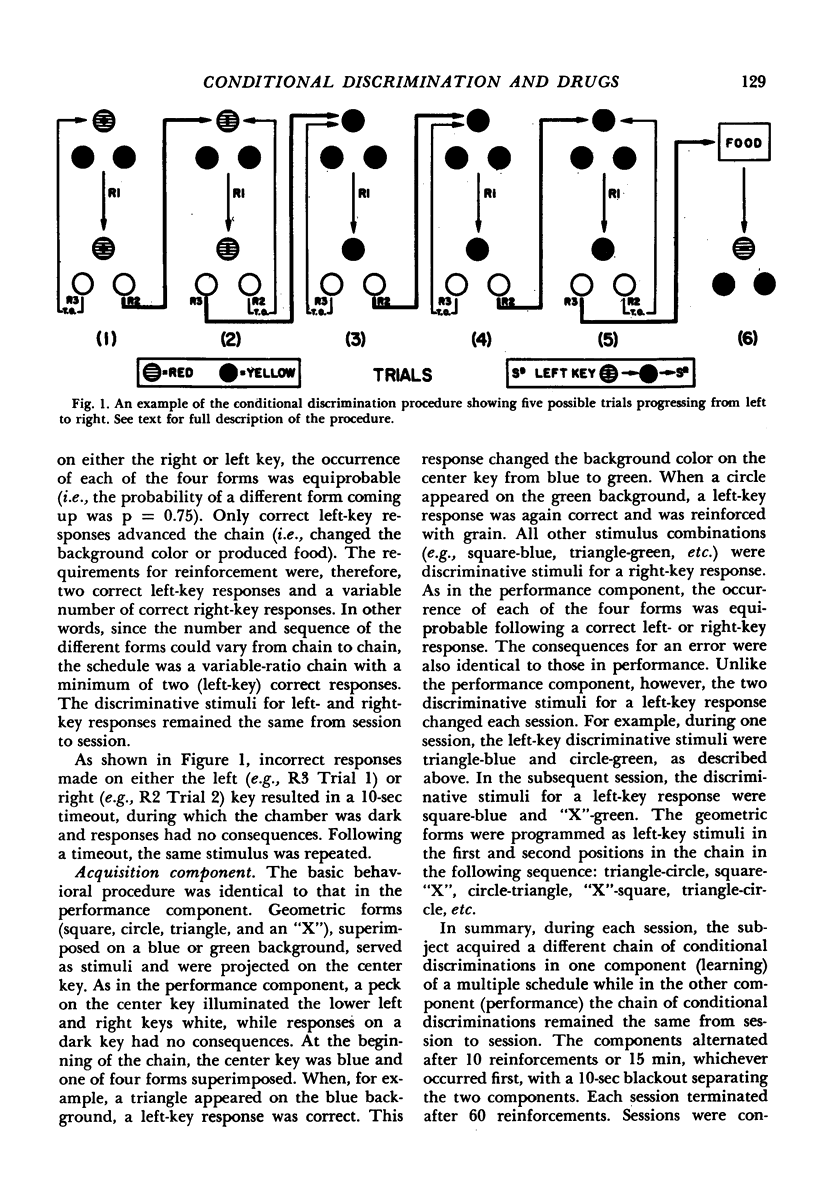
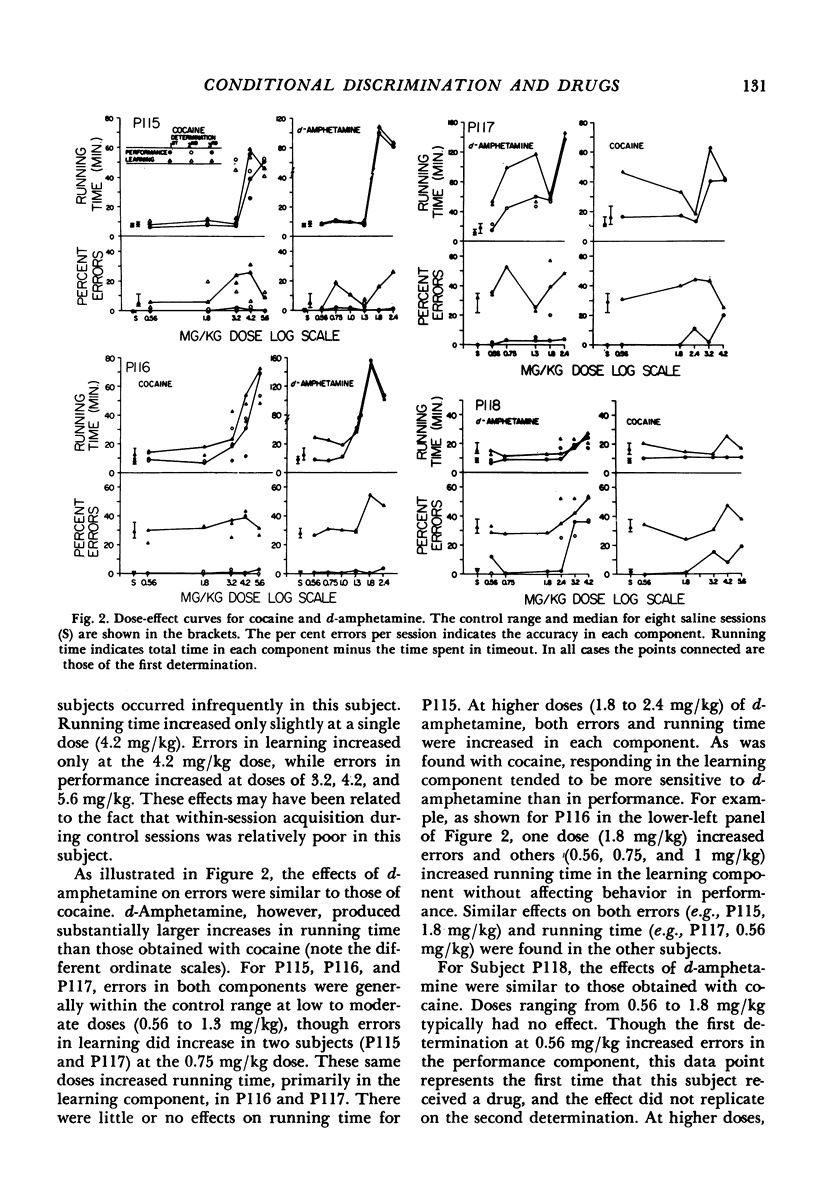
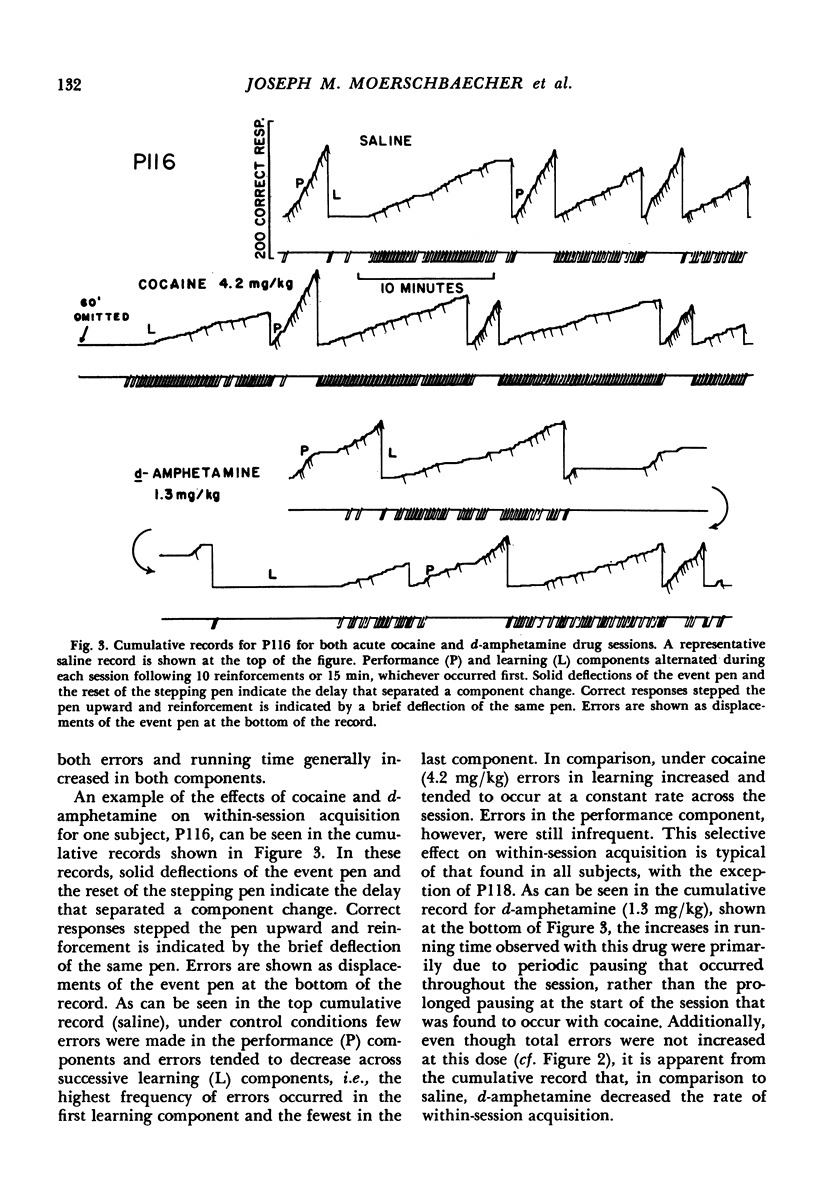
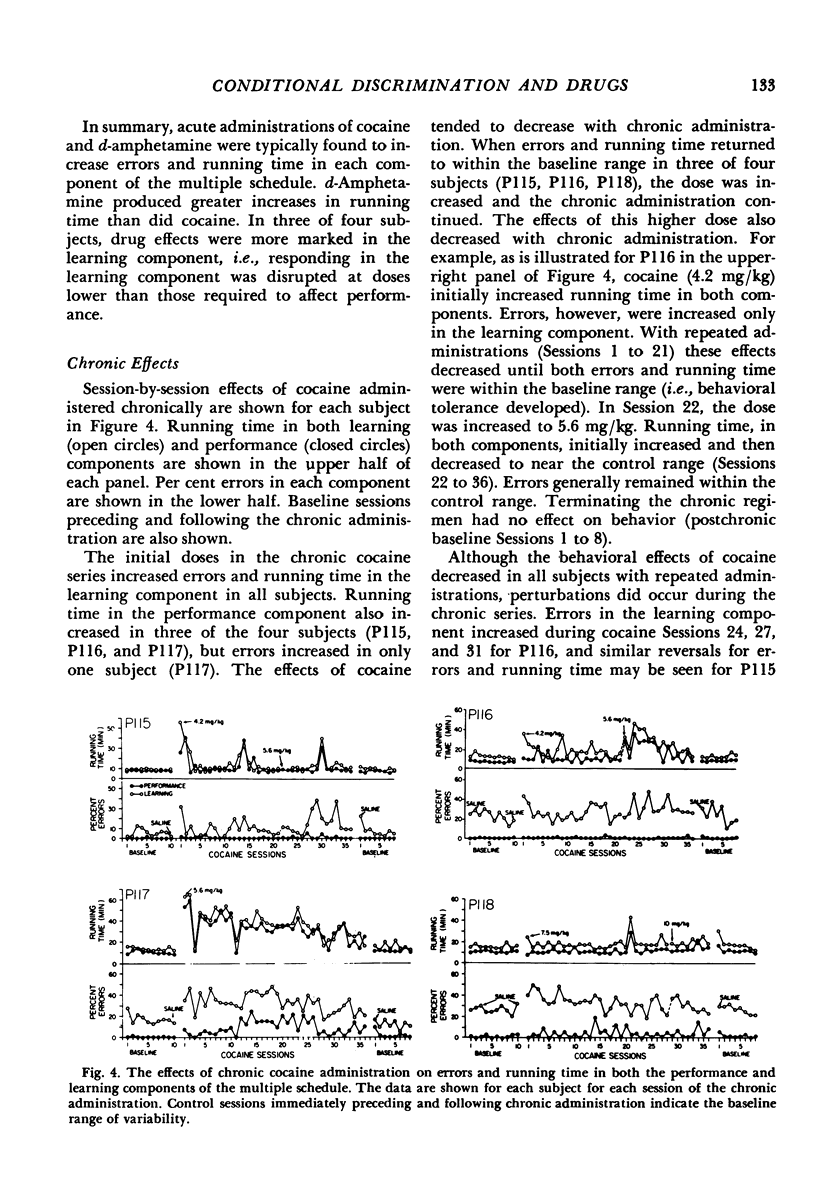
Abstract
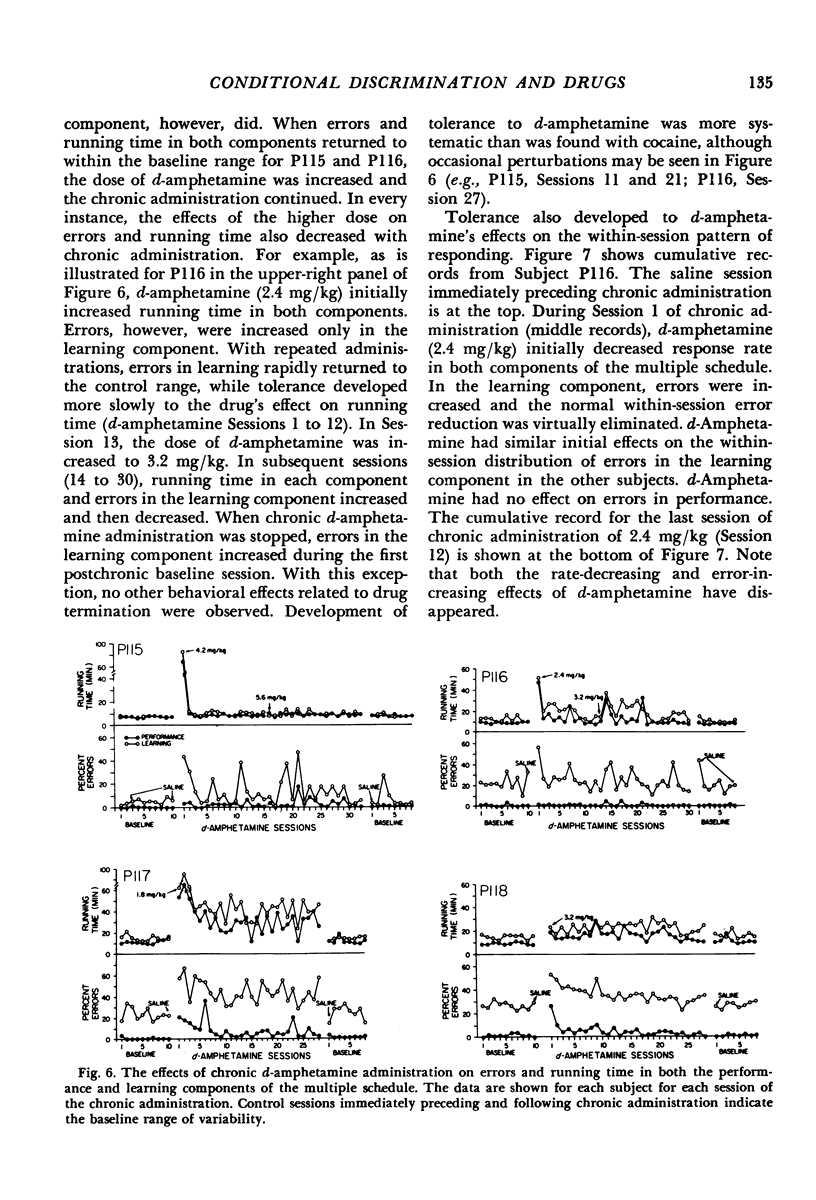
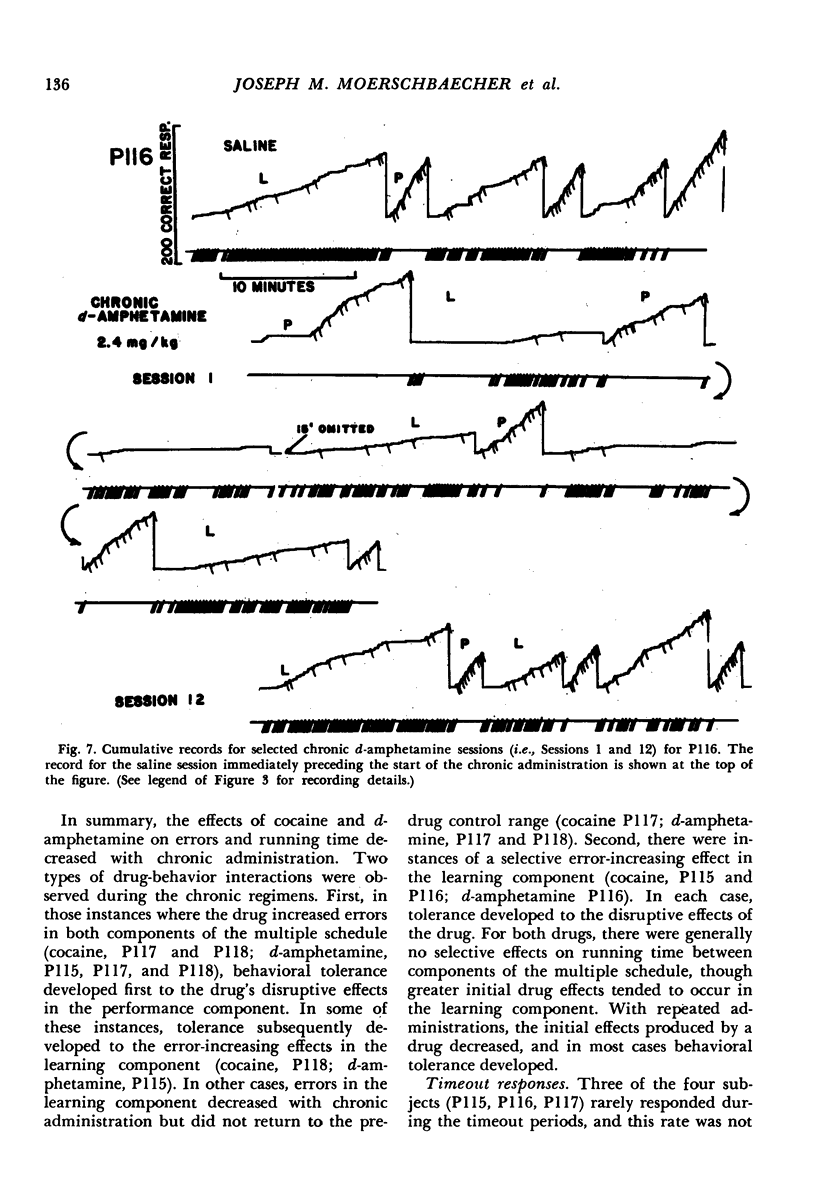
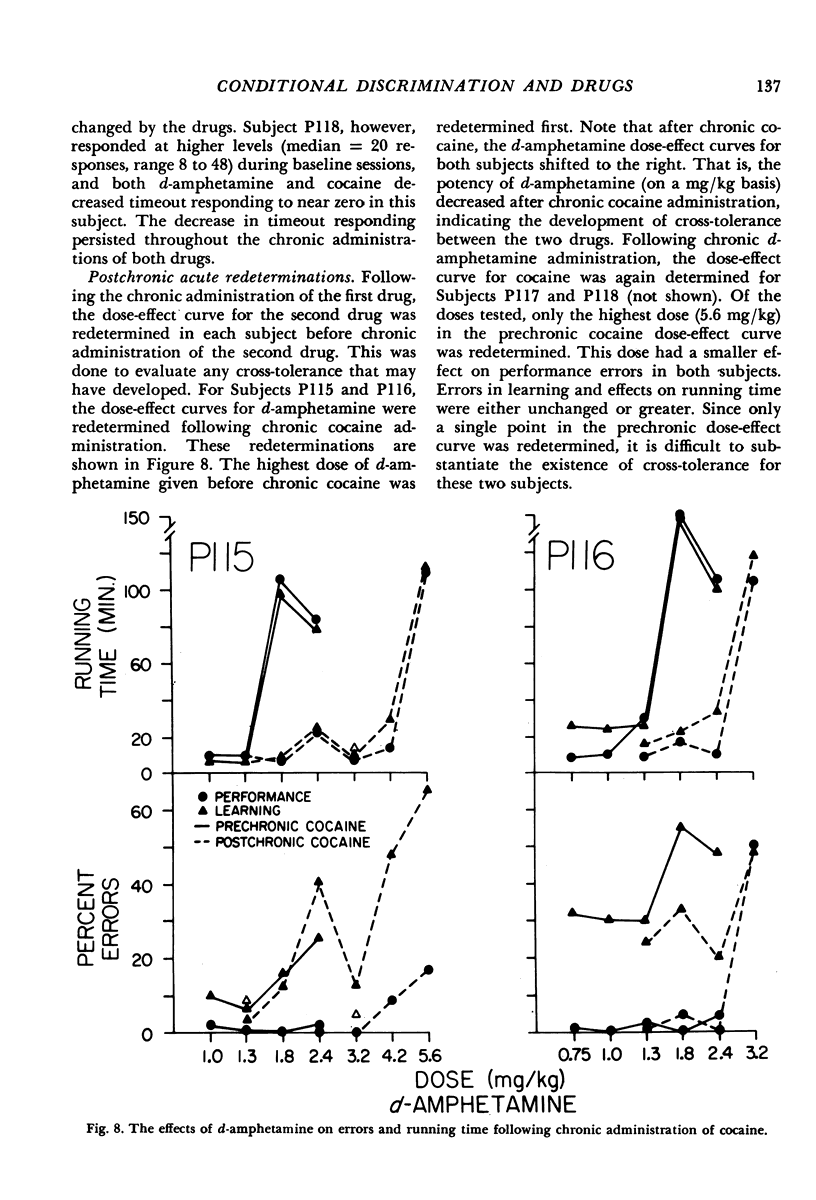
The acute and chronic effects of cocaine and d-amphetamine on food-reinforced behavior were investigated in pigeons responding on a two-component multiple schedule. In one component, the behavioral task consisted of the same chain of conditional discriminations each session (performance). In the other component, the chain of conditional discriminations was changed from session to session (learning). In comparison to control sessions, both acute cocaine and d-amphetamine increased errors in each component of the multiple schedule. Responding in the learning component, however, was generally disrupted at lower doses than those that affected responding in the performance component. At high doses, both drugs produced pauses in responding in each component in three of the four subjects. Pausing engendered by d-amphetamine was approximately twice as long as that under cocaine. Upon chronic administration, both the pausing and error-increasing effects of each drug diminished. Drug-induced changes in timeout responding, however, did not decrease during chronic administration. Redeterminations of the d-amphetamine dose-effect curves following chronic cocaine administration suggested the existence of cross-tolerance between cocaine and d-amphetamine. Both the acute and chronic data are consistent with the view that conditions of stimulus control may modulate the behavioral effects of drugs.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackman D. Response rate, reinforcement frequency, and conditioned suppression. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Sep;11(5):503–516. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boren J. J., Devine D. D. The repeated acquisition of behavioral chains. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):651–660. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boren J. J. Some variables affecting the superstitious chaining of responses. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):959–969. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laties V. G. The modification of drug effects on behavior by external discriminative stimuli. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Oct;183(1):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laties V. G. The role of discriminative stimuli in modulating drug action. Fed Proc. 1975 Aug;34(9):1880–1888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laties V. G., Weiss B. Influence of drugs on behavior controlled by internal and external stimuli. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Jun;152(3):388–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leander J. D., McMillan D. E. Rate-dependent effects of drugs. I. Comparisons of d-amphetamine, pentobarbital and chlorpromazine on multiple and mixed schedules. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 Mar;188(3):726–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPhail R. C., Gollub L. R. Separating the effects of response rate and reinforcement frequency in the rate-dependent effects of amphetamine and scopolamine on the schedule-controlled performance of rats and pigeons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Aug;194(2):332–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moerschbaecher J. M., Boren J. J., Schrot J. Repeated acquisition of conditional discriminations. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Mar;29(2):225–232. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.29-225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A. Response strength in multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 May;21(3):389–408. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster C. R., Dockens W. S., Woods J. H. Behavioral variables affecting the development of amphetamine tolerance. Psychopharmacologia. 1966;9(2):170–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00404721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. R. Differential effects of two phenothiazines on chain and tandem schedule performance. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 May;152(2):354–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. M., Corr P. B. Behavioral parameters of drug action: signaled and response-independent reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jan;21(1):151–158. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. M. Development of tolerance to the disruptive effects of cocaine on repeated acquisition and performance of response sequences. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Nov;203(2):294–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. M. Repeated acquisition as a behavioral base line for studying drug effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Feb;184(2):506–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. M. Repeated acquisition of behavioral chains under chronic drug conditions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 Mar;188(3):700–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. M. Repeated acquisition of response sequences: stimulus control and drugs. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 May;23(3):429–436. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.23-429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


