Abstract
1. Intracellular ion concentrations, measured in rat liver perfused with saline solutions were, at steady state:
[K]1 = 113; [Na]1 = 16·4; [Cl]1 = 25·5 m-mole l.-1 of cells.
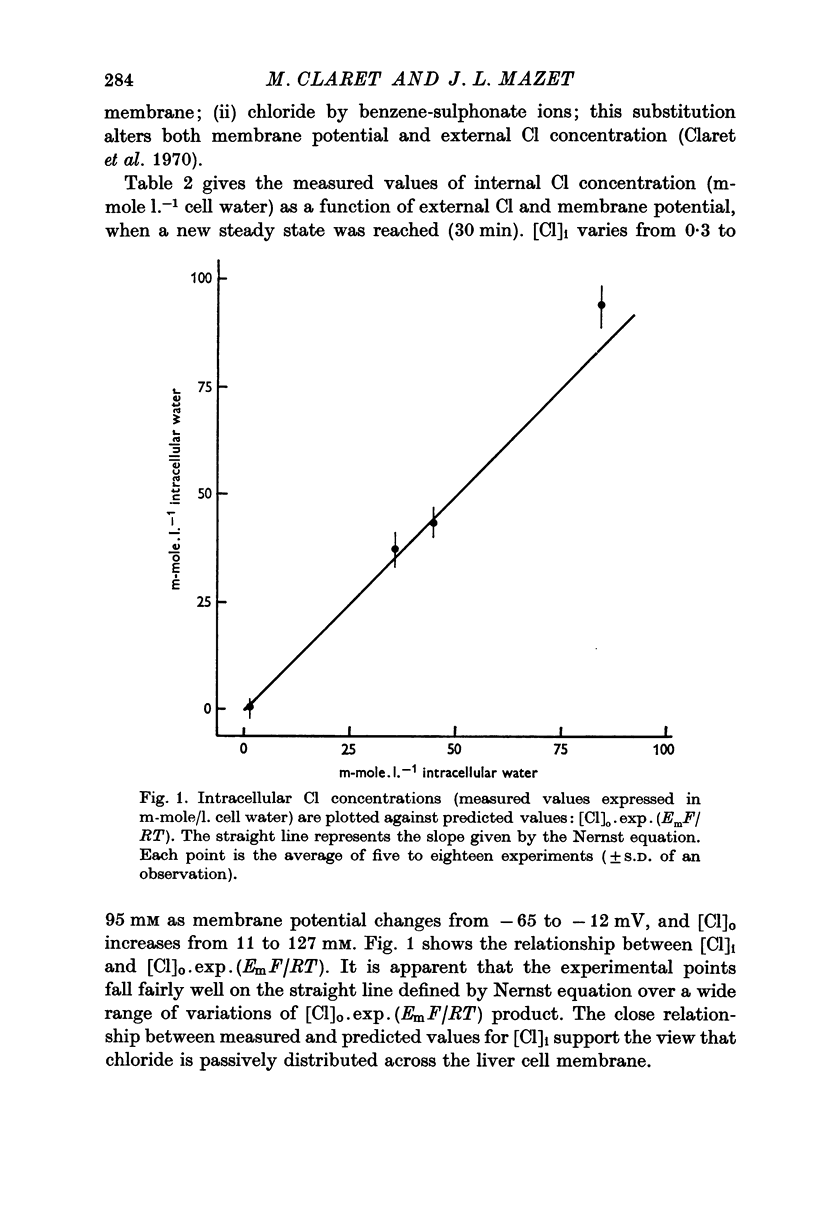
2. Intracellular Cl concentration was measured when both [Cl]o and membrane potential were changed. The experimental values were close to the predicted ones by the Nernst equation, indicating a passive distribution of this ion across the cell membrane.
3. Fluxes were determined by means of radioactive tracers and had the following values:
mK = 6·6; mNa = 12·4 and mCl = 8 × 10-12 mole cm-2 sec-1.
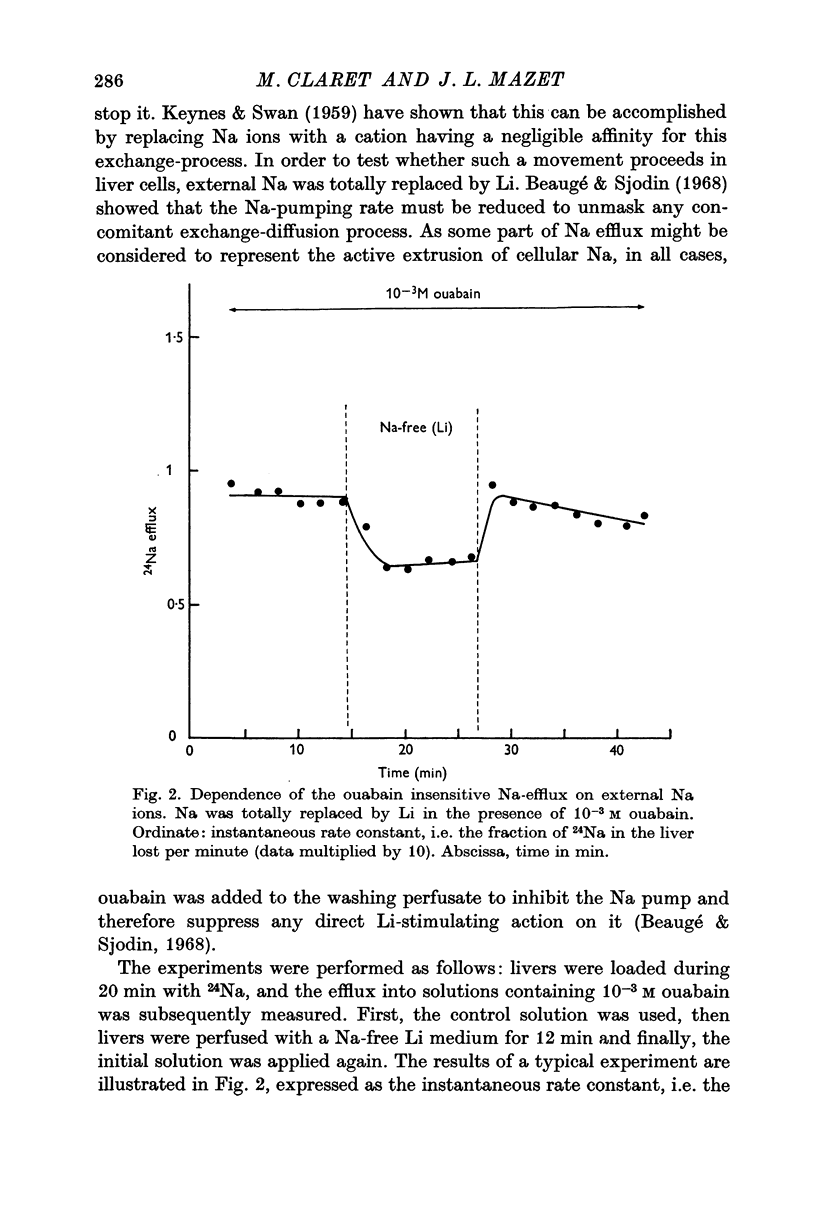
4. When Na was replaced by Li in the perfusing solutions, the Na efflux was decreased by 3·3 × 10-12 mole cm-2 sec-1. This was attributed to a Na-for-Na exchange (exchange-diffusion).
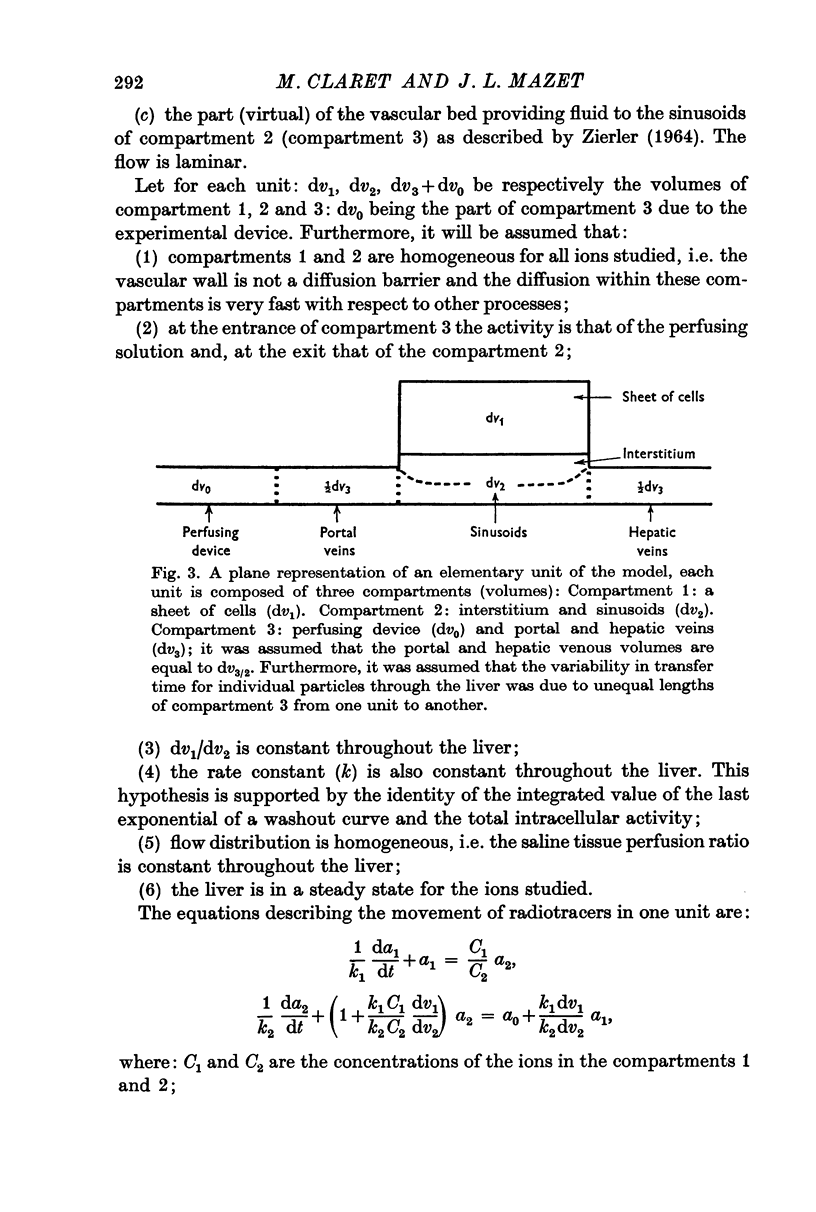
5. A mathematical model was applied to the perfused liver. It allowed estimation of the actual fluxes across the membrane. Corrections resulting from the application of the model remain small.
6. The permeability coefficients were calculated from the passive fluxes and were:
PK = 7·6; PNa = 4·0; PCl = 12·3 × 10-8 cm sec-1, corresponding to relative permeabilities of PNa/PK = 0·52 and PCl/PK = 1·6.
7. The membrane potential calculated from the Goldman equation was significantly different from the measured one. This may be accounted for by an electrogenic activity of the Na—K pump. Applying the Mullins & Noda equation, the ratio of active Na flux to active K flux becomes 3/2.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRISTOW D. A., KERLY M. TRANSAMINATION IN PERFUSED RAT LIVER. J Physiol. 1964 Mar;170:318–327. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L. A., Sjodin R. A. The dual effect of lithium ions on sodium efflux in skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Sep;52(3):408–423. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.3.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEVALLIER F., MAURICE J. P. [Fate of cholesterol in chylomicrons in the rat. I. Research on storage in chylomicrons]. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1961;43:827–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteels R. Calculation of the membrane potential in smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig's taenia coli by the Goldman equation. J Physiol. 1969 Nov;205(1):193–208. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claret M., Coraboeuf E., Ehrhart J. C. Modification des potentiels transmembranaires hépatiques du rat sous l'influence de la thyroïdectomie et de la surrénalectomie. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1966;160(3):476–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claret M., Coraboeuf E., Favier M. P. Effect of ionic concentration changes on membrane potential of perfused rat liver. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1970 Aug;78(3):531–545. doi: 10.3109/13813457009075204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claret M., Coraboeuf E. Membrane potential of perfused and isolated rat liver. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):137P–138P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claret M., Favier M. P. Concentrations intracellulaires et perméabilités relatives ioniques des membranes de cellules de foie isolé et perfusé de rat. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1971 Feb 22;272(8):1123–1125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann N., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Cyclic adenosine and guaosine monophosphates and gucagon: effect on liver membrane potentials. Science. 1971 Jan 29;171(3969):400–402. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3969.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORESKY C. A. A linear method for determining liver sinusoidal and extravascular volumes. Am J Physiol. 1963 Apr;204:626–640. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.204.4.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. E. POTENTIAL, IMPEDANCE, AND RECTIFICATION IN MEMBRANES. J Gen Physiol. 1943 Sep 20;27(1):37–60. doi: 10.1085/jgp.27.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HECKMANN K. D., PARSONS D. S. Changes in the water and electrolyte content of rat-liver slices in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Nov;36:203–213. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Active transport of cations in giant axons from Sepia and Loligo. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):28–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haylett D. G., Jenkinson D. H. Effects of noradrenaline on the membrane potential and ionic permeability of parenchymal cells in the liver of the guinea-pig. Nature. 1969 Oct 4;224(5214):80–81. doi: 10.1038/224080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., LEWIS P. R. The resting exchange of radioactive potassium in crab nerve. J Physiol. 1951 Mar;113(1):73–98. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., SWAN R. C. The effect of external sodium concentration on the sodium fluxes in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147:591–625. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D. The ionic fluxes in frog muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1954 May 27;142(908):359–382. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1954.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIMBERGER J. MESSUNG VON MEMBRANPOTENTIALEN NORMALER LEBER-PARENCHYMZELLEN UND HEPATOCELLULAERER LEBER-CARCINOME DER RATTE. Z Krebsforsch. 1963 Oct 4;65:590–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLINS L. J., NODA K. THE INFLUENCE OF SODIUM-FREE SOLUTIONS ON THE MEMBRANE POTENTIAL OF FROG MUSCLE FIBERS. J Gen Physiol. 1963 Sep;47:117–132. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons D. S., van Rossum G. D. Observations on the size of the fluid compartments of rat liver slices in vitro. J Physiol. 1962 Oct;164(1):116–126. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp007006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritchie J. M. On the electrogenic sodium pump in mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres and its activation by various external cations. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):183–221. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schanne O., Coraboeuf E. Potential and resistance measurements of rat liver cells in situ. Nature. 1966 Jun 25;210(5043):1390–1391. doi: 10.1038/2101390a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- USSING H. H. Transport of ions across cellular membranes. Physiol Rev. 1949 Apr;29(2):127–155. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1949.29.2.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A., Withrow C. D., Woodbury D. M. Effects of nephrectomy and KC1 on transmembrane potentials, intracellular electrolytes, and cell pH of rat muscle and liver in vivo. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(1):117–128. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A., Withrow C. D., Woodbury D. M. Effects of ouabain and diphenylhydantoin on transmembrane potentials, intracellular electrolytes, and cell pH of rat muscle and liver in vivo. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(1):101–115. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


