Abstract
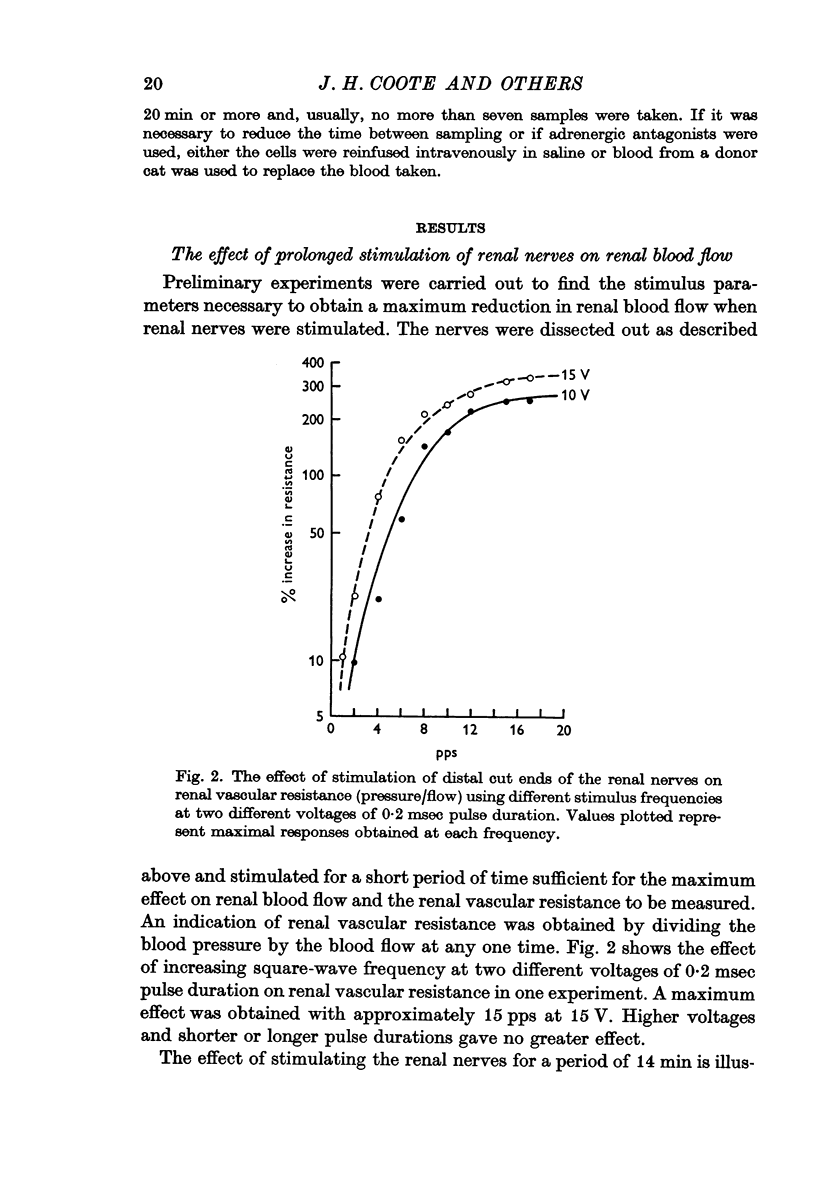
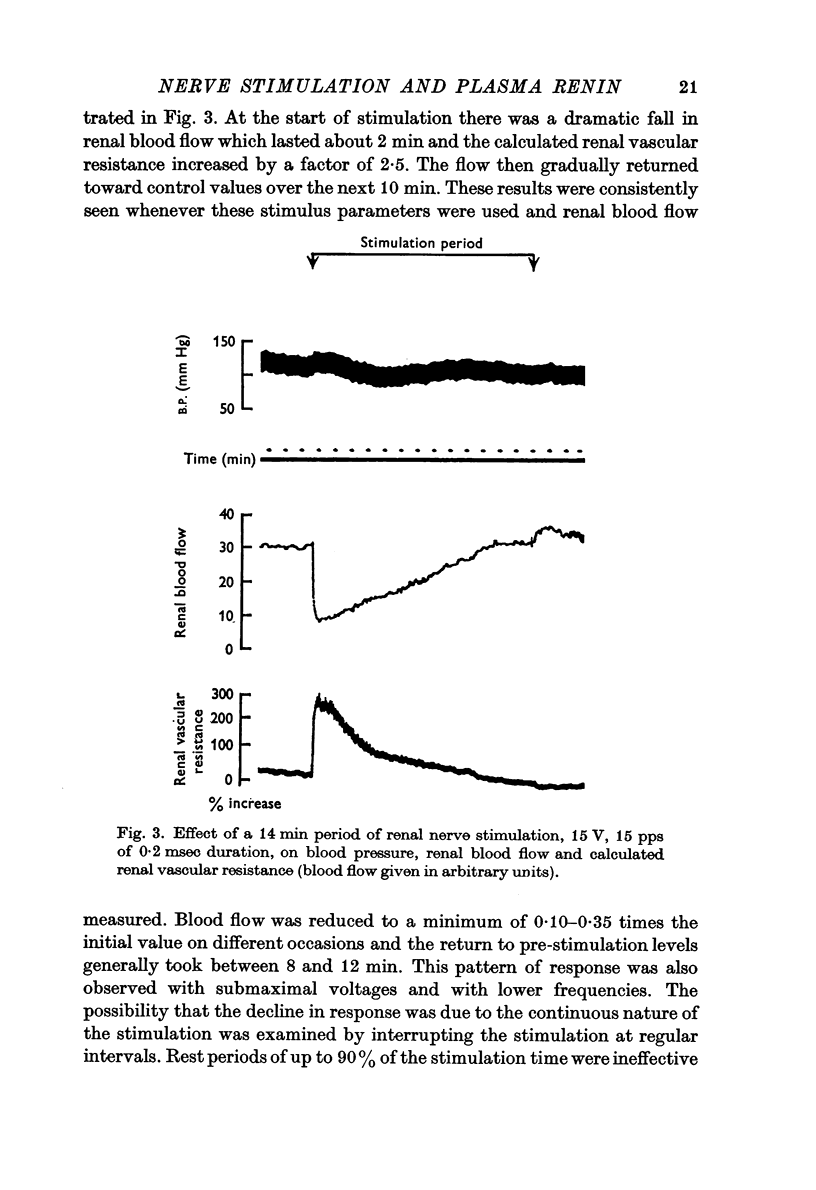
1. The effect of electrical stimulation of the distal cut ends of the renal nerves of unilaterally nephrectomized, anaesthetized cats was studied. Using stimulation parameters of 15 pulses per second (pps), 15 V and 0·2 msec duration, there was an immediate sharp drop in renal blood flow, as determined by an electromagnetic flowmeter, which was maintained for about 2 min. Flow gradually returned to control values over approximately the next 10 min in spite of continued stimulation for up to 30 min.
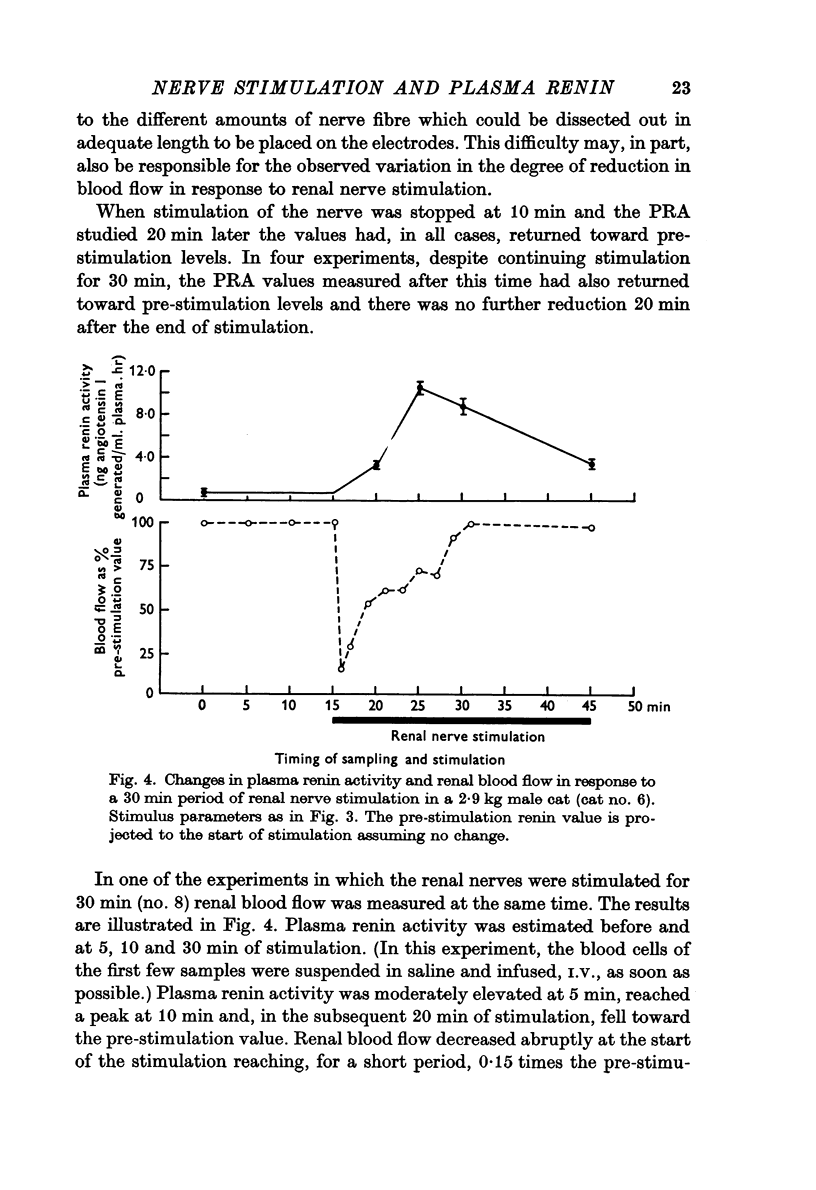
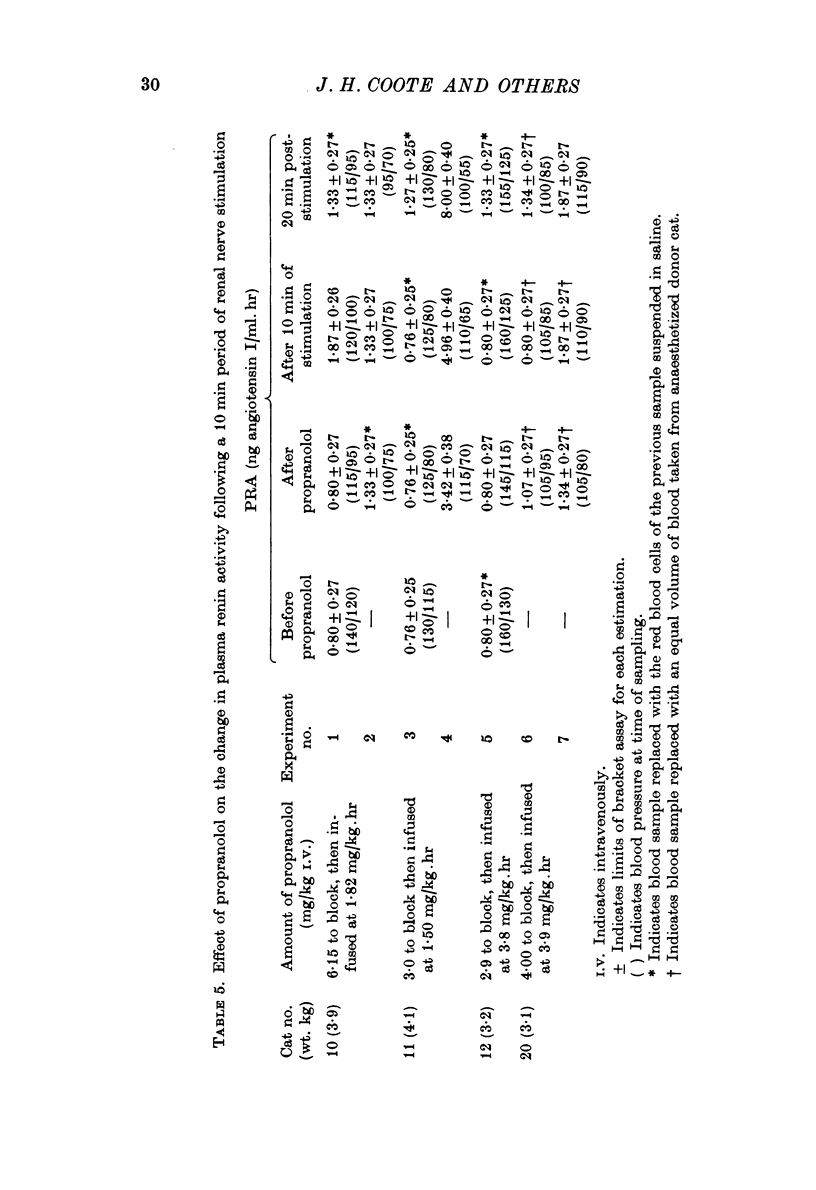
2. Plasma renin activity (PRA) increased markedly after 10 min of stimulation but 20 min later fell towards pre-stimulation values whether stimulation was maintained or not.
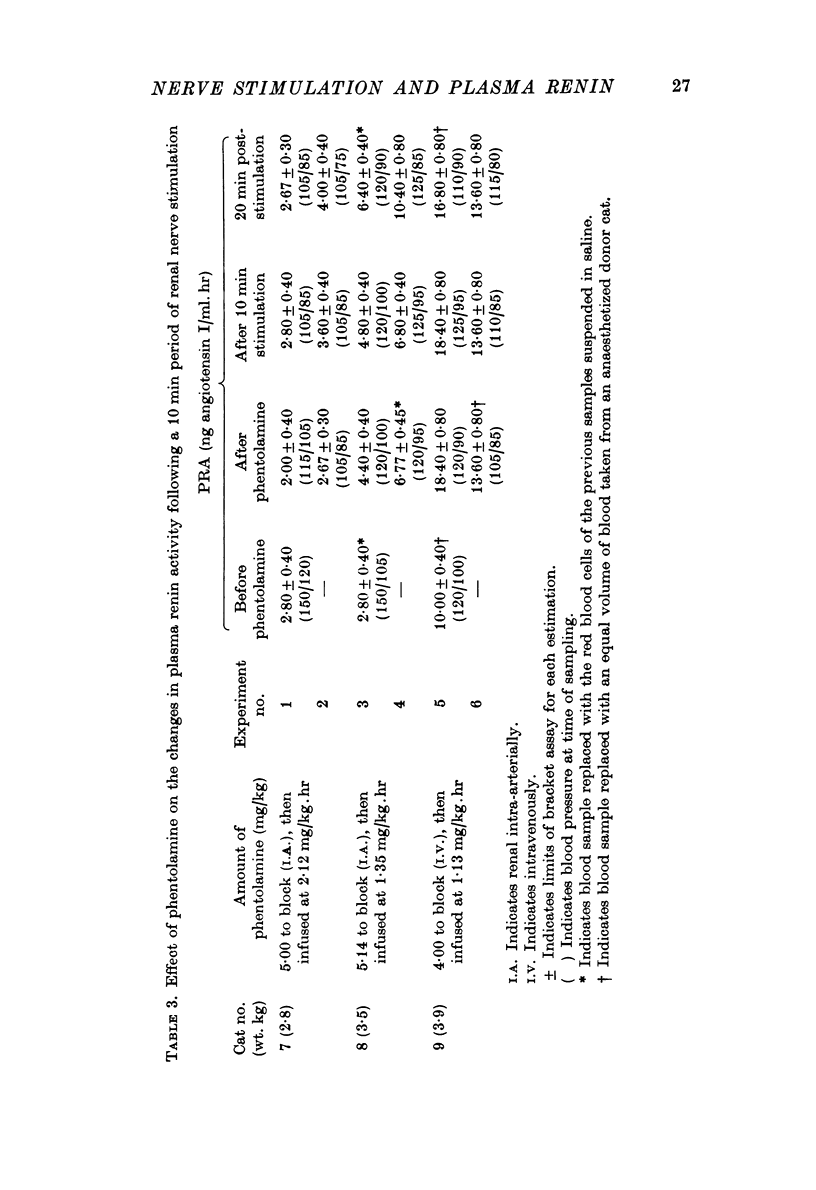
3. Phentolamine, an α-adrenergic-receptor antagonist, abolished both the blood flow and PRA responses to a 10 min period of renal nerve stimulation.
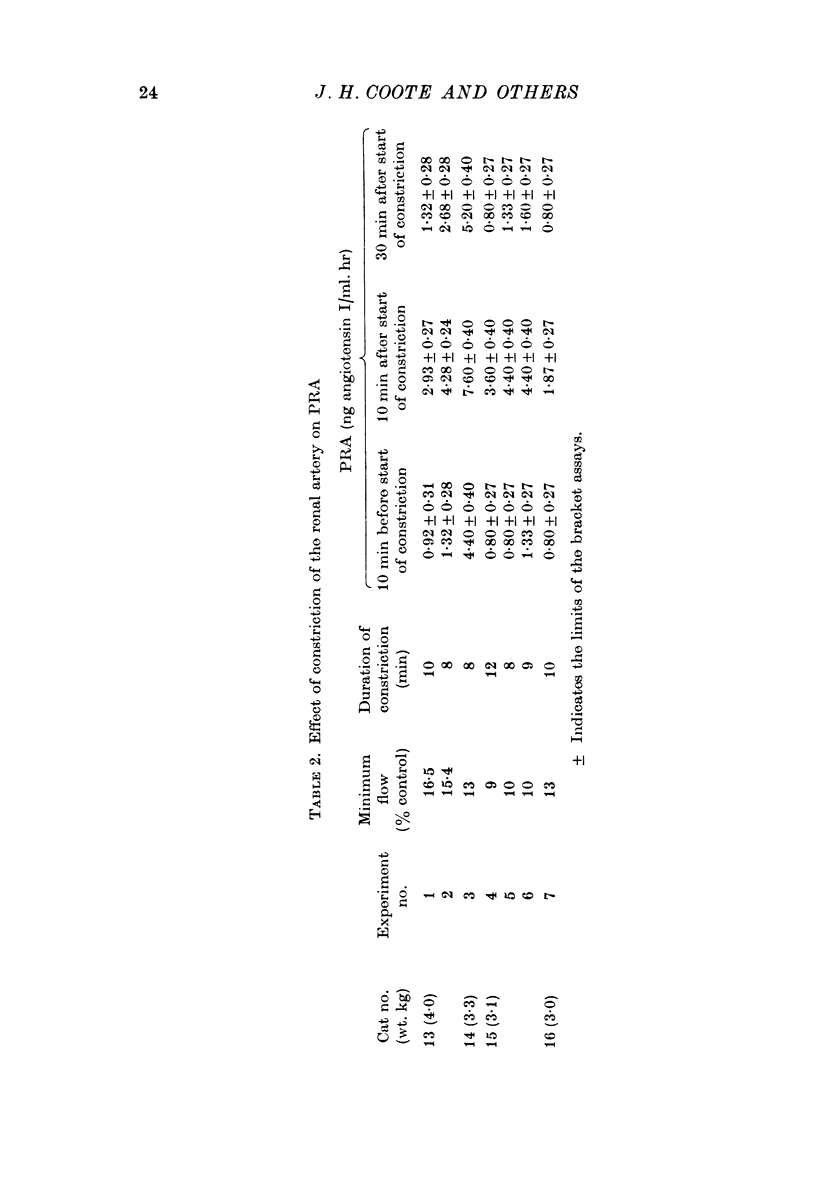
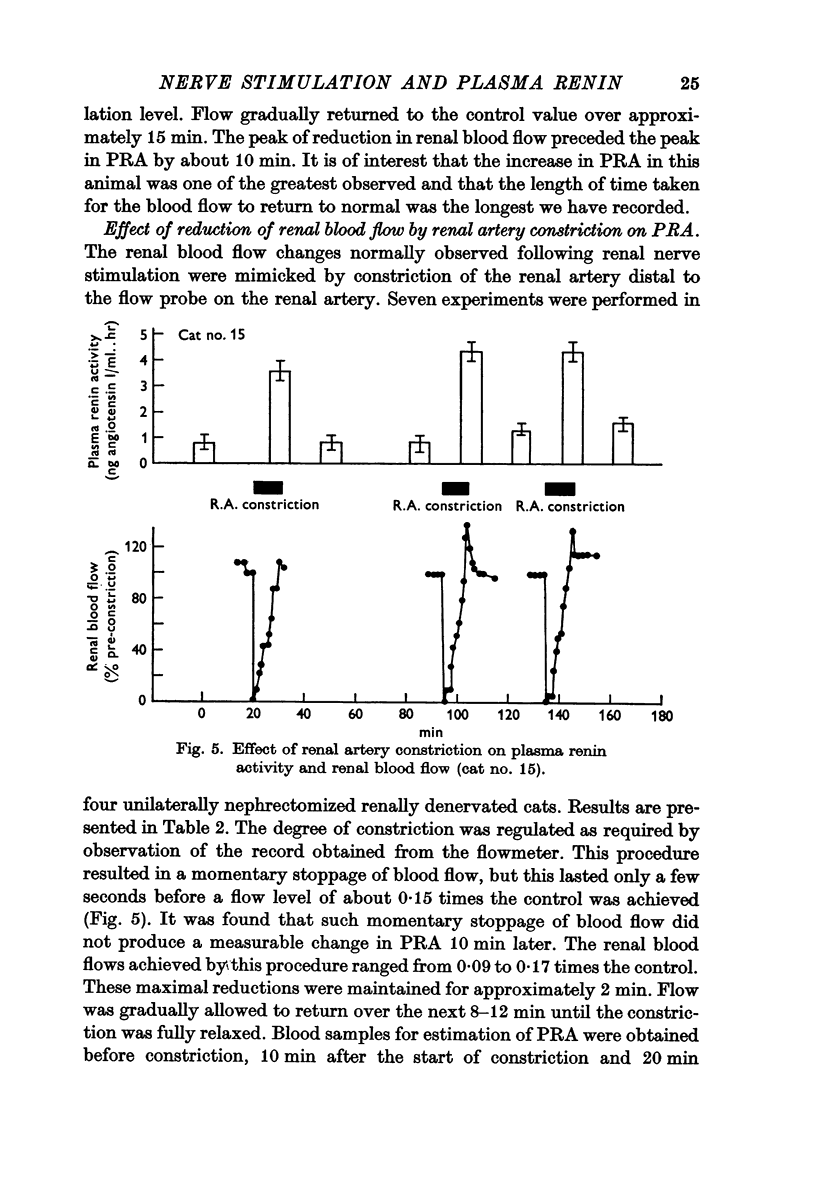
4. When the renal artery was constricted in order to produce blood flow changes similar to those found with renal nerve stimulation, the rise in PRA was similar to that observed with renal stimulation.
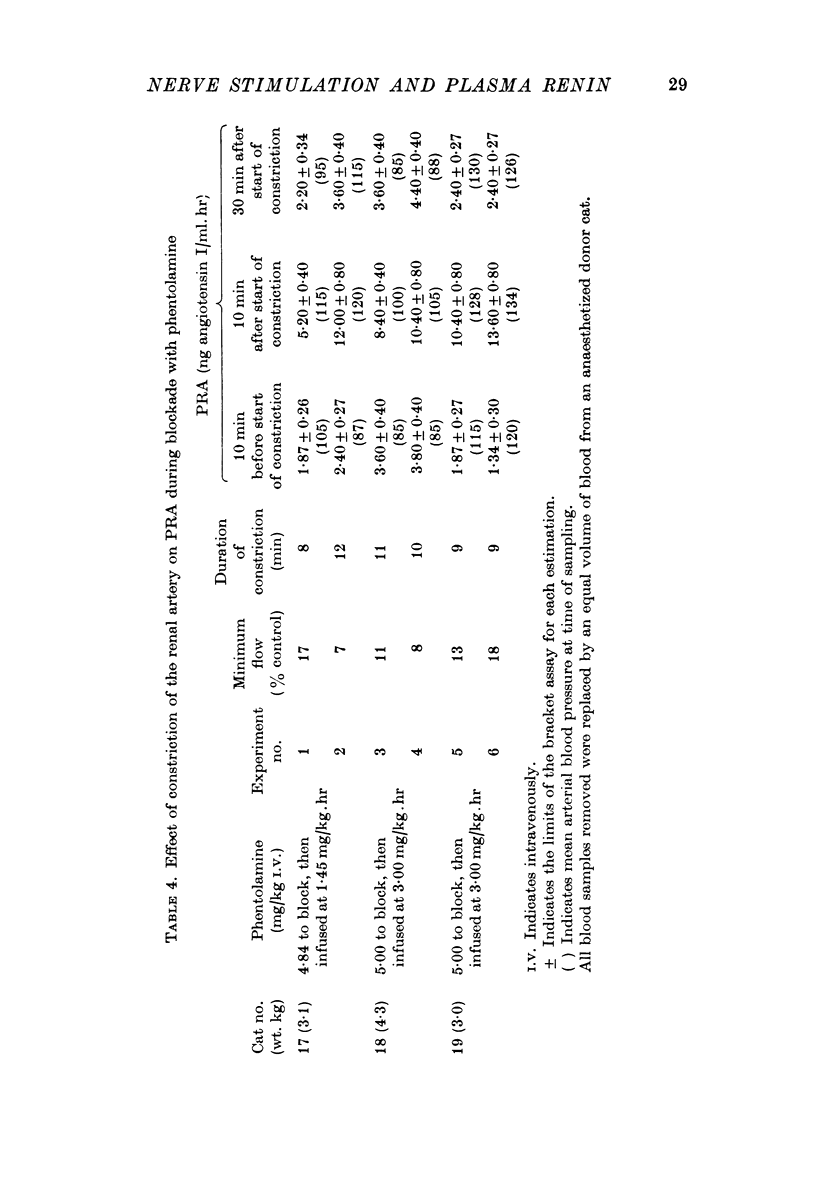
5. In phentolamine-blocked animals, renal artery constriction, as described, produced the same effect on PRA as was observed with renal nerve stimulation.
6. Propranolol, a β-adrenergic-receptor antagonist, did not block the blood flow response to renal nerve stimulation, but did block the rise in PRA normally associated with renal nerve stimulation.
7. It is suggested that the effect of renal nerve stimulation on PRA is mediated, primarily, by changes in renal blood flow and that one of the steps leading to renin release following stimulation is sensitive to propranolol. This step must be distal to the effect on vascular smooth muscle.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assaykeen T. A., Clayton P. L., Goldfien A., Ganong W. F. The effect of alpha- and beta-adrenergic blocking agents on the renin response to hypoglycemia and epinephrine in dogs. Endocrinology. 1970 Dec;87(6):1318–1322. doi: 10.1210/endo-87-6-1318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birbari A. Effect of sympathetic nervous system on renin release. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jan;220(1):16–18. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R., Ménard J., Genest J. A micromethod for measurement of renin in the plasma and kidney of rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1967 Sep;45(5):881–890. doi: 10.1139/y67-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubacher E. S., Vander A. J. Sodium deprivation and renin secretion in unanesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jan;214(1):15–21. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunag R. D., Page I. H., McCubbin J. W. Neural stimulation of release of renin. Circ Res. 1966 Oct;19(4):851–858. doi: 10.1161/01.res.19.4.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiSalvo J., Fell C. Changes in renal blood flow during renal nerve stimulation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Jan;136(1):150–153. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLKOW B., LEWIS D. H., LUNDGREN O., MELLANDER S., WALLENTIN I. THE EFFECT OF GRADED VASOCONSTRICTOR FIBRE STIMULATION ON THE INTESTINAL RESISTANCE AND CAPACITANCE VESSELS. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Aug;61:445–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. D., Küchel O., Liddle G. W., Island D. P. Role of the sympathetic nervous system in regulating renin and aldosterone production in man. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):599–605. doi: 10.1172/JCI105561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodge R. L., Lowe R. D., Vane J. R. The effects of alteration of blood-volume on the concentration of circulating angiotensin in anaesthetized dogs. J Physiol. 1966 Aug;185(3):613–626. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lever A. F., Robertson J. I., Tree M. The estimation of renin in plasma by an enzyme kinetic technique. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):346–352. doi: 10.1042/bj0910346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelakis A. M., Caudle J., Liddle G. W. In vitro stimulation of renin production by epinephrine, norepinephrine, and cyclic AMP. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Mar;130(3):748–753. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogil R. A., Itskovitz H. D., Russell J. H., Murphy J. J. Renal innervation and renin activity in salt metabolism and hypertension. Am J Physiol. 1969 Apr;216(4):693–697. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.4.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka K., Assaykeen T. A., Goldfien A., Ganong W. F. Effect of hypoglycemia on plasma renin activity in dogs. Endocrinology. 1970 Dec;87(6):1306–1317. doi: 10.1210/endo-87-6-1306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passo S. S., Assaykeen T. A., Goldfien A., Ganong W. F. Effect of alpha- and beta-adrenergic blocking agents on the increase in renin secretion produced by stimulation of the medulla oblongata in dogs. Neuroendocrinology. 1971;7(2):97–104. doi: 10.1159/000121957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passo S. S., Assaykeen T. A., Otsuka K., Wise B. L., Goldfien A., Ganong W. F. Effect of stimulation of the medulla oblongata on renin secretion in dogs. Neuroendocrinology. 1971;7(1):1–10. doi: 10.1159/000121949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickens P. T., Bumpus F. M., Lloyd A. M., Smeby R. R., Page I. H. Measurement of renin activity in human plasma. Circ Res. 1965 Nov;17(5):438–448. doi: 10.1161/01.res.17.5.438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robison G. A., Sutherland E. W. Sympathin E, sympathin I, and the intracellular level of cyclic AMP. Circ Res. 1970 Jul;27(1 Suppl 1):147–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. The regional circulation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1971;33:445–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.33.030171.002305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. W., McKenzie J. K., Lee M. R. A rapid simple method for the assay of renin in rabbit plasma. Biochem J. 1968 Jul;108(4):679–685. doi: 10.1042/bj1080679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. W., McKenzie J. K. Properties of renin substrate in rabbit plasma with a note on its assay. Biochem J. 1968 Jul;108(4):687–692. doi: 10.1042/bj1080687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner S. L. Improved assay methods for renin "concentration" and "activity" in human plasma. Methods using selective denaturation of renin substrate. Circ Res. 1967 Apr;20(4):391–402. doi: 10.1161/01.res.20.4.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Control of renin release. Physiol Rev. 1967 Jul;47(3):359–382. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1967.47.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Effect of catecholamines and the renal nerves on renin secretion in anesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1965 Sep;209(3):659–662. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.3.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen R. L., Kingsbury W. S., Stouder D. A., Schneider E. G., Rostorfer H. H. Effects of infusion of catecholamines and angiotensin II on renin release in anesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1965 Nov;209(5):1012–1024. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.5.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winer N., Chokshi D. S., Walkenhorst W. G. Effects of cyclic AMP, sympathomimetic amines, and adrenergic receptor antagonists on renin secretion. Circ Res. 1971 Sep;29(3):239–248. doi: 10.1161/01.res.29.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winer N., Chokshi D. S., Yoon M. S., Freedman A. D. Adrenergic receptor mediation of renin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Sep;29(9):1168–1175. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-9-1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


