Abstract
1. Cable parameters, component conductances, excitability and membrane potentials in isolated external intercostal fibre bundles at 38° C from normal and myotonic goats were measured in normal and low-chloride Ringer, and in the presence of monocarboxylic aromatic acids that produce myotonic responses in mammalian muscle.
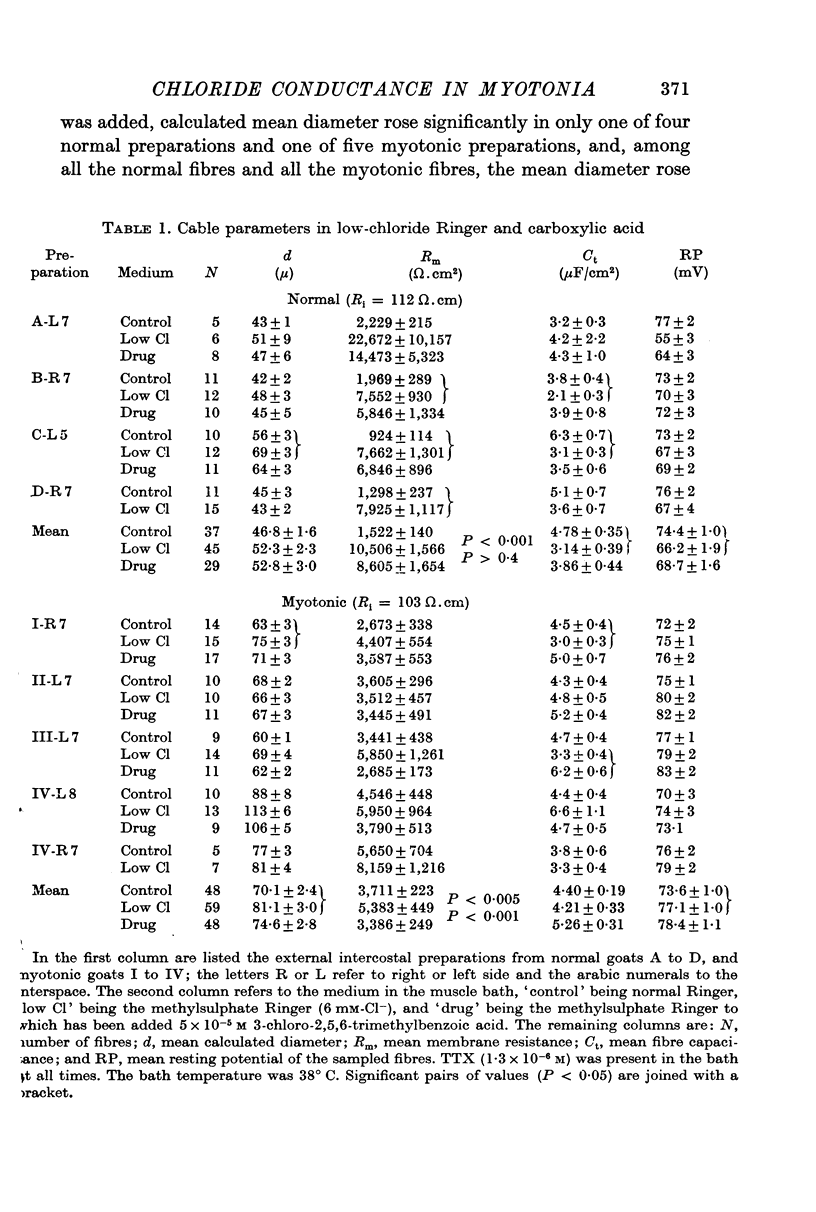
2. The mean resting chloride conductance in μmho/cm2 of myotonic fibres (range 0-147) was significantly less than that of normal fibres (range 376-951). The mean resting potassium conductance was higher in myotonic fibres (range 123-285) than in normal fibres (range 44-132). Potassium conductance increased about 10 μmho/cm2 per mV increase in absolute resting potential.
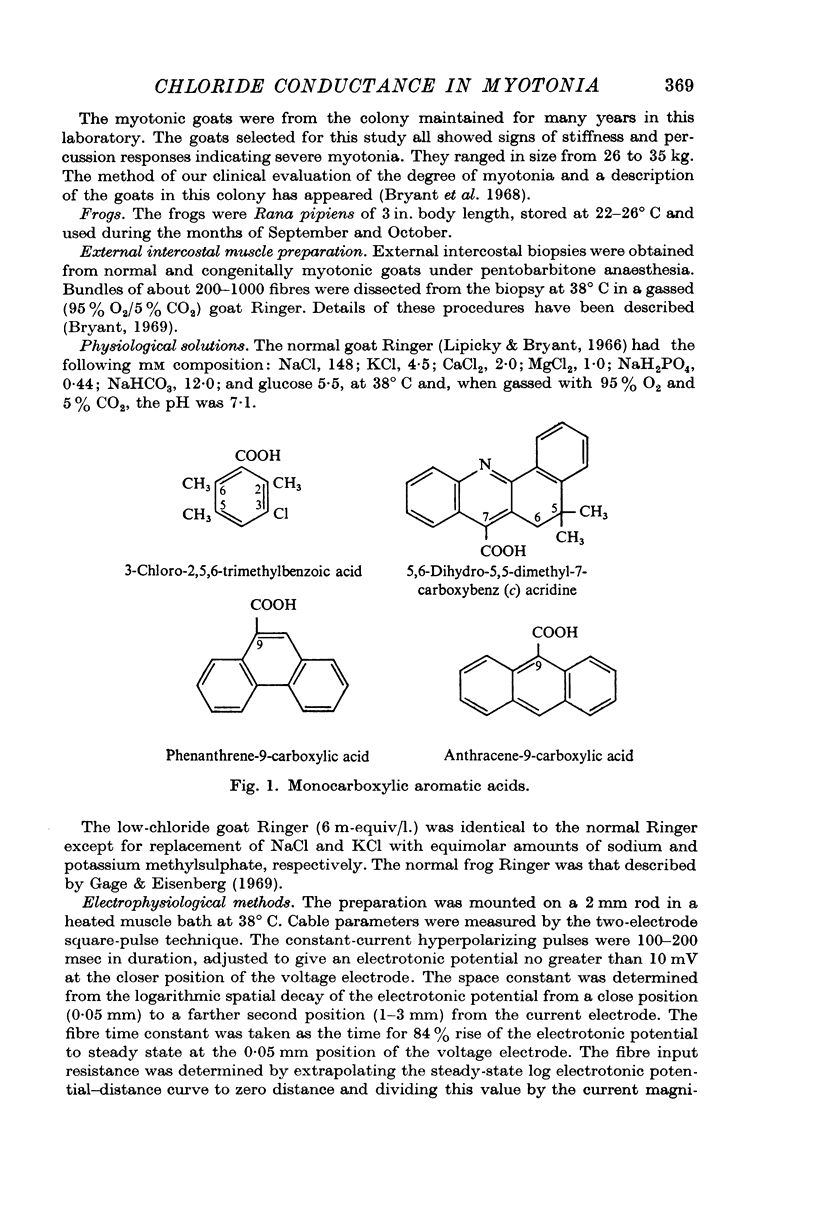
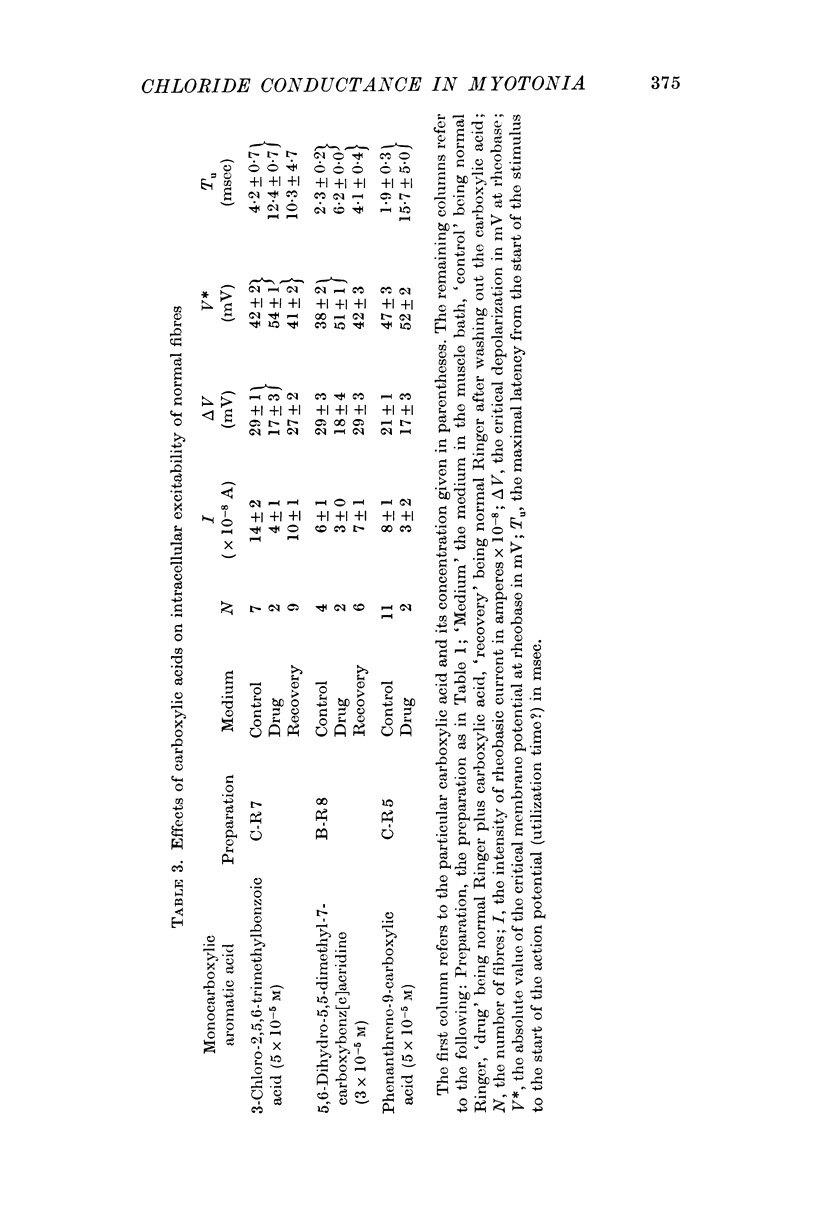
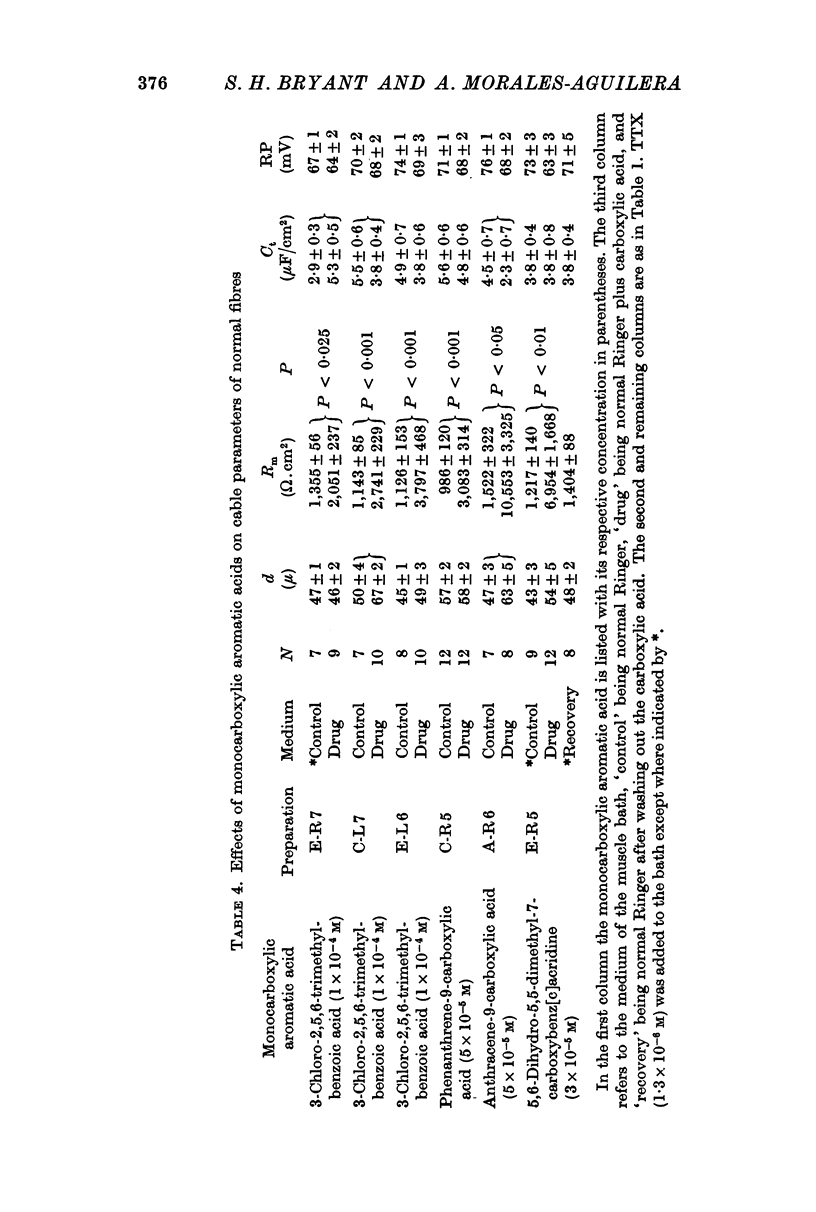
3. In normal fibres in normal Ringer 3-chloro-2,5,6-trimethylbenzoic acid; 5,6-dihydro-5,5-dimethyl-7-carboxybenz[c]acridine; phenanthrene-9-carboxylic acid; and anthracene-9-carboxylic acid at 10-5-10-4 M decreased membrane conductance without consistently changing diameter or capacitance. In low-chloride Ringer 3-chloro-2,5,6-trimethylbenzoic acid (5 × 10-5 M) increased potassium conductance in myotonic and normal fibres. It is concluded that these compounds block chloride conductance.
4. The carboxylic acids produced myotonia in normal fibres similar to that in untreated myotonic fibres.
5. Anthracene-9-carboxylic acid intravenously (8 mg/kg) in normal goats produced acutely a condition resembling myotonia congenita. The carboxylic acids produced no myotonic effects in frog muscle.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H. Internal chloride concentration and chloride efflux of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1961 May;156:623–632. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albuquerque E. X., Thesleff S. A comparative study of membrane properties of innervated and chronically denervated fast and slow skeletal muscles of the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1968 Aug;73(4):471–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-201x.1968.tb10886.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berwick P. 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid poisoning in man. Some interesting clinical and laboratory findings. JAMA. 1970 Nov 9;214(6):1114–1117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant S. H. Cable properties of external intercostal muscle fibres from myotonic and nonmyotonic goats. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(3):539–550. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant S. H., Lipicky R. J., Herzog W. H. Variability of myotonic signs in myotonic goats. Am J Vet Res. 1968 Dec;29(12):2371–2381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EYZAGUIRRE C., FOLK B. P. Experimental myotonia and repetitive phenomena; the veratrinic effects of 2,4-dichlorphenoxyacetate in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1948 Oct;155(1):69–77. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1948.155.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. S., Gage P. W. Ionic conductances of the surface and transverse tubular membranes of frog sartorius fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Mar;53(3):279–297. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.3.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Eisenberg R. S. Capacitance of the surface and transverse tubular membrane of frog sartorius muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Mar;53(3):265–278. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. The potassium permeability of a giant nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):61–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD S. J. The electrical constants and the component conductances of frog skeletal muscle after denervation. J Physiol. 1963 Mar;165:443–456. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTTER O. F., NOBLE D. The chloride conductance of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:89–102. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann W. W., Alston W., Rowe G. A study of individual neuro-muscular junctions in myotonia. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1966 Dec;21(6):521–537. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(66)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg J., Williams E. J. The membrane electrical parameters of Nitella translucens. J Theor Biol. 1969 Sep;24(3):317–334. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(69)80056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutter O. F., Warner A. E. Action of some foreign cations and anions on the chloride permeability of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(3):445–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutter O. F., Warner A. E. The effect of pH on the 36-Cl efflux from frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(3):427–443. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutter O. F., Warner A. E. The pH sensitivity of the chloride conductance of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(3):403–425. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson A., Hinkes M. J., Taylor S. R. Contracture and twitch potentiation of fast and slow muscles of the rat at 20 and 37 C. Am J Physiol. 1970 Jan;218(1):33–41. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D. The ionic fluxes in frog muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1954 May 27;142(908):359–382. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1954.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLAUS W., LUELLMANN H., MUSCHOLL E. [Potassium flux of normal and denervated rat diaphragm]. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1960;271:761–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipicky R. J., Bryant S. H. Sodium, potassium, and chloride fluxes in intercostal muscle from normal goats and goats with hereditary myotonia. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Sep;50(1):89–111. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASHIMA H., WASHIO H. THE EFFECT OF ZINC ON THE ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF MEMBRANE AND THE TWITCH TENSION IN FROG MUSCLE FIBRES. Jpn J Physiol. 1964 Oct 15;14:538–550. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.14.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffett R. B., Tang A. H. Skeletal muscle stimulants. Substituted benzoic acids. J Med Chem. 1968 Sep;11(5):1020–1022. doi: 10.1021/jm00311a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougier O., Stämpfli R. Influence des ions bicarbonate sur les propriétés de rectification et la conductance membranaire de la fibre musculaire squelettique. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1965;23(3):230–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandow A. Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Pharmacol Rev. 1965 Sep;17(3):265–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperelakis N. Changes in conductances of frog sartorius fibers produced by CO2, ReO4-, and temperature. Am J Physiol. 1969 Oct;217(4):1069–1075. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.4.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. The differential effects of tetraethylammonium and zinc ions on the resting conductance of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;209(1):231–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang A. H., Schroeder L. A., Keasling H. H. U-23,223 (3-chloro-2,5,6-trimiethylbenzoic acid), a veratricic agent selective for the skeletal muscles. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1968 Oct;175(2):319–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulbricht W. The effect of veratridine on excitable membranes of nerve and muscle. Ergeb Physiol. 1969;61:18–71. doi: 10.1007/BFb0111446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


