Abstract
1. Micro-electrode recordings were made from ascending axons of the spinocervical tract in unanaesthetized decerebrate cats before, during and after reversible cold block of impulse conduction in the spinal cord rostral to the recording site.
2. Most units (forty-one of forty-four) fell into one of four categories as defined by their evoked responses to mechanical stimulation of identified cutaneous receptors. These categories were; Type I excited by movement of tylotrichs (hairs) in the decerebrate preparation but by movement of all types of hairs after block of descending impulses; Type II excited by movement of guard hairs and usually weakly by pressure in the decerebrate state but by movement of all types of hairs and by pressure in the spinal state; Type III excited by movement of all types of hairs and often by pressure in the decerebrate animal but by movement of all types of hairs and always by pressure in the spinal animal; Type IV weakly excited by heavy pressure or with no receptive field in the decerebrate state but excited by pressure in the spinal state.
3. The descending influences depressed the spontaneous activity and the evoked responses to harmful stimuli.
4. The descending influences depressed inhibitory inputs from segmental levels.
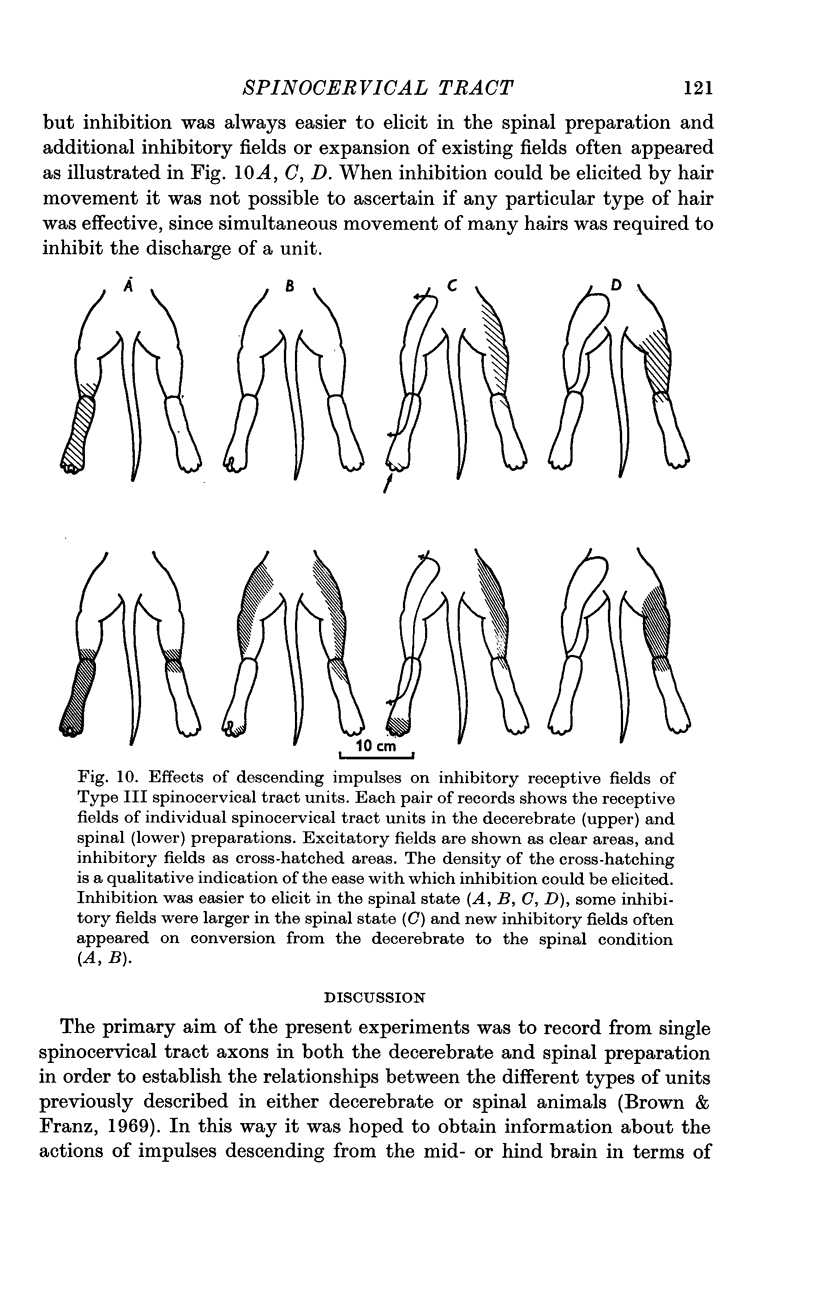
5. The functional significance of the descending control is discussed.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bessou P., Perl E. R. Response of cutaneous sensory units with unmyelinated fibers to noxious stimuli. J Neurophysiol. 1969 Nov;32(6):1025–1043. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.6.1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G. Descending control of the spinocervical tract in decerebrate cats. Brain Res. 1970 Jan 6;17(1):152–155. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90319-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Franz D. N. Responses of spinocervical tract neurones to natural stimulation of identified cutaneous receptors. Exp Brain Res. 1969;7(3):231–249. doi: 10.1007/BF00239031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Iggo A. A quantitative study of cutaneous receptors and afferent fibres in the cat and rabbit. J Physiol. 1967 Dec;193(3):707–733. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess P. R., Perl E. R. Myelinated afferent fibres responding specifically to noxious stimulation of the skin. J Physiol. 1967 Jun;190(3):541–562. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetz E. E. Pyramidal tract effects on interneurons in the cat lumbar dorsal horn. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Jan;31(1):69–80. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillman P., Wall P. D. Inhibitory and excitatory factors influencing the receptive fields of lamina 5 spinal cord cells. Exp Brain Res. 1969;9(4):284–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00235240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. Post-synaptic excitation and inhibition from primary afferents in neurones of the spinocervical tract. J Physiol. 1968 Dec;199(3):569–592. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IGGO A. Cutaneous heat and cold receptors with slowly conducting (C) afferent fibres. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1959 Oct;44:362–370. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1959.sp001417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IGGO A. Cutaneous mechanoreceptors with afferent C fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Jul;152:337–353. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iggo A., Muir A. R. The structure and function of a slowly adapting touch corpuscle in hairy skin. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(3):763–796. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A. ASCENDING SPINAL HINDLIMB PATHWAYS IN THE CAT. Prog Brain Res. 1964;12:135–163. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60621-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A., OSCARSSON O. Functional organization of the dorsal spino-cerebellar tract in the cat. VII. Identification of units by antidromic activation from the cerebellar cortex with recognition of five functional subdivisions. Acta Physiol Scand. 1960 Dec 30;50:356–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1960.tb00189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIN F. A new spinal pathway for cutaneous impulses. Am J Physiol. 1955 Nov;183(2):245–252. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.183.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORRSELL U., VOORHOEVE P. Tactile pathways from the hindlimb to the cerebral cortex in cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1962 Jan;54:9–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1962.tb02324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrington C. S., Sowton S. C. Observations on reflex responses to single break-shocks. J Physiol. 1915 Jul 5;49(5):331–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1915.sp001713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUB A. LOCAL, SEGMENTAL AND SUPRASPINAL INTERACTION WITH A DORSOLATERAL SPINAL CUTANEOUS AFFERENT SYSTEM. Exp Neurol. 1964 Oct;10:357–374. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(64)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALL P. D. Cord cells responding to touch, damage, and temperature of skin. J Neurophysiol. 1960 Mar;23:197–210. doi: 10.1152/jn.1960.23.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall P. D. The laminar organization of dorsal horn and effects of descending impulses. J Physiol. 1967 Feb;188(3):403–423. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


