Abstract
1. A method is described by which mammalian motor nerve terminals may be uniformly polarized by focally applied current, and the extra-cellular potential in the synaptic cleft, corresponding to any current, estimated.
2. The relationship between log m.e.p.p. frequency and local extra-cellular field is flat for hyperpolarization and ascends linearly with depolarization. With depolarization, m.e.p.p. frequency is multiplied about tenfold for every — 18 mV. This characteristic becomes steeper the closer the polarizing electrode to the nerve terminal with a limiting value of ten-fold per — 15 mV.
3. There exists a population of small m.e.p.p.s which are generated at the same end-plate as normal m.e.p.p.s.
4. Following a prolonged depolarizing pulse there is an increase of m.e.p.p. frequency which continues for periods of up to several minutes.
5. With hyperpolarizing pulses m.e.p.p. frequency may increase in a characteristic `bursty' manner. Similar bursts of m.e.p.p.s also occur spontaneously, but far less frequently, without polarization.
6. During a depolarizing pulse, m.e.p.p. frequency becomes maximal or near maximal within 2 sec. There is little subsequent alteration of m.e.p.p. frequency. Numbers of m.e.p.p.s occurring during depolarizing pulses follow the Poisson distribution.
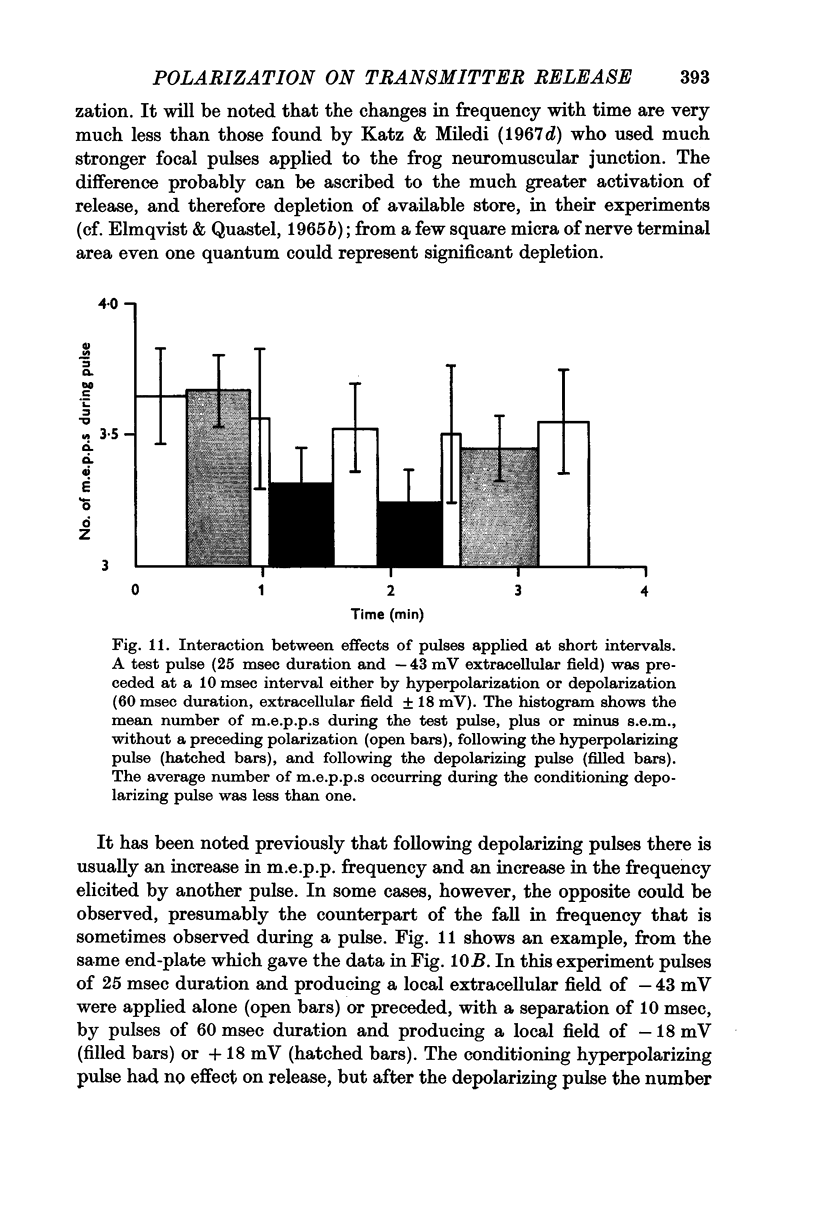
7. Following a depolarizing pulse, numbers of m.e.p.p.s released by a subsequent pulse may be either increased or diminished.
8. Comparison of the response of m.e.p.p. frequency to raised [K] and to extrinsic presynaptic polarization leads to the conclusion that the presynaptic transmembrane potential change corresponding to any focal current pulse is about two thirds of the local extracellular potential field. Hence the slope of the linear portion of the presynaptic transfer function is about tenfold per 10 mV presynaptic depolarization.
Full text
PDF

























Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooke J. D., Okamoto K., Quastel D. M. The role of calcium in depolarization-secretion coupling at the motor nerve terminal. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(2):459–497. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke J. D., Quastel D. M. Cumulative and persistent effects of nerve terminal depolarization on transmitter release. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(2):407–434. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke J. D., Quastel D. M. The specific effect of potassium on transmitter release by motor nerve terminals and its inhibition by calcium. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(2):435–458. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Changes in end-plate activity produced by presynaptic polarization. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):586–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELMQVIST D., QUASTEL D. M. PRESYNAPTIC ACTION OF HEMICHOLINIUM AT THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION. J Physiol. 1965 Apr;177:463–482. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmqvist D., Quastel D. M. A quantitative study of end-plate potentials in isolated human muscle. J Physiol. 1965 Jun;178(3):505–529. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. An analysis of the end-plate potential recorded with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol. 1951 Nov 28;115(3):320–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURSHPAN E. J. The effects of osmotic pressure changes on the spontaneous activity at motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1956 Dec 28;134(3):689–697. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Quastel D. M. Dual effect of potassium on transmitter release. Nature. 1965 May 8;206(984):625–626. doi: 10.1038/206625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F., TAYLOR R. E. Local activation of striated muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1958 Dec 30;144(3):426–441. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell J. N. A lesion of the transverse tubules of skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1969 May;201(3):515–533. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I., Willis W. D. The effects of depolarization of motor nerve terminals upon the release of transmitter by nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(2):381–405. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. PROPAGATION OF ELECTRIC ACTIVITY IN MOTOR NERVE TERMINALS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:453–482. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. A study of synaptic transmission in the absence of nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):407–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Modification of transmitter release by electrical interference with motor nerve endings. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Jan 31;167(1006):1–7. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Spontaneous and evoked activity of motor nerve endings in calcium Ringer. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(3):689–706. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Tetrodotoxin and neuromuscular transmission. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Jan 31;167(1006):8–22. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Tetrodotoxin-resistant electric activity in presynaptic terminals. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):459–487. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Tomita T. Noradrenaline action on nerve terminal in the rat diaphragm. J Physiol. 1971 Aug;217(1):19–31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano K., Livengood D. R., Werman R. Correlation of transmitter release with membrane properties of the presynaptic fiber of the squid giant synapse. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Dec;50(11):2579–2601. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.11.2579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W., NORTH K. A. An electrical investigation of effects of repetitive stimulation on mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Neurophysiol. 1953 Sep;16(5):509–527. doi: 10.1152/jn.1953.16.5.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. The effects of presynaptic polarization on the spontaneous activity at the mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):427–443. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau E. M. The interaction of presynaptic polarization with calcium and magnesium in modifying spontaneous transmitter release from mammalian motor nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):281–299. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quastel D. M., Hackett J. T., Cooke J. D. Calcium: is it required for transmitter secretion? Science. 1971 Jun 4;172(3987):1034–1036. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3987.1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. Active phase of frog's end-plate potential. J Neurophysiol. 1959 Jul;22(4):395–411. doi: 10.1152/jn.1959.22.4.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. Changes in potassium concentration around motor nerve terminals, produced by current flow, and their effects on neuromuscular transmission. J Physiol. 1961 Jan;155:46–58. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. On the permeability of end-plate membrane during the action of transmitter. J Physiol. 1960 Nov;154:52–67. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


