Abstract
1. The contractile strength generated by isolated frog auricular trabeculae has been determined by perfusion with high-K Ringer over a range of [Ca]o.
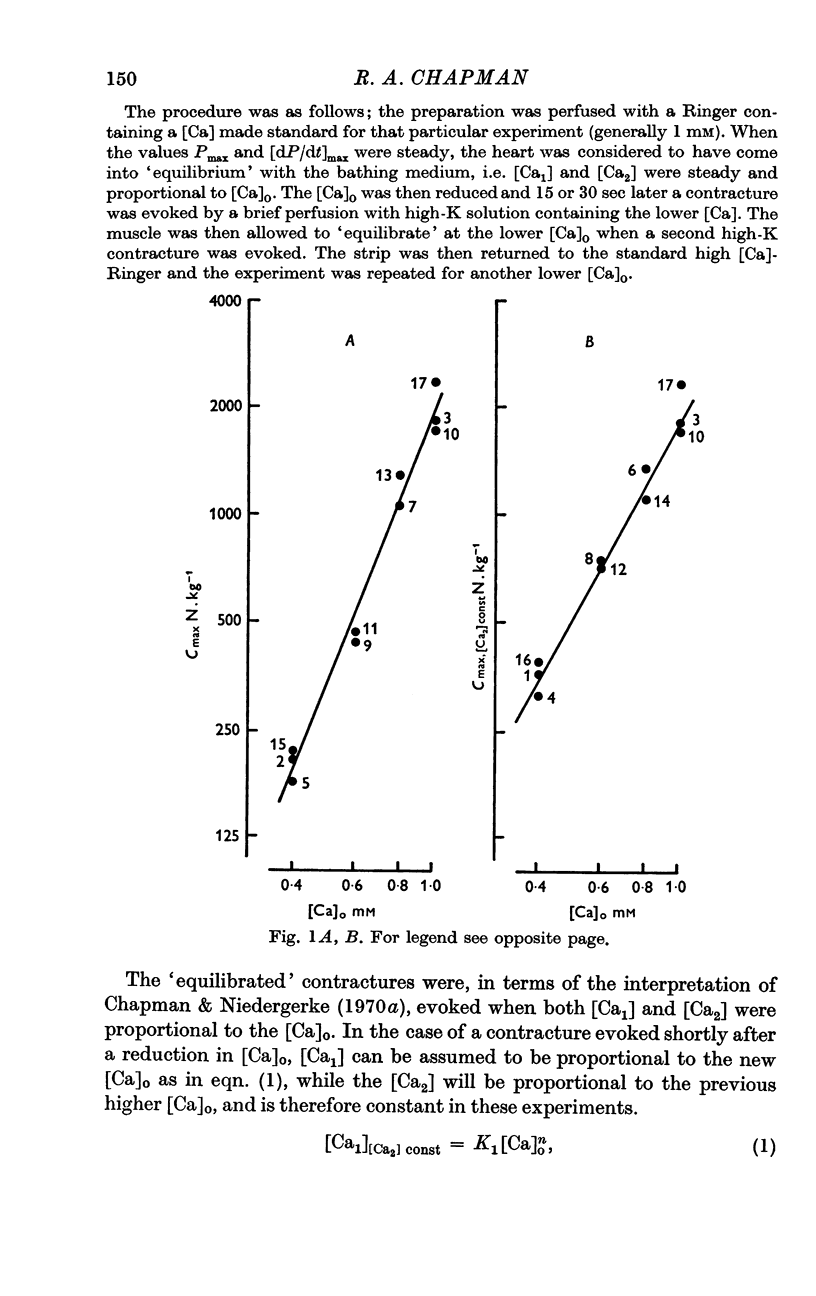
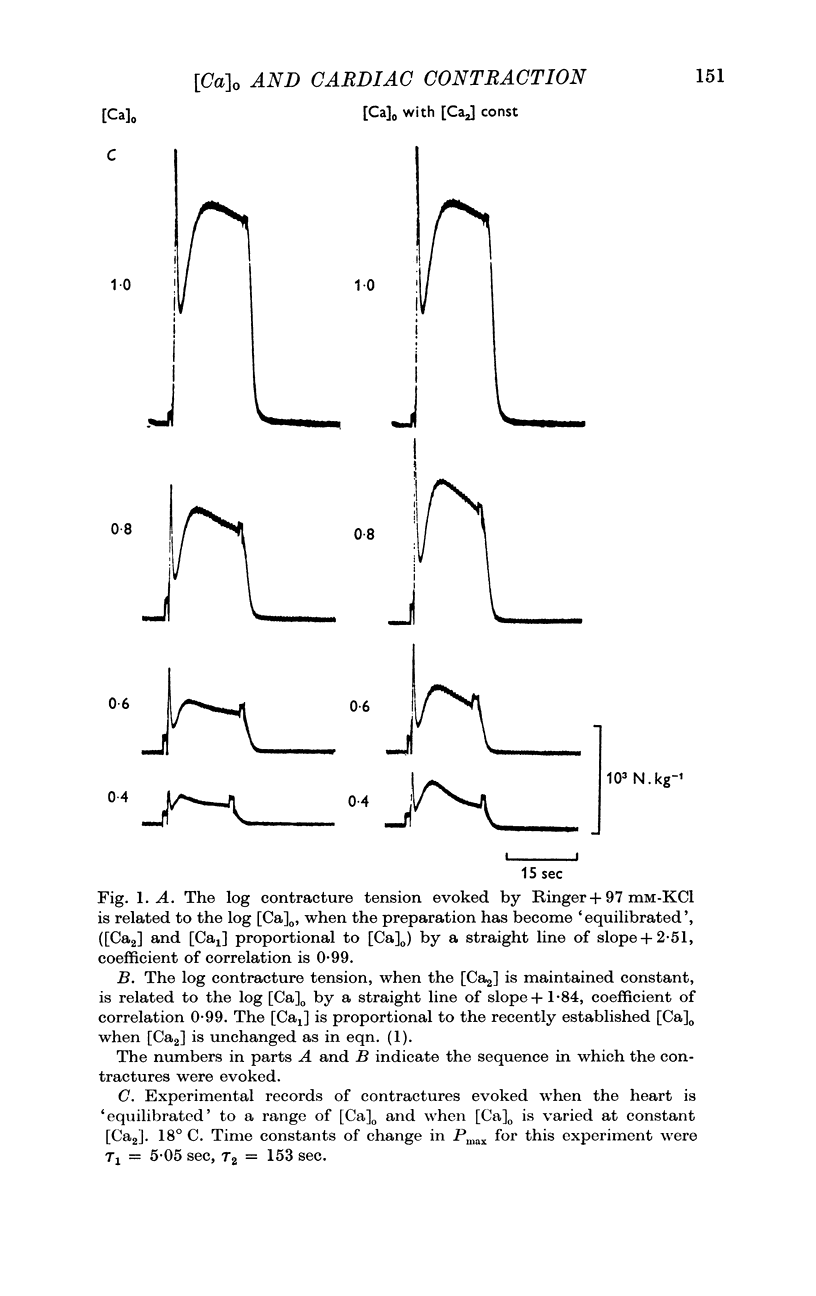
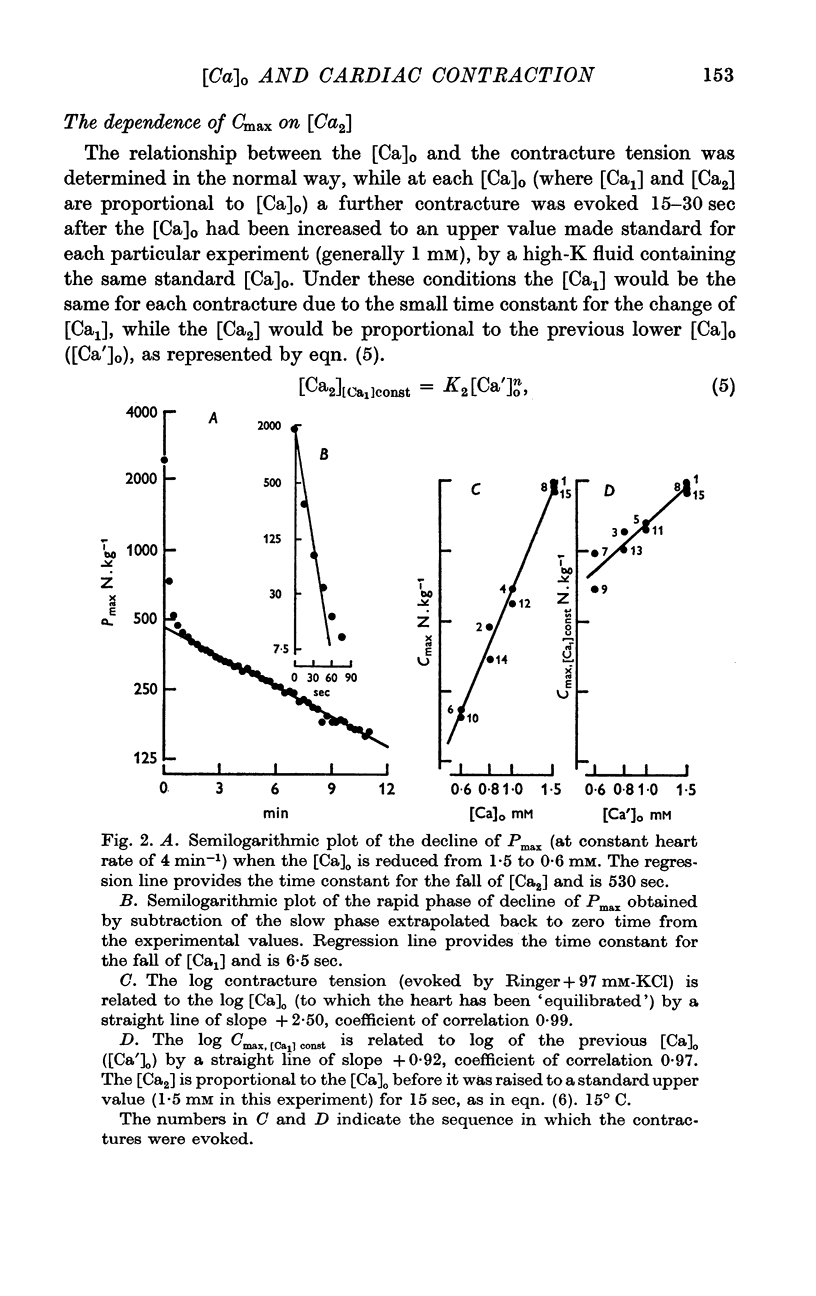
2. Experiments are described in which the cubic relationship between the contracture tension and [Ca]o has been changed to a square or a linear relationship.
3. These results have been interpreted by proposing that three Ca compounds, whose concentrations are proportional to [Ca]o, act co-operatively at some stage of the process leading to the generation of tension.
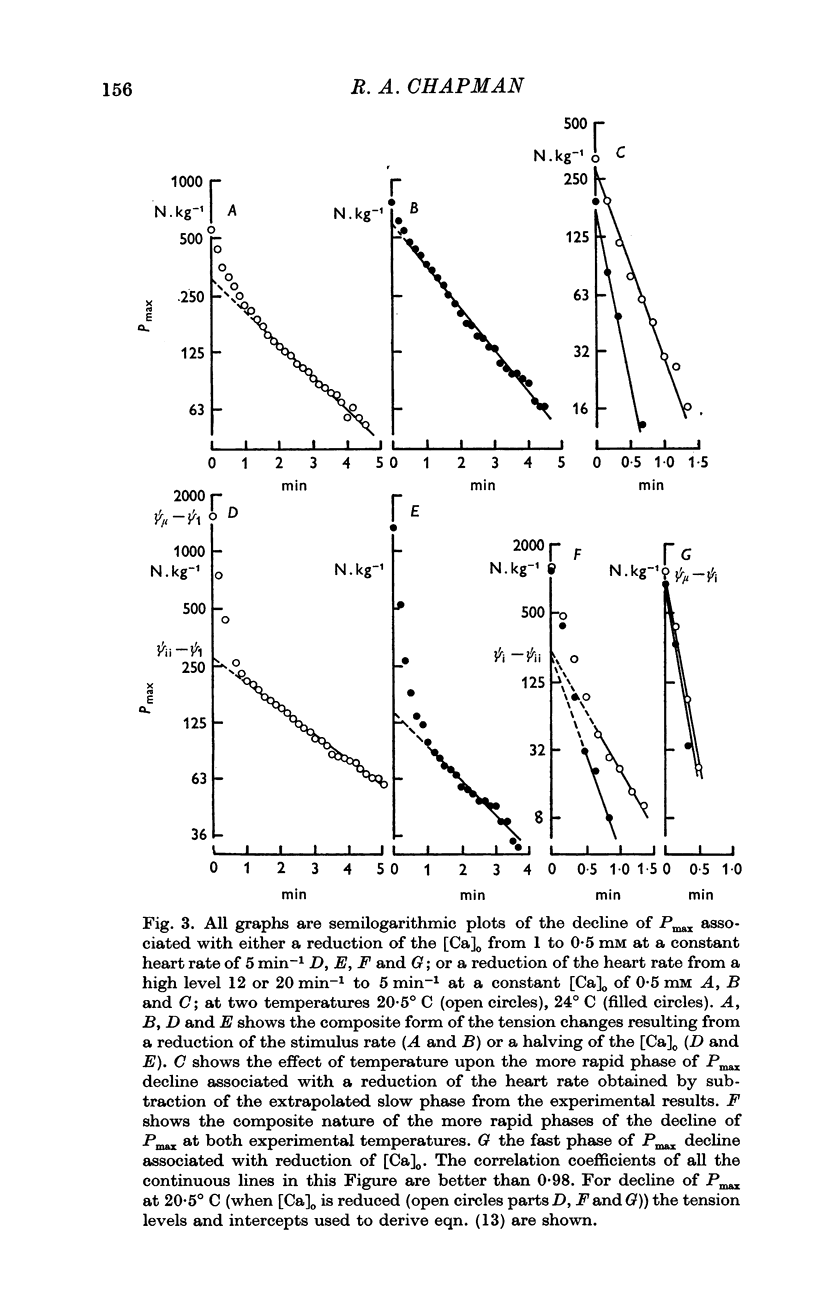
4. The change in contractile strength, determined by regular electrically evoked twitches, has been investigated at different temperatures and the results have been explained by assuming that the concentrations of the three hypothetical activating compounds vary at different rates when [Ca]o is altered.
5. The staircase response is supposed to develop as the consequence of an increase in the concentrations of the two activating Ca compounds with the slowest time constants.
6. The possible physical representations of the hypothetical activating compounds are discussed.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chapman R. A., Niedergerke R. Effects of calcium on the contraction of the hypodynamic frog heart. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(2):389–421. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman R. A., Niedergerke R. Interaction between heart rate and calcium concentration in the control of contractile strength of the frog heart. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(2):423–443. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman R. A., Tunstall J. The dependence of the contractile force generated by frog auricular trabeculae upon the external calcium concentration. J Physiol. 1971 May;215(1):139–162. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M., Otsuki I. Control of muscle contraction. Q Rev Biophys. 1969 Nov;2(4):351–384. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M., Tanaka M., Ogawa Y. Calcium induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skinned skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1970 Oct 3;228(5266):34–36. doi: 10.1038/228034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs F., Briggs F. N. The site of calcium binding in relation to the activation of myofibrillar contraction. J Gen Physiol. 1968 May;51(5):655–676. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.5.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIEDERGERKE R. Movements of Ca in beating ventricles of the frog heart. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167:551–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedergerke R., Orkand R. K. The dual effect of calcium on the action potential of the frog's heart. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(2):291–311. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedergerke R., Page S., Talbot M. S. Calcium fluxes in frog heart ventricles. Pflugers Arch. 1969;306(4):357–360. doi: 10.1007/BF00589161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougier O., Vassort G., Garnier D., Gargouil Y. M., Coraboeuf E. Existence and role of a slow inward current during the frog atrial action potential. Pflugers Arch. 1969;308(2):91–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00587018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands S. D., Winegrad S. Treppe and total calcium content of the frog ventricle. Am J Physiol. 1970 Mar;218(3):908–910. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.3.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


