Abstract
1. By applying atomized chemical solutions on to gecko and carp retinae, neuropharmacological reactions of the photoreceptors and horizontal cells were observed.
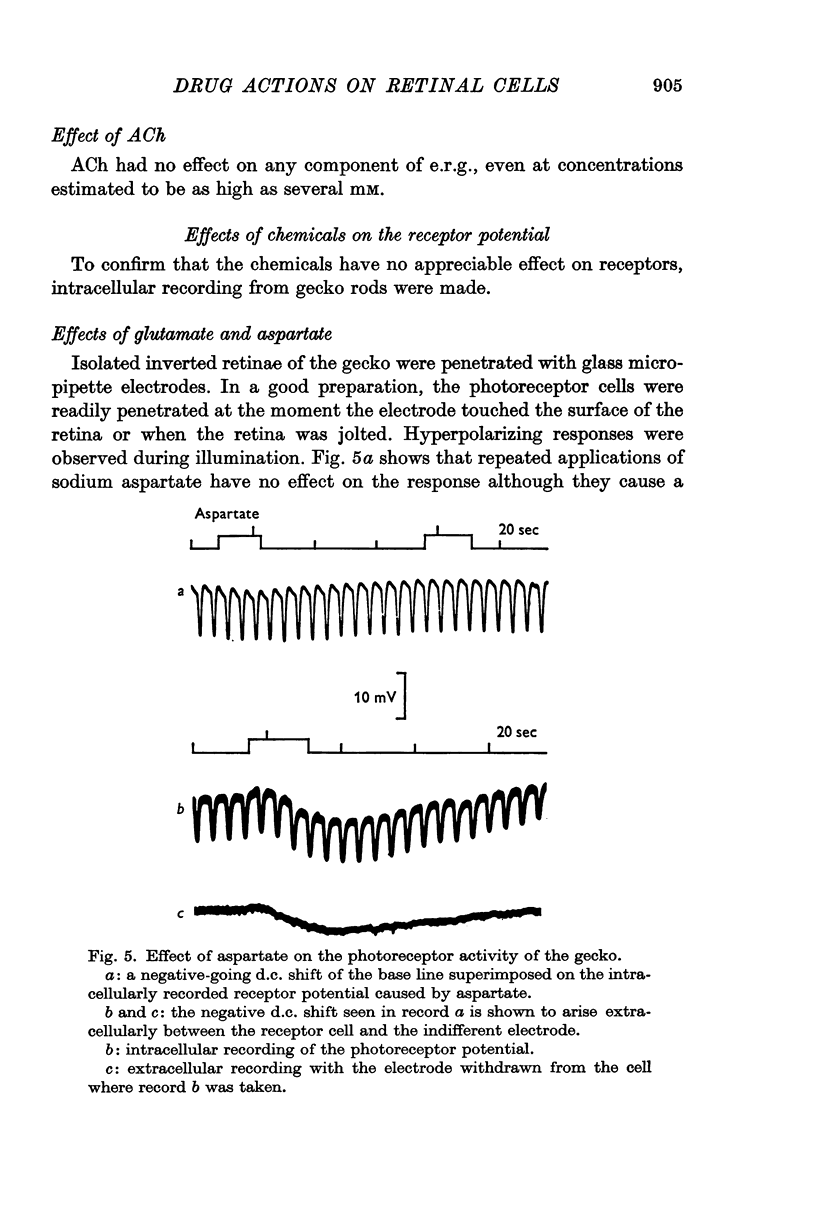
2. Sodium L-glutamate and L-aspartate, glycine, ACh and GABA, had no appreciable effect on the photoreceptor activity.
3. Carp horizontal cells were depolarized by both L-glutamate and L-aspartate. When maximally depolarized, the action of the endogenous transmitter from the receptor terminals was completely masked, resulting in abolition of the S-potentials.
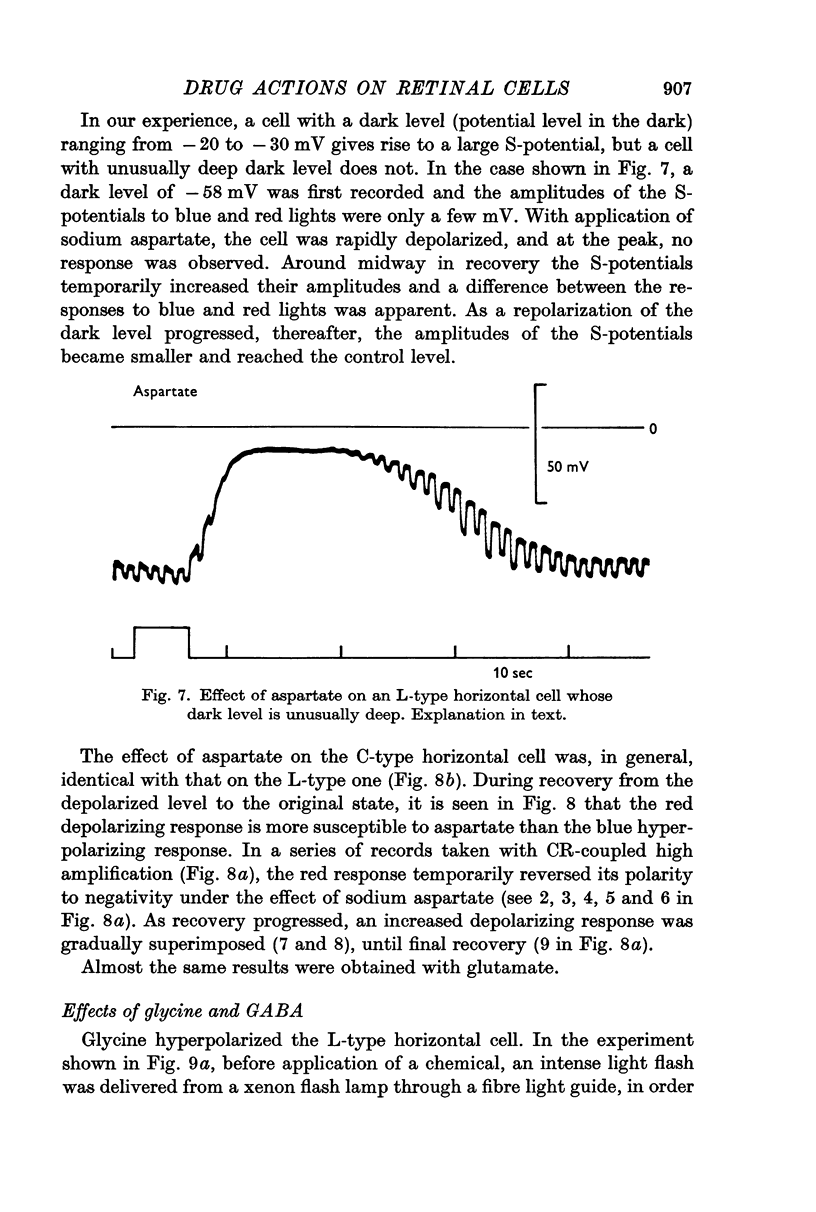
4. Responses to red light in both L- and C-type horizontal cells were more strongly affected by aspartate than responses to blue light.
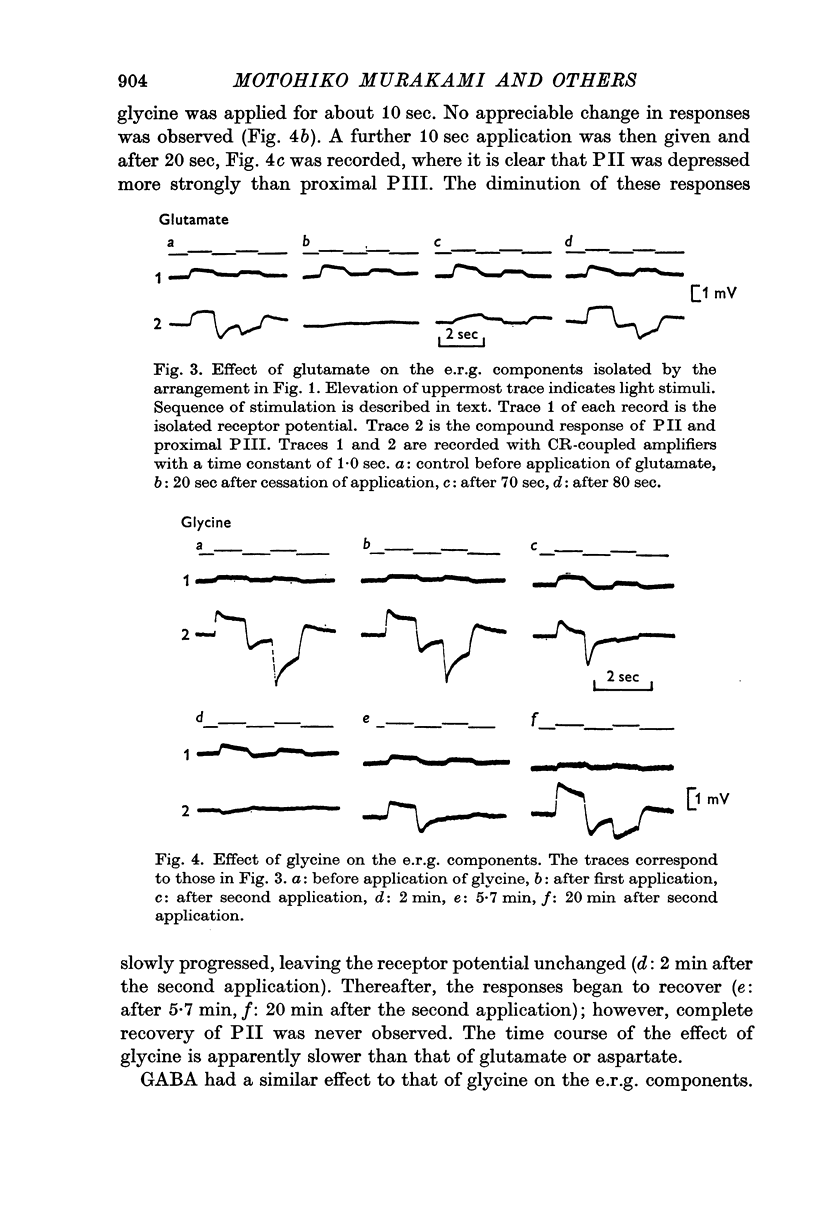
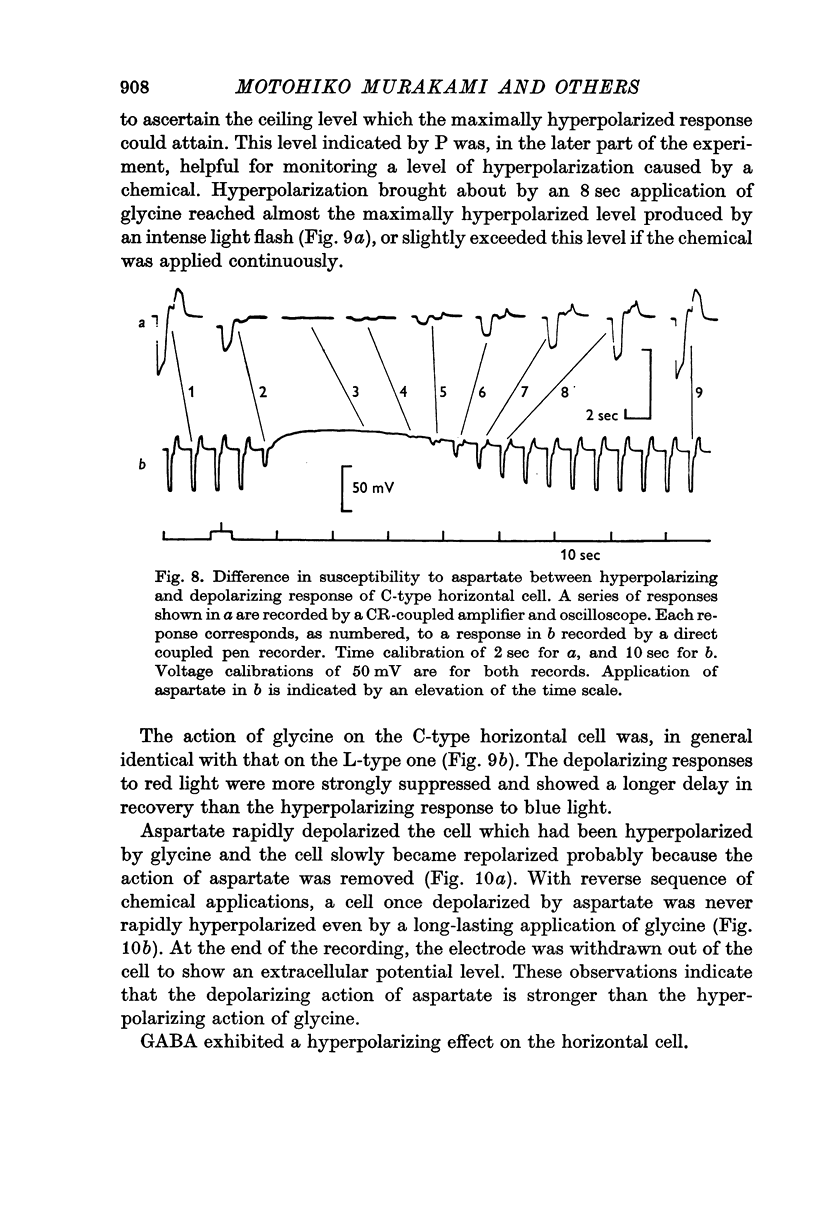
5. Glycine and GABA hyperpolarized the horizontal cells, and the S-potentials were diminished.
6. ACh had no effect on the activity of the horizontal cells.
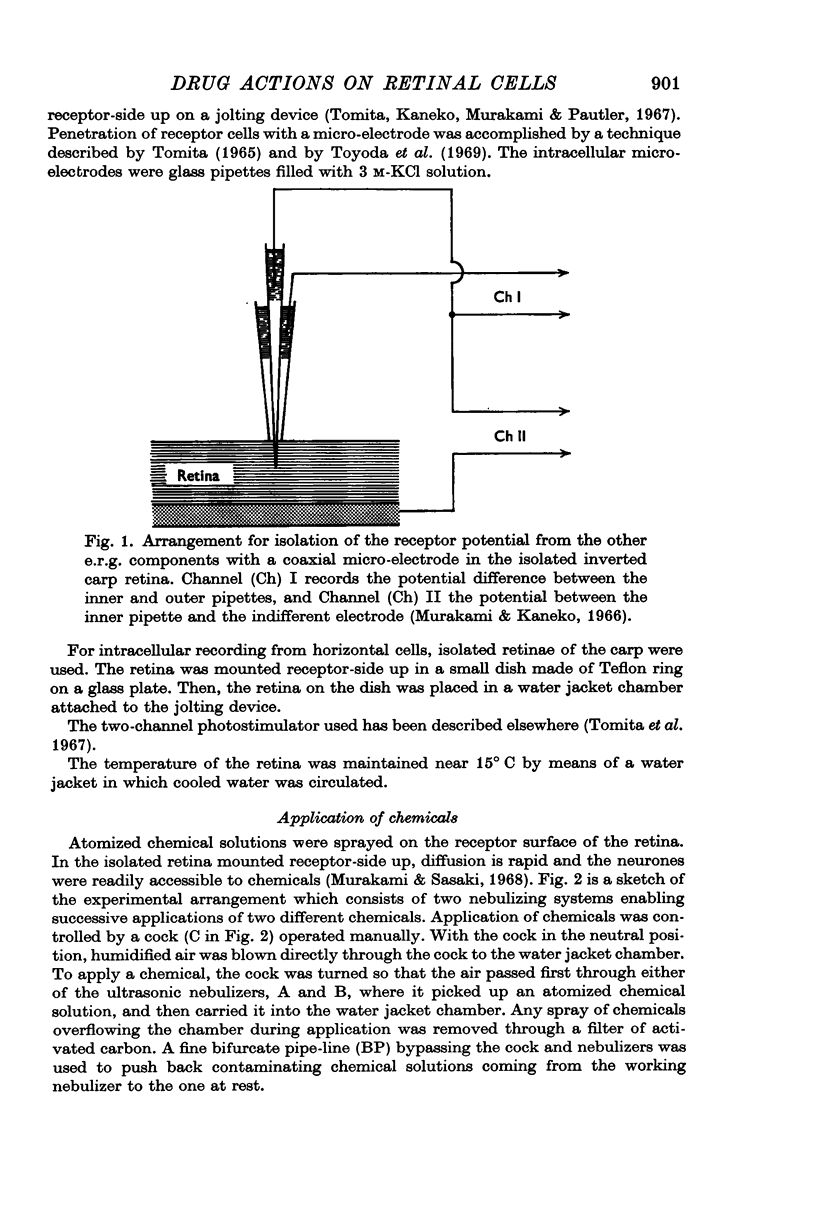
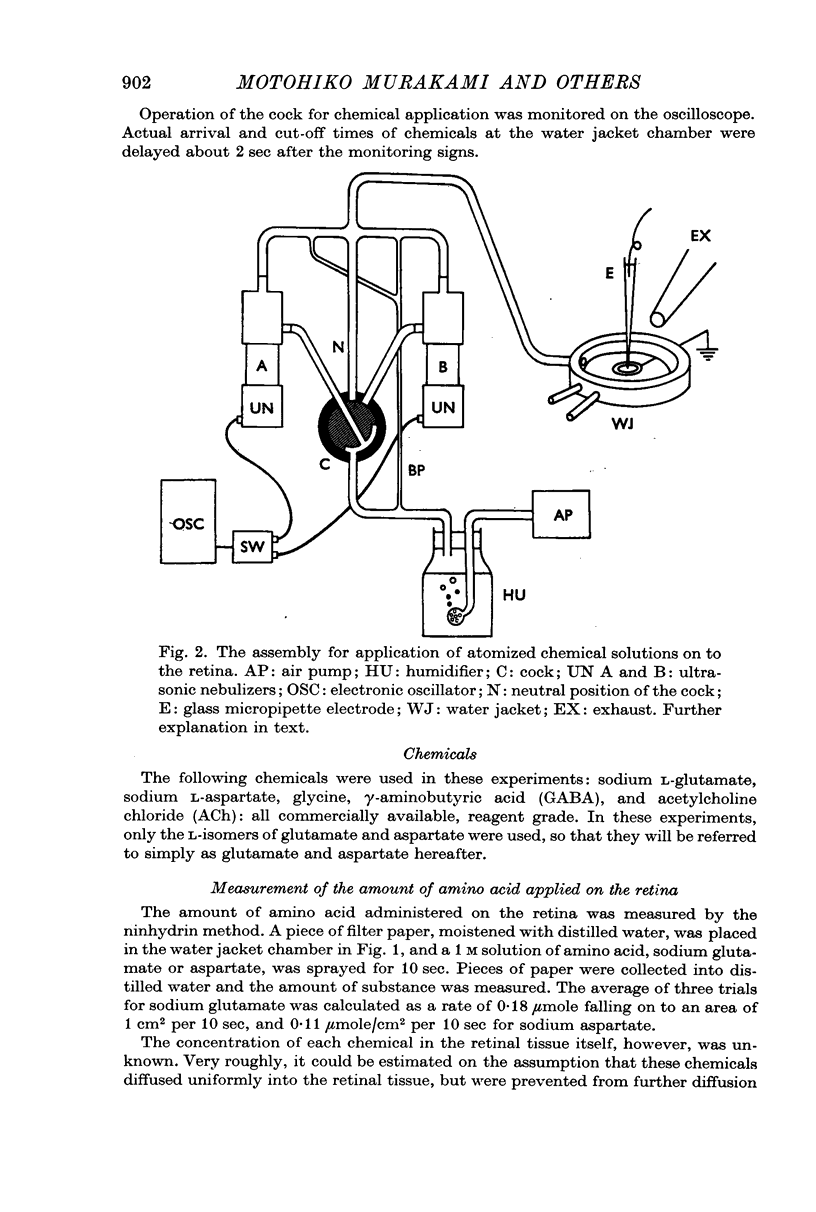
Full text
PDF



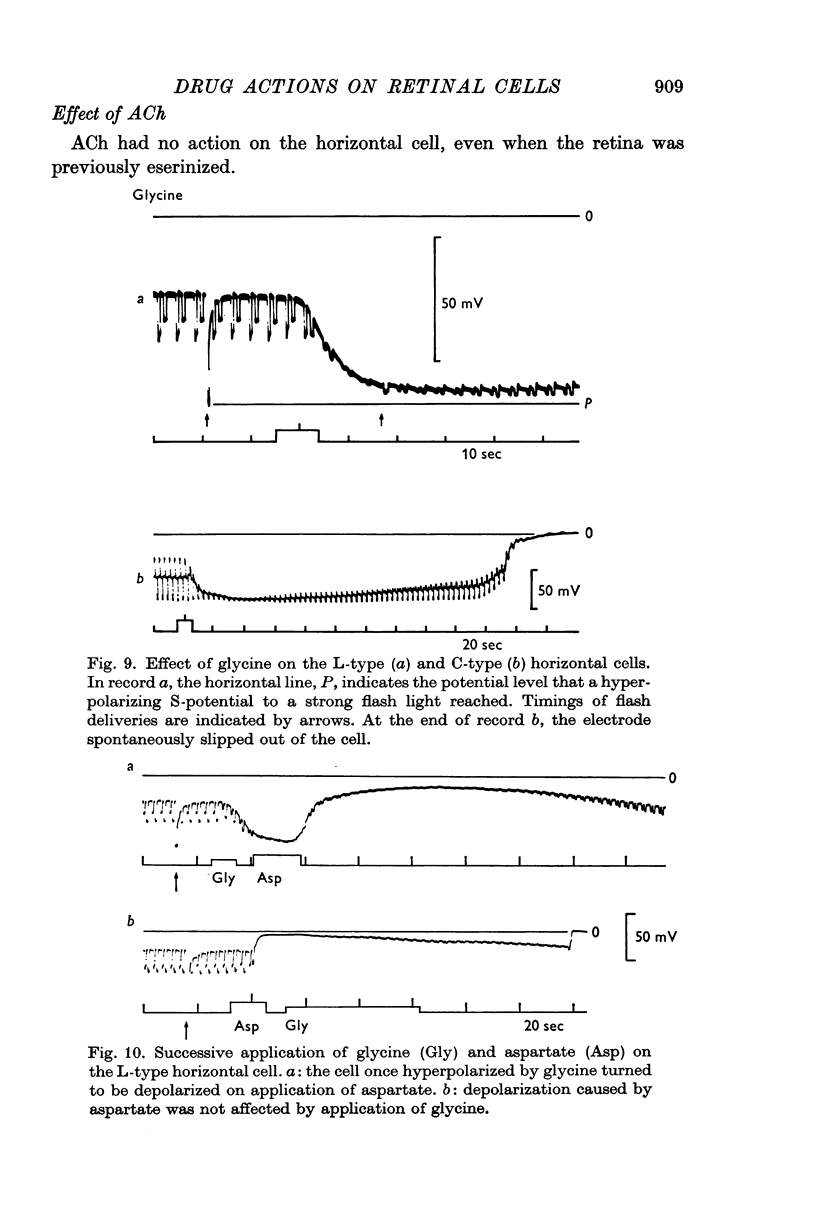




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dowling J. E., Werblin F. S. Organization of retina of the mudpuppy, Necturus maculosus. I. Synaptic structure. J Neurophysiol. 1969 May;32(3):315–338. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.3.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURUKAWA T., HANAWA I. Effects of some common cations on electroretinogram of the toad. Jpn J Physiol. 1955 Dec 15;5(4):289–300. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.5.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanawa I., Tateishi T. The effect of aspartate on the electroretinogram of the vertebrate retina. Experientia. 1970 Dec 15;26(12):1311–1312. doi: 10.1007/BF02112997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., PHILLIS J. W. Iontophoretic studies of neurones in the mammalian cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Feb;165:274–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko A. Physiological and morphological identification of horizontal, bipolar and amacrine cells in goldfish retina. J Physiol. 1970 May;207(3):623–633. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko A. Physiological studies of single retinal cells and their morphological identification. Vision Res. 1971;Suppl 3:17–26. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(71)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLINAS R. MECHANISMS OF SUPRASPINAL ACTIONS UPON SPINAL CORD ACTIVITIES. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN RETICULAR AND CEREBELLAR INHIBITORY ACTIONS UPON ALPHA EXTENSOR MOTONEURONS. J Neurophysiol. 1964 Nov;27:1117–1126. doi: 10.1152/jn.1964.27.6.1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Kaneko A. Differentiation of P 3 subcomponents in cold-blooded vertebrate retinas. Vision Res. 1966 Dec;6(12):627–636. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(66)90074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Sasaki Y. Analysis of spatial distribution of the ERG components in the carp retina. Jpn J Physiol. 1968 Jun 15;18(3):326–336. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.18.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillman A. J., Ito H., Tomita T. Studies on the mass receptor potential of the isolated frog retina. I. General properties of the response. Vision Res. 1969 Dec;9(12):1435–1442. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(69)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spekreijse H., Norton A. L. The dynamic characteristics of color-coded S-potentials. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jul;56(1):1–15. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stell W. K. The structure and relationships of horizontal cells and photoreceptor-bipolar synaptic complexes in goldfish retina. Am J Anat. 1967 Sep;121(2):401–423. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001210213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. THE EFFECT ON CRAYFISH MUSCLE OF IONTOPHORETICALLY APPLIED GLUTAMATE. J Physiol. 1964 Mar;170:296–317. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMITA T. A compensation circuit for coaxial and double-barreled microelectrodes. Ire Trans Biomed Electron. 1962 Apr;BME-9:138–141. doi: 10.1109/tbmel.1962.4322979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita T. Electrical activity of vertebrate photoreceptors. Q Rev Biophys. 1970 May;3(2):179–222. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita T. Electrophysiological study of the mechanisms subserving color coding in the fish retina. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1965;30:559–566. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1965.030.01.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita T., Kaneko A., Murakami M., Pautler E. L. Spectral response curves of single cones in the carp. Vision Res. 1967 Jul;7(7):519–531. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(67)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyama K., Tsukahara N., Udo M. Nature of the cerebellar influences upon the red nucleus neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1968;4(4):292–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00235697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda J., Nosaki H., Tomita T. Light-induced resistance changes in single photoreceptors of Necturus and Gekko. Vision Res. 1969 Apr;9(4):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(69)90134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifonov I. U. Izuchenie sinapticheskoi peredachi mezhdu fotoretseptorom i gorizontal'noi kletkoi pri pomoshchi élektricheskikh razdrazhenii setchatki. Biofizika. 1968 Sep-Oct;13(5):809–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukahara N., Toyama K., Kosaka K., Udo M. "Disfacilitation" of red nucleus neurones. Experientia. 1965 Sep 15;21(9):544–545. doi: 10.1007/BF02138988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkovsky P., Dowling J. E. Synaptic relationships in the plexiform layers of carp retina. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1969;100(1):60–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00343821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkovsky P. Peripheral mechanisms of vision. Annu Rev Physiol. 1971;33:257–280. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.33.030171.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


