Abstract
1. The electrical activity of single motor units has been recorded from the first dorsal interosseus muscle of normal human subjects during voluntary, isometric contractions, together with the force generated by the muscle.
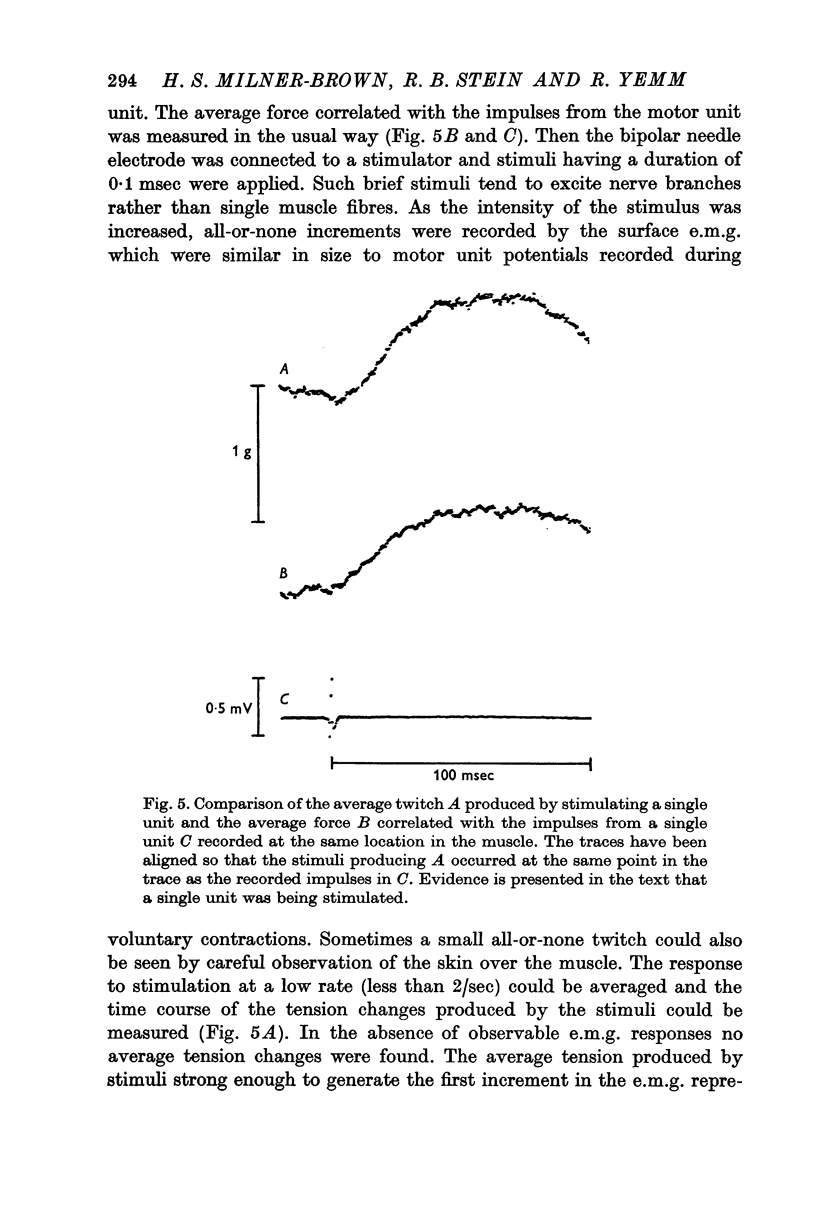
2. By averaging the force correlated with the impulses from a single motor unit, the contraction time and twitch tension generated by that motor unit could be measured. When the rate of discharge was limited, either voluntarily or by automatic selection of intervals for analysis, the time for the tension to decline to half its maximum value (half-relaxation time) could also be measured for some motor units.
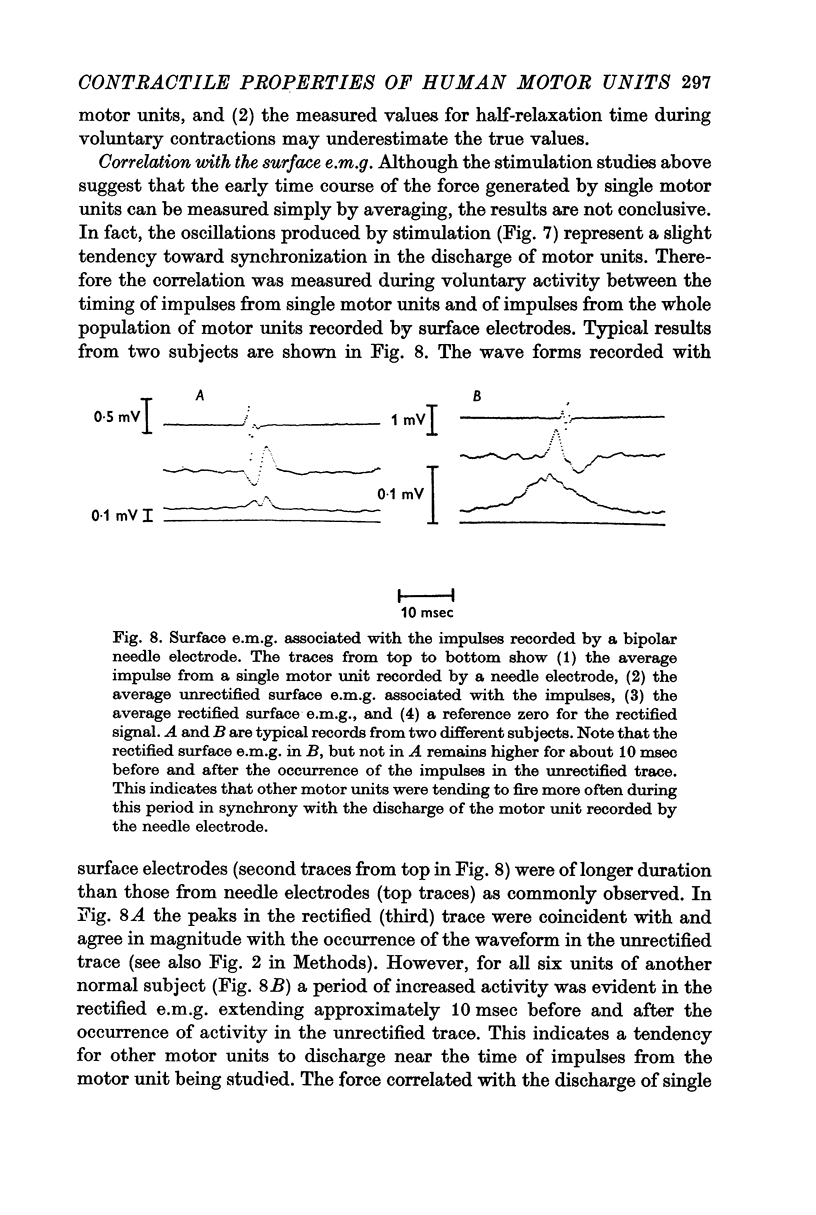
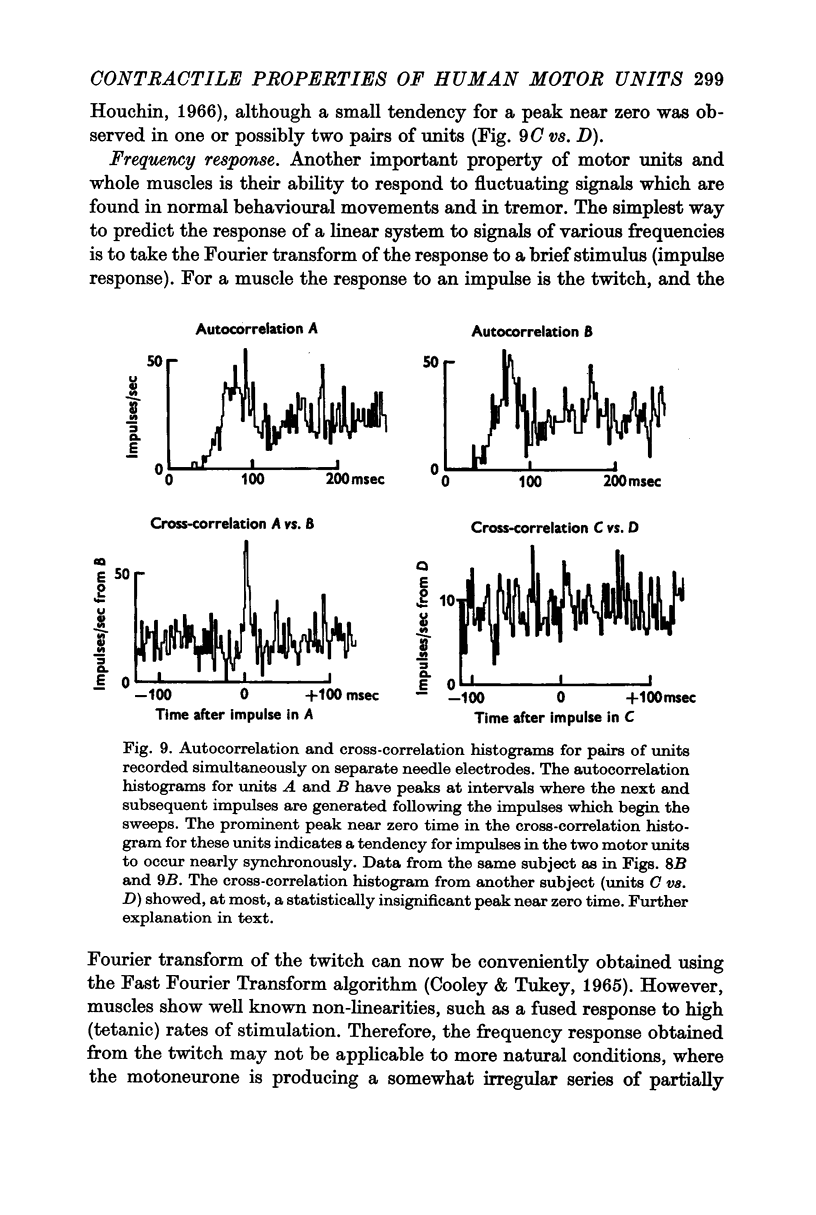
3. Under our experimental conditions the trains of impulses from different motor units in most subjects were generated quite independently as tested by (a) measuring the correlation between activity in single units and that in the whole muscle as recorded by the surface electromyogram (e.m.g.), (b) measuring the cross-correlations between pairs of single units and (c) comparing the tension generated by stimulating single motor units with the average tension correlated in time with voluntary activity of single units in the same location.
4. In one normal subject evidence of synchronization between separate motor units was obtained. Cross-correlation studies suggested that the cause of the synchronization was the presence of substantial common excitation received by the various motor units in the muscle.
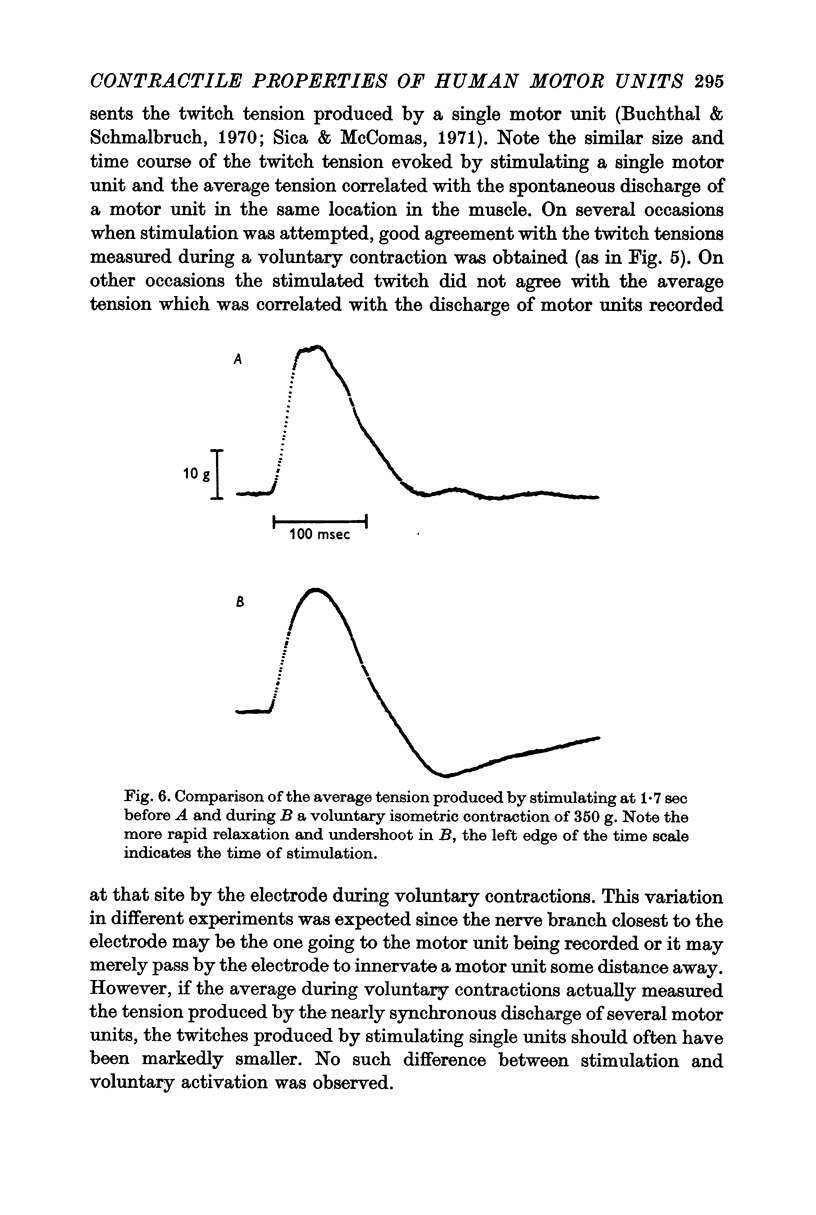
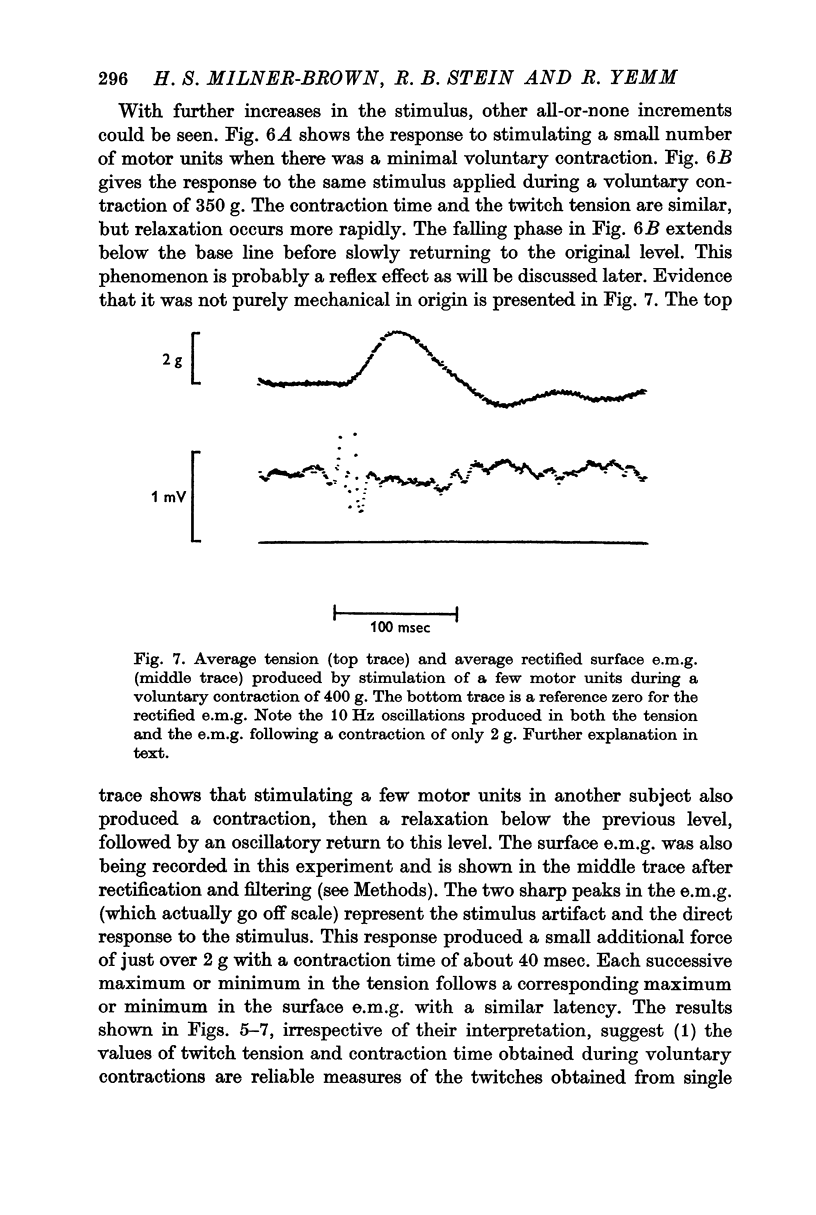
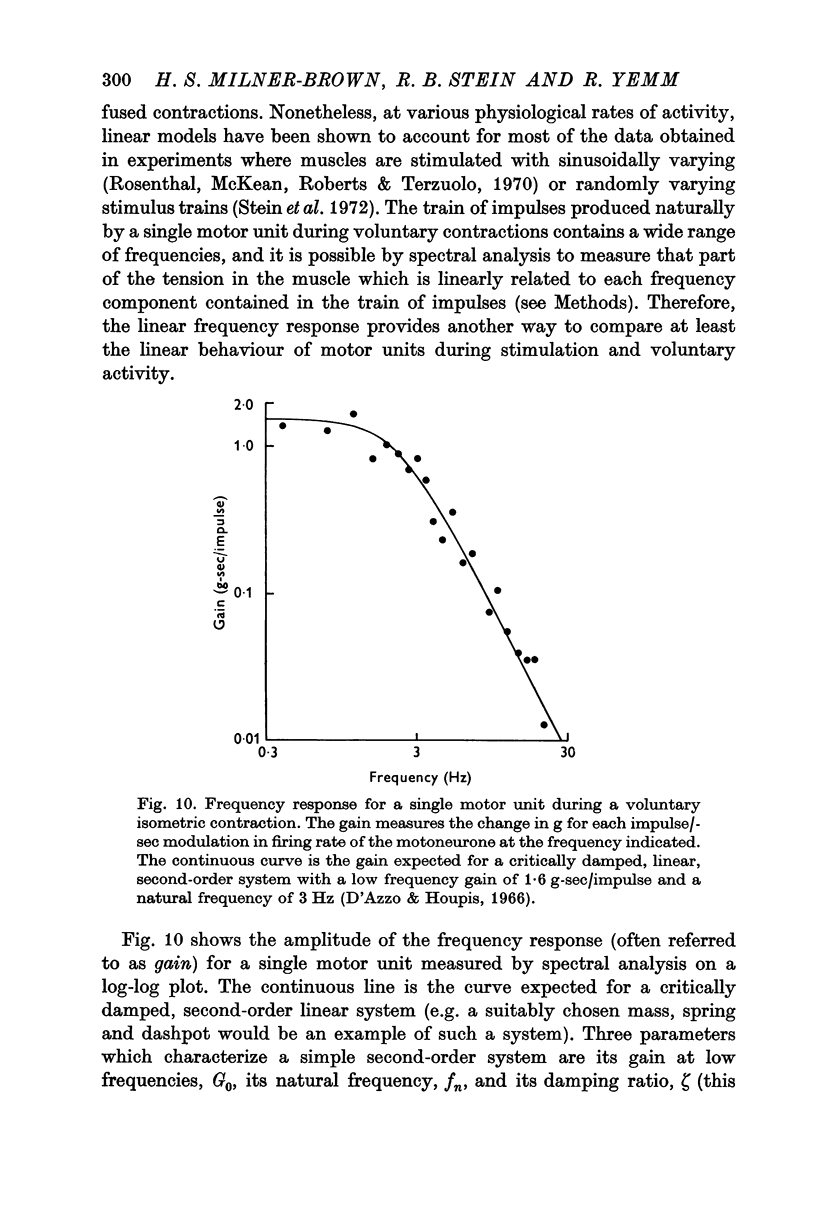
5. The frequency response for the contractions of single motor units was well fitted by that for a linear, second-order system with nearly critical damping. However, when stimulation of a few motor units was superimposed on a voluntary contraction, underdamped (oscillatory) responses were seen which were probably of reflex origin.
6. The significance of these results in relation to the normal postural tremor in hand muscles is discussed.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUCHTHAL F., MADSEN A. Synchronous activity in normal and atrophic muscle. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1950 Nov;2(4):425–444. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(50)90079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchthal F., Schmalbruch H. Contraction times and fibre types in intact human muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 Aug;79(4):435–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04744.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clamann H. P. Activity of single motor units during isometric tension. Neurology. 1970 Mar;20(3):254–260. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.3.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French A. S., Holden A. V. Alias-free sampling of neuronal spike trains. Kybernetik. 1971 May;8(5):165–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00291117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French A. S., Holden A. V. Semi-on-line implementation of an alias-free sampling system for neuronal signals. Comput Programs Biomed. 1971 Dec;2(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(71)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb G. L., Agarwal G. C. Filtering of electromyographic signals. Am J Phys Med. 1970 Apr;49(2):142–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMMOND P. H., MERTON P. A., SUTTON G. G. Nervous gradation of muscular contraction. Br Med Bull. 1956 Sep;12(3):214–218. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes O., Houchin J. Units in the cerebral cortex of the anaesthetized rat and the correlations between their discharges. J Physiol. 1966 Dec;187(3):651–671. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPPOLD O. C., REDFEARN J. W., VUCO J. The rhythmical activity of groups of motor units in the voluntary contraction of muscle. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 6;137(3):473–487. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippold O. C. Oscillation in the stretch reflex arc and the origin of the rhythmical, 8-12 C-S component of physiological tremor. J Physiol. 1970 Feb;206(2):359–382. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Merton P. A., Morton H. B. Changes in loop gain with force in the human muscle servo. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(1):32P–34P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendell L. M., Henneman E. Terminals of single Ia fibers: location, density, and distribution within a pool of 300 homonymous motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Jan;34(1):171–187. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. P., Perkel D. H., Segundo J. P. Statistical analysis and functional interpretation of neuronal spike data. Annu Rev Physiol. 1966;28:493–522. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.28.030166.002425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. P., Segundo J. P., Perkel D. H., Levitan H. Statistical signs of synaptic interaction in neurons. Biophys J. 1970 Sep;10(9):876–900. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86341-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Person R. S., Kudina L. P. Cross-correlation of electromyograms showing interference patterns. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1968 Jul;25(1):58–68. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(68)90087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rescigno A., Stein R. B., Purple R. L., Poppele R. E. A neuronal model for the discharge patterns produced by cyclic inputs. Bull Math Biophys. 1970 Sep;32(3):337–353. doi: 10.1007/BF02476873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal N. P., McKean T. A., Roberts W. J., Terzuolo C. A. Frequency analysis of stretch reflex and its main subsystems in triceps surae muscles of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1970 Nov;33(6):713–749. doi: 10.1152/jn.1970.33.6.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer E. A. On the Rhythm of Muscular Response to Volitional Impulses in Man. J Physiol. 1886 Apr;7(2):111–117. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1886.sp000210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sica R. E., McComas A. J. Fast and slow twitch units in a human muscle. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Apr;34(2):113–120. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.2.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. B., French A. S., Mannard A., Yemm R. New methods for analysing motor function in man and animals. Brain Res. 1972 May 12;40(1):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90126-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. B. Modules for neurophysiology using integrated circuits. J Physiol. 1968 Jul;197(1):1P–2P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens J. A., Taylor A. Fatigue of maintained voluntary muscle contraction in man. J Physiol. 1972 Jan;220(1):1–18. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton G. G., Sykes K. The variation of hand tremor with force in healthy subjects. J Physiol. 1967 Aug;191(3):699–711. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR A. The significance of grouping of motor unit activity. J Physiol. 1962 Jul;162:259–269. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


