Abstract
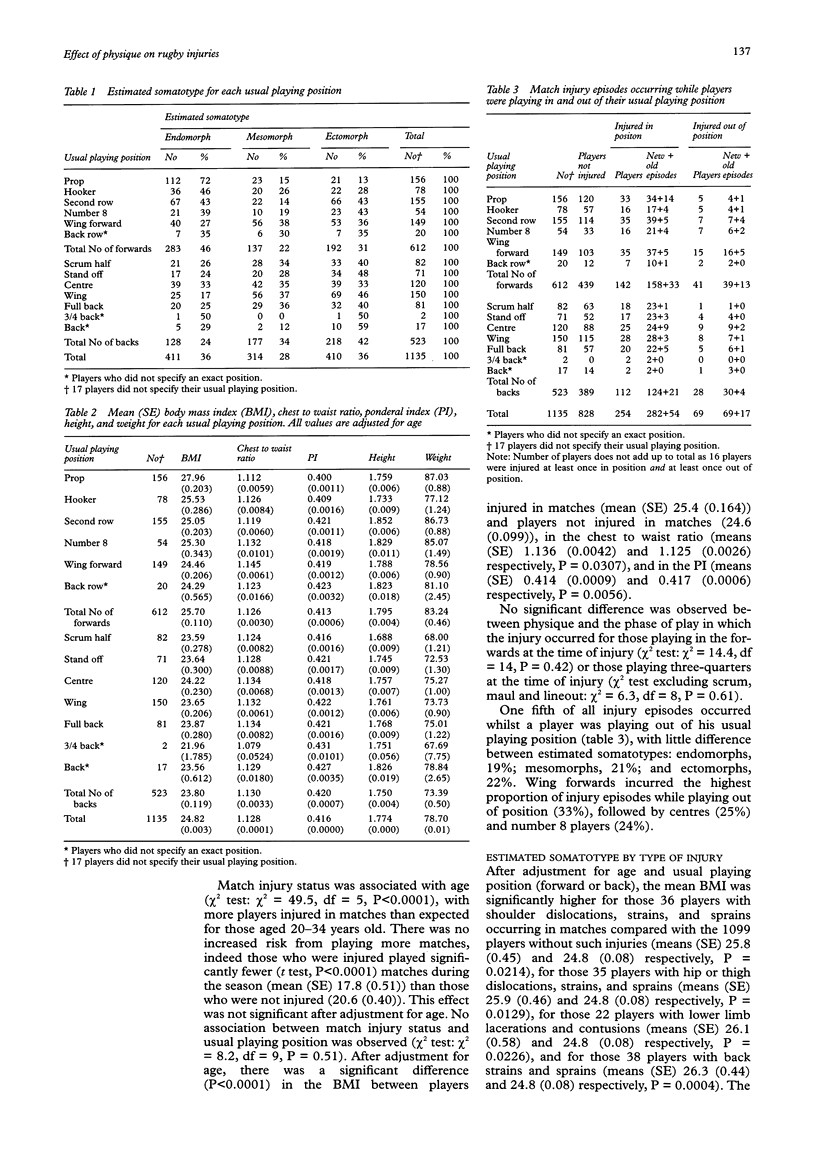
OBJECTIVES: To determine whether there is an association between a player's physique and injuries incurred while playing rugby football. METHODS: A cohort study was carried out involving all senior rugby clubs in the Scottish Borders during the 1993-1994 rugby season. Somatotype estimates were determined for 1152 (95%) of the 1216 eligible players. Body mass index (BMI), chest to waist ratio, and the ponderal index (PI) were used to classify players' physique as endomorphic (obese), mesomorphic (muscular), and ectomorphic (linear). RESULTS: A strong association was found between physique and age (chi 2 test: chi 2 = 317.2, df = 10, P < 0.0001). More younger players were ectomorphs. Older players were more often endomorphic. The physiques of forwards and backs were significantly different (chi 2 test: chi 2 = 58.6, df = 2, P < 0.0001), with forwards being of a heavier build than three-quarters, even after adjustment for age. Endomorphic players were more likely than ectomorphs to be injured in a match after adjustment for age (age-adjusted mean BMI for players who were injured in a match was 25.4 compared with 24.6 for players who were not injured in a match, P < 0.0001; adjusted chest to waist ratio means were 1.136 and 1.125 respectively, P = 0.0307; adjusted PI means were 0.414 and 0.417 respectively, P = 0.0056). Increased risk of injury may occur when players play out of position, since one fifth of all injuries occurred in this circumstance. CONCLUSIONS: Further research needs to be conducted using a more objective method of measuring somatotype on a further cohort of players so that the risk of injury for different body types can be examined more closely and related to other potential confounding factors. The level of increased risk for individuals playing out of their usual playing position needs to be established with a greater degree of certainty.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addley K., Farren J. Irish rugby injury survey: Dungannon Football Club (1986-87). Br J Sports Med. 1988 Mar;22(1):22–24. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.22.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell W. Body composition of rugby union football players. Br J Sports Med. 1979 Apr;13(1):19–23. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.13.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson B. R., Carter J. E., Patterson P., Petti K., Orfanos S. M., Noffal G. J. Physique and motor performance characteristics of US national rugby players. J Sports Sci. 1994 Aug;12(4):403–412. doi: 10.1080/02640419408732187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casagrande G., Viviani F. Somatotype of Italian rugby players. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 1993 Mar;33(1):65–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. R., Roux C., Noakes T. D. A prospective study of the incidence and nature of injuries to adult rugby players. S Afr Med J. 1990 Jun 2;77(11):559–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. E., Gibson T. Injuries in Rugby Union football. Br Med J. 1978 Dec 23;2(6154):1759–1761. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6154.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garraway M., Macleod D. Epidemiology of rugby football injuries. Lancet. 1995 Jun 10;345(8963):1485–1487. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath B. H., Carter J. E. A modified somatotype method. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1967 Jul;27(1):57–74. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330270108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maud P. J. Physiological and anthropometric parameters that describe a rugby union team. Br J Sports Med. 1983 Mar;17(1):16–23. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.17.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers P. T. Injuries presenting from rugby union football. Med J Aust. 1980 Jul 12;2(1):17–20. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1980.tb131804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien C. Retrospective survey of rugby injuries in the Leinster province of Ireland 1987-1989. Br J Sports Med. 1992 Dec;26(4):243–244. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.26.4.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarrie K. L., Handcock P., Toomey M. J., Waller A. E. The New Zealand rugby injury and performance project. IV. Anthropometric and physical performance comparisons between positional categories of senior A rugby players. Br J Sports Med. 1996 Mar;30(1):53–56. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.30.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarrie K. L., Handcock P., Waller A. E., Chalmers D. J., Toomey M. J., Wilson B. D. The New Zealand rugby injury and performance project. III. Anthropometric and physical performance characteristics of players. Br J Sports Med. 1995 Dec;29(4):263–270. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.29.4.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seward H., Orchard J., Hazard H., Collinson D. Football injuries in Australia at the élite level. Med J Aust. 1993 Sep 6;159(5):298–301. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1993.tb137863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton P. A., Roux C. E., Noakes T. D. Inadequate pre-season preparation of schoolboy rugby players--a survey of players at 25 Cape Province high schools. S Afr Med J. 1996 May;86(5):531–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


