Abstract
1. Fast axoplasmic transport in mammalian nerve fibres was determined by the presence of a crest of activity in the sciatic nerve after injection of [3H]leucine into the L7 dorsal root ganglion or the L7 motoneurone region in the ventral horn region of the spinal cord. After incorporation into proteins by the cell bodies, a rate of transport close to 410 mm/day was found for cat sensory nerves. A closely similar rate was found in the motor and sensory sciatic nerve fibres of the monkey, dog, rabbit, goat and rat. In the longer nerves where longer downflow times were possible, there was no decrement of rate with distance, or presence of later appearing crests of activity indicative of multiple fast transport systems.
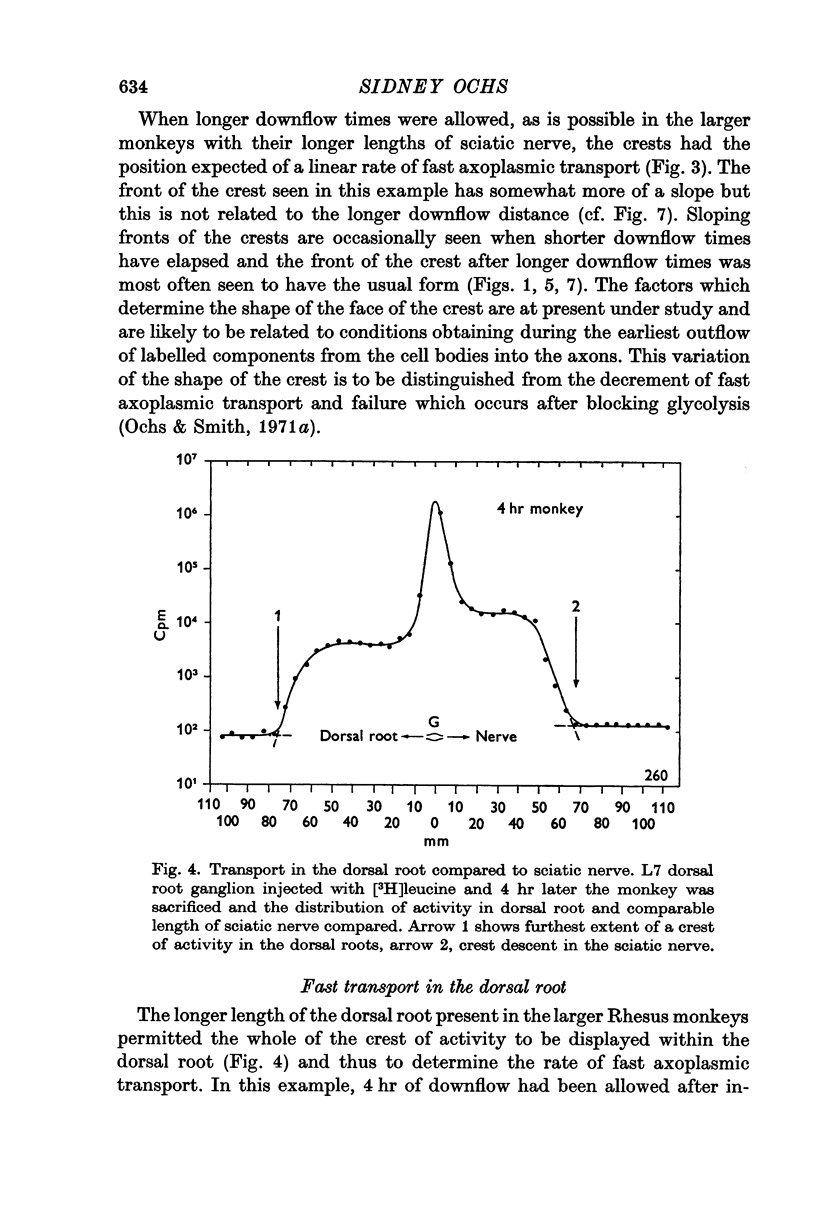
2. The rate of fast transport found in the long L7 dorsal roots of the rhesus monkey was the same as that in the corresponding length of sciatic nerve and the same fast rate was shown by the crest of activity ascending in the dorsal columns of the spinal cord.
3. Labelled activity was found present inside myelinated nerve fibres ranging in diameter from 3 to 23 μm in nerve segments taken at the forward part of the crest suggesting that the rate of fast axoplasmic transport is independent of fibre diameter.
Full text
PDF

















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DROZ B., LEBLOND C. P. Migration of proteins along the axons of the sciatic nerve. Science. 1962 Sep 28;137(3535):1047–1048. doi: 10.1126/science.137.3535.1047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez H. L., Huneeus F. C., Davison P. F. Studies on the mechanism of axoplasmic transport in the crayfish cord. J Neurobiol. 1970;1(4):395–409. doi: 10.1002/neu.480010404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson A. E., Cowan W. M. Changes in the rate of axoplasmic transport during postnatal development of the rabbit's optic nerve and tract. Exp Neurol. 1971 Mar;30(3):403–422. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(71)90142-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson J. O., Sjöstrand J. Synthesis, migration and turnover of protein in retinal ganglion cells. J Neurochem. 1971 May;18(5):749–767. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb12005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy R. D., Fink B. R., Byers M. R. The effect of halothane on rapid axonal transport in the rabbit vagus. Anesthesiology. 1972 May;36(5):433–443. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197205000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidwai A. M., Ochs S. Components of fast and slow phases of axoplasmic flow. J Neurochem. 1969 Jul;16(7):1105–1112. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb05955.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasek R. J. Axoplasmic transport of labeled proteins in rat ventral motoneurons. Exp Neurol. 1968 May;21(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(68)90032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Slater C. R. On the degeneration of rat neuromuscular junctions after nerve section. J Physiol. 1970 Apr;207(2):507–528. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OCHS S. BEADING OF MYELINATED NERVE FIBERS. Exp Neurol. 1965 May;12:84–95. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(65)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OCHS S., BURGER E. Movement of substance proximo-distally in nerve axons as studied with spinal cord injections of radioactive phosphorus. Am J Physiol. 1958 Sep;194(3):499–506. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.194.3.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OCHS S., DALRYMPLE D., RICHARDS G. Axoplasmic flow in ventral root nerve fibers of the cat. Exp Neurol. 1962 May;5:349–363. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(62)90049-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs S. Fast transport of materials in mammalian nerve fibers. Science. 1972 Apr 21;176(4032):252–260. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4032.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs S., Hollingsworth D. Dependence of fast axoplasmic transport in nerve on oxidative metabolism. J Neurochem. 1971 Jan;18(1):107–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs S., Johnson J. Fast and slow phases of axoplasmic flow in ventral root nerve fibres. J Neurochem. 1969 Jun;16(3):845–853. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb08972.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs S., Johnson J., Ng M. H. Protein incorporation and axoplasmic flow in motoneuron fibres following intra-cord injection of labelled leucine. J Neurochem. 1967 Mar;14(3):317–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb09529.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs S., Ranish N. Characteristics of the fast transport system in mammalian nerve fibers. J Neurobiol. 1969;1(2):247–261. doi: 10.1002/neu.480010211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs S., Ranish N. Metabolic dependence of fast axoplasmic transport in nerve. Science. 1970 Feb 6;167(3919):878–879. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3919.878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs S., Sabri M. I., Johnson J. Fast transport system of materials in mammalian nerve fibers. Science. 1969 Feb 14;163(3868):686–687. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3868.686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs S., Smith C. B. Fast axoplasmic transport in mammalian nerve in vitro after block of glycolysis with iodoacetic acid. J Neurochem. 1971 Jun;18(6):833–843. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb12013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt F. O. Fibrous proteins--neuronal organelles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1092–1101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




