Abstract
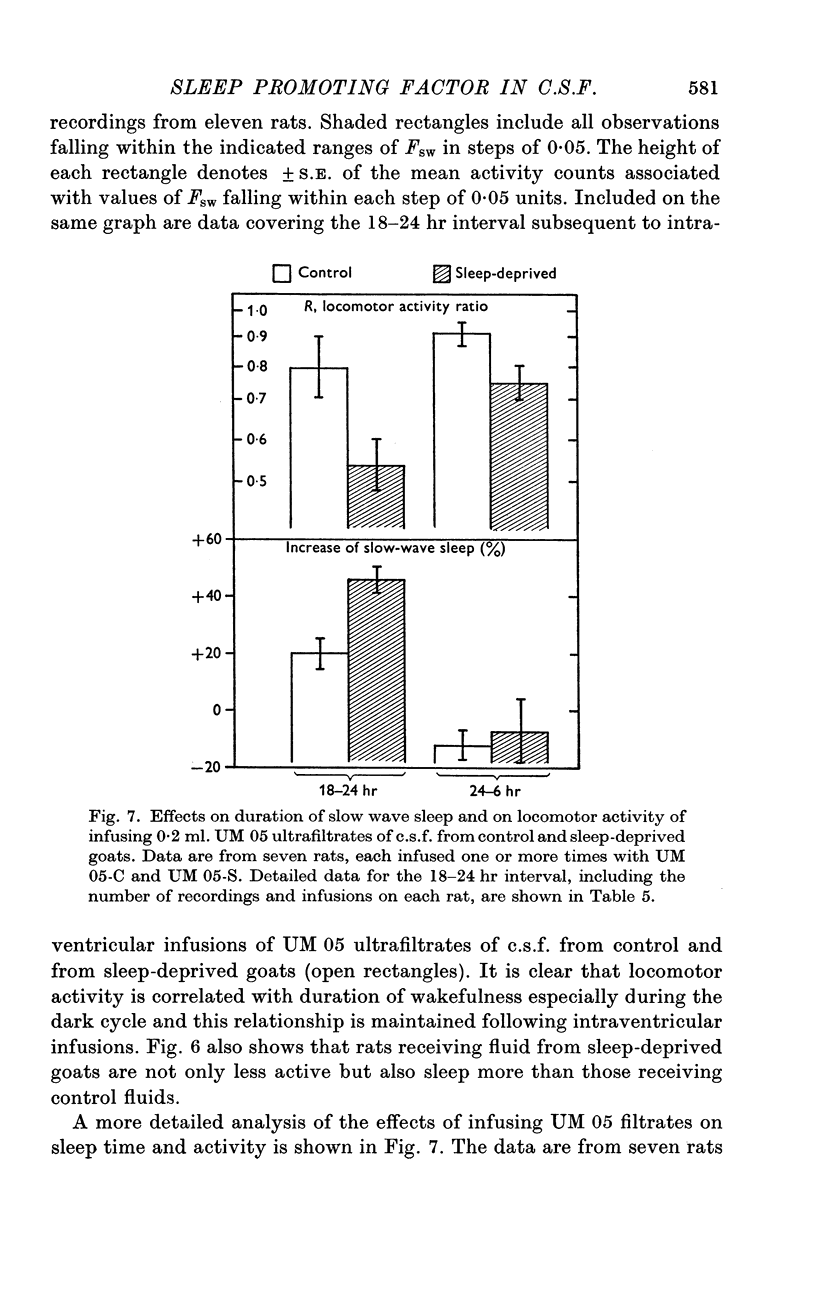
1. Intraventricular infusion in the rat of 0·1 ml. cerebrospinal fluid (c.s.f.) from sleep-deprived goats increases the duration of sleep (measured by e.e.g.) and decreases locomotor activity (measured photo-electrically) for at least 6 hr subsequent to the infusion. Subarachnoid infusions are ineffective.
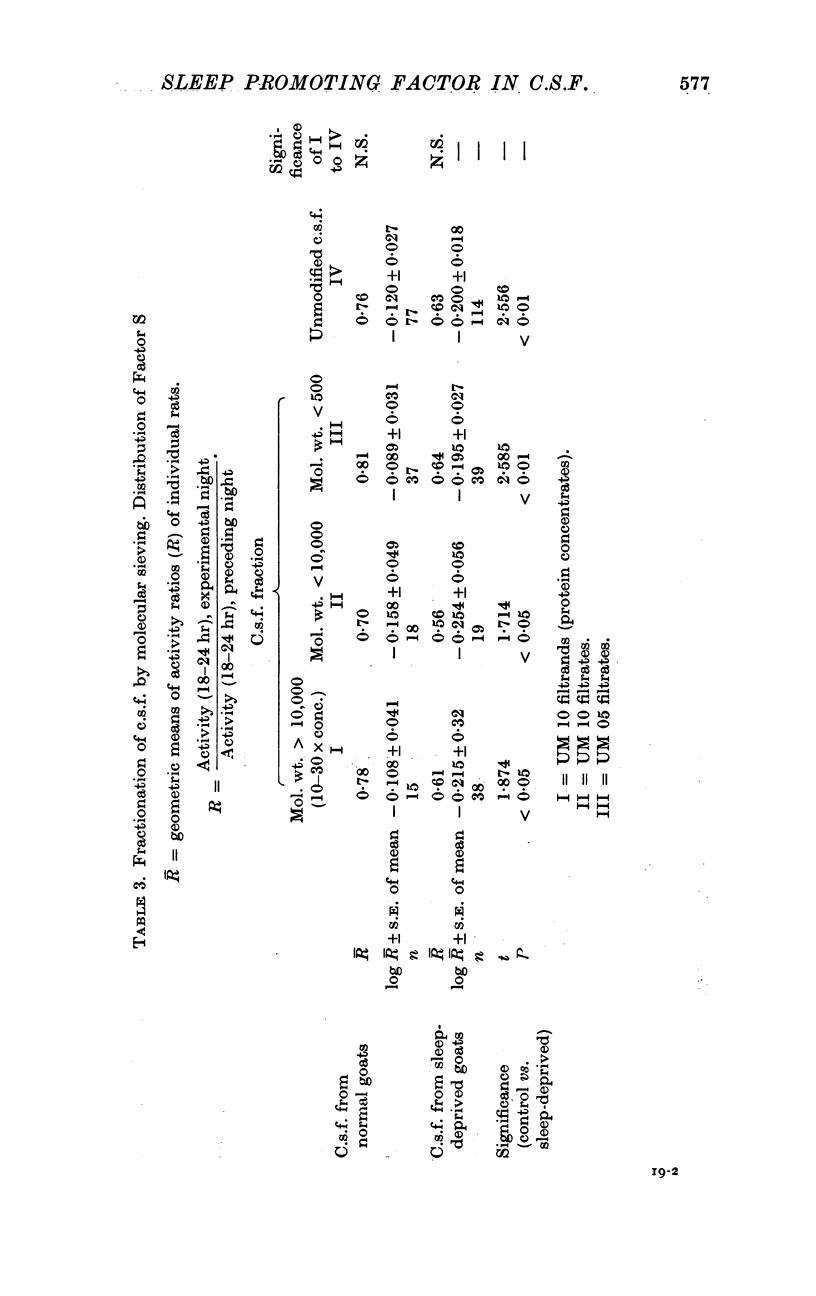
2. C.s.f. from control and sleep-deprived goats was fractionated by ultrafiltration through molecular sieves. The sleep-promoting Factor S is found in the low molecular weight fraction (mol. wt. < 500) of c.s.f. from sleep-deprived but not from control goats.
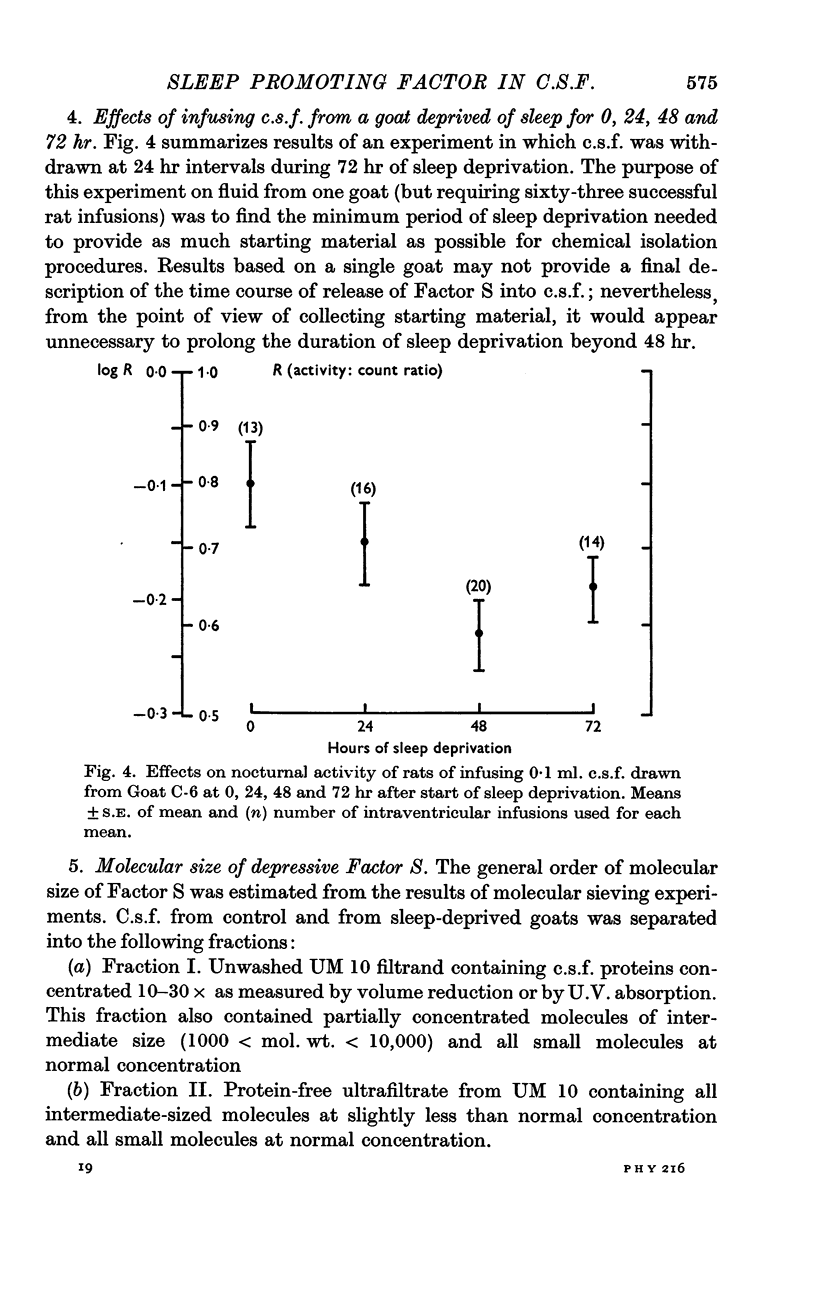
3. The concentration of Factor S in c.s.f. increases progressively during the first 48 hr of sleep deprivation.
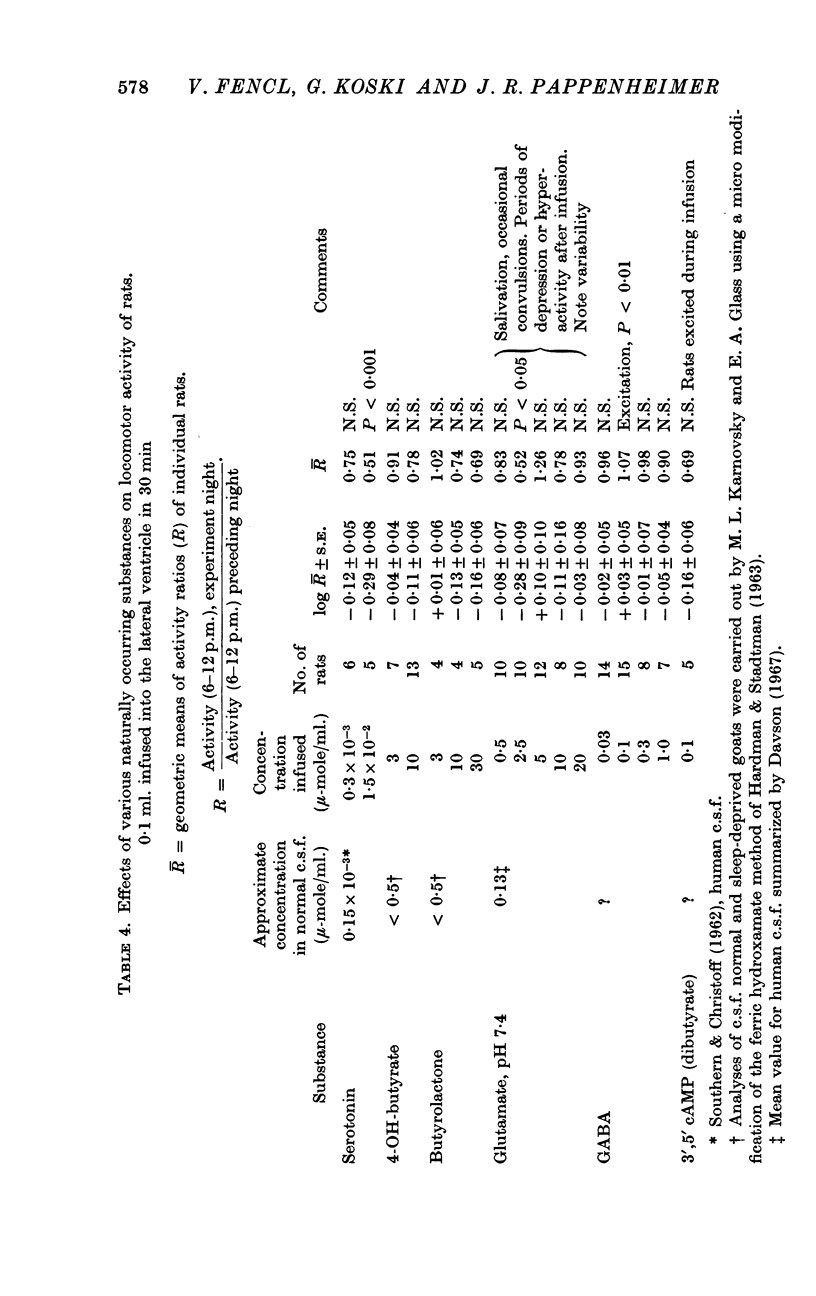
4. The sleep promoting effects of Factor S cannot be duplicated by serotonin, 4-OH-butyrate, butyrolactone, GABA (γ-amino butyric acid), glutamic acid or 3′,5′-cyclic AMP when these substances are added to control fluids in concentrations up to 10 times greater than those found in normal c.s.f.
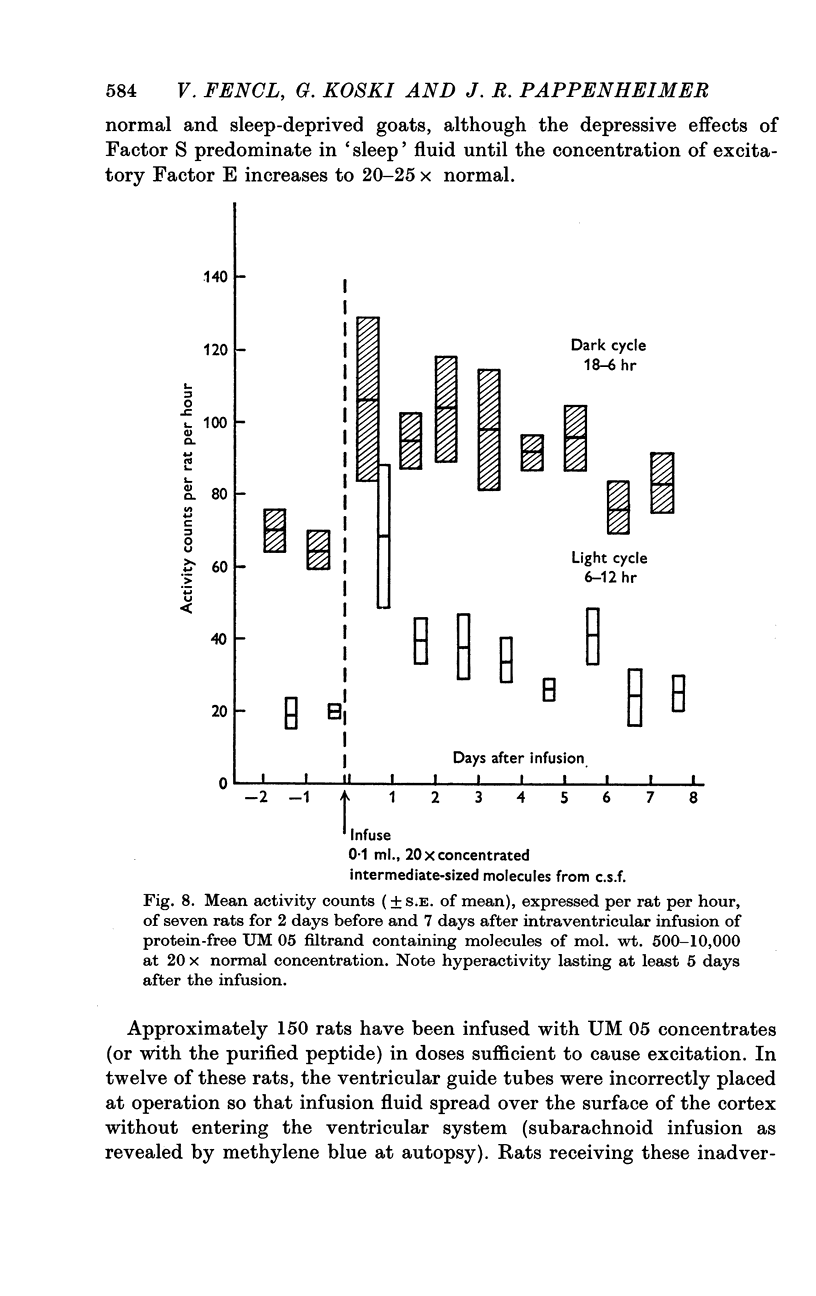
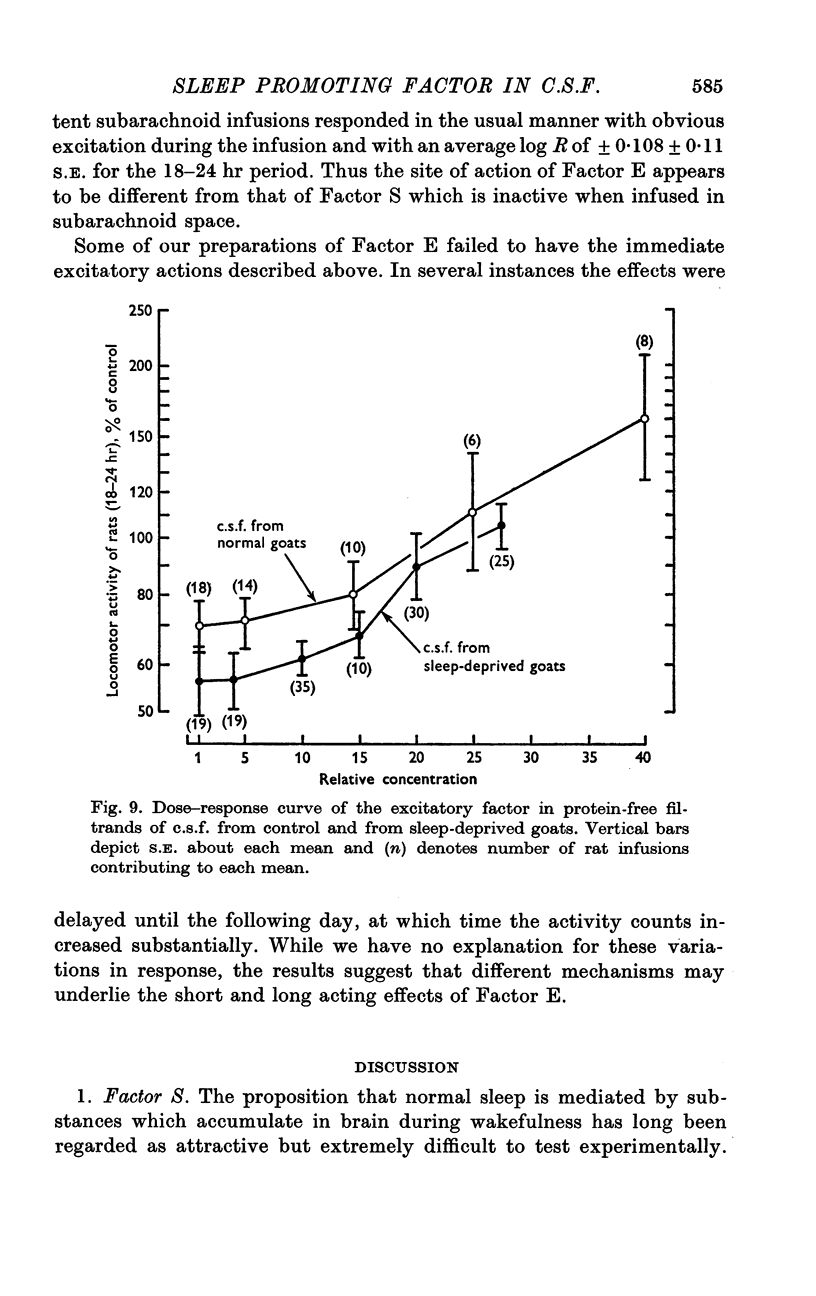
5. Intraventricular or subarchnoid infusion in the rat of 0·1 ml. proteinfree c.s.f. containing molecules in the mol. wt. range of 500-10,000 at 10-30 × normal concentration causes hyperactivity which persists for several days and nights following the infusion. The excitatory material, probably a peptide, is present in c.s.f. from both control and sleep-deprived goats.
6. The properties of Factor S suggest that it may play a role in the normal regulation of sleep and wakefulness.
Full text
PDF














Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BESSMAN S. P., SKOLNIK S. J. GAMMA HYDROXYBUTYRATE AND GAMMA BUTYROLACTONE: CONCENTRATION IN RAT TISSUES DURING ANESTHESIA. Science. 1964 Mar 6;143(3610):1045–1047. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3610.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brightman M. W. The distribution within the brain of ferritin injected into cerebrospinal fluid compartments. II. Parenchymal distribution. Am J Anat. 1965 Sep;117(2):193–219. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001170204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
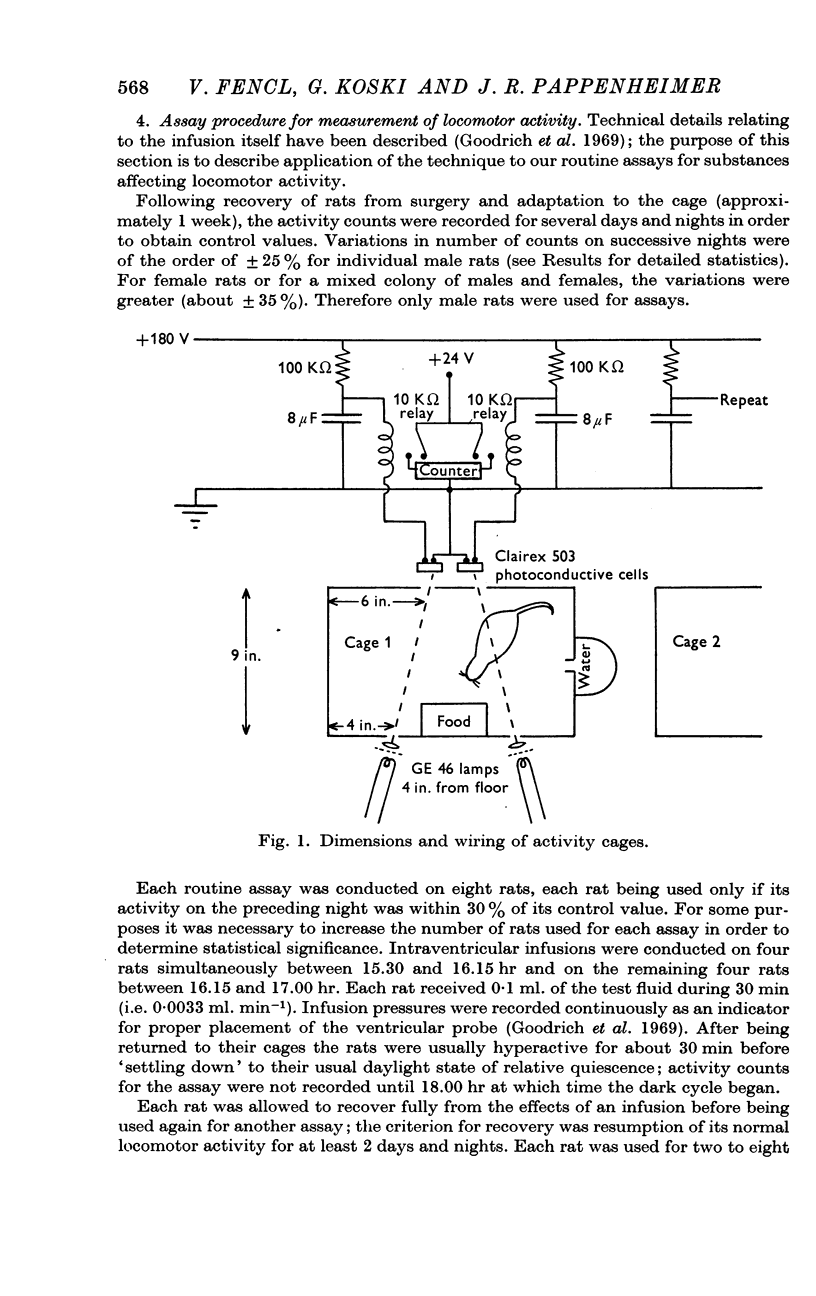
- Goodrich C. A., Greehey B., Miller T. B., Pappenheimer J. R. Cerebral ventricular infusions in unrestrained rats. J Appl Physiol. 1969 Jan;26(1):137–140. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1969.26.1.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDMAN J. K., STADTMAN T. C. Metabolism of amega-amino acids. III. Mechanism of conversion of gamma-aminobutyrate to gamma-hydroxybutryate by Clostridium aminobutyricum. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jun;238:2081–2087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEISEY S. R., HELD D., PAPPENHEIMER J. R. Bulk flow and diffusion in the cerebrospinal fluid system of the goat. Am J Physiol. 1962 Nov;203:775–781. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.203.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi T. Pavlov's sleep theory under a new light. Keio J Med. 1965 Sep;14(3):135–144. doi: 10.2302/kjm.14.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouvet M. Biogenic amines and the states of sleep. Science. 1969 Jan 3;163(3862):32–41. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3862.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONNIER M., HOESLI L. DIALYSIS OF SLEEP AND WAKING FACTORS IN BLOOD OF THE RABBIT. Science. 1964 Nov 6;146(3645):796–798. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3645.796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONNIER M., HOESLI L. HUMORAL TRANSMISSION OF SLEEP AND WAKEFULNESS II. HEMODIALYSIS OF A SLEEP INDUCING HUMOR DURING STIMULATION OF THE THALAMIC SOMNOGENIC AREA. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1965;282:60–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer J. R., Miller T. B., Goodrich C. A. Sleep-promoting effects of cerebrospinal fluid from sleep-deprived goats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):513–517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
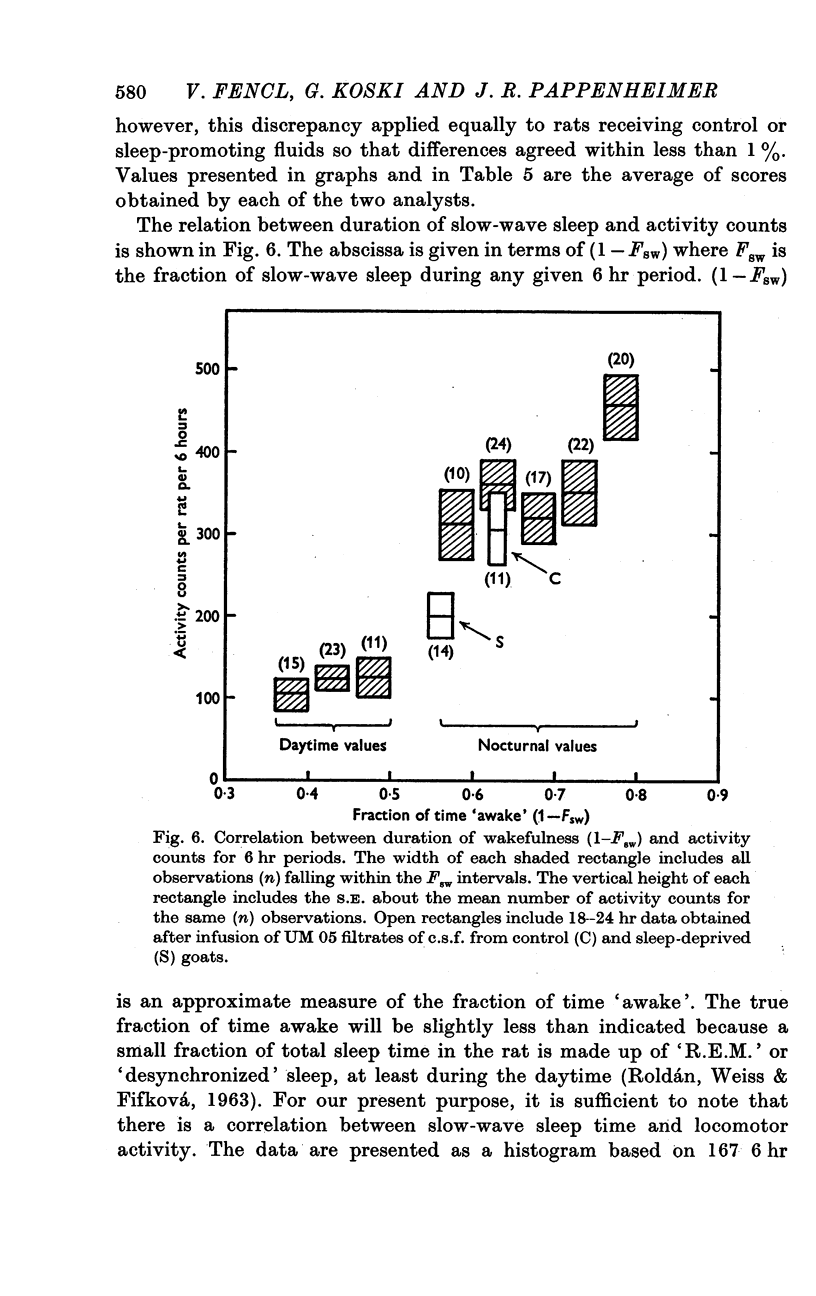
- ROLDAN E., WEISS T., FIFKOVA E. EXCITABILITY CHANGES DURING THE SLEEP CYCLE OF THE RAT. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1963 Oct;15:775–785. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(63)90168-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter C. P. Sleep and activity: their relation to the 24-hour clock. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1967;45:8–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOUTHERN A. L., CHRISTOFF N. Cerebrospinal fluid serotonin in brain tumor and other neurological disorders determined by a spectrophotofluorometric technique. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 Feb;59:320–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


