Abstract
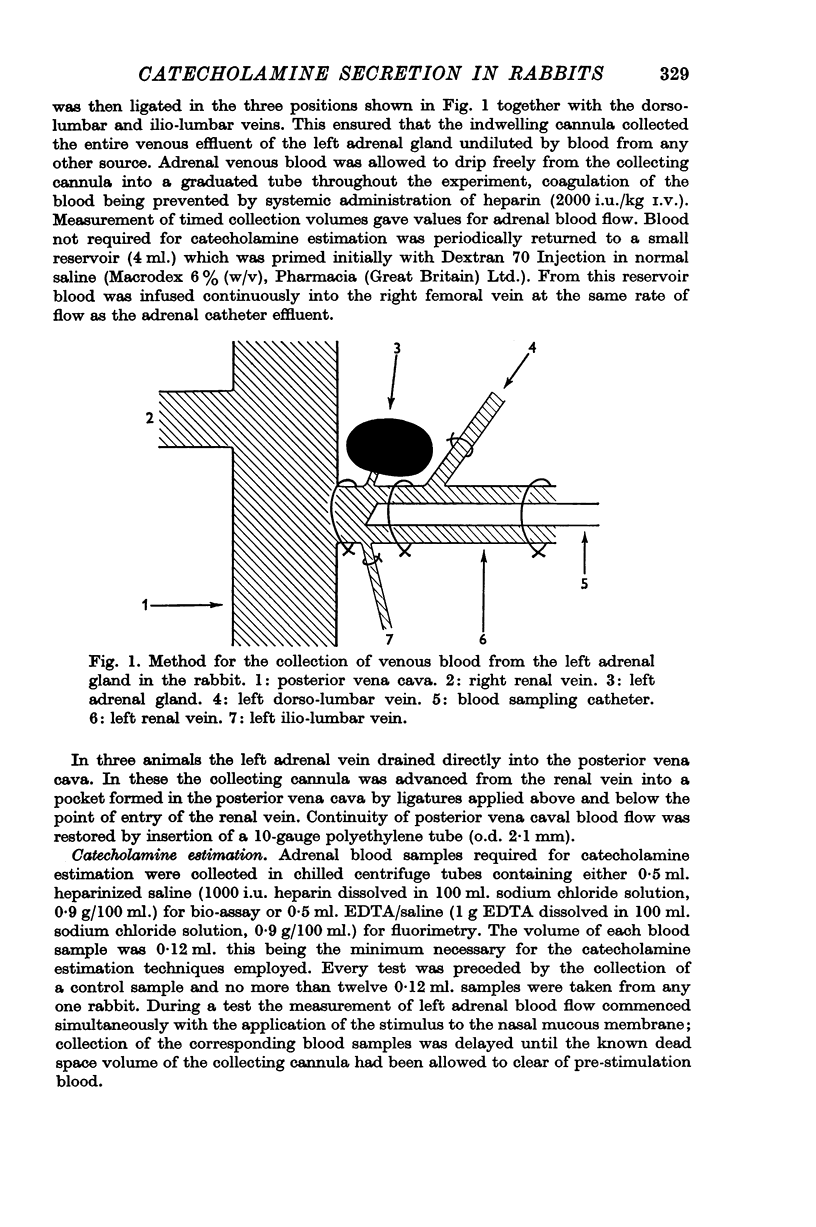
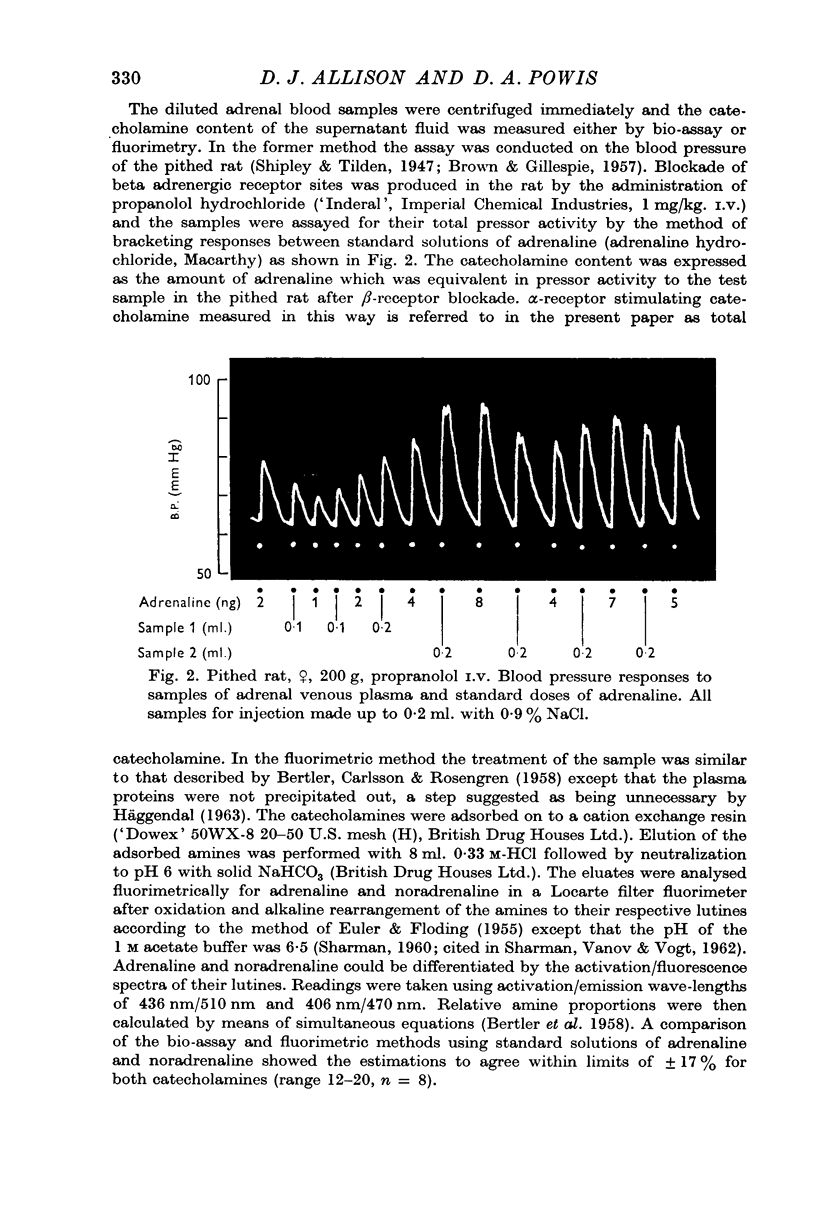
1. Left adrenal venous blood was collected in anaesthetized rabbits and analysed for catecholamine content by either a fluorimetric technique or a bio-assay method using the blood pressure of the pithed rat.
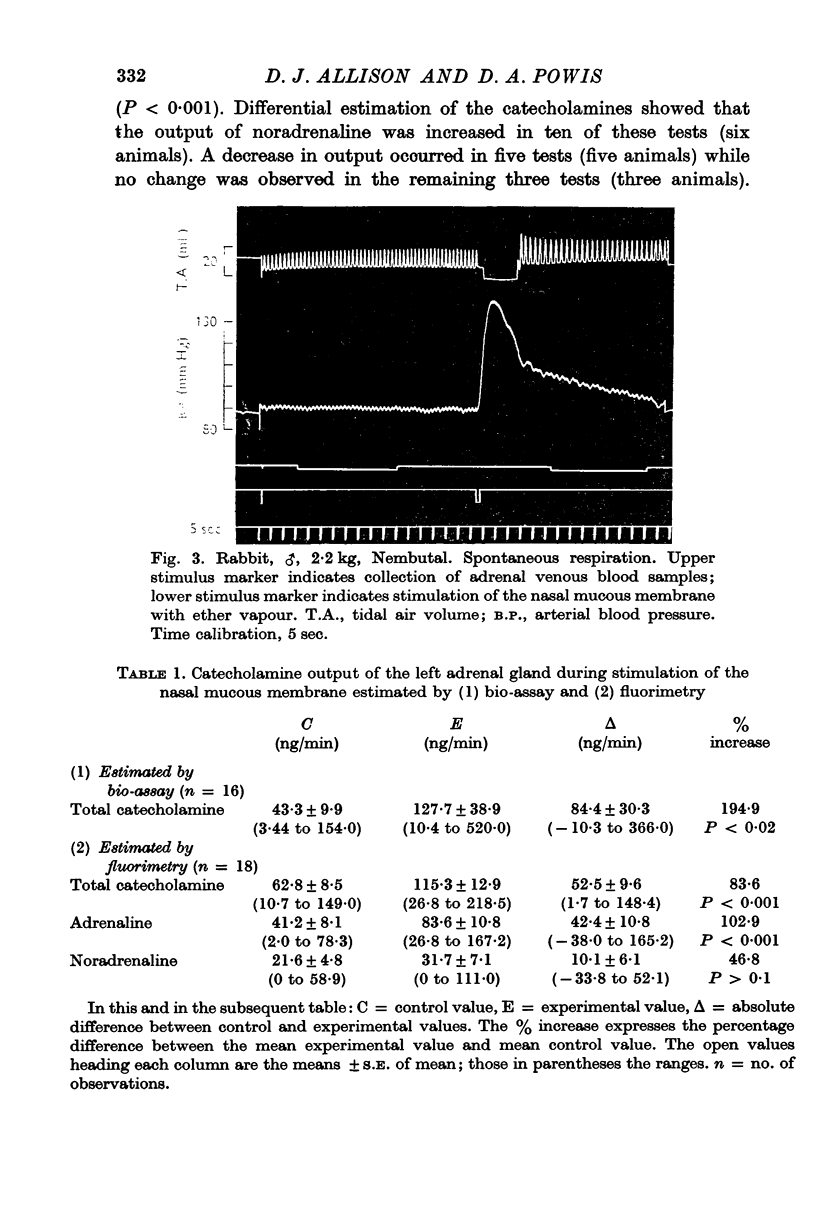
2. Stimulation of the nasal mucous membrane with ether vapour or water caused apnoea, bradycardia, a rise in arterial blood pressure and an increase in adrenal medullary catecholamine secretion.
3. During the pre-stimulation control periods adrenaline constituted 66% of the total catecholamine present in adrenal venous blood and noradrenaline 34%. These proportions altered during stimulation of the nasal mucous membrane to 72 and 28% respectively. Electrical stimulation of the left splanchnic nerve produced a secretion composed almost entirely of adrenaline.
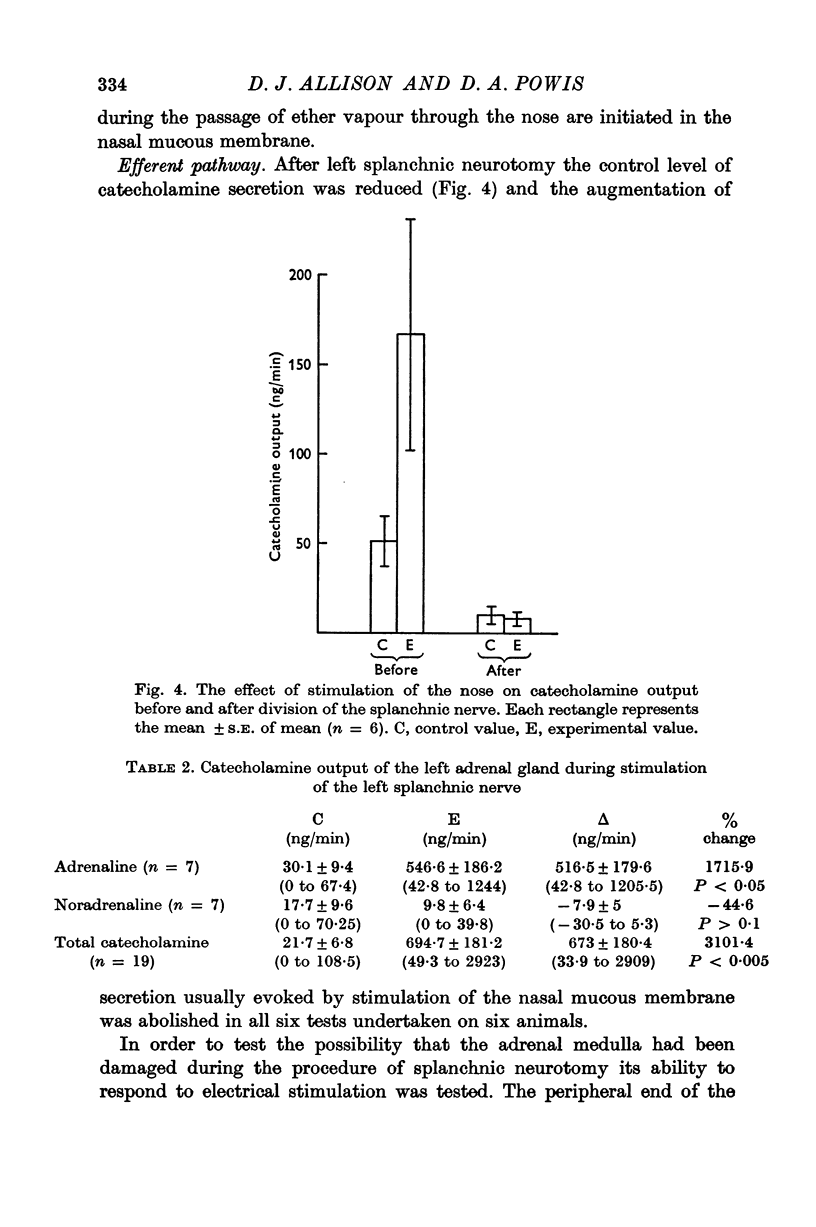
4. The increased catecholamine output elicited during stimulation of the nose occurred in animals whose pulmonary ventilation was maintained constant by means of a pump. It was abolished, however, by local anaesthesia of the nasal passages or by surgical division of the left splanchnic nerve.
5. The increased secretion of catecholamines is therefore reflex in nature, and evidence is presented that it is the result of a primary reflex from the nose.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angell James J. E., Daly M. de B. Nasal reflexes. Proc R Soc Med. 1969 Dec 12;62(12):1287–1293. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAUGH C. W., CORNETT R. W., HATCHER J. D. The adrenal gland and the cardiovascular changes in acute anoxic anoxia in dogs. Circ Res. 1959 Jul;7(4):513–520. doi: 10.1161/01.res.7.4.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERTLER A., CARLSSON A., ROSENGREN E. A method for the fluorimetric determination of adrenaline and noradrenaline in tissues. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Dec 15;44(3-4):273–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN G. L., GILLESPIE J. S. The output of sympathetic transmitter from the spleen of the cat. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):81–102. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Burn J. H., De Elio F. J. The secretion of adrenaline from the perfused suprarenal gland. J Physiol. 1948 Mar 15;107(2):222–232. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1948.sp004265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon W. E. Contributions to the physiology of the lungs: Part I. The bronchial muscles, their innervation, and the action of drugs upon them. J Physiol. 1903 Mar 16;29(2):97–173. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1903.sp000947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKFELT B. Noradrenaline and adrenaline in mammalian tissues; distribution under normal and pathological conditions with special reference to the endocrine system. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1951;25(92):1–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLTZ P., SCHUMANN H. J. Arterenol content of the mammalian and human adrenal medulla. Nature. 1950 Apr 29;165(4200):683–683. doi: 10.1038/165683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. P. The metabolic requirements from catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla. J Physiol. 1969 May;202(1):197–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARMAN D. F., VANOV S., VOGT M. Noradrenaline content in the heart and spleen of the mouse under normal conditions and after administration of some drugs. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1962 Dec;19:527–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1962.tb01458.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPHERD D. M., WEST G. B. Noradrenaline and accessory chromaffin tissue. Nature. 1952 Jul 5;170(4314):42–43. doi: 10.1038/170042b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomori Z., Widdicombe J. G. Muscular, bronchomotor and cardiovascular reflexes elicited by mechanical stimulation of the respiratory tract. J Physiol. 1969 Jan;200(1):25–49. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT M. Inhibition by hexoestrol of adrenocortical secretion in the rat. J Physiol. 1955 Dec 29;130(3):601–614. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT M. The secretion of the denervated adrenal medulla of the cat. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1952 Jun;7(2):325–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1952.tb01329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON EULER U. S., FLODING I. A fluorimetric micromethod for differential estimation of adrenaline and noradrenaline. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1955;33(118):45–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEST G. B. Liberation of adrenaline from the suprarenal gland of the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1950 Dec;5(4):542–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1950.tb00606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


