Abstract
1. The effects of impulses in recurrent motor axon collaterals on reflex transmission from different types of primary afferents to motoneurones were investigated in the cat by conditioning of PSPs evoked in motoneurones.
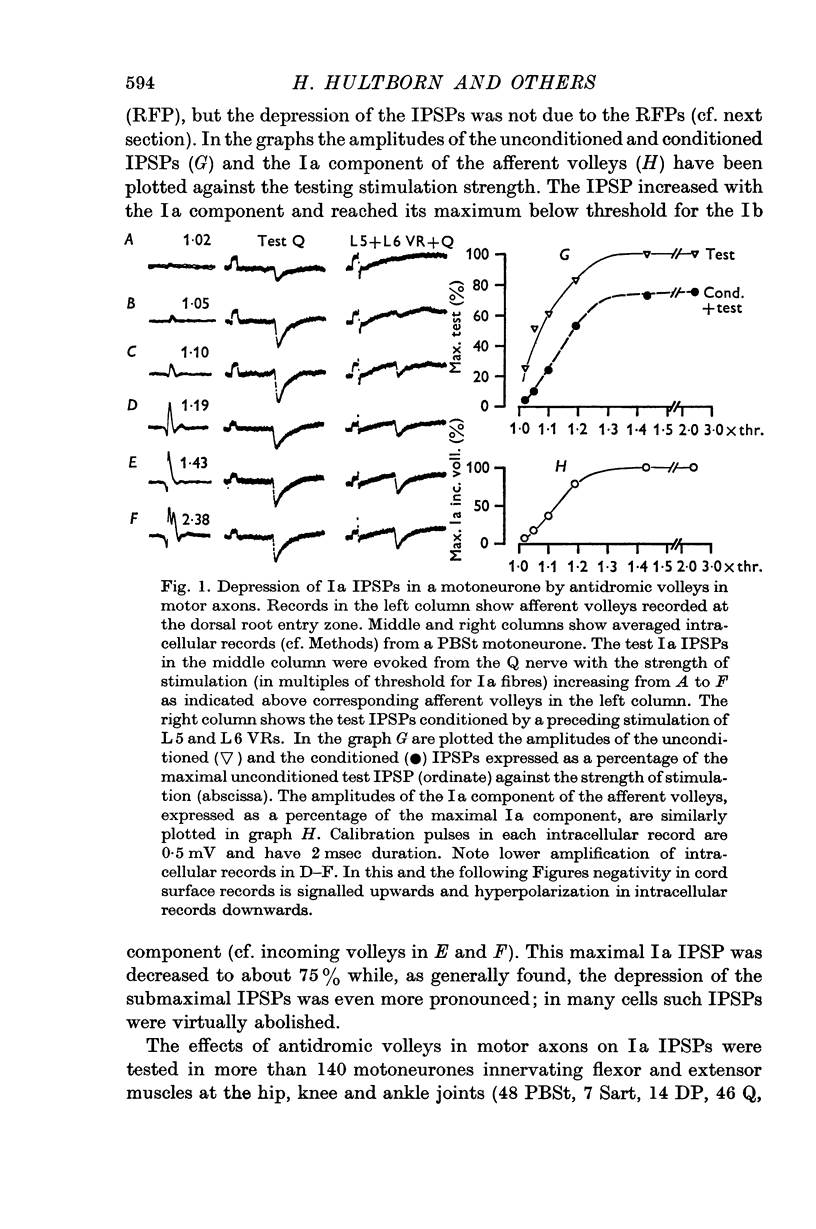
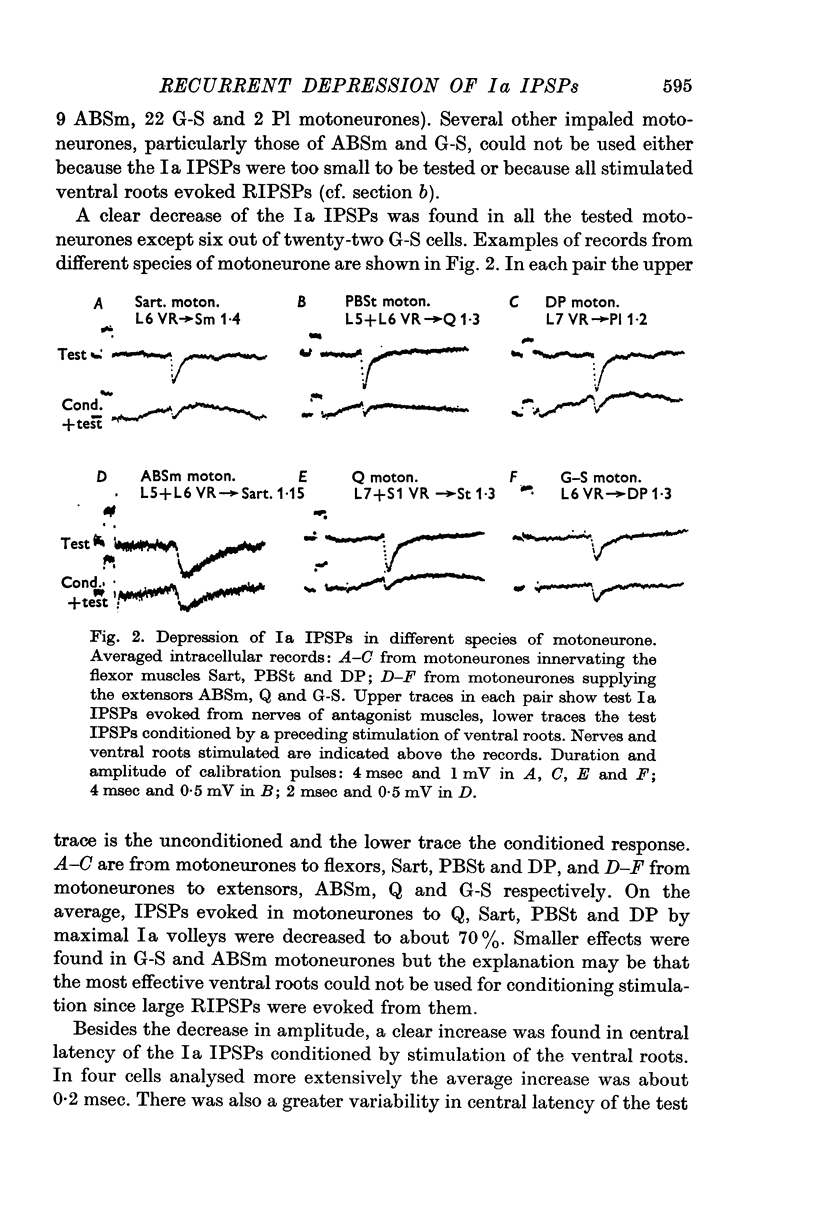
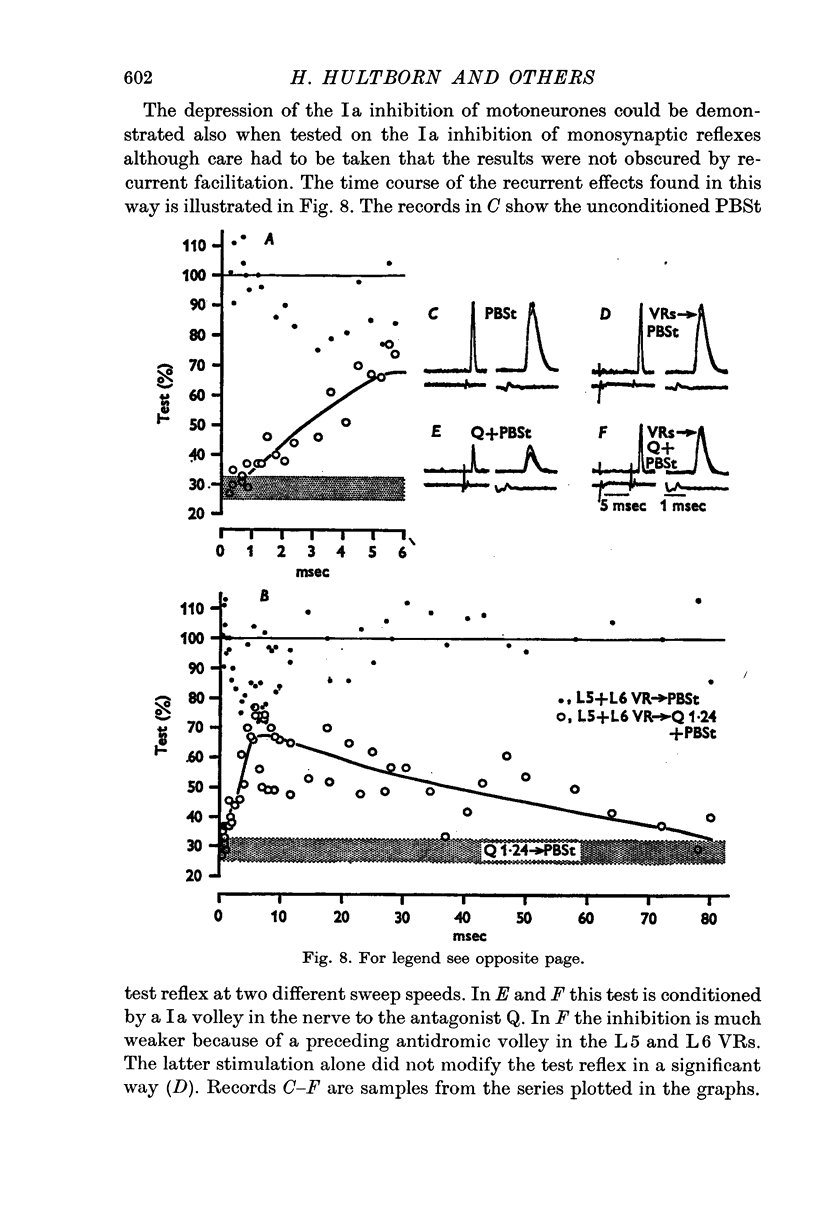
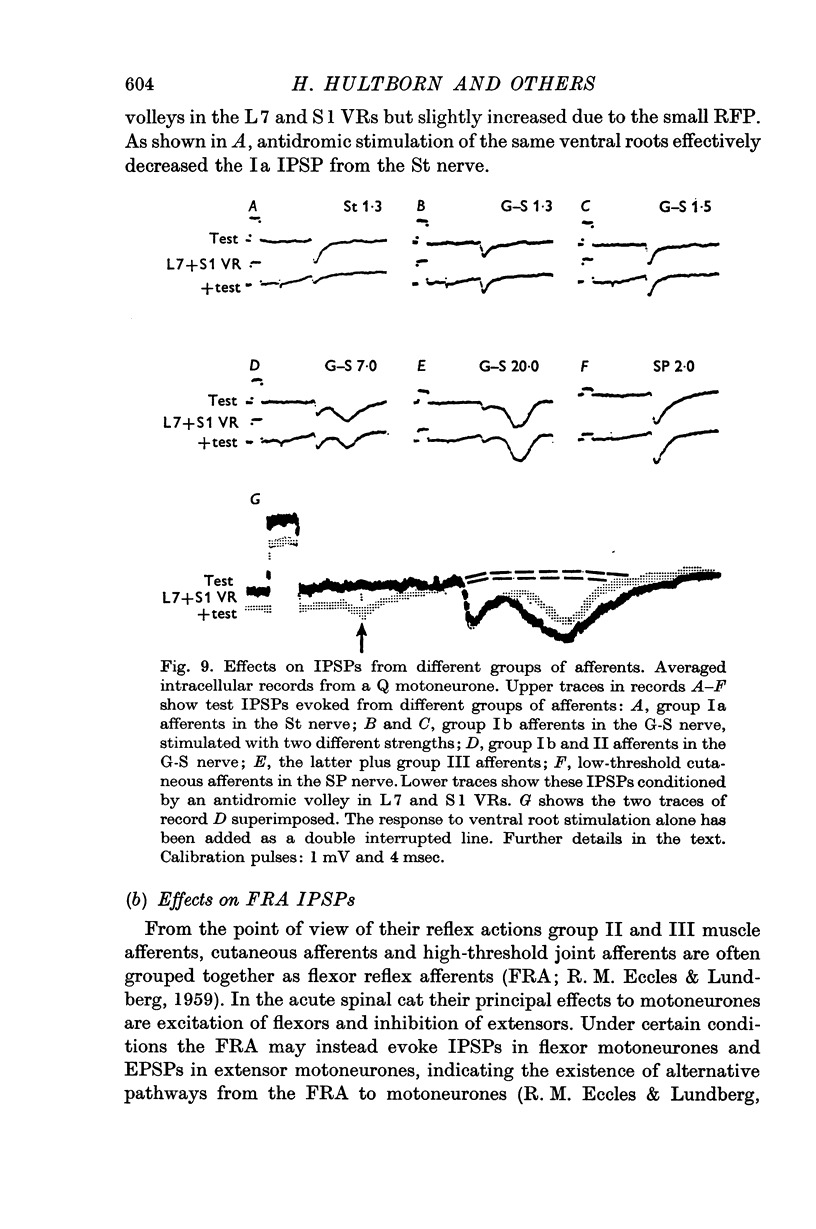
2. IPSPs evoked by volleys in large muscle spindle (Ia) afferents were effectively decreased when preceded by an antidromic stimulation of ventral roots. Some IPSPs from group II muscle afferents and low threshold cutaneous afferents were also slightly depressed, while other PSPs were unaffected.
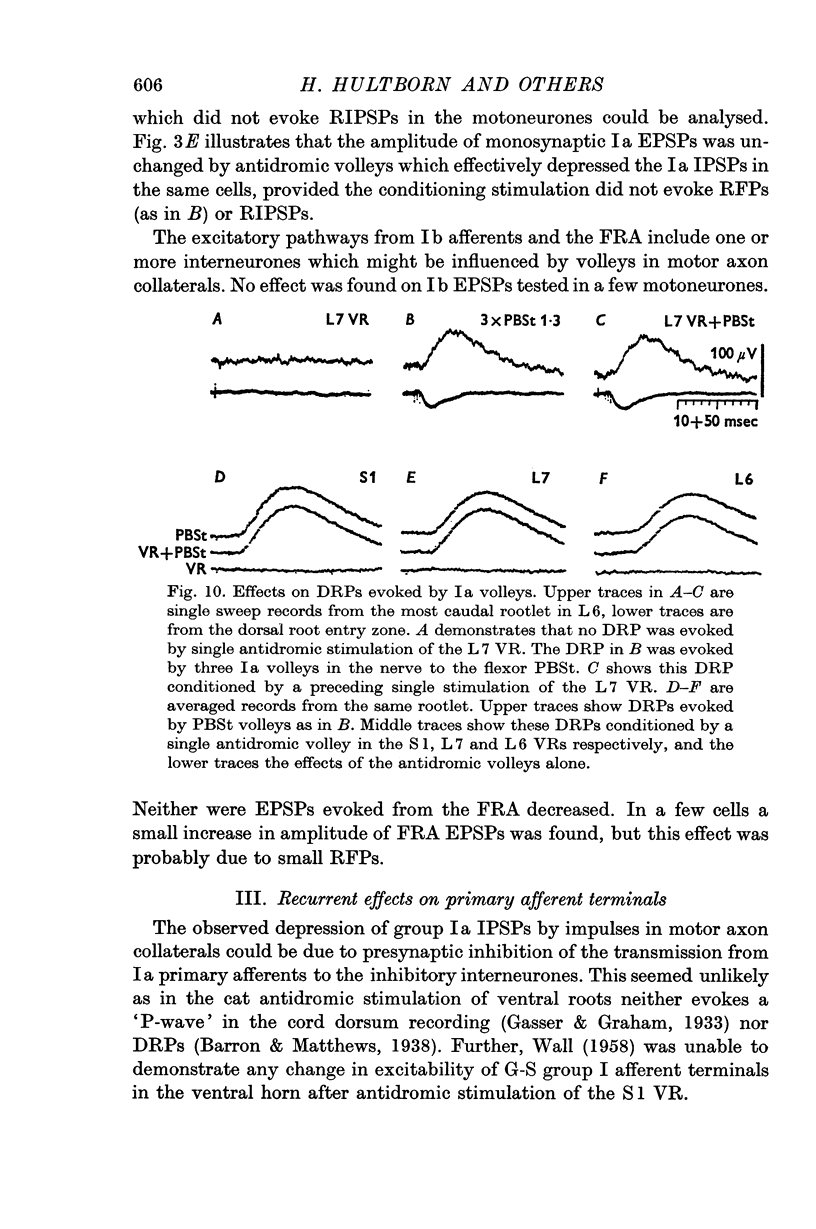
3. The depression of the IPSPs could be evoked by antidromic volleys, which produced neither conductance changes in the motoneurones nor depolarization of Ia afferent terminals.
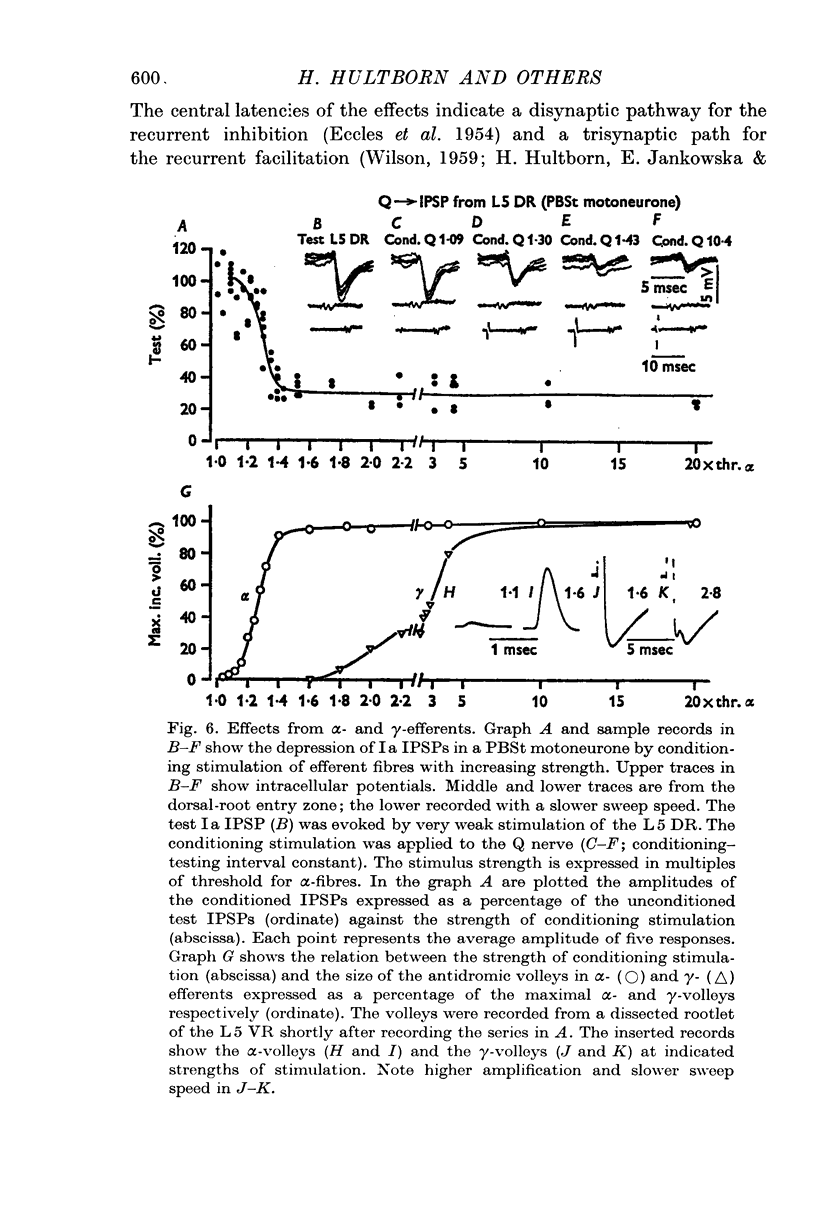
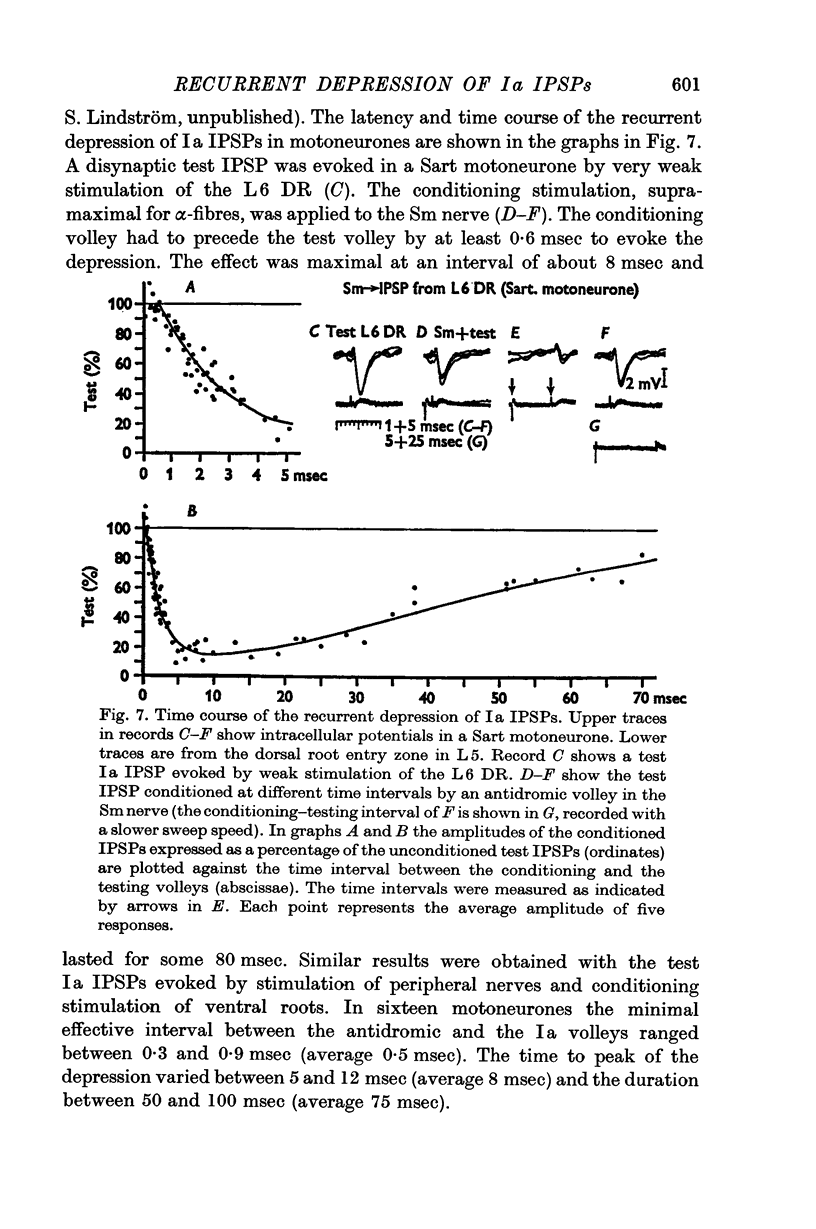
4. The effect on the Ia IPSPs is most likely due to post-synaptic inhibition of the Ia inhibitory interneurones, evoked through α-motor axon collaterals and Renshaw cells. The depression of some IPSPs from flexor reflex afferents is explained by a convergence of excitatory effects from these afferents on the Ia inhibitory interneurones.
5. The results indicate a selective recurrent control from motor axon collaterals of the interneurones in the reciprocal Ia inhibitory pathway to motoneurones.
Full text
PDF














Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andén N. E., Jukes M. G., Lundberg A., Vyklický L. The effect of DOPA on the spinal cord. 1. Influence on transmission from primary afferents. Acta Physiol Scand. 1966 Jul-Aug;67(3):373–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1966.tb03324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY K., ECCLES J. C. Analysis of the fast afferent impulses from thigh muscles. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):462–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barron D. H., Matthews B. H. The interpretation of potential changes in the spinal cord. J Physiol. 1938 Apr 14;92(3):276–321. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1938.sp003603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. C., Lawrence D. G., Matthews P. B. Antidromic inhibition of presumed fusimotor neurones by repetitive stimulation of the ventral root in the decerebrate cat. Experientia. 1968 Dec 15;24(12):1210–1212. doi: 10.1007/BF02146625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., ECCLES J. C. The time courses of excitatory and inhibitory synaptic actions. J Physiol. 1959 Mar 12;145(3):529–546. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decima E. E. An effect of postsynaptic neurons upon presynaptic terminals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 May;63(1):58–64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.1.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decima E. E., Goldberg L. J. Centrifugal dorsal root discharges induced by motoneurone activation. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;207(1):103–118. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Synaptic actions on motoneurones caused by impulses in Golgi tendon organ afferents. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):227–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Synaptic actions on motoneurones in relation to the two components of the group I muscle afferent volley. J Physiol. 1957 May 23;136(3):527–546. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. The convergence of monosynaptic excitatory afferents on to many different species of alpha motoneurones. J Physiol. 1957 Jun 18;137(1):22–50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., FATT P., KOKETSU K. Cholinergic and inhibitory synapses in a pathway from motor-axon collaterals to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1954 Dec 10;126(3):524–562. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Integrative pattern of Ia synaptic actions on motoneurones of hip and knee muscles. J Physiol. 1958 Dec 4;144(2):271–298. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles J. C., Magni F., Willis W. D. Depolarization of central terminals of Group I afferent fibres from muscle. J Physiol. 1962 Jan;160(1):62–93. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. The rubrospinal tract. II. Facilitation of interneuronal transmission in reflex paths to motoneurones. Exp Brain Res. 1969;7(4):365–391. doi: 10.1007/BF00237321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Jankowska E., Lindström S. Inhibition in IA inhibitory pathway by impulses in recurrent motor axon collaterals. Life Sci. 1968 Apr 1;7(7):337–339. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(68)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Jankowska E., Lindström S. Recurrent inhibition of interneurones monosynaptically activated from group Ia afferents. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;215(3):613–636. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Jankowska E., Lindström S. Relative contribution from different nerves to recurrent depression of Ia IPSPs in motoneurones. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;215(3):637–664. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. G., Wuerker R. B., Frank K. Membrane impedance changes during synaptic transmission in cat spinal motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1072–1096. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALL P. D. Excitability changes in afferent fibre terminations and their relation to slow potentials. J Physiol. 1958 Jun 18;142(1):1–21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON V. J., BURGESS P. R. Disinhibition in the cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1962 May;25:392–404. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.3.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON V. J. Recurrent facilitation of spinal reflexes. J Gen Physiol. 1959 Mar 20;42(4):703–713. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.4.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON V. J., TALBOT W. H. Recurrent conditioning in the cat spinal cord. Differential effect of meprobamate on recurrent facilitation and inhibition. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Jan;43:495–502. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.3.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


