Abstract
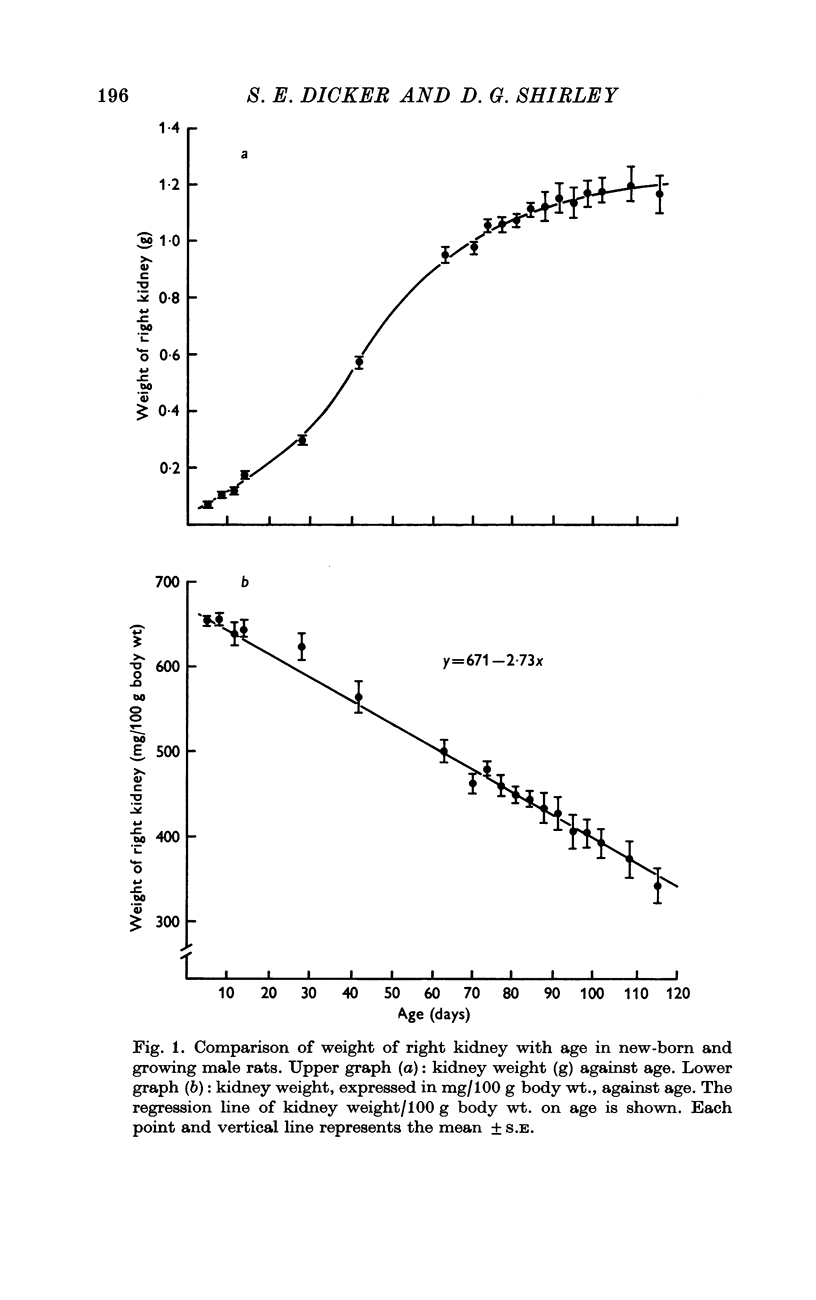
1. The right kidney in a series of control rats aged between 5 days and 115 days was weighed. The kidney weight/body weight ratio was greater in young than in older rats, but decreased linearly with increasing age.
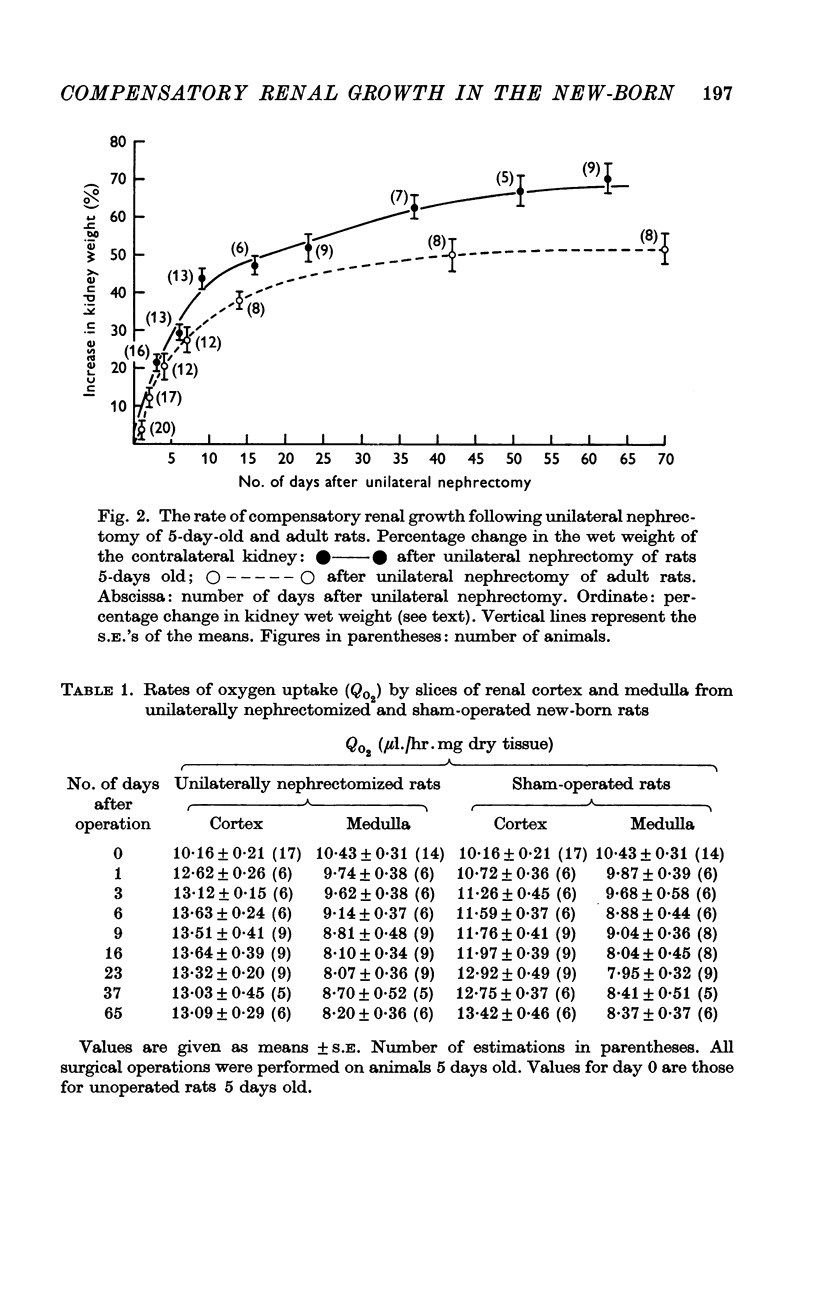
2. After unilateral nephrectomy of rats 5 days old, the remaining kidney underwent compensatory growth. The rate and extent of this growth were greater than in adult rats.
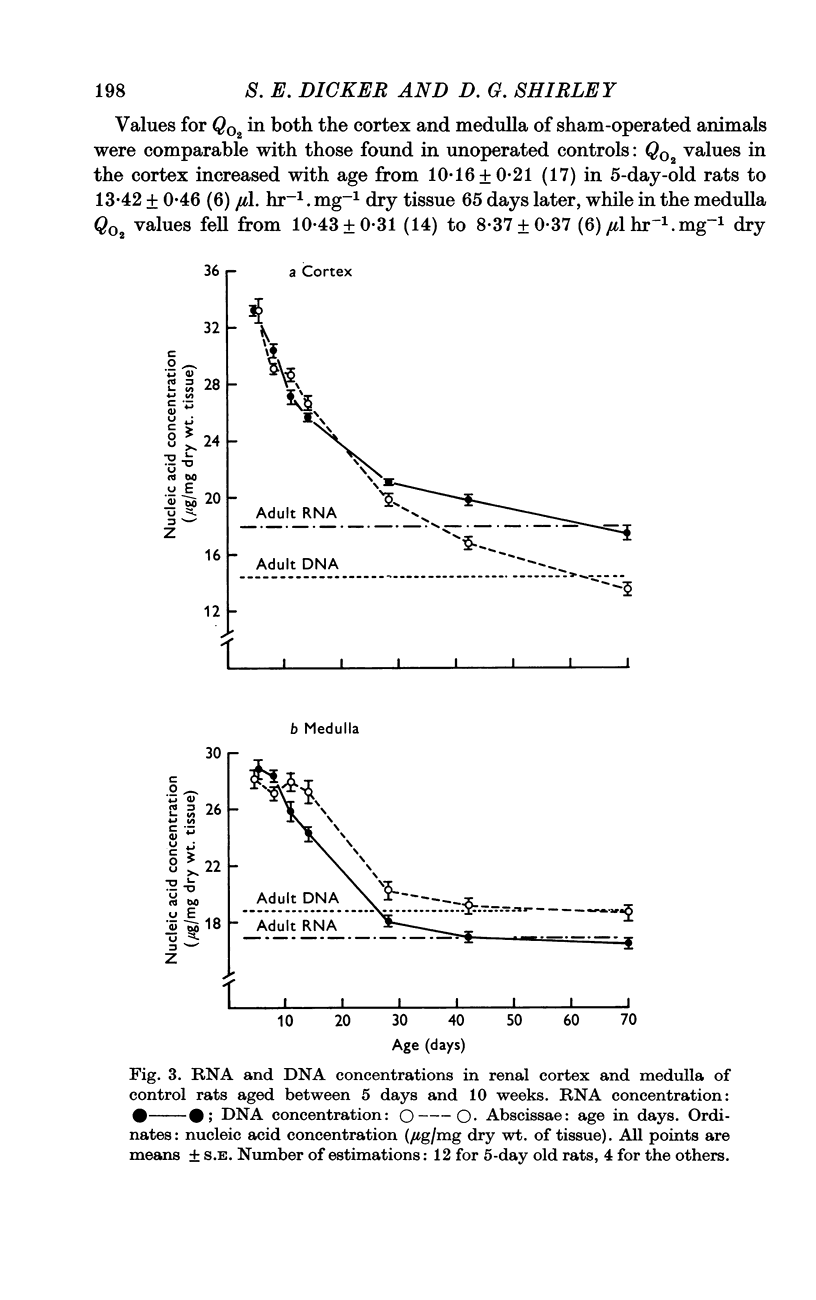
3. The concentrations of RNA and DNA in the renal cortex and medulla of rats 5 days old were higher than in adult animals. The concentrations of the two nucleic acids fell with age, and reached adult levels after approximately 6 weeks.
4. After unilateral nephrectomy of rats 5 days old, the concentrations of RNA and DNA in the medulla were not significantly different from those in control animals. In the cortex, however, there was a delayed increase in the RNA/DNA ratio, which reached a level some 12% higher than that in control rats. This increase was smaller than that observed in unilaterally nephrectomized adult rats.
5. The cortical QO2 of the remaining kidney of unilaterally nephrectomized new-born rats was elevated by some 20% within 1 day of unilateral nephrectomy. Cortical QO2's remained higher than those of control animals for 3-4 weeks.
6. Since after unilateral nephrectomy, the increase in renal mass in new-borns was greater than that in adults, whereas the degree of cortical cellular hypertrophy (as estimated by the RNA/DNA ratio) was smaller than in adults, it is likely that in new-born animals a significant contribution to compensatory growth comes from cellular hyperplasia.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. A. The fine structure of compensatory growth in the rat kidney after unilateral nephrectomy. Am J Anat. 1967 Sep;121(2):217–247. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001210204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasel J. A. Age dependent differences in DNA polymerase activity following uninephrectomy in rats. Growth. 1972 Mar;36(1):45–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKER S. E. Effect of diuretics in newborn rats and puppies. J Physiol. 1952 Nov;118(3):384–394. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicker S. E., Shirley D. G. Compensatory hypertrophy of the contralateral kidney after unilateral ureteral ligation. J Physiol. 1972 Jan;220(1):199–210. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicker S. E., Shirley D. G. Mechanism of compensatory renal hypertrophy. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(3):507–523. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicker S. E., Shirley D. G. Rates of oxygen consumption and of anaerobic glycolysis in renal cortex and medulla of adult and new-born rats and guinea-pigs. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(1):235–243. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALK G. Maturation of renal function in infant rats. Am J Physiol. 1955 Apr;181(1):157–170. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.181.1.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanestil D. D. Renal Na-K ATPase relationship to total functional renal mass. Nature. 1968 Apr 13;218(5137):176–177. doi: 10.1038/218176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliburton I. W., Thomson R. Y. Chemical aspects of compensatory renal hypertrophy. Cancer Res. 1965 Dec;25(11):1882–1887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller H. The response of newborn rats to administration of water by the stomach. J Physiol. 1947 Jul 31;106(3):245–255. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1947.sp004207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. A., Amendola F. Mitochondrial proliferation in compensatory growth of the kidney. Am J Pathol. 1969 Jan;54(1):35–45. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. A., Vera Roman J. M. Compensatory renal enlargement. Hypertrophy versus hyperplasia. Am J Pathol. 1966 Jul;49(1):1–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A. I., Epstein F. H. The role of sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase in the reabsorption of sodium by the kidney. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):1999–2011. doi: 10.1172/JCI105689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCANCE R. A., WIDDOWSON E. M. New thoughts on renal function in the early days of life. Br Med Bull. 1957 Jan;13(1):3–6. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malt R. A., Lemaitre D. A. Accretion and turnover of RNA in the renoprival kidney. Am J Physiol. 1968 May;214(5):1041–1047. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.5.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malt R. A., Lemaittre D. A. Nucleic acids in fetal kidney after maternal nephrectomy. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Feb;130(2):539–542. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-35600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance R. A., Wilkinson E. The response of adult and suckling rats to the administration of water and of hypertonic solutions of urea and salt. J Physiol. 1947 Jul 31;106(3):256–263. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1947.sp004208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIVER I. T., BALLARD F. J., SHIELD J., BENTLEY P. J. Liver growth in early postpartum rat. Dev Biol. 1962 Feb;4:108–116. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(62)90035-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priestley G. C., Malt R. A. Development of the metanephric kidney. Protein and nucleic acid synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jun;37(3):703–715. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.3.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERZAR F., HUGIN F. Einfluss des Alters auf die Entwicklung der Arbeitshypertrophie von Organen; kompensatorische Hypertrophie der Niere und der Nebenniere. Acta Anat (Basel) 1957;30(1-4):918–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


