of intracellular calcium on the potassium permeability of human red cells. J Physiol. 1970 Feb;206(2):35P–36P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Permeability of membrane junctions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):441–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D. Ammonium and chloride extrusion: hyperpolarizing synaptic inhibition in spinal motoneurons. Science. 1971 Aug 6;173(3996):555–557. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3996.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D., Pollen D. A. Electrical constants of neurons in the motor cortex of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1966 Mar;29(2):207–220. doi: 10.1152/jn.1966.29.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTZEHL H., CALDWELL P. C., RUEEGG J. C. THE DEPENDENCE OF CONTRACTION AND RELAXATION OF MUSCLE FIBRES FROM THE CRAB MAIA SQUINADO ON THE INTERNAL CONCENTRATION OF FREE CALCIUM IONS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 25;79:581–591. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSSI C. S., LEHNINGER A. L. STOICHIOMETRIC RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN ACCUMULATION OF IONS BY MITOCHONDRIA AND THE ENERGY-COUPLING SITES IN THE RESPIRATORY CHAIN. Biochem Z. 1963;338:698–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero P. J., Whittam R. The control by internal calcium of membrane permeability to sodium and potassium. J Physiol. 1971 May;214(3):481–507. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. P. The role of calcium in the release of neurotransmitter substances and hormones. Pharmacol Rev. 1970 Sep;22(3):389–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles W., Adair G. S. The Penetration of Electrolytes into Gels: The Influence of the Concentration of the Gel on the Coefficient of Diffusion of Sodium Chloride. Biochem J. 1921;15(5):620–628. doi: 10.1042/bj0150620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKII, WATANABE A., TAKENAKA T. Resting and action potential of intracellularly perfused squid giant axon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1177–1184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASINGTON F. D., MURPHY J. V. Ca ion uptake by rat kidney mitochondria and its dependence on respiration and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2670–2677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam R. Control of membrane permeability to potassium in red blood cells. Nature. 1968 Aug 10;219(5154):610–610. doi: 10.1038/219610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



