Abstract
1. The effect of tetanus toxin on neuromuscular transmission in the abductor superficialis muscle of the goldfish fin has been investigated.
2. The abductor superficialis muscle is multiply innervated and junction potentials (j.p.s) and miniature junction potentials (min.j.p.s) can be recorded with an intracellular micro-electrode at any point of impalement. Intracellular recordings have been made from muscles in which neuromuscular transmission has been blocked, either completely, or partially, by I.M. injection of tetanus toxin. In addition, the tension response of both acutely and chronically toxin-blocked muscles to carbachol (1 × 10-4 M) has been investigated.
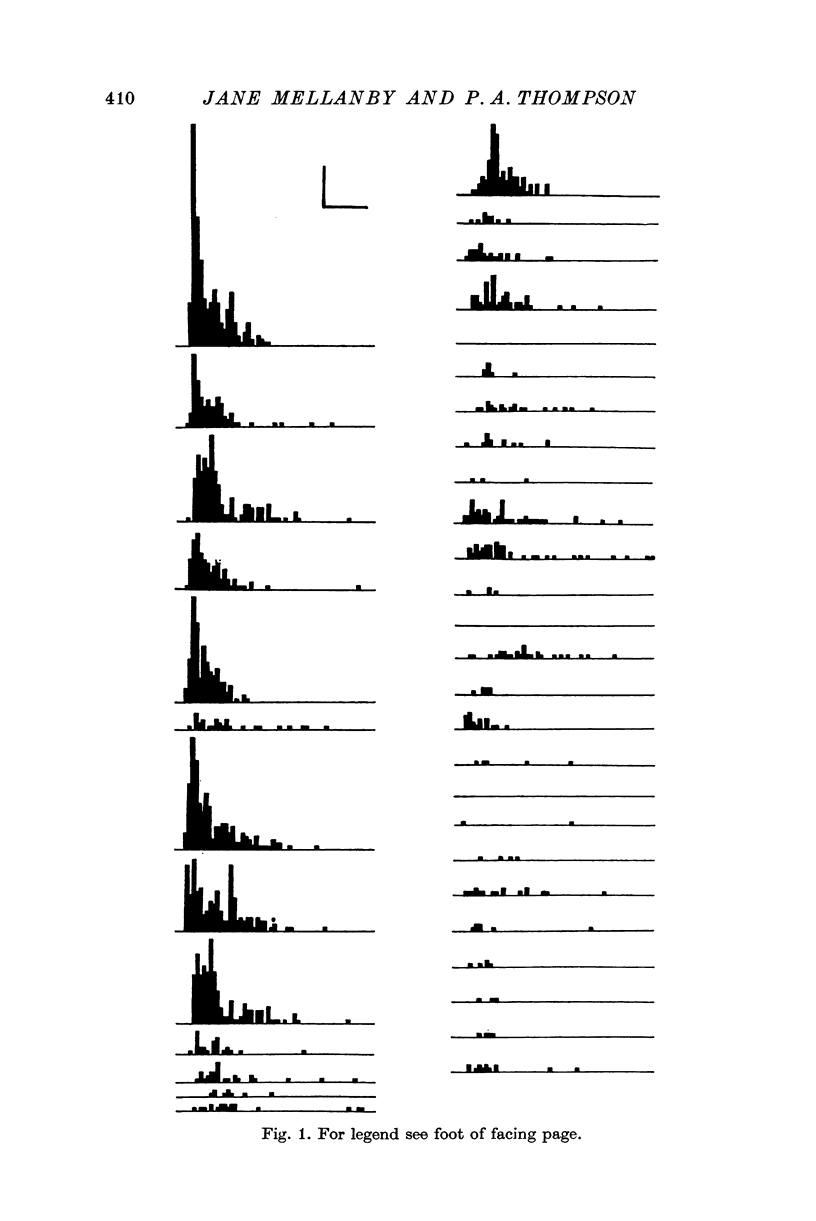
3. As the neuromuscular block proceeds, the frequency of min.j.p.s falls, and some time after the muscle has stopped responding to nerve stimulation the min.j.p.s disappear.
4. In muscles in which the block has not yet proceeded to completion, it has been found that the reduction in the frequency of the min.j.p.s is unaccompanied by any change in their range of amplitudes.
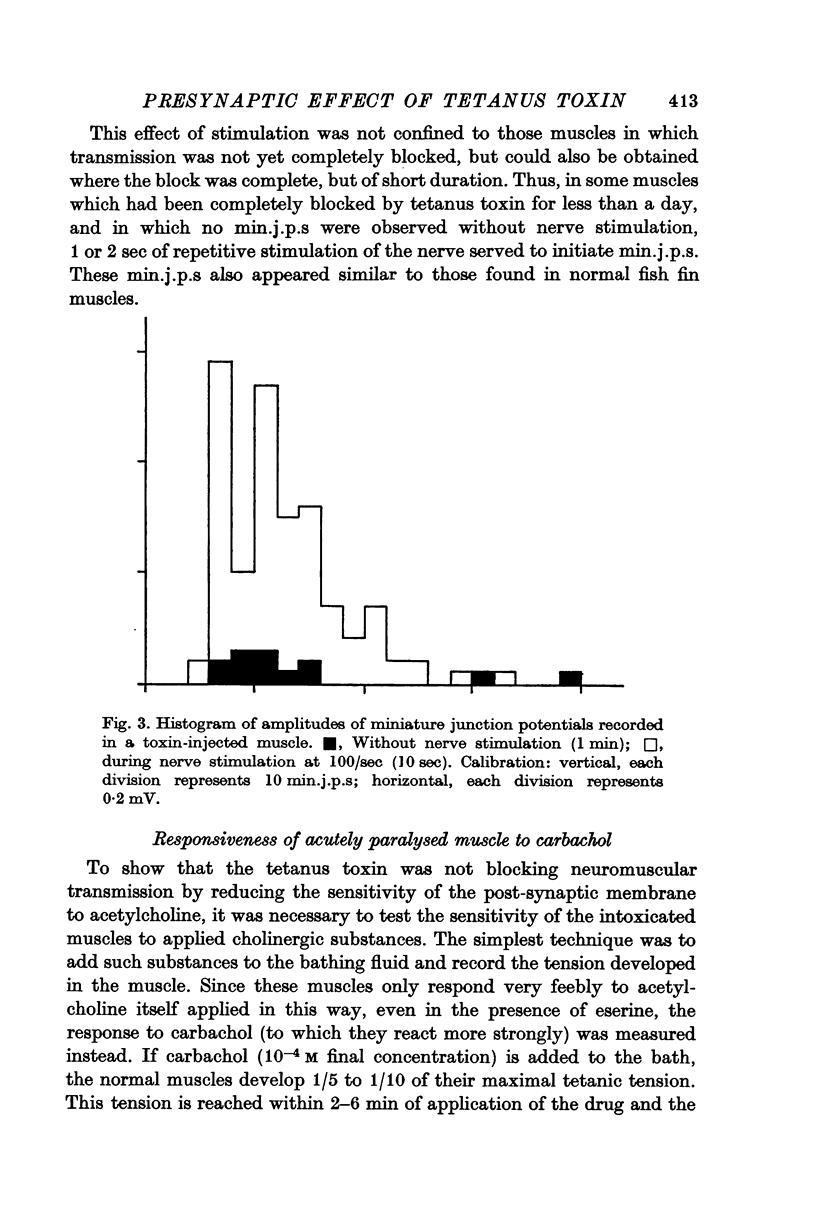
5. The min.j.p. frequency can be greatly increased in such incompletely blocked preparations by repetitive stimulation of the nerve (at, for example, 100/sec for 10 sec). The min.j.p.s obtained are indistinguishable from those seen in the absence of stimulation. Additionally, min.j.p.s can be evoked by similar repetitive stimulation in muscles which are completely blocked, and in which no min.j.p.s are seen without stimulation, so long as the block has only been complete for a short time.
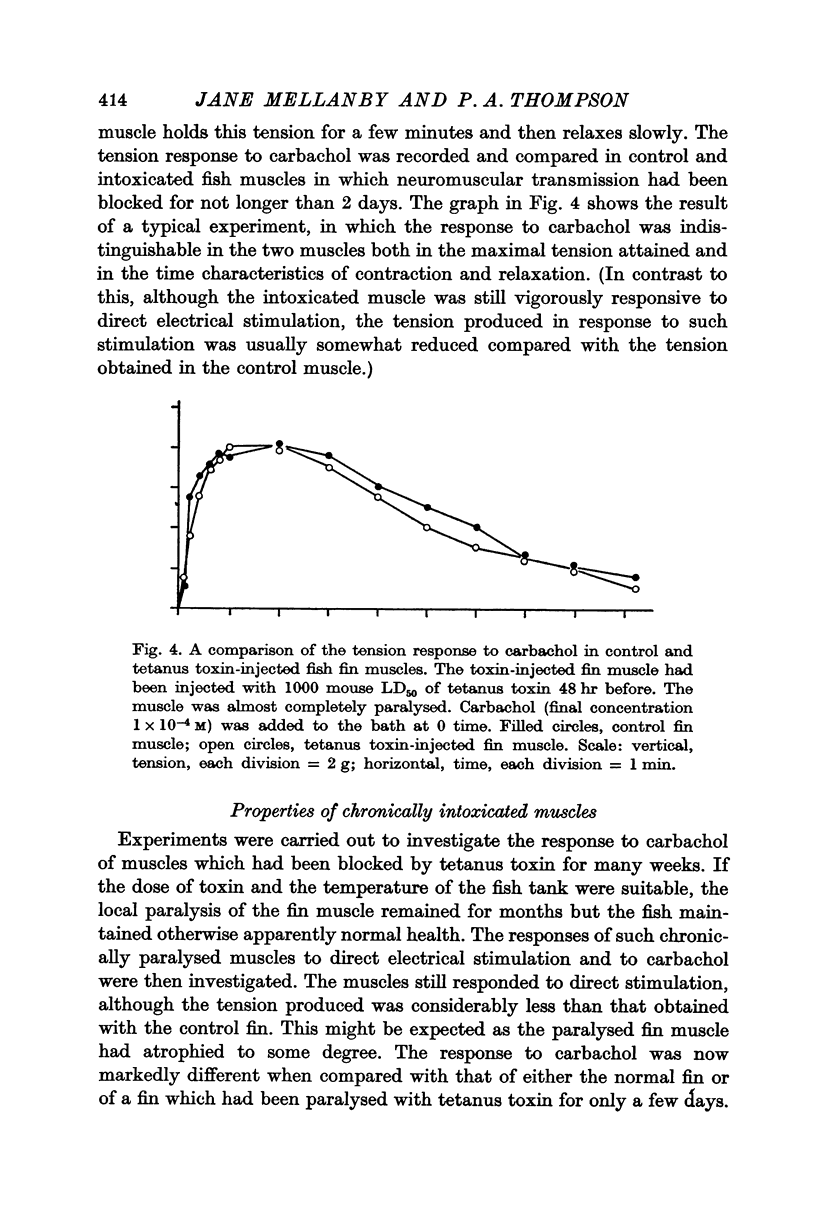
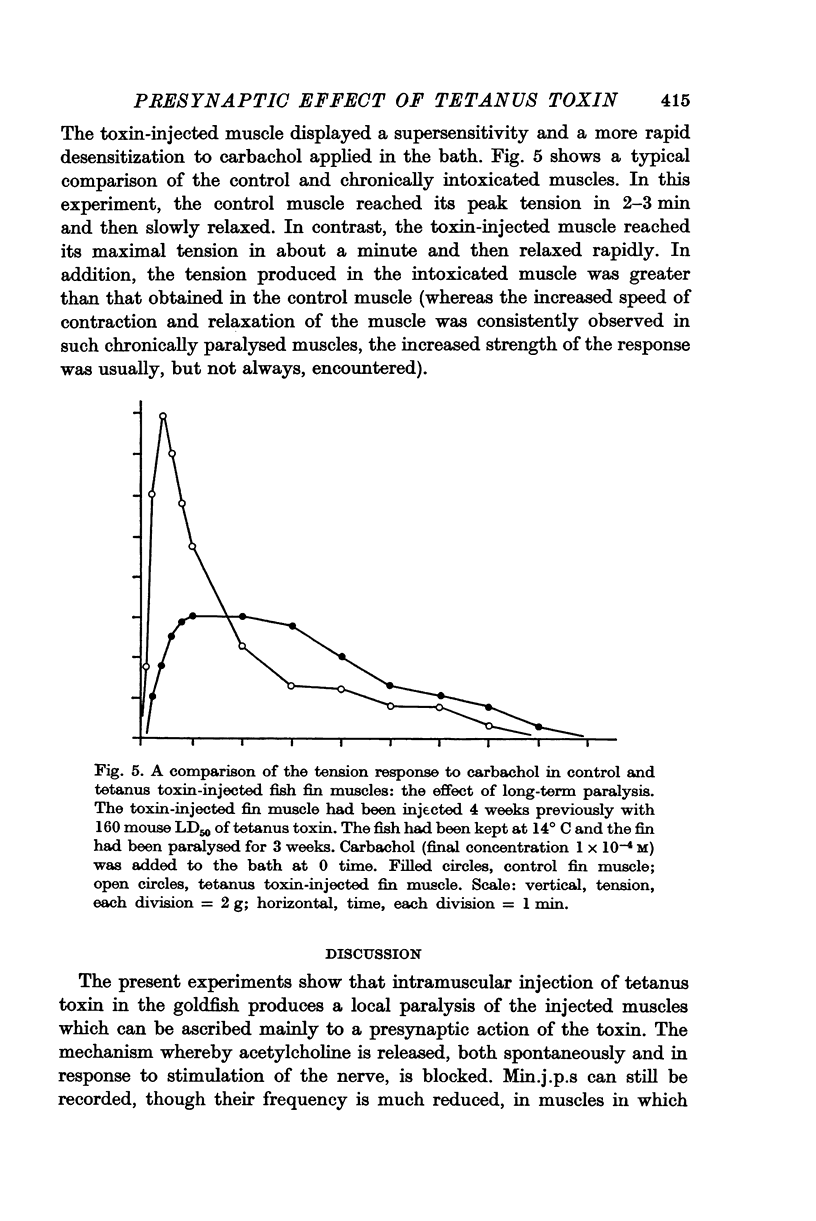
6. The tension response to carbachol of muscles which have been paralysed by tetanus toxin for only a few days is identical with that of normal muscles. In contrast, chronically toxin-paralysed muscles contract more rapidly, usually more vigorously, and relax more rapidly than normal muscles.
7. It is concluded that tetanus toxin prevents both the nerve-stimulated and spontaneous release of acetycholine from the presynaptic terminals in the abductor superficialis muscle of the goldfish fin.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambache N., Morgan R. S., Wright G. P. The action of tetanus toxin on the rabbit's iris. J Physiol. 1948 Jan 1;107(1):45–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1948.sp004248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROOKS V. B. An intracellular study of the action of repetitive nerve volleys and of botulinum toxin on miniature end-plate potentials. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):264–277. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROOKS V. B., CURTIS D. R., ECCLES J. C. The action of tetanus toxin on the inhibition of motoneurones. J Physiol. 1957 Mar 11;135(3):655–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., De Groat W. C. Tetanus toxin and spinal inhibition. Brain Res. 1968 Aug 26;10(2):208–212. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J., Mellanby J. H. Effect of tetanus toxin in the goldfish. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):186P–187P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J., Mellanby J. The effect of tetanus toxin in the goldfish. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;215(3):727–741. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEIGEN G. A., PETERSON N. S., HOFMANN W. W., GENTHER G. H., VANHEYNINGEN W. E. THE EFFECT OF IMPURE TETANUS TOXIN ON THE FREQUENCY OF MINIATURE END-PLATE POTENTIALS. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Dec;33:489–495. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-3-489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. J., Miledi R. The effect of type D botulinum toxin on frog neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1971 Sep;217(2):497–515. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey A. M. The peripheral action of tetanus toxin. J Physiol. 1939 Aug 14;96(3):348–365. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1939.sp003780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka T., Toida N. Biophysical and mechanical properties of red and white muscle fibres in fish. J Physiol. 1969 Mar;201(1):49–59. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka T., Toida N. Neuromuscular transmission and excitation-contraction coupling in fish red muscle. Jpn J Physiol. 1969 Feb 15;19(1):130–142. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.19.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurlbut W. P., Longenecker H. B., Jr, Mauro A. Effects of calcium and magnesium on the frequency of miniature end-plate potentials during prolonged tetanization. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(1):17–38. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaeser H. E., Saner A. The effect of tetanus toxin on neuromuscular transmission. Eur Neurol. 1970;3(4):193–205. doi: 10.1159/000113971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamanna C., Carr C. J. The botulinal, tetanal, and enterostaphylococcal toxins: a review. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1967 Mar-Apr;8(2):286–332. doi: 10.1002/cpt196782286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellanby J., Pope D., Ambache N. The effect of the treatment of crude tetanus toxin with ganglioside cerebroside complex on sphincter paralysis in the rabbit's eye. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Mar;50(3):479–486. doi: 10.1099/00221287-50-3-479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaki S., Okada K., Muto S., Iokazu T., Matsui M. [On the mode of action of tetanus toxin in rabbit. I. Distribution of tetanus toxin in vivo and development of paralytic signs under some conditions]. Jpn J Exp Med. 1967 Jun;37(3):217–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R. L., Hofmann W. W., Feigen G. A. Mode of action of tetanus toxin on the neuromuscular junction. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jan;210(1):84–90. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.1.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


