Abstract
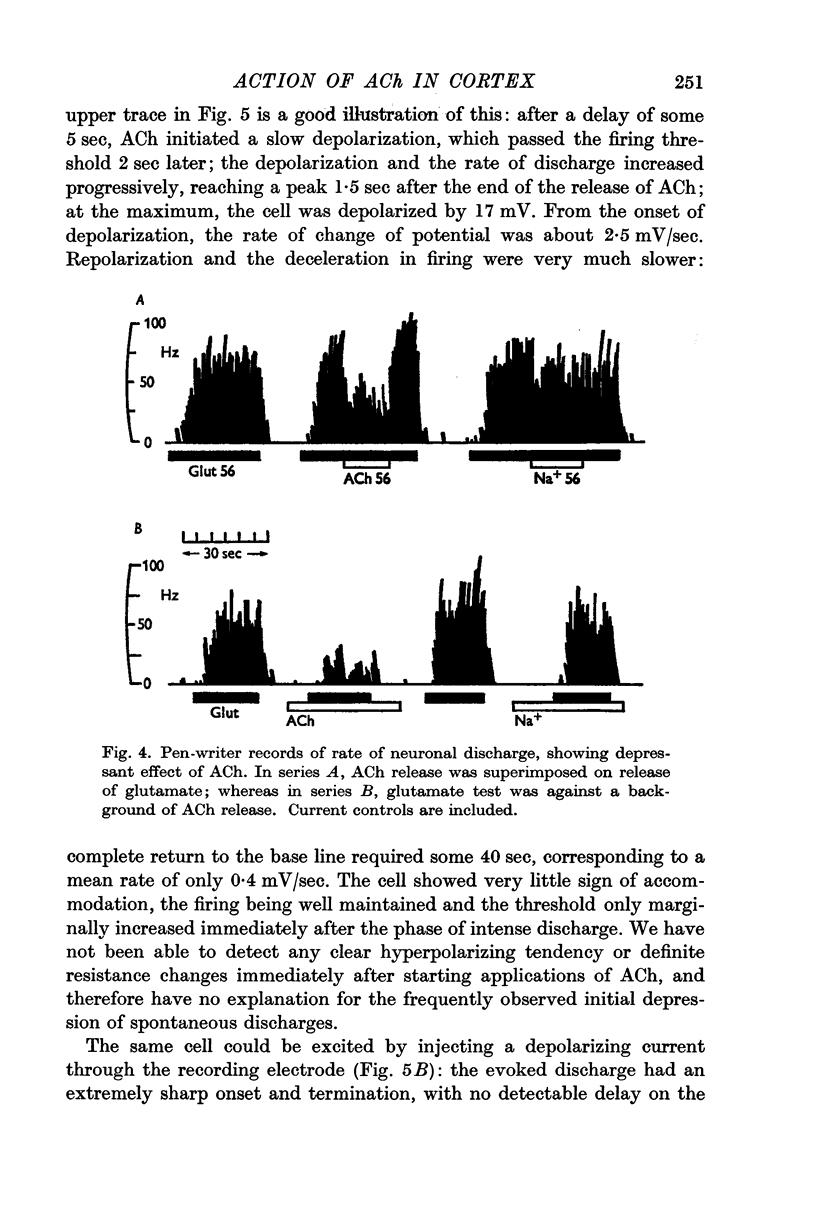
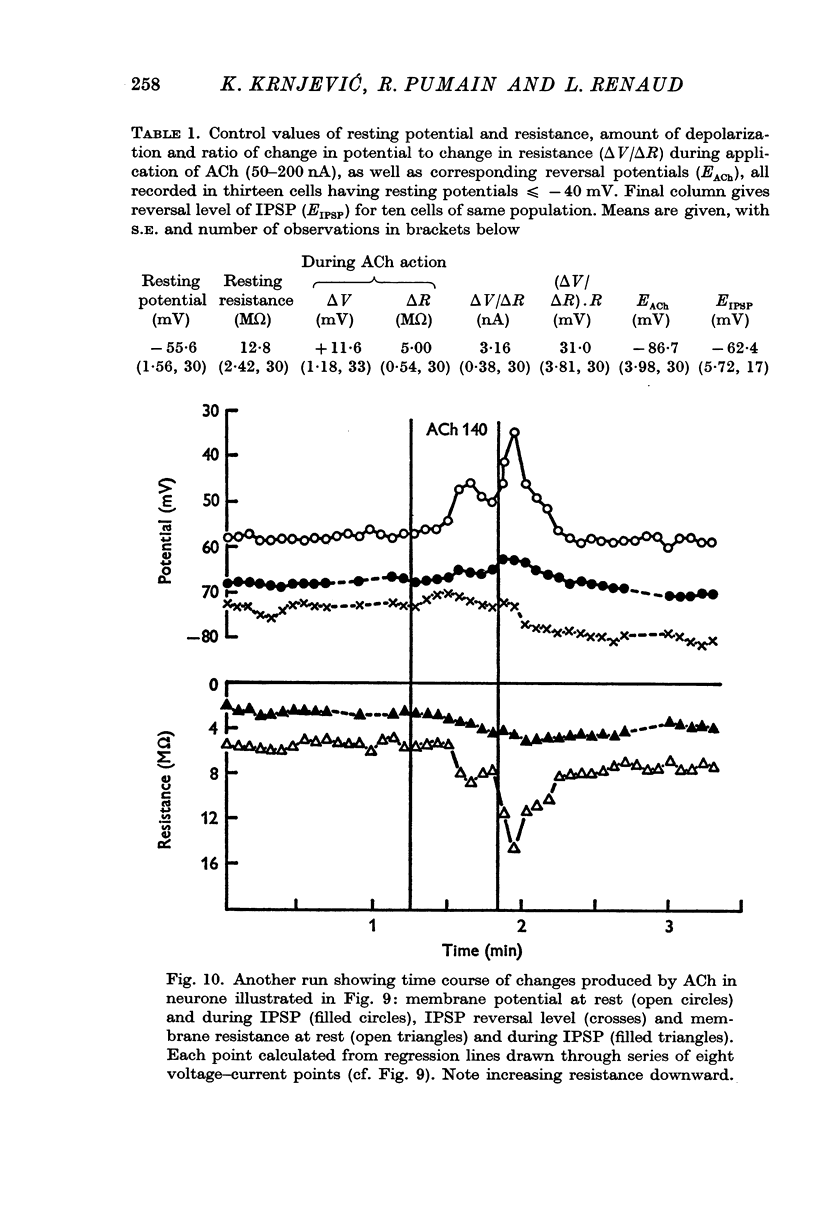
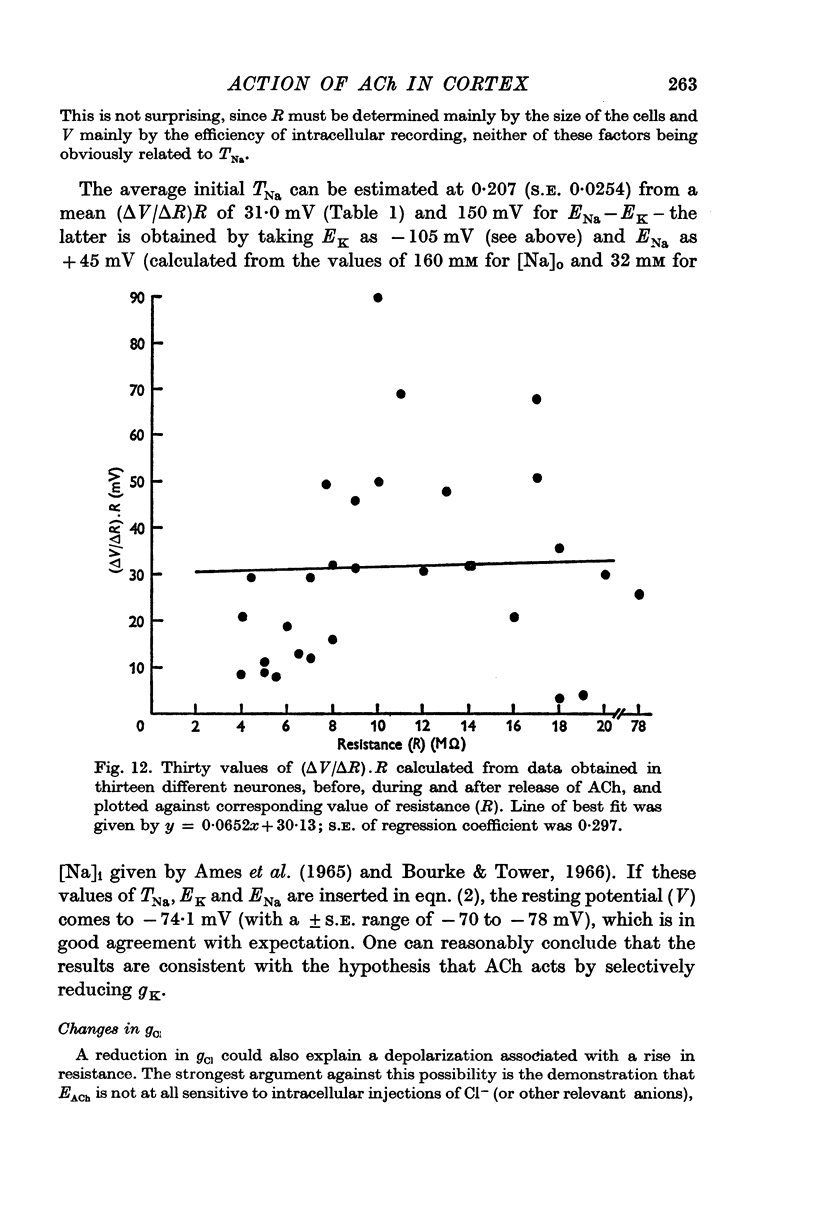
1. The muscarinic depolarizing action of ACh on cortical neurones is associated with an increase in membrane resistance (mean ΔV/ΔR = 3·16 mV/MΩ).
2. ACh also promotes repetitive firing by slowing repolarization after spikes.
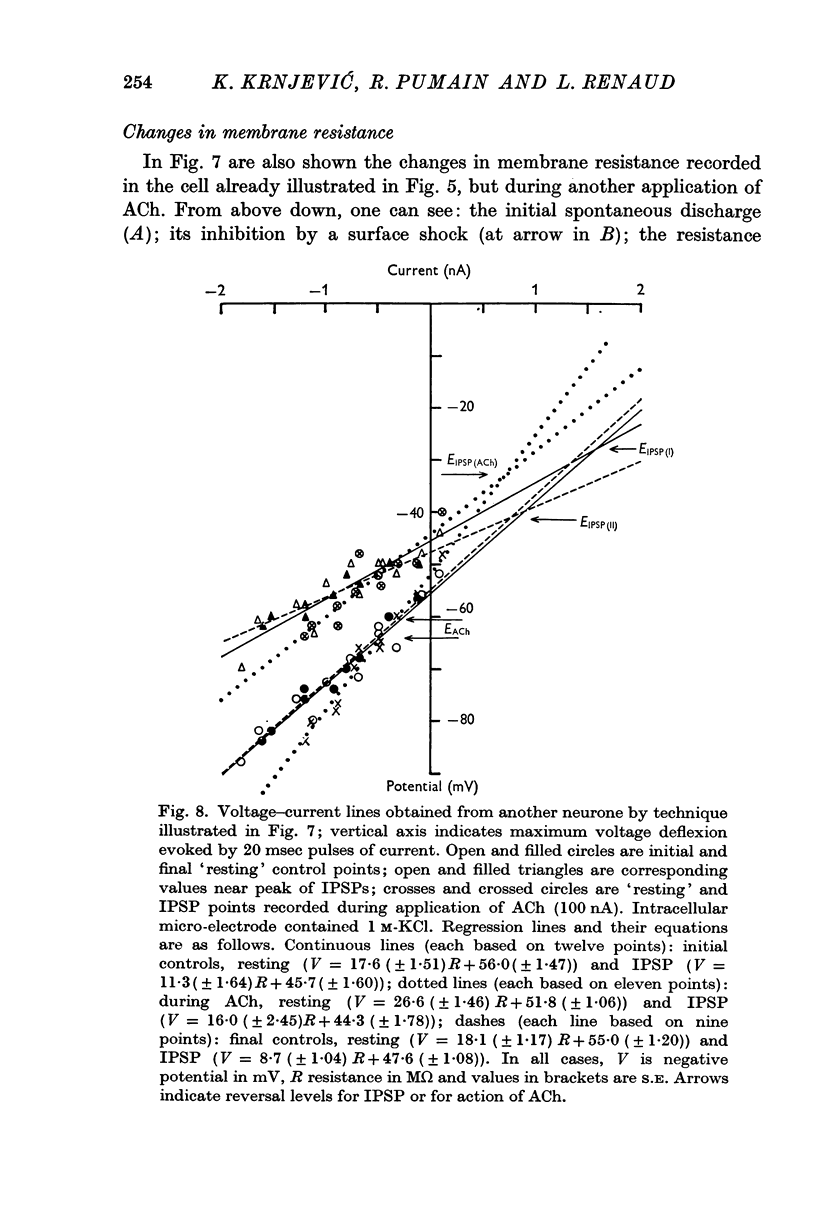
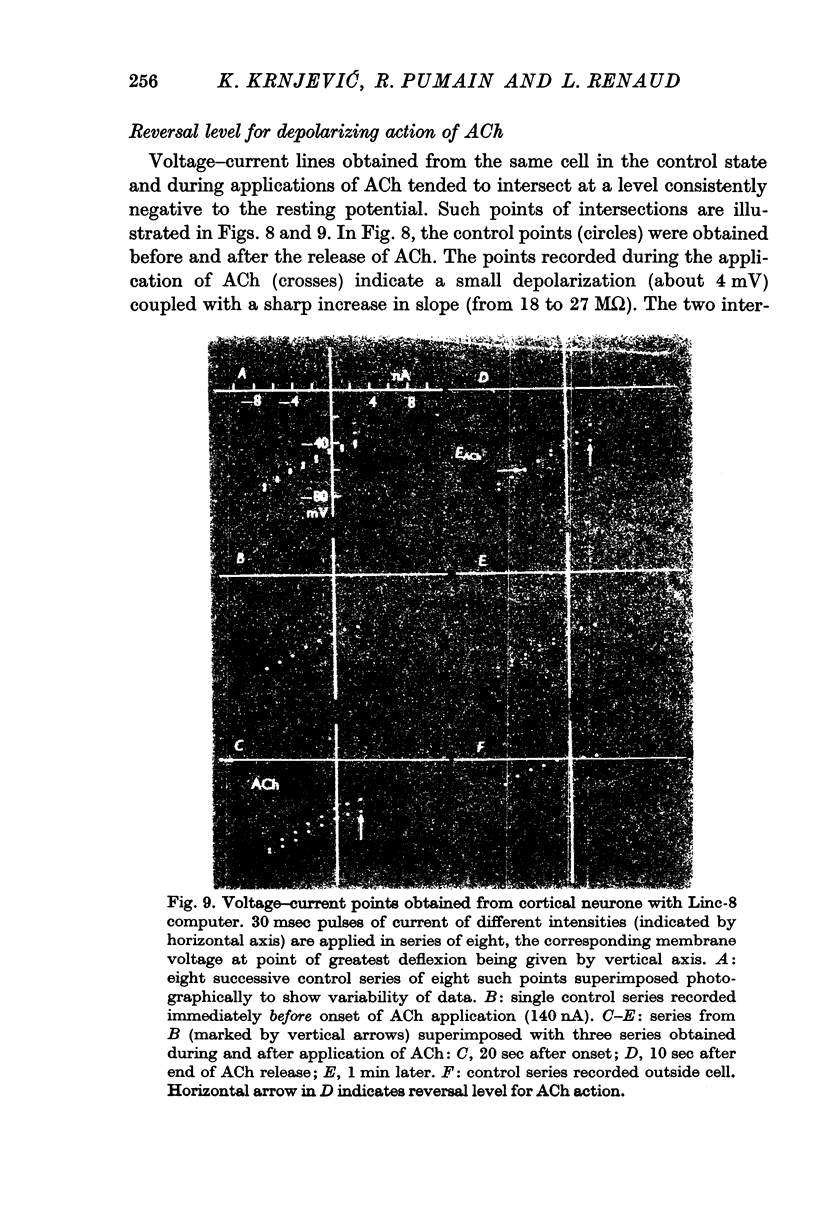
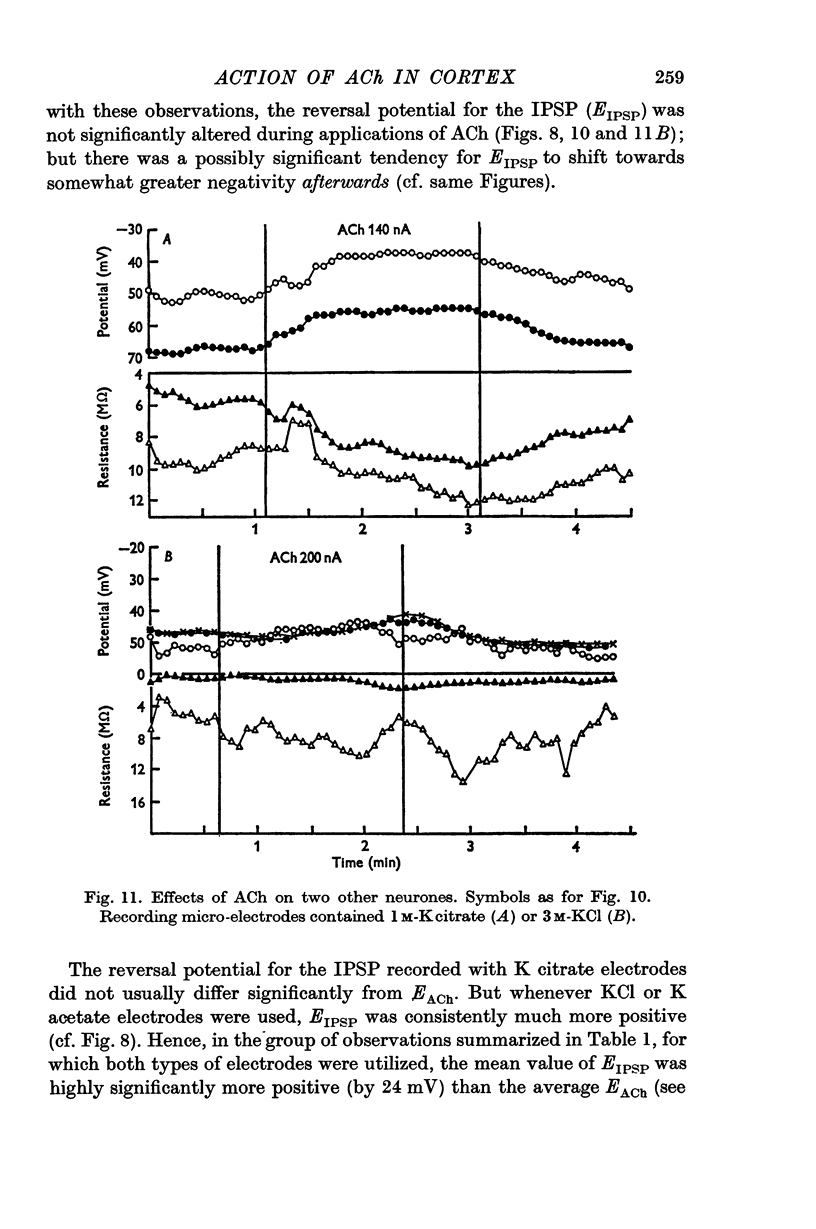
3. The depolarizing effect has a mean reversal level of -86·7 mV (with mean resting potential -56 mV).
4. It is concluded that as a muscarinic excitatory agent, ACh probably acts by reducing the resting K+ conductance of cortical neurones, and also the delayed K+ current of the action potential.
5. These results are discussed in relation to the possible role of ACh in cortical function.
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Freygang W. H. The potassium and chloride conductance of frog muscle membrane. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163(1):61–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames A., 3rd, Higashi K., Nesbett F. B. Relation of potassium concentration in choroidplexus fluid to that in plasma. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(3):506–515. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULBRING E. Changes in configuration of spontaneously discharged spike potentials from smooth muscle of the guinea-pig's taenia coli; the effect of electrotonic currents and of adrenaline, acetylcholine and histamine. J Physiol. 1957 Feb 15;135(2):412–425. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourke R. S., Tower D. B. Fluid compartmentation and electrolytes of cat cerebral cortex in vitro. II. Sodium, potassium and chloride of mature cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1966 Nov;13(11):1099–1117. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb04268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREUTZFELDT O. D., LUX H. D., NACIMIENTO A. C. INTRACELLULAERE REIZUNG CORTICALER NERVENZELLEN. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1964 Oct 5;281:129–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford J. M., Curtis D. R. Pharmacological studies on feline Betz cells. J Physiol. 1966 Sep;186(1):121–138. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVSON H. THE CEREBROSPINAL FLUID. Ergeb Physiol. 1963;52:20–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DURBIN R. P., JENKINSON D. H. The calcium dependence of tension development in depolarized smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1961 Jun;157:90–96. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DURBIN R. P., JENKINSON D. H. The effect of carbachol on the permeability of depolarized smooth muscle to inorganic ions. J Physiol. 1961 Jun;157:74–89. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M. J., Gerschenfeld H. M. Some physiological properties of identified mammalian neuroglial cells. J Physiol. 1969 Jul;203(1):211–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreifuss J. J., Kelly J. S., Krnjević K. Cortical inhibition and gamma-aminobutyric acid. Exp Brain Res. 1969;9(2):137–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00238327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERARD R. W. The biological roots of psychiatry. Am J Psychiatry. 1955 Aug;112(2):81–90. doi: 10.1176/ajp.112.2.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfraind J. M., Kawamura H., Krnjević K., Pumain R. Actions of dinitrophenol and some other metabolic inhibitors on cortical neurones. J Physiol. 1971 May;215(1):199–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfraind J. M., Krnjević K., Pumain R. Unexpected features of the action of dinitrophenol on cortical neurones. Nature. 1970 Nov 7;228(5271):562–564. doi: 10.1038/228562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND W. C., GREIG M. E. Studies on the permeability of erythrocytes. III. The effect of physostigmine and acetylcholine on the permeability of dog, cat and rabbit erythrocytes to sodium and potassium. Am J Physiol. 1950 Sep;162(3):610–615. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1950.162.3.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JASPER H., STEFANIS C. INTRACELLULAR OSCILLATORY RHYTHMS IN PYRAMIDAL TRACT NEURONES IN THE CAT. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1965 May;18:541–553. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(65)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOELLE G. B. The histochemical localization of cholinesterases in the central nervous system of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1954 Feb;100(1):211–235. doi: 10.1002/cne.901000108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. S., Krnjević K., Morris M. E., Yim G. K. Anionic permeability of cortical neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1969;7(1):11–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00236105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Libet B. Actions of noradrenaline and acetylcholine on sympathetic ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1970 Jun;208(2):353–372. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Libet B. Generation of slow postsynaptic potentials without increases in ionic conductance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1304–1311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike H., Okada Y., Oshima T., Takahashi K. Accommodative behavior of cat pyramidal tract cells investigated with intracellular ijection of currents. Exp Brain Res. 1968;5(3):173–188. doi: 10.1007/BF00238662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Phillis J. W. Pharmacological properties of acetylcholine-sensitive cells in the cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 May;166(2):328–350. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Pumain R., Renaud L. Effects of Ba2+ and tetraethylammonium on cortical neurones. J Physiol. 1971 May;215(1):223–245. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Randić M., Straughan D. W. Pharmacology of cortical inhibition. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(1):78–105. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Reiffenstein R. J., Silver A. Chemical sensitivity of neurons in long-isolated slabs of cat cerebral cortex. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1970 Sep;29(3):269–282. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(70)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Schwartz S. Some properties of unresponsive cells in the cerebral cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1967;3(4):306–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00237557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Silver A. A histochemical study of cholinergic fibres in the cerebral cortex. J Anat. 1965 Oct;99(Pt 4):711–759. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuffler S. W., Nicholls J. G. The physiology of neuroglial cells. Ergeb Physiol. 1966;57:1–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libet B., Alberts W. W., Wright E. W., Jr, Feinstein B. Responses of human somatosensory cortex to stimuli below threshold for conscious sensation. Science. 1967 Dec 22;158(3808):1597–1600. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3808.1597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libet B. Cortical activation in conscious and unconscious experience. Perspect Biol Med. 1965 Autumn;9(1):77–86. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1965.0023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D., Pollen D. A. Electrical constants of neurons in the motor cortex of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1966 Mar;29(2):207–220. doi: 10.1152/jn.1966.29.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan H. Inhibitions of long duration in the cerebral cortex. A quantitative difference between excitatory amino acids. Exp Brain Res. 1970;10(4):417–426. doi: 10.1007/BF02324767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Frank K. Anomalous rectification in cat spinal motoneurons and effect of polarizing currents on excitatory postsynaptic potential. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1097–1113. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS C. G. Actions of antidromic pyramidal volleys on single Betz cells in the cat. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1959 Jan;44(1):1–25. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1959.sp001364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., York D. H. Pharmacological studies on a cholinergic inhibition in the cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1968 Sep;10(3):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purpura D. P., Prelevic S., Santini M. Hyperpolarizing increase in membrane conductance in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1968 Feb;7(2):310–312. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90109-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDIC M., SIMINOFF R., STRAUGHAN D. W. ACETYLCHOLINE DEPRESSION OF CORTICAL NEURONS. Exp Neurol. 1964 Mar;9:236–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(64)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPEHLMANN R. Acetylcholine and prostigmine electrophoresis at visual cortex neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1963 Jan;26:127–139. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.1.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. G., Wuerker R. B., Frank K. Membrane impedance changes during synaptic transmission in cat spinal motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1072–1096. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K. Slow and fast groups of pyramidal tract cells and their respective membrane properties. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Sep;28(5):908–924. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.5.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weight F. F., Votava J. Slow synaptic excitation in sympathetic ganglion cells: evidence for synaptic inactivation of potassium conductance. Science. 1970 Nov 13;170(3959):755–758. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3959.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


