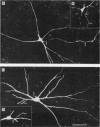
Abstract
1. Interneurones identified by physiological criteria (Hultborn, Jankowska & Lindström, 1971b) to mediate Ia reciprocal inhibition of motoneurones in the spinal cord of the cat were stained by intracellular injection of a fluorescent dye (Procion Yellow).
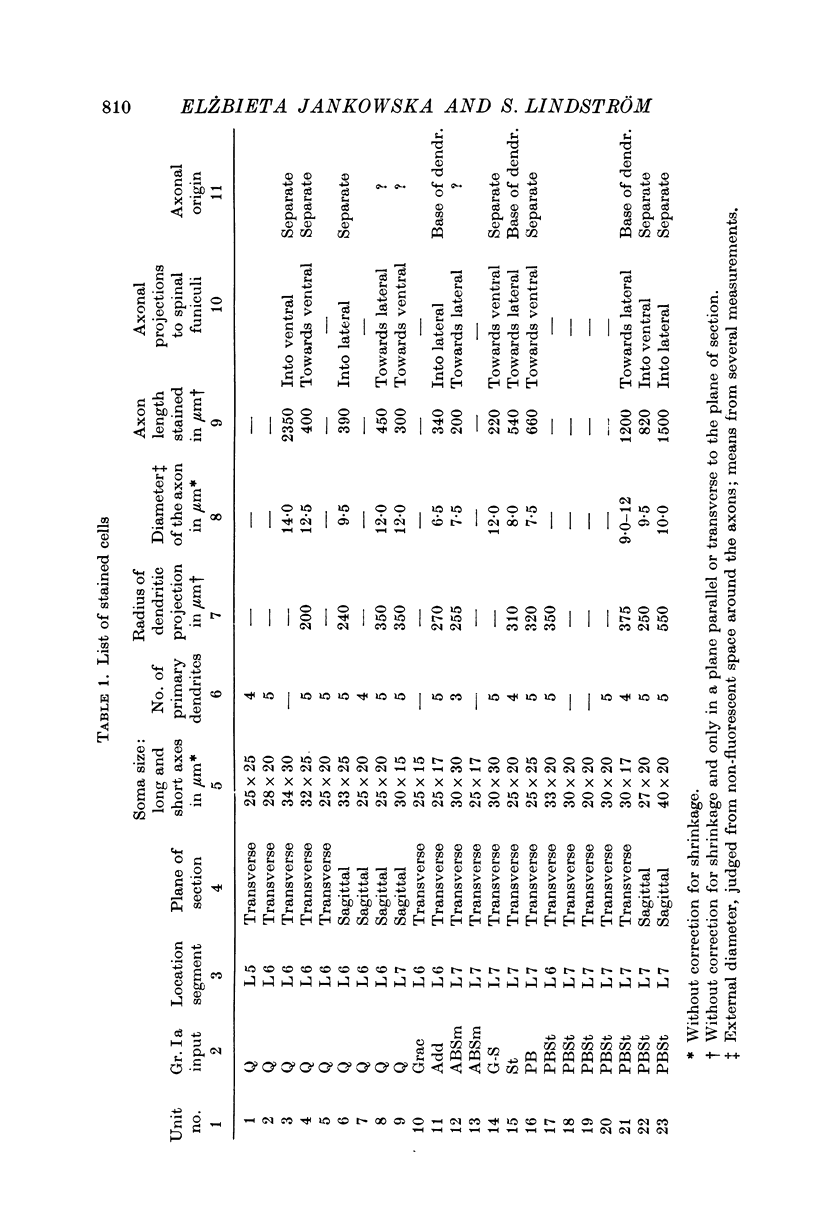
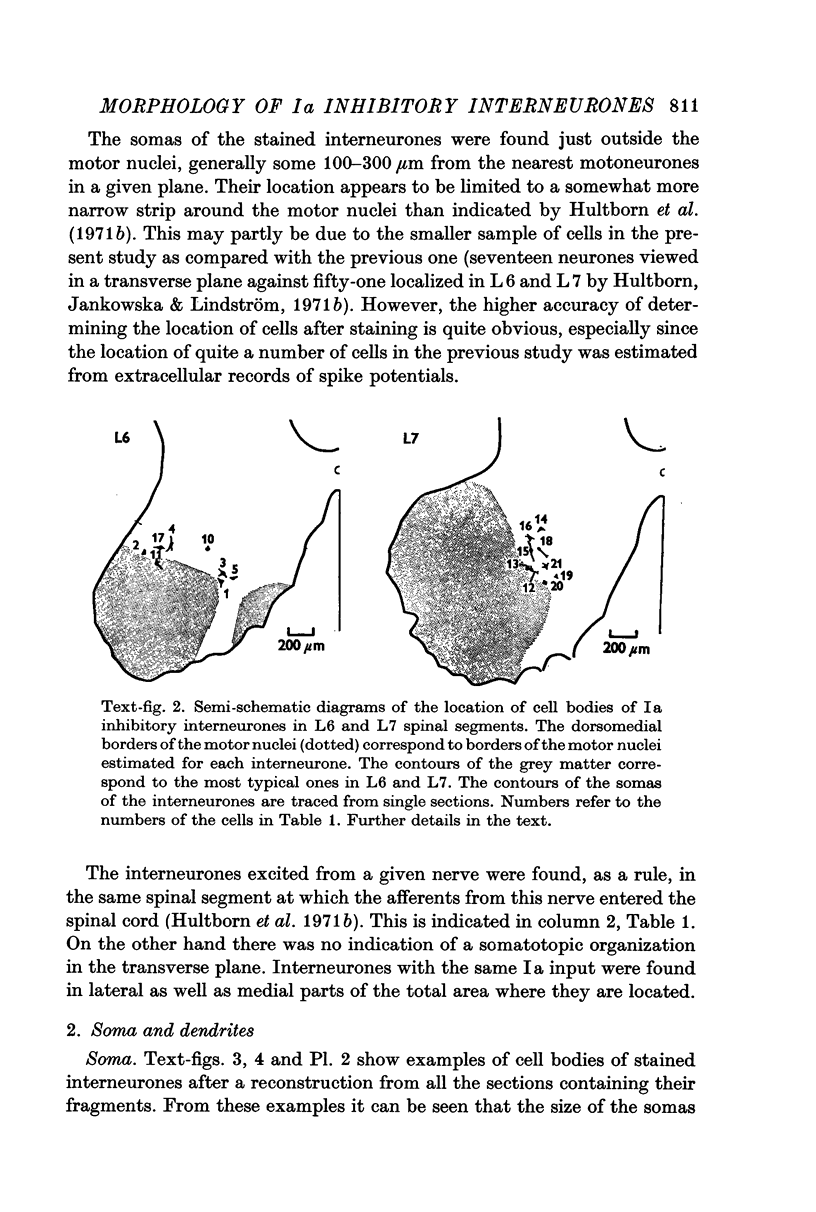
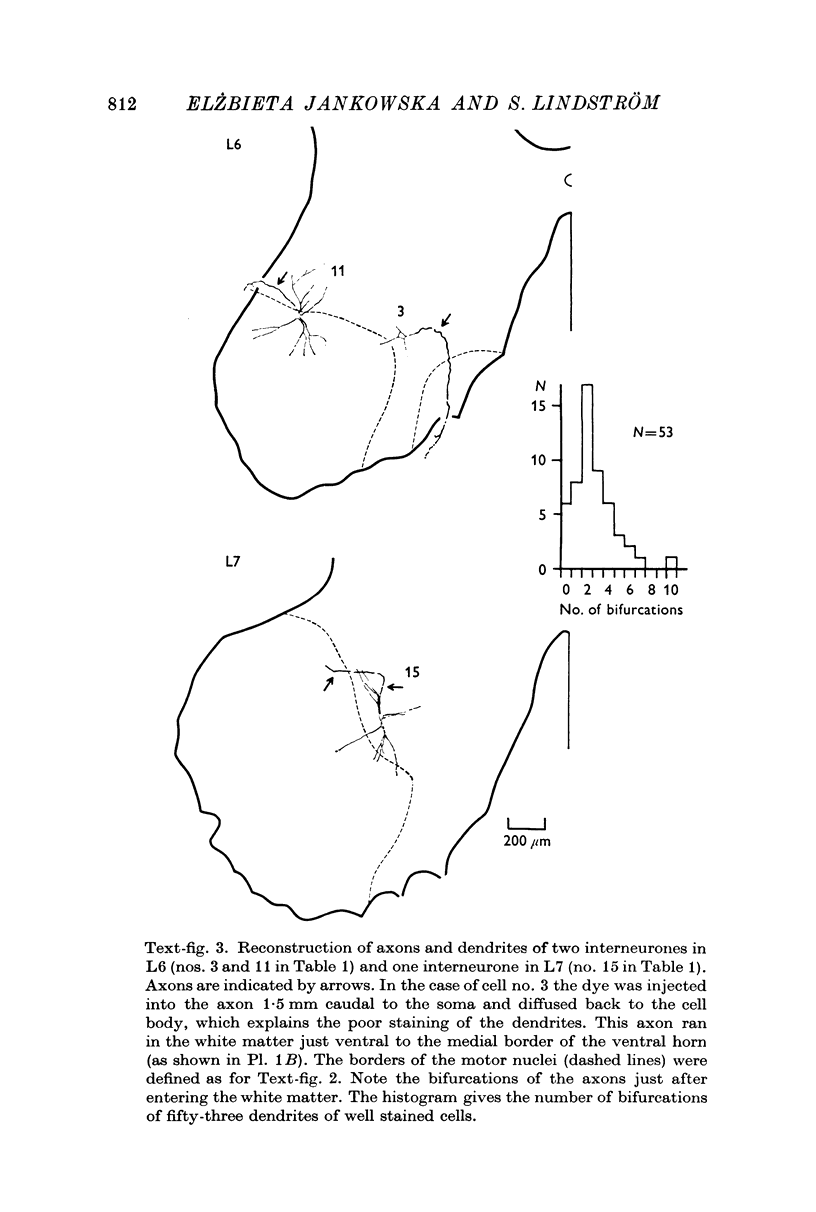
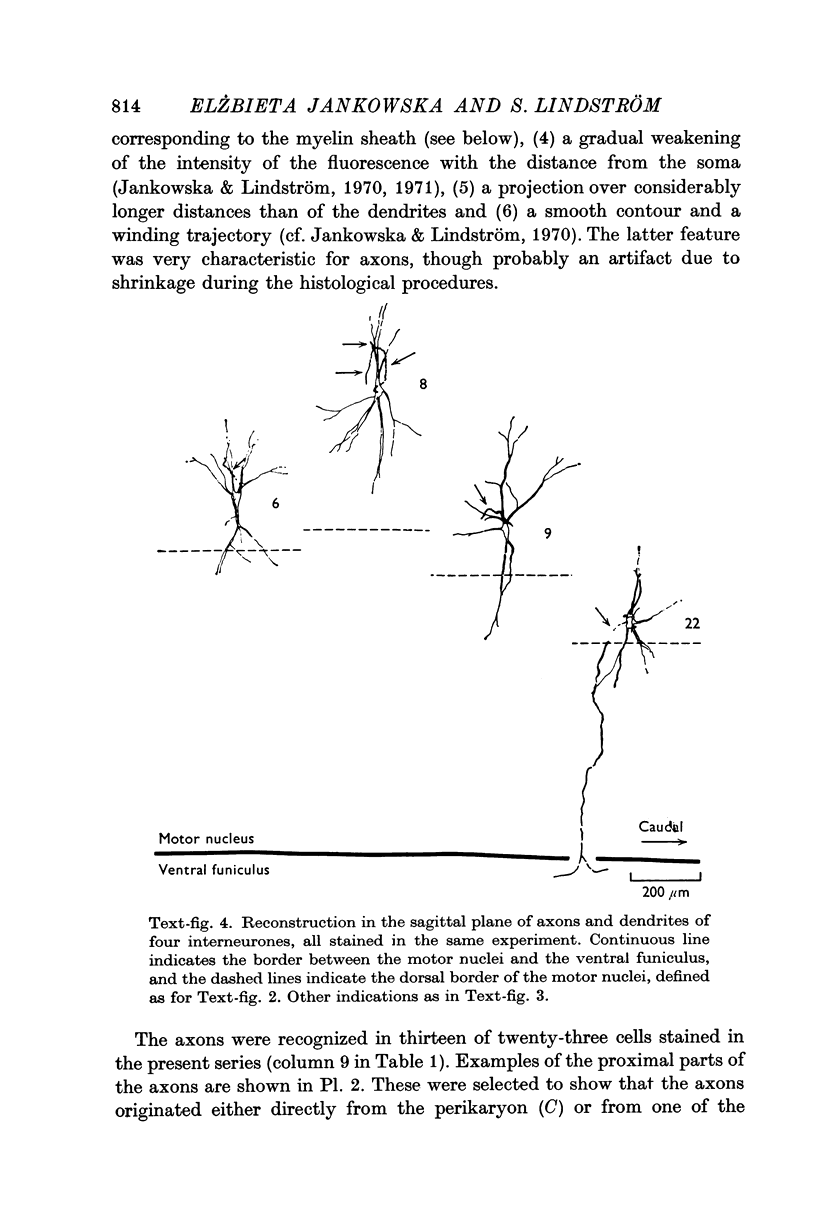
2. The somas of the stained cells were found in Rexed's lamina VII, just dorsal or dorsomedial to the motor nuclei. Their size was about 30 × 20 μm. The cells had four to five slender, weakly branching dendrites. The total extension of their dendritic trees was about 600 μm dorsoventrally, 400 μm mediolaterally and 300 μm rostrocaudally.
3. The axons originated from a separate axon hillock or from the base of a dendrite. They were myelinated with external diameter of about 6-14 μm and projected to either the ipsilateral ventral or lateral funiculi. Early collaterals were found only exceptionally. Some axons bifurcated into an ascending and a descending branch within the funiculi.
4. The possibility of identifying the Ia inhibitory interneurones on purely morphological grounds is discussed.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARAKI T., EOCLES J. C., ITO M. Correlation of the inhibitory post-synaptic potential of motoneurones with the latency and time course of inhibition of monosynaptic reflexes. J Physiol. 1960 Dec;154:354–377. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY K., ECCLES J. C. Analysis of the fast afferent impulses from thigh muscles. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):462–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan R. N., Trevino D. L., Willis W. D. Evidence for a common location of alpha and gamma motoneurons. Brain Res. 1972 Mar 10;38(1):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90602-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Fedina L., Lundberg A. Spatial synaptic distribution of recurrent and group Ia inhibitory systems in cat spinal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1971 Apr;214(2):305–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R., Lundberg A., Weight F. Spinal border cell origin of the ventral spinocerebellar tract. Exp Brain Res. 1971;12(3):283–294. doi: 10.1007/BF00237921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., IGGO A., LUNDBERG A. Electrophysiological studies on gamma motoneurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1960 Sep 30;50:32–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1960.tb02070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., FATT P., LANDGREN S. Central pathway for direct inhibitory action of impulses in largest afferent nerve fibres to muscle. J Neurophysiol. 1956 Jan;19(1):75–98. doi: 10.1152/jn.1956.19.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. The synaptic linkage of direct inhibition. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Oct 8;43(3-4):204–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01589.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfan S., Kao G., Ruchkin D. S. The dendritic tree of spinal neurons. J Comp Neurol. 1970 Aug;139(4):385–411. doi: 10.1002/cne.901390402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Lindström S. Depression of Ia IPSP in spinal border cells by impulses in recurrent motor axon collaterals. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 Dec;80(4):13A–14A. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04837.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. The rubrospinal tract. IV. Effects on interneurones. Exp Brain Res. 1972;15(1):54–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00234958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H. Convergence on interneurones in the reciprocal Ia inhibitory pathway to motoneurones. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1972;375:1–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1972.tb05298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Jankowska E., Lindström S. Recurrent inhibition from motor axon collaterals of transmission in the Ia inhibitory pathway to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;215(3):591–612. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Jankowska E., Lindström S. Recurrent inhibition of interneurones monosynaptically activated from group Ia afferents. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;215(3):613–636. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Jankowska E., Lindström S. Relative contribution from different nerves to recurrent depression of Ia IPSPs in motoneurones. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;215(3):637–664. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Jankowska E., Lindström S., Roberts W. Neuronal pathway of the recurrent facilitation of motoneurones. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(2):495–514. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Santini M. Supraspinal control of monosynaptically activated group Ia interneurones in the ventral horn. Acta Physiol Scand. 1972 Jan;84(1):142–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1972.tb05164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Lindström S. Morphological identification of Renshaw cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Mar;81(3):428–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04918.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Lindström S. Morphological identification of physiologically defined neurones in the cat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1970 Jun 3;20(2):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90300-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Roberts W. J. An electrophysiological demonstration of the axonal projections of single spinal interneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1972 May;222(3):597–622. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Roberts W. J. Synaptic actions of single interneurones mediating reciprocal Ia inhibition of motoneurones. J Physiol. 1972 May;222(3):623–642. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A., VOORHOEVE P. Effects from the pyramidal tract on spinal reflex arcs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1962 Nov-Dec;56:201–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1962.tb02498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A. Convergence of excitatory and inhibitory action on interneurones in the spinal cord. UCLA Forum Med Sci. 1969;11:231–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita M. Dendritic organization of the ventral spinal gray matter in the cat. Acta Anat (Basel) 1970;76(2):263–288. doi: 10.1159/000143496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita M. Some aspects of interneuronal connections cat's spinal gray matter. J Comp Neurol. 1969 May;136(1):57–80. doi: 10.1002/cne.901360105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita M. The axonal pathways of spinal neurons in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1970 Apr;138(4):391–417. doi: 10.1002/cne.901380402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMON-MOLINER E. An attempt at classifying nerve cells on the basis of their dendritic patterns. J Comp Neurol. 1962 Oct;119:211–227. doi: 10.1002/cne.901190207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REXED B. A cytoarchitectonic atlas of the spinal cord in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1954 Apr;100(2):297–379. doi: 10.1002/cne.901000205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rustioni A., Kuypers H. G., Holstege G. Propiospinal projections from the ventral and lateral funiculi to the motoneurons in the lumbosacral cord of the cat. Brain Res. 1971 Nov;34(2):255–275. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPRAGUE J. M. Motor and propriospinal cells in the thoracic and lumbar ventral horn of the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1951 Aug;95(1):103–123. doi: 10.1002/cne.900950107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheibel M. E., Scheibel A. B. A structural analysis of spinal interneurons and Renshaw cells. UCLA Forum Med Sci. 1969;11:159–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheibel M. E., Scheibel A. B. Inhibition and the Renshaw cell. A structural critique. Brain Behav Evol. 1971;4(1):53–93. doi: 10.1159/000125424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling P., Kuypers H. G. Anatomical organization of the brachial spinal cord of the cat. 3. The propriospinal connections. Brain Res. 1968 Mar;7(3):419–443. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stretton A. O., Kravitz E. A. Neuronal geometry: determination with a technique of intracellular dye injection. Science. 1968 Oct 4;162(3849):132–134. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3849.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TESTA C. FUNCTIONAL IMPLICATIONS OF THE MORPHOLOGY OF SPINAL VENTRAL HORN NEURONS OF THE CAT. J Comp Neurol. 1964 Dec;123:425–443. doi: 10.1002/cne.901230309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C., Wilson V. J. Precise localization of Renshaw cells with a new marking technique. Nature. 1965 Apr 10;206(980):211–213. doi: 10.1038/206211b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]