Abstract
1. The reflex effects of pulses of intense radiant heat applied to the skin of the central plantar pad have been studied in unanaesthetized (decerebrate) spinal cats.
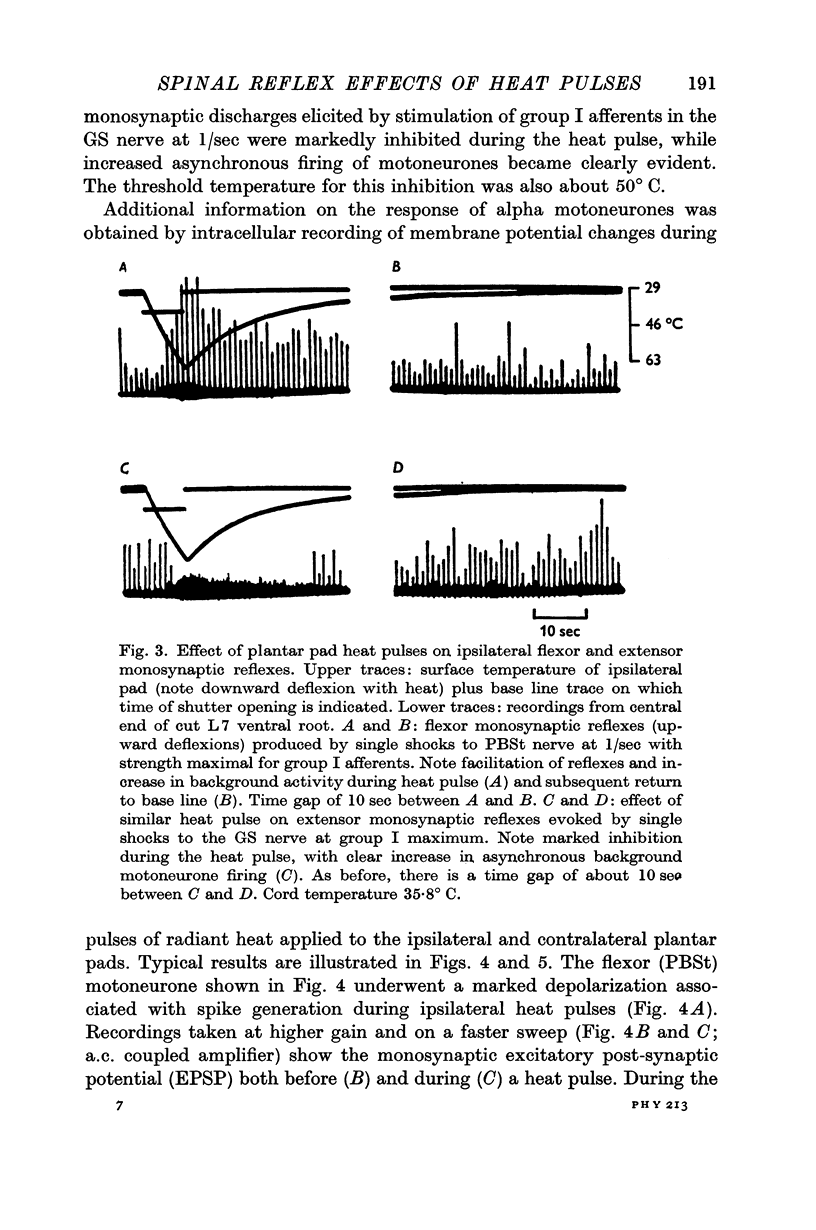
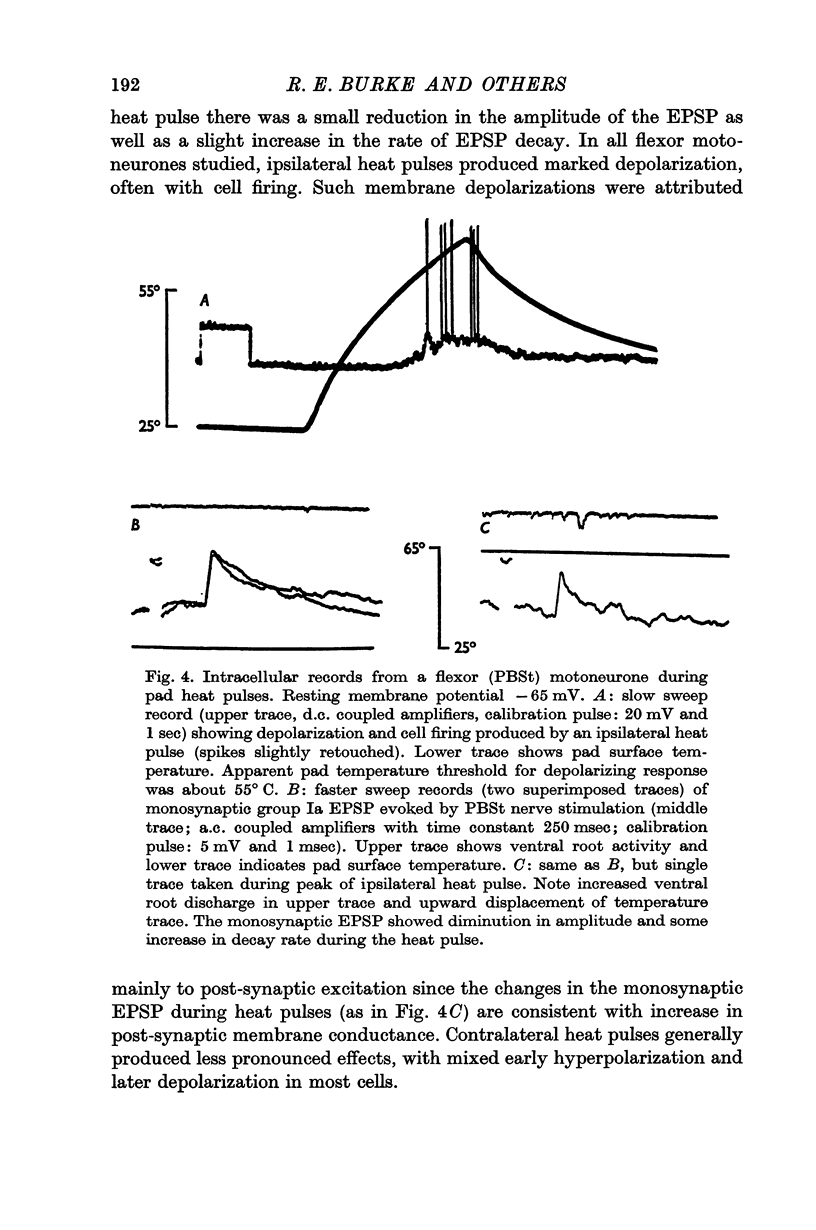
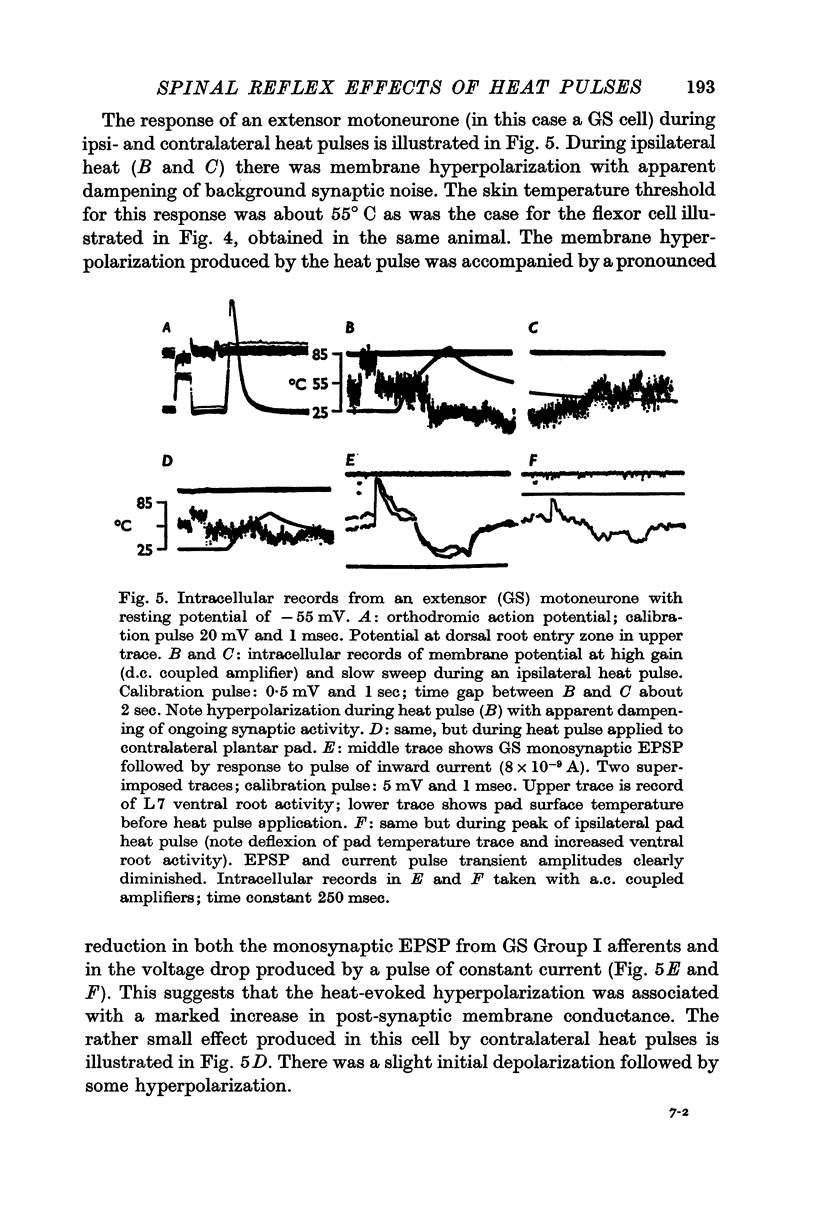
2. Pad heat pulses produced flexion of the ipsilateral hind limb and increased ipsilateral flexor monosynaptic reflexes, due to post-synaptic excitation of flexor alpha motoneurones. These effects were accompanied by reduction of extensor monosynaptic reflexes and post-synaptic inhibition of extensor motoneurones.
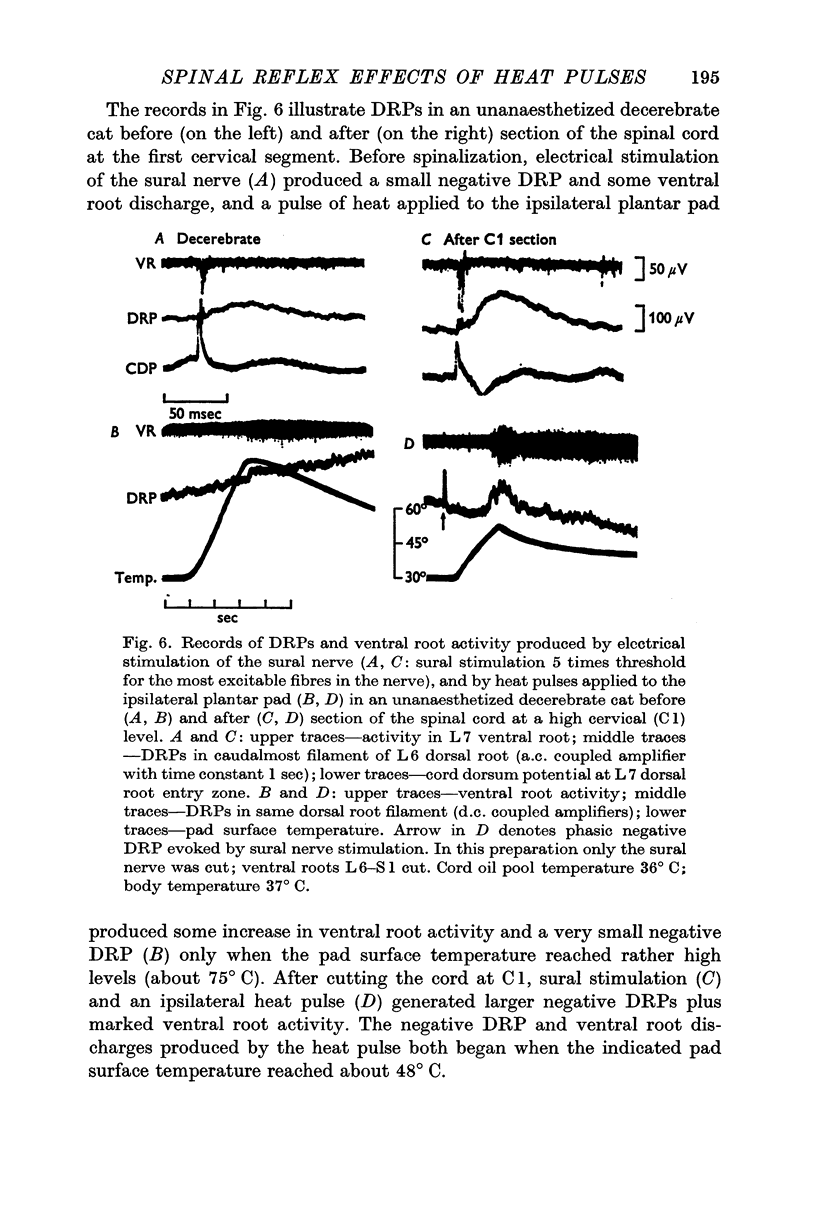
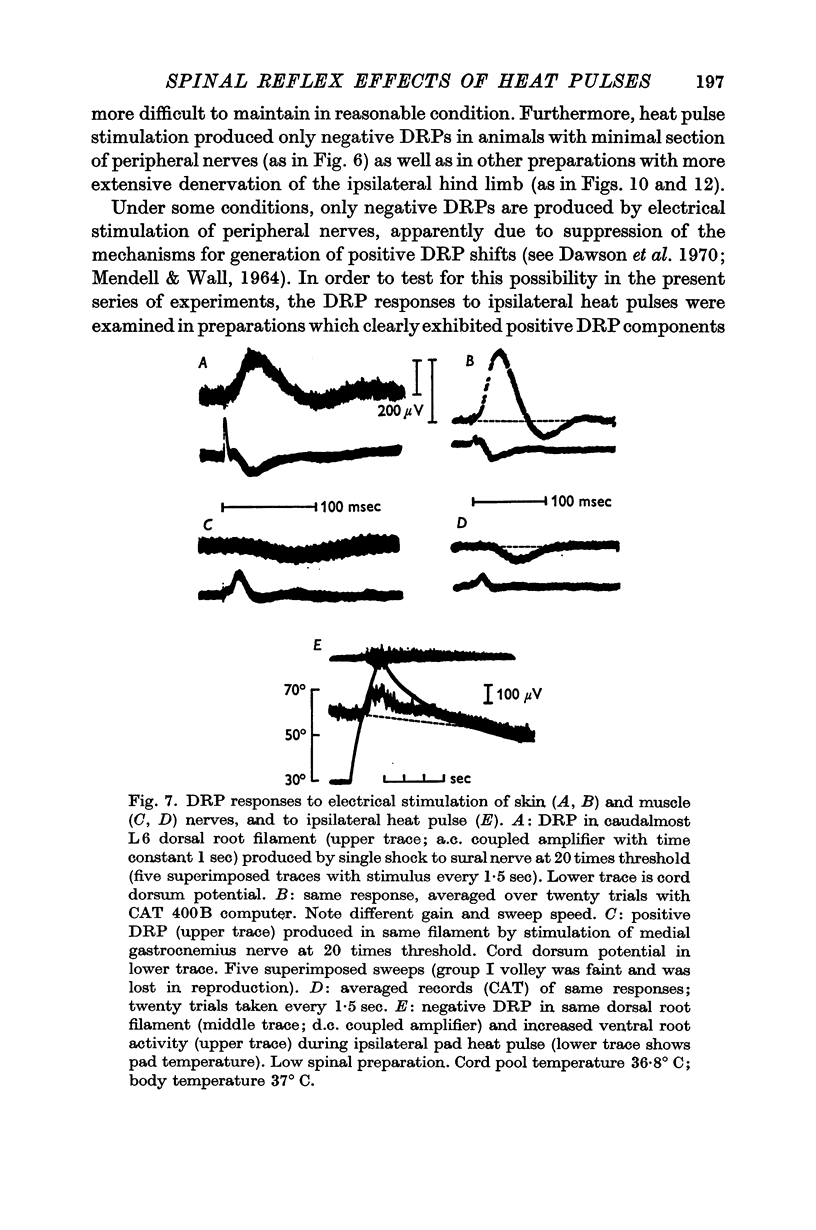
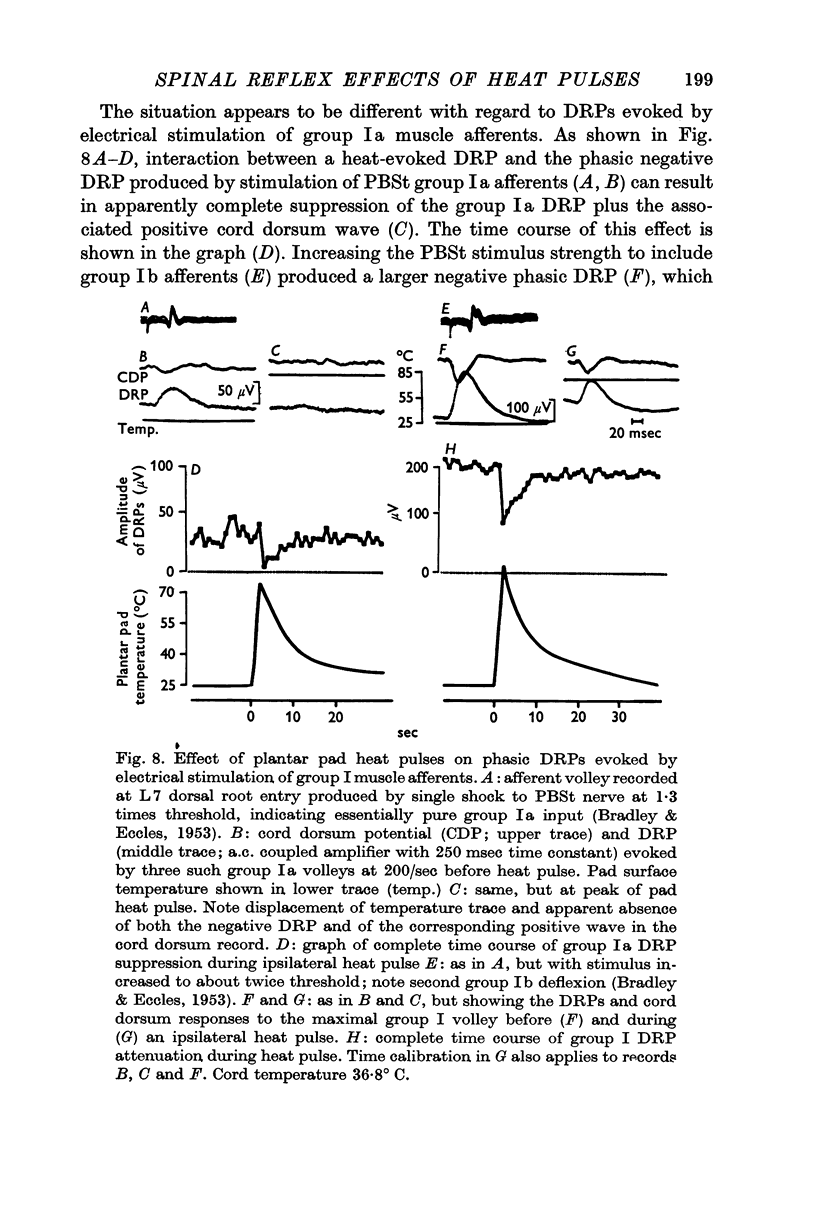
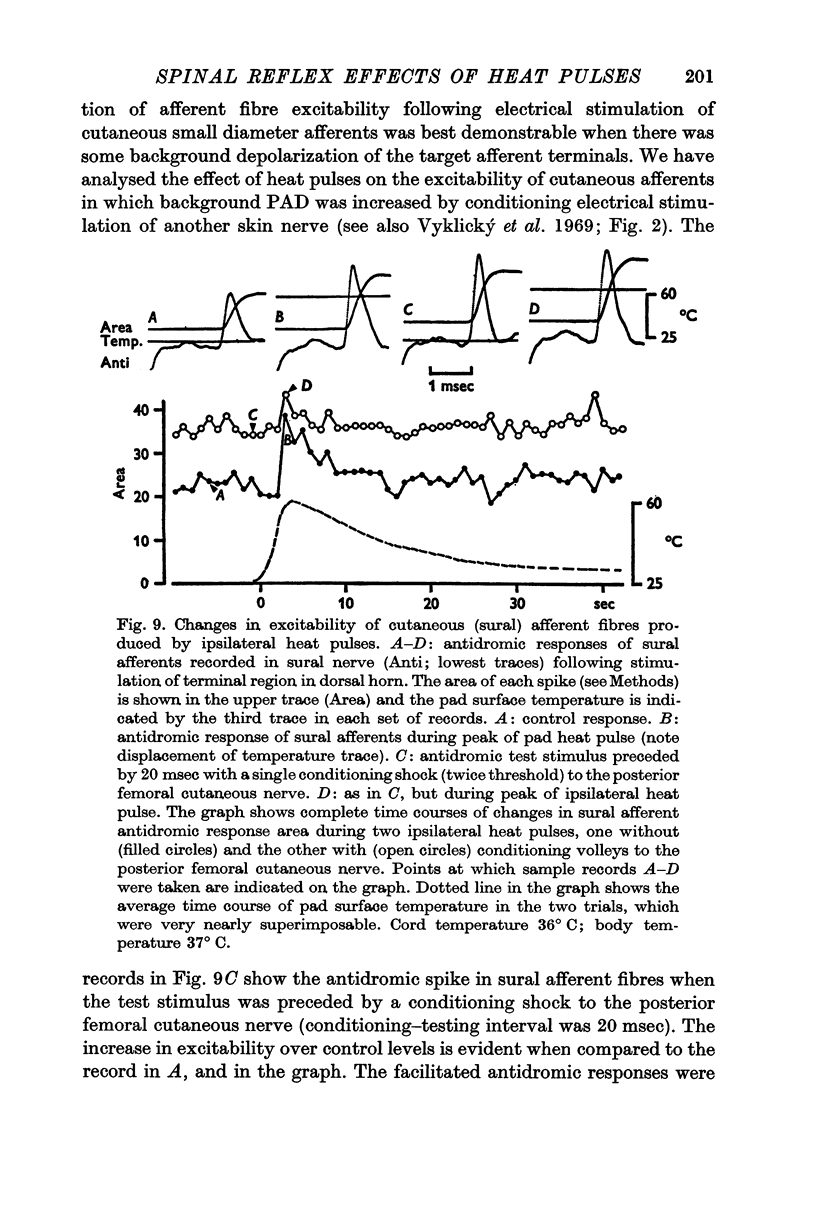
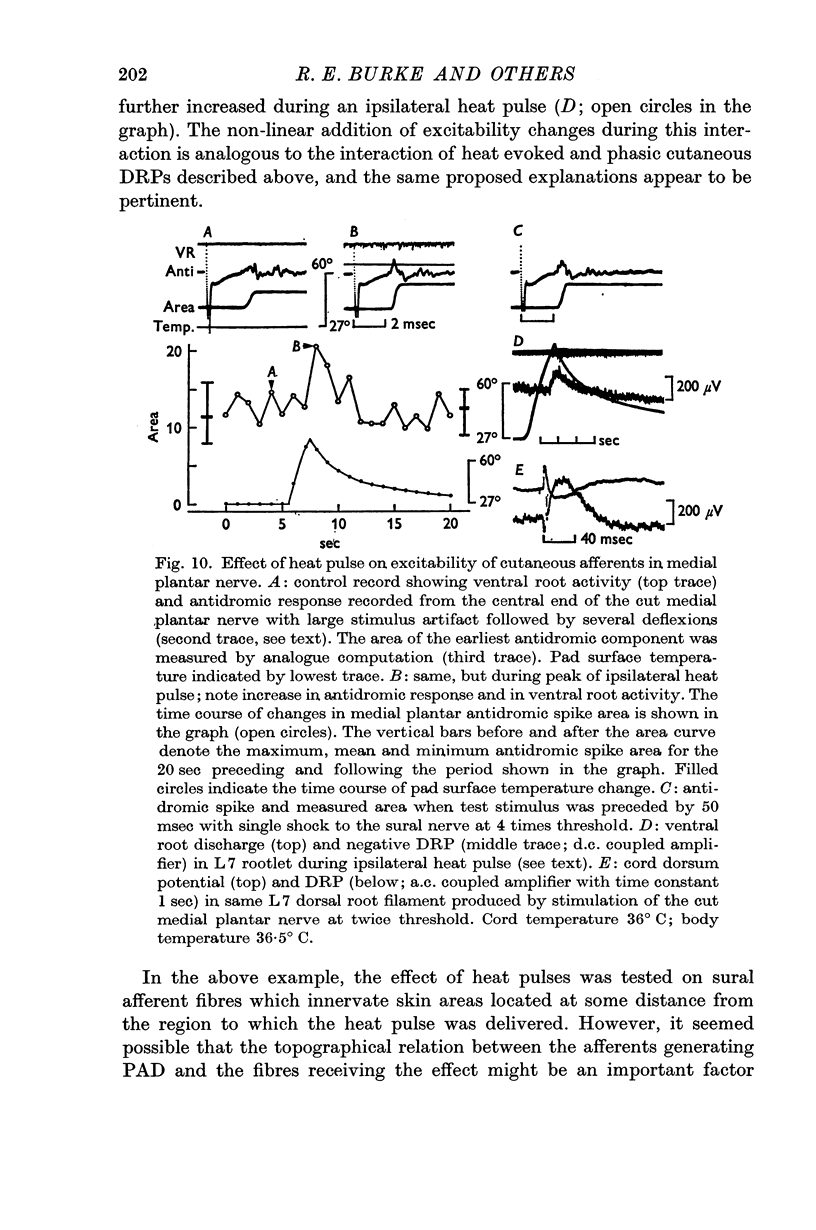
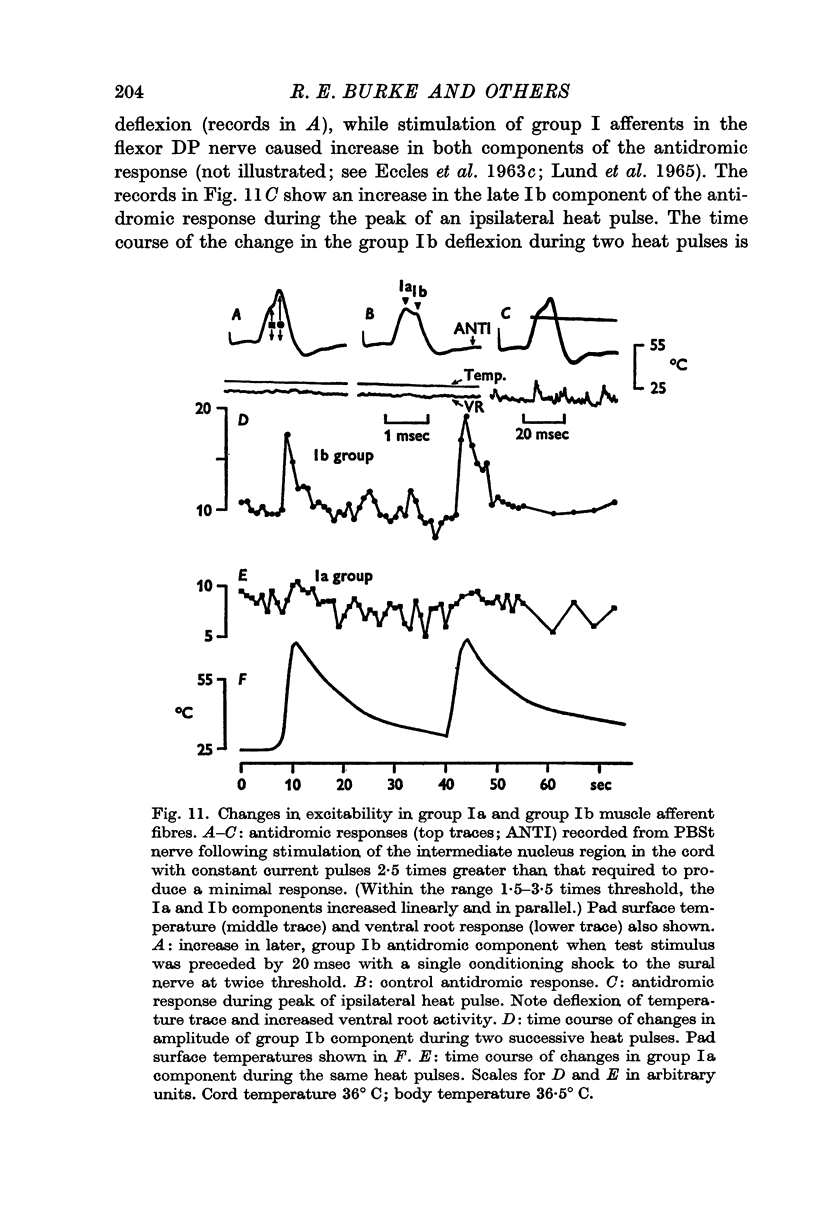
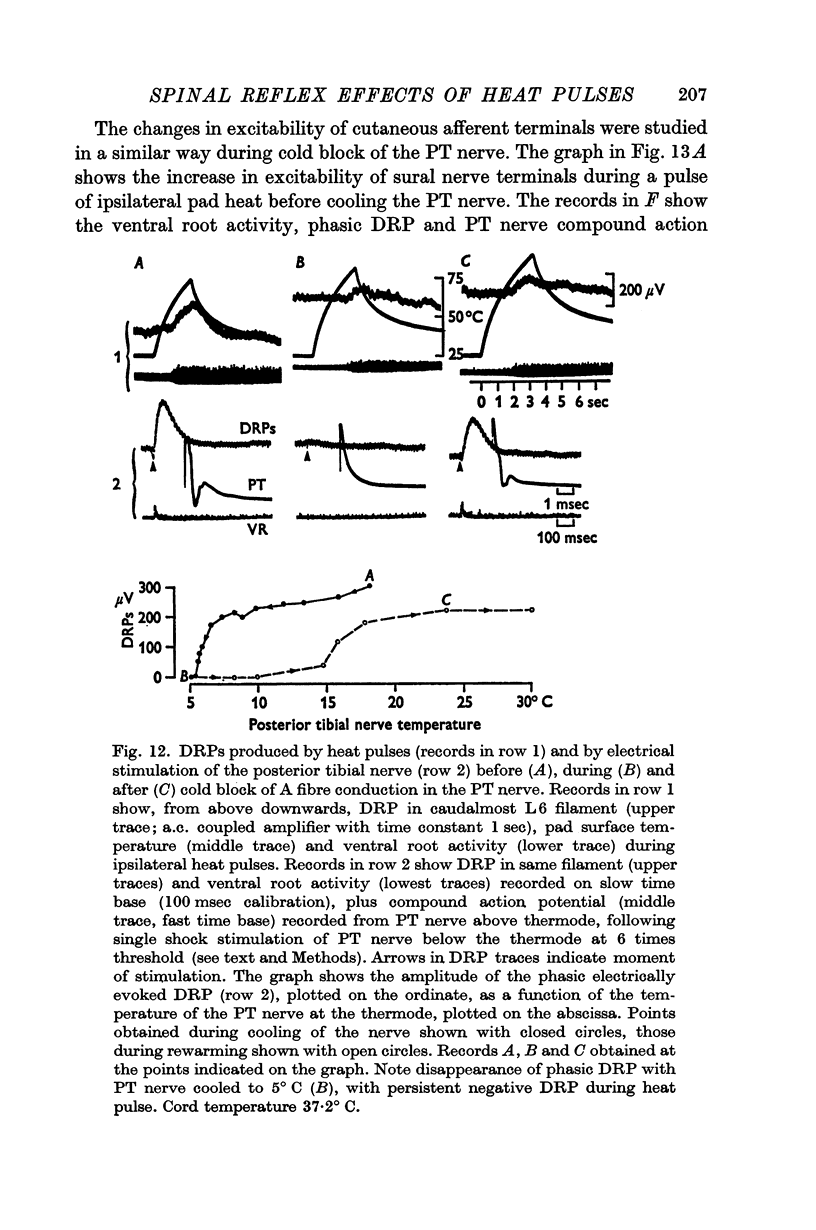
3. Ipsilateral (and contralateral) pad heat pulses consistently evoked negative dorsal root potentials (DRPs) as well as increased excitability of both cutaneous and group Ib muscle afferent terminals. The excitability of group Ia afferents was sometimes also increased during pad heat pulses, but to a lesser extent.
4. Pad heat pulses produced negative DRPs in preparations in which positive DRP components could be demonstrated following electrical stimulation of both skin and muscle nerves.
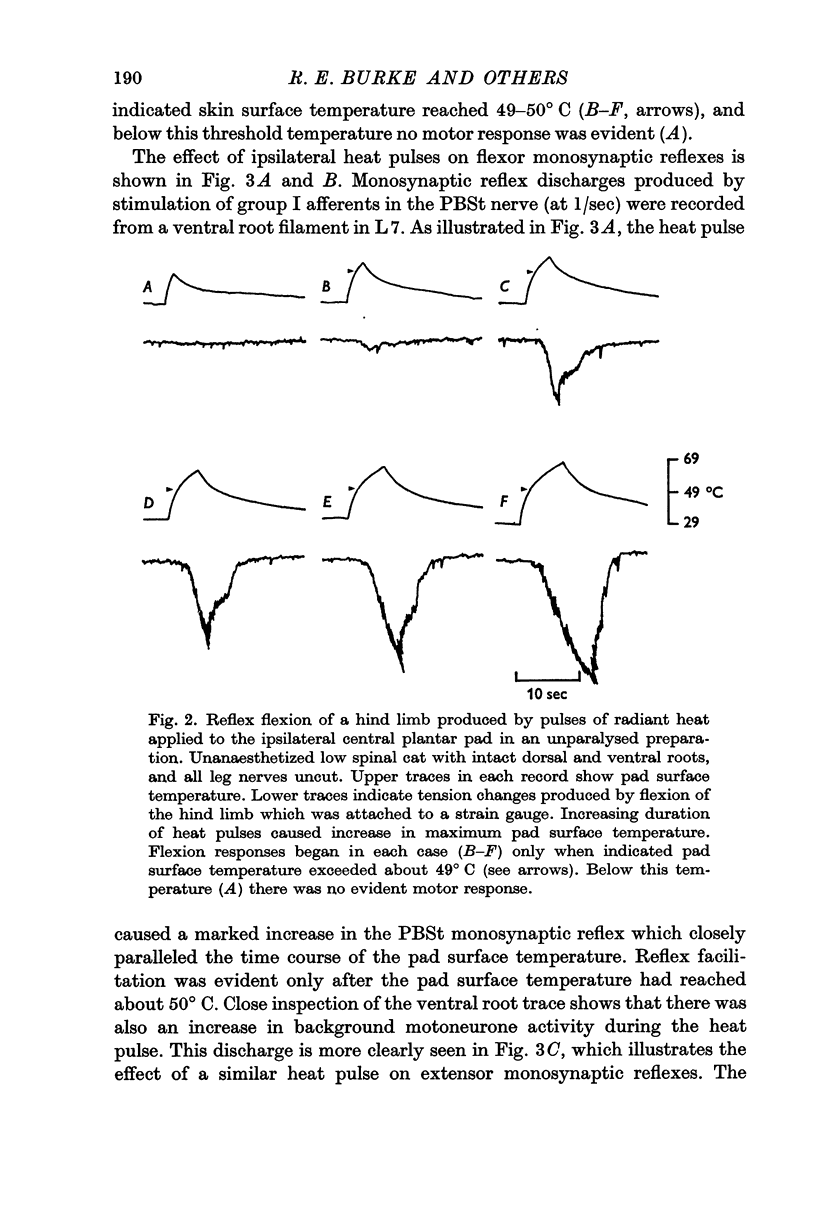
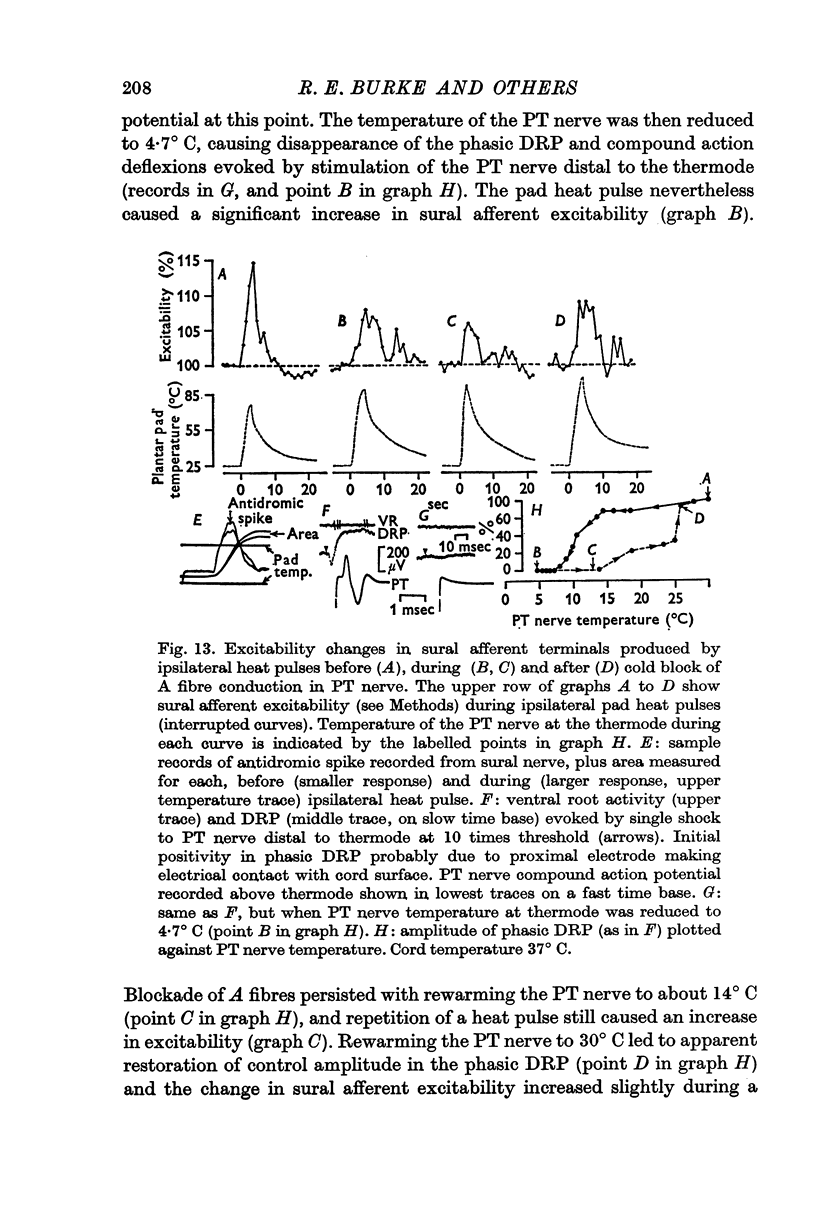
5. The motor and primary afferent effects of heat pulses always accompanied one another, beginning after the pad surface temperature had reached rather high levels (usually 48-55° C).
6. Negative DRPs increased excitability of cutaneous and group Ib afferents, and motoneurone activation produced by pad heat pulses was essentially unmodified when conduction in large myelinated afferents from the central plantar pad was blocked by cooling the posterior tibial nerve trunk.
7. It is concluded that adequate noxious activation of cutaneous afferents of small diameter produces primary afferent depolarization in a variety of large diameter afferent fibres, as well as post-synaptic effects in alpha motoneurones.
Full text
PDF



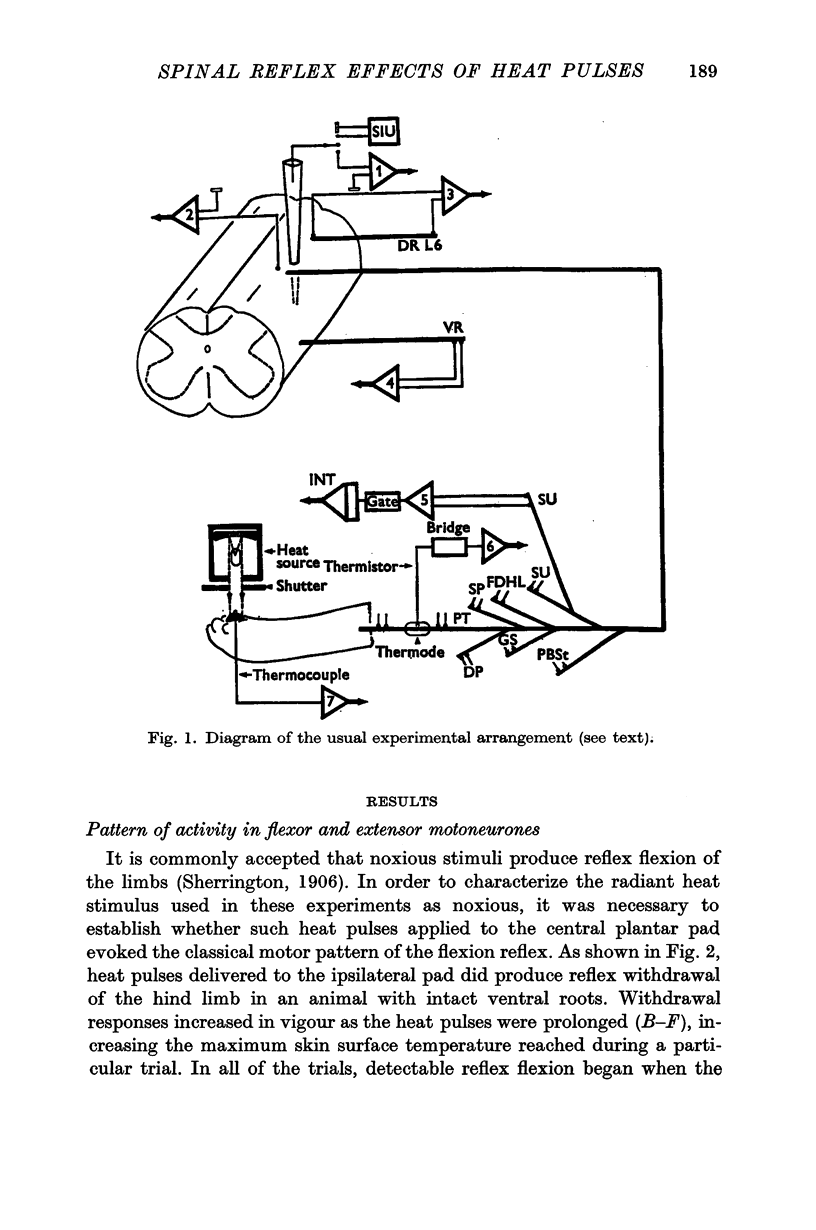













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRADLEY K., ECCLES J. C. Analysis of the fast afferent impulses from thigh muscles. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):462–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessou P., Perl E. R. Response of cutaneous sensory units with unmyelinated fibers to noxious stimuli. J Neurophysiol. 1969 Nov;32(6):1025–1043. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.6.1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess P. R., Perl E. R. Myelinated afferent fibres responding specifically to noxious stimulation of the skin. J Physiol. 1967 Jun;190(3):541–562. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess P. R., Petit D., Warren R. M. Receptor types in cat hairy skin supplied by myelinated fibers. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Nov;31(6):833–848. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.6.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARPENTER D., ENGBERG I., FUNKENSTEIN H., LUNDBERG A. DECEREBRATE CONTROL OF REFLEXES TO PRIMARY AFFERENTS. Acta Physiol Scand. 1963 Dec;59:424–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1963.tb02758.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. The specific ionic conductances and the ionic movements across the motoneuronal membrane that produce the inhibitory post-synaptic potential. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):326–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen B. N., Perl E. R. Spinal neurons specifically excited by noxious or thermal stimuli: marginal zone of the dorsal horn. J Neurophysiol. 1970 Mar;33(2):293–307. doi: 10.1152/jn.1970.33.2.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., RITCHIE J. M. Mammalian nonmyelinated nerve fibers. Physiol Rev. 1962 Apr;42:297–334. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1962.42.2.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decima E. E. An effect of postsynaptic neurons upon presynaptic terminals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 May;63(1):58–64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.1.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton H., Rudomin P. Continuous analog estimation of neural statistical parameters. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1968 Oct;15(4):324–326. doi: 10.1109/tbme.1968.4502585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., FATT P., LANDGREN S., WINSBURY G. J. Spinal cord potentials generated by volleys in the large muscle afferents. J Physiol. 1954 Sep 28;125(3):590–606. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., KOSTYUK P. G., SCHMIDT R. F. Presynaptic inhibition of the central actions of flexor reflex afferents. J Physiol. 1962 May;161:258–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Supraspinal control of interneurones mediating spinal reflexes. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147:565–584. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles J. C., Magni F., Willis W. D. Depolarization of central terminals of Group I afferent fibres from muscle. J Physiol. 1962 Jan;160(1):62–93. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK K., FUORTES M. G. Stimulation of spinal motoneurones with intracellular electrodes. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):451–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz D. N., Iggo A. Conduction failure in myelinated and non-myelinated axons at low temperatures. J Physiol. 1968 Dec;199(2):319–345. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz D. N., Iggo A. Dorsal root potentials and ventral root reflexes evoked by nonmyelinated fibers. Science. 1968 Dec 6;162(3858):1140–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3858.1140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillman P., Wall P. D. Inhibitory and excitatory factors influencing the receptive fields of lamina 5 spinal cord cells. Exp Brain Res. 1969;9(4):284–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00235240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IGGO A. Cutaneous heat and cold receptors with slowly conducting (C) afferent fibres. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1959 Oct;44:362–370. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1959.sp001417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IGGO A. Cutaneous mechanoreceptors with afferent C fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Jul;152:337–353. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IRIUCHIJIMA J., ZOTTERMAN Y. The specificity of afferent cutaneous C fibres in mammals. Acta Physiol Scand. 1960 Jul 15;49:267–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1960.tb01952.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNO M., PERL E. R. Alteration of spinal reflexes by interaction with suprasegmental and dorsal root activity. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:103–122. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund S., Lundberg A., Vyklický L. Inhibitory action from the flexor reflex afferents on transmission to Ia afferents. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Aug;64(4):345–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MENDELL L. M., WALL P. D. PRESYNAPTIC HYPERPOLARIZATION: A ROLE FOR FINE AFFERENT FIBRES. J Physiol. 1964 Aug;172:274–294. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manfredi M. Differential block of conduction of larger fibers in peripheral nerve by direct current. Arch Ital Biol. 1970 Jan;108(1):52–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manfredi M. Modulation of sensory projections in anterolateral column of cat spinal cord by peripheral afferents of different size. Arch Ital Biol. 1970 Jan;108(1):72–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin H. F., Manning J. W. Rapid thermal cutaneous stimulation: peripheral nerve responses. Brain Res. 1969 Dec;16(2):524–526. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90246-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzack R., Wall P. D. Pain mechanisms: a new theory. Science. 1965 Nov 19;150(3699):971–979. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3699.971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendell L. Positive dorsal root potentials produced by stimulaton of small diameter muscle afferents. Brain Res. 1970 Mar 3;18(2):375–379. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90339-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perl E. R. Myelinated afferent fibres innervating the primate skin and their response to noxious stimuli. J Physiol. 1968 Aug;197(3):593–615. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomeranz B., Wall P. D., Weber W. V. Cord cells responding to fine myelinated afferents from viscera, muscle and skin. J Physiol. 1968 Dec;199(3):511–532. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W. Distinguishing theoretical synaptic potentials computed for different soma-dendritic distributions of synaptic input. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1138–1168. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. G., Wuerker R. B., Frank K. Membrane impedance changes during synaptic transmission in cat spinal motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1072–1096. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyklický L., Rudomin P., Zajac F. E., 3rd, Burke R. E. Primary afferent depolarization evoked by a painful stimulus. Science. 1969 Jul 11;165(3889):184–186. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3889.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALL P. D. Excitability changes in afferent fibre terminations and their relation to slow potentials. J Physiol. 1958 Jun 18;142(1):1–21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagman I. H., Price D. D. Responses of dorsal horn cells of M. mulatta to cutaneous and sural nerve A and C fiber stimuli. J Neurophysiol. 1969 Nov;32(6):803–817. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.6.803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann M. Dorsal root potentials after C-fiber stimulation. Science. 1968 May 24;160(3830):896–898. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3830.896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


