Abstract
1. Excitation-contraction coupling was studied in myotomal muscles of amphioxus, Branchiostoma californiense.
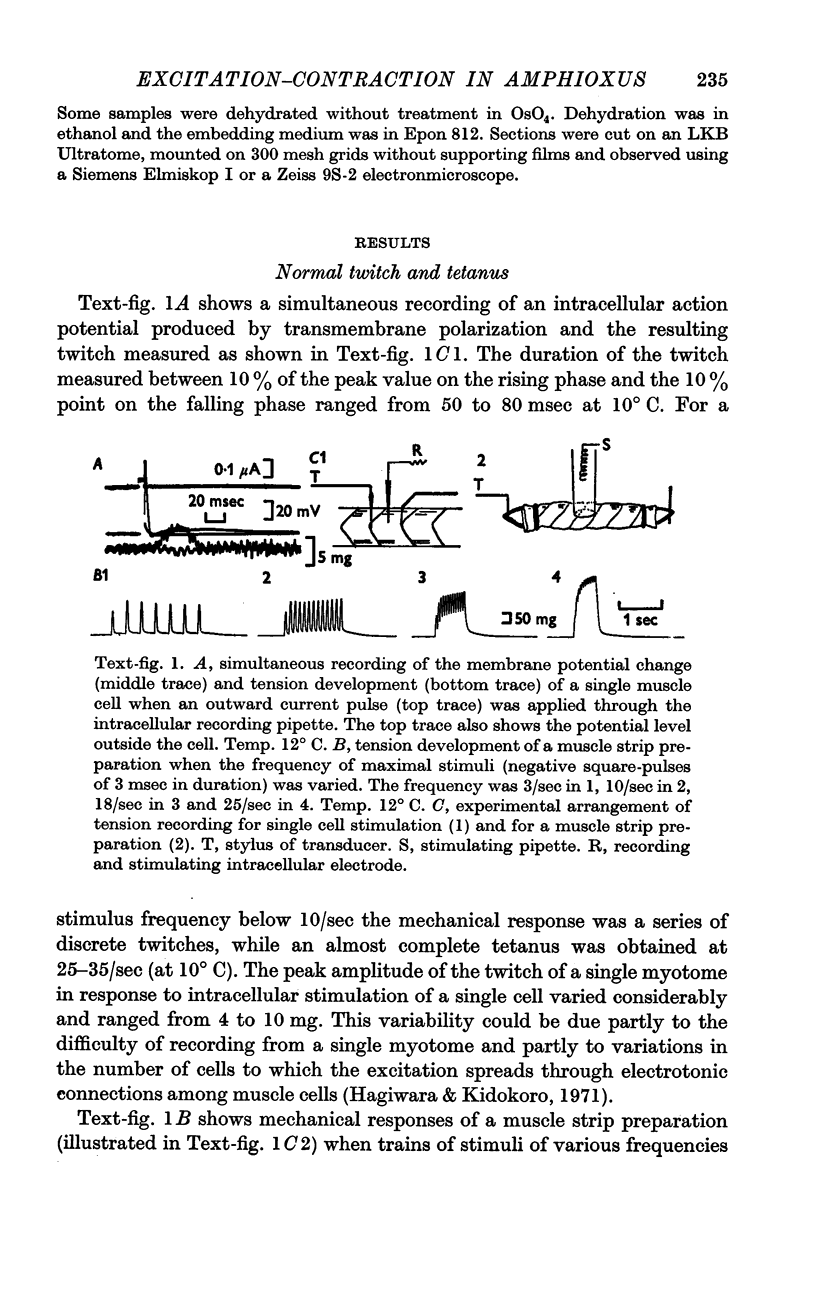
2. The action potential of a muscle cell produces a twitch with a rise time of 30-40 msec at 11° C and its Q10 is about 2·2.
3. The twitch increases in amplitude with increasing external Ca concentration and is abolished in Ca-free saline (1 mM-EGTA and 55·7 mM-MgCl2); the twitch amplitude is suppressed by Co or La ions.
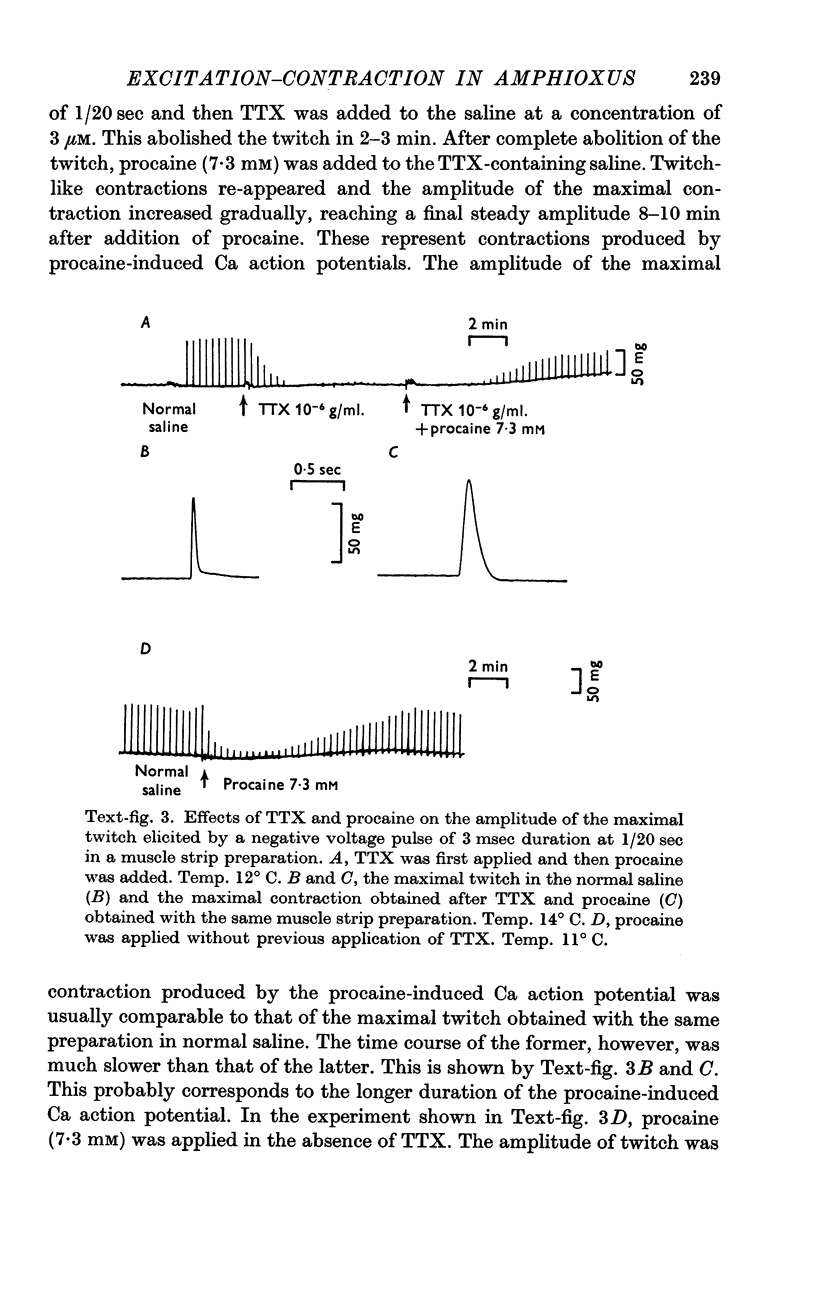
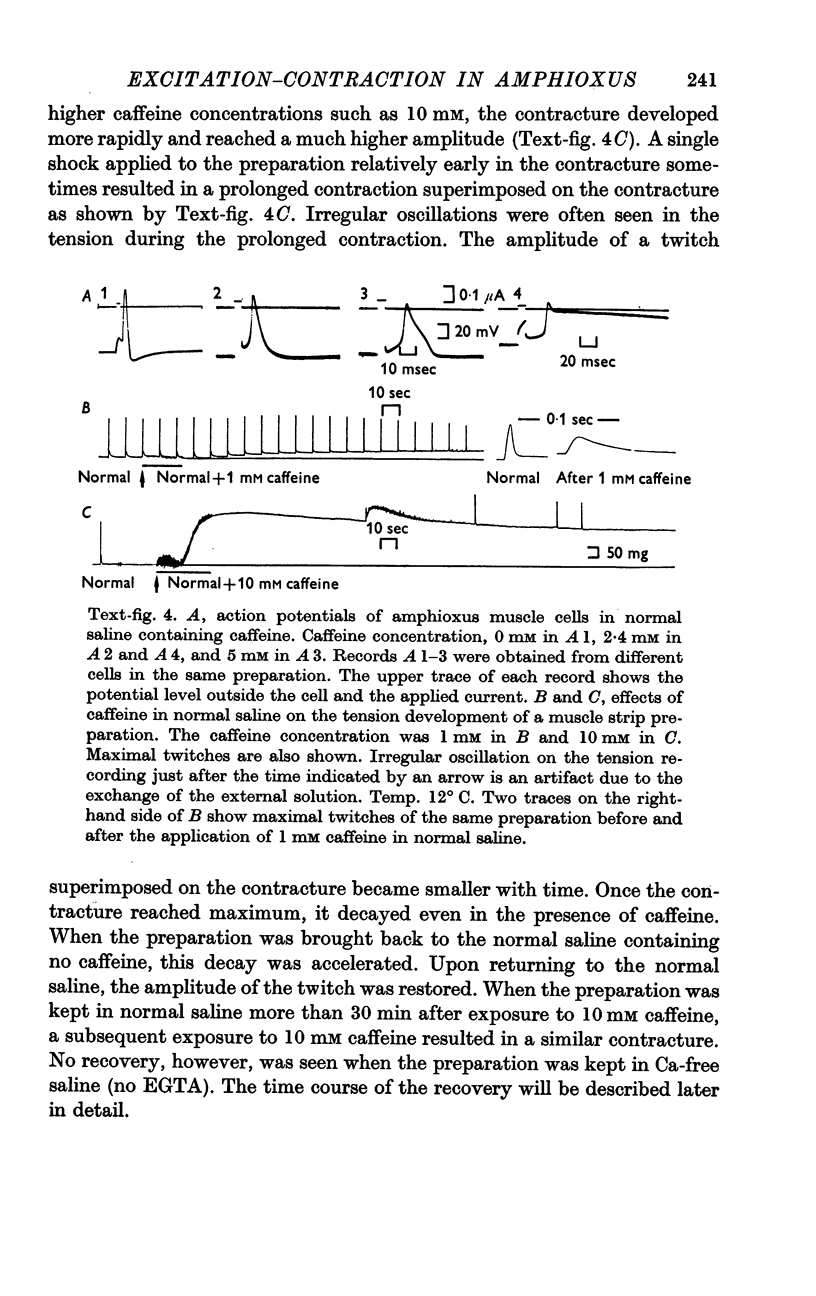
4. Caffeine at concentrations above 1 mM in the external saline causes a prolongation of the action potential and a contracture which lasts several minutes.
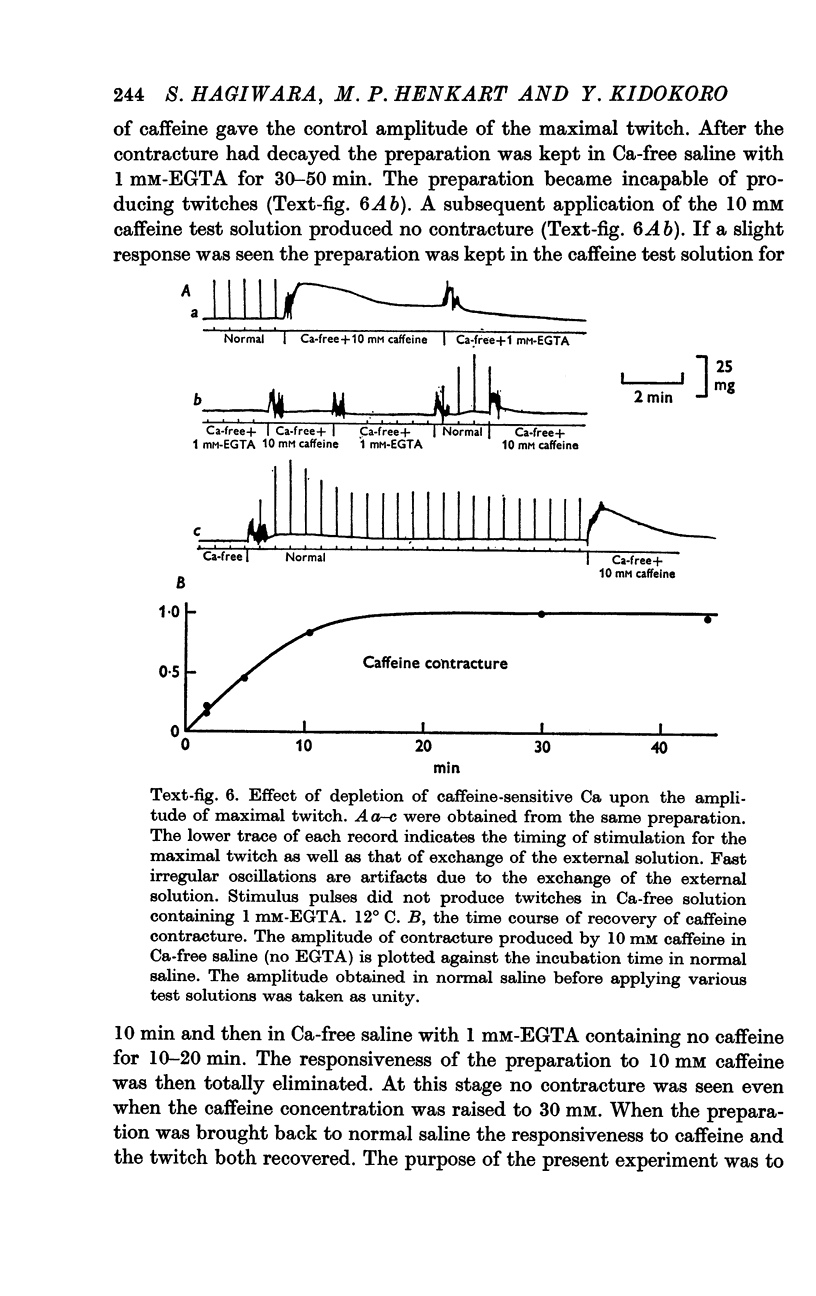
5. After exposure to caffeine the responsiveness of the muscle to subsequent applications of caffeine recovers in normal saline in 20-30 minutes but not in Ca-free saline.
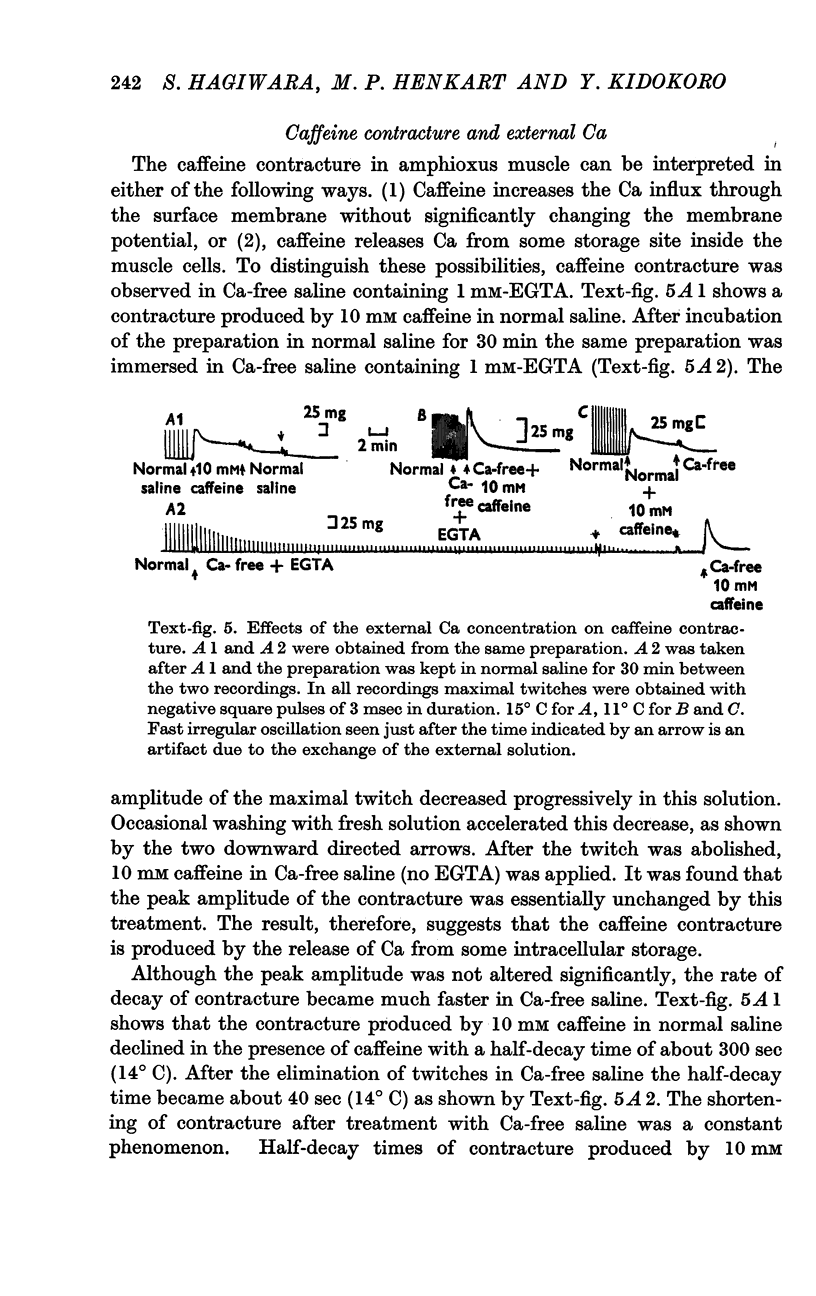
6. The amplitude of the caffeine contracture is independent of the external Ca concentration and is unaltered after the twitch is eliminated in Ca-free saline.
7. After exposure to caffeine a full-sized twitch can be obtained before the responsiveness to caffeine shows any significant recovery.
8. It is concluded that the twitch is produced by the Ca influx resulting from the increased permeability of the muscle cell membrane to Ca during the action potential and that the Ca mobilized by caffeine is not necessary to the initiation of the twitch.
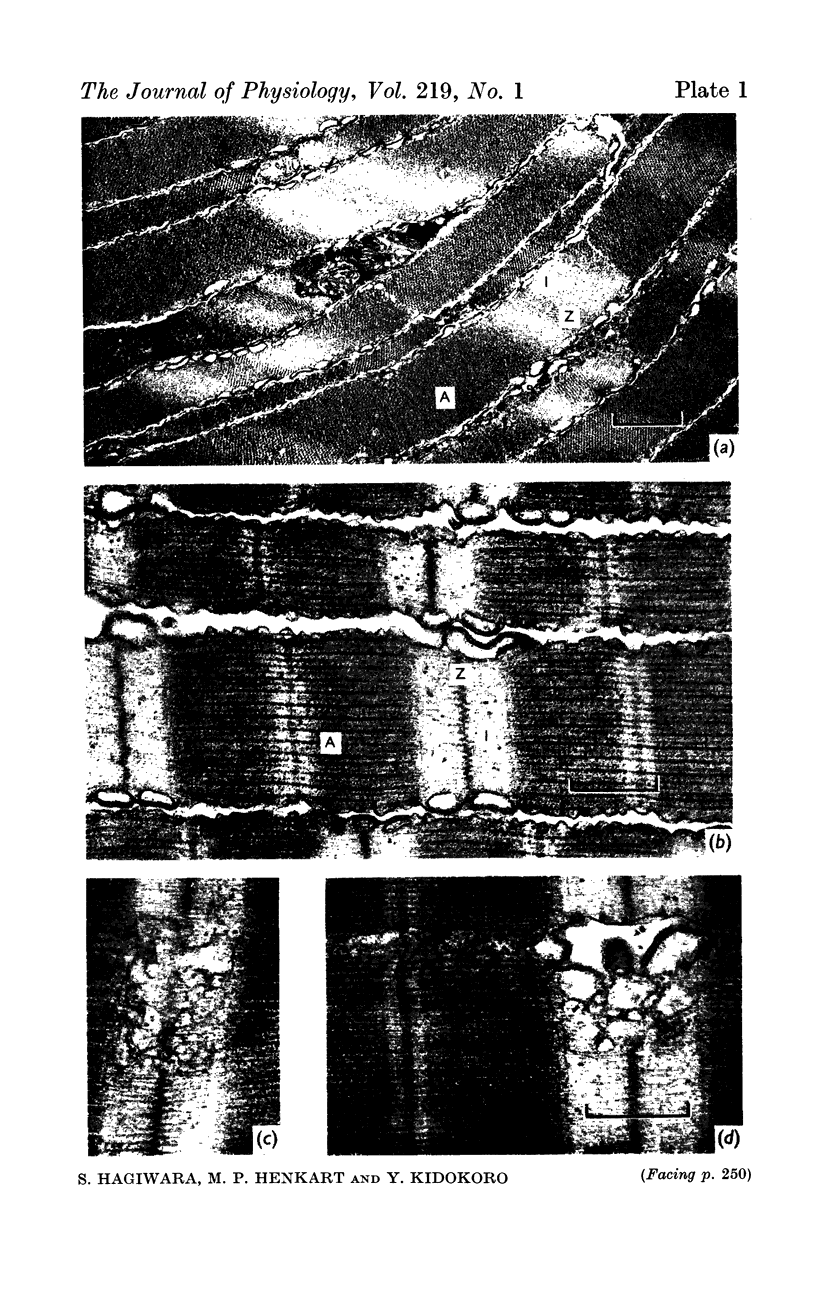
9. Electronmicroscopy shows the existence of sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELSSON J., THESLEFF S. Activation of the contractile mechanism in striated muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Oct 28;44(1):55–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley C. C., Ridgway E. B. On the relationships between membrane potential, calcium transient and tension in single barnacle muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;209(1):105–130. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiarandini D. J., Reuben J. P., Brandt P. W., Grundfest H. Effects of caffeine on crayfish muscle fibers. I. Activation of contraction and induction of Ca spike electrogenesis. J Gen Physiol. 1970 May;55(5):640–664. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.5.640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ETZENSPERGER J. Modifications du potentiel d'action de la fibre musculaire striée provoquées par la caféine et la quinine. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1957;151(3):587–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M., Otsuki I. Control of muscle contraction. Q Rev Biophys. 1969 Nov;2(4):351–384. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Lipmann F. ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE-LINKED CONCENTRATION OF CALCIUM IONS IN A PARTICULATE FRACTION OF RABBIT MUSCLE. J Cell Biol. 1962 Sep 1;14(3):389–400. doi: 10.1083/jcb.14.3.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M., Tanaka M., Ogawa Y. Calcium induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skinned skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1970 Oct 3;228(5266):34–36. doi: 10.1038/228034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flood P. R. Structure of the segmental trunk muscle in amphioxus. With notes on the course and "endings" of the so-called ventral root fibres. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;84(3):389–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Podolsky R. J. Regenerative calcium release within muscle cells. Science. 1970 Jan 2;167(3914):58–59. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3914.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Kidokoro Y. Na and Ca components of action potential in amphioxus muscle cells. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(1):217–232. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Nakajima S. Effects of the intracellular Ca ion concentration upon the excitability of the muscle fiber membrane of a barnacle. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Mar;49(4):807–818. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.4.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Takahashi K., Junge D. Excitation-contraction coupling in a barnacle muscle fiber as examined with voltage clamp technique. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Feb;51(2):157–175. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jöbsis F. F., O'Connor M. J. Calcium release and reabsorption in the sartorius muscle of the toad. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Oct 20;25(2):246–252. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90588-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüttgau H. C., Oetliker H. The action of caffeine on the activation of the contractile mechanism in straited muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):51–74. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORKAND R. K. The relation between membrane potential and contraction in single crayfish muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1962 Apr;161:143–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEACHEY L. D. Structure of the longitudinal body muscles of amphioxus. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Aug;10(4):159–176. doi: 10.1083/jcb.10.4.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTZEHL H., CALDWELL P. C., RUEEGG J. C. THE DEPENDENCE OF CONTRACTION AND RELAXATION OF MUSCLE FIBRES FROM THE CRAB MAIA SQUINADO ON THE INTERNAL CONCENTRATION OF FREE CALCIUM IONS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 25;79:581–591. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peachey L. D. The sarcoplasmic reticulum and transverse tubules of the frog's sartorius. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jun;25(3 Suppl):209–231. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.3.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Herz R. The relationship between caffeine contracture of intact muscle and the effect of caffeine on reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Nov;52(5):750–759. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.5.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winegrad S. The intracellular site of calcium activaton of contraction in frog skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jan;55(1):77–88. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]