Abstract
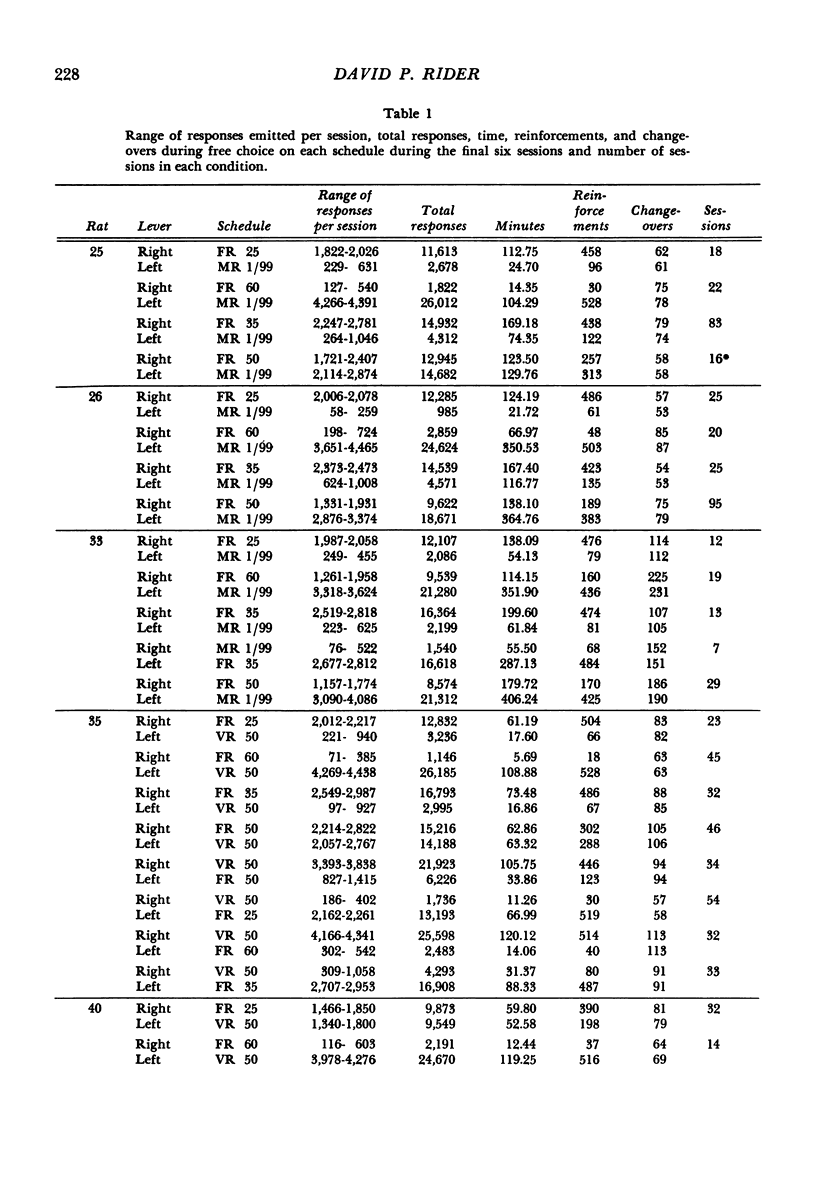
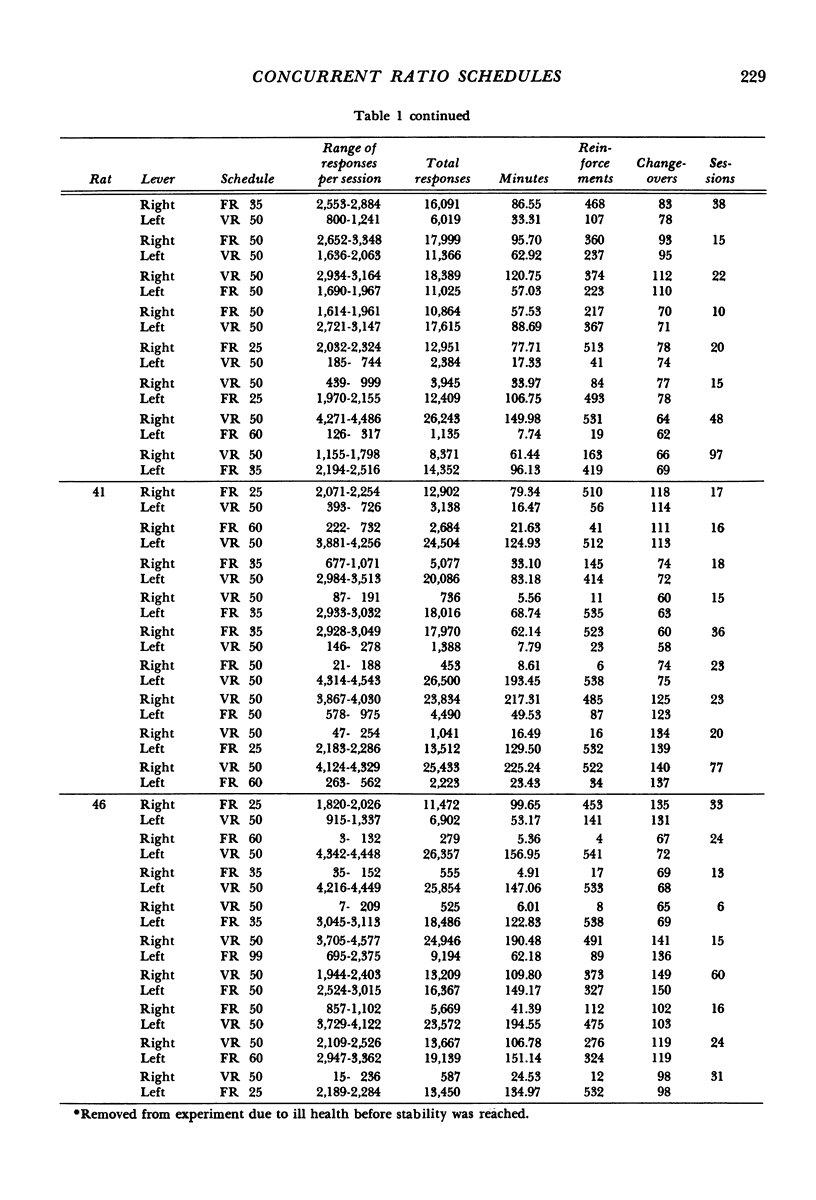
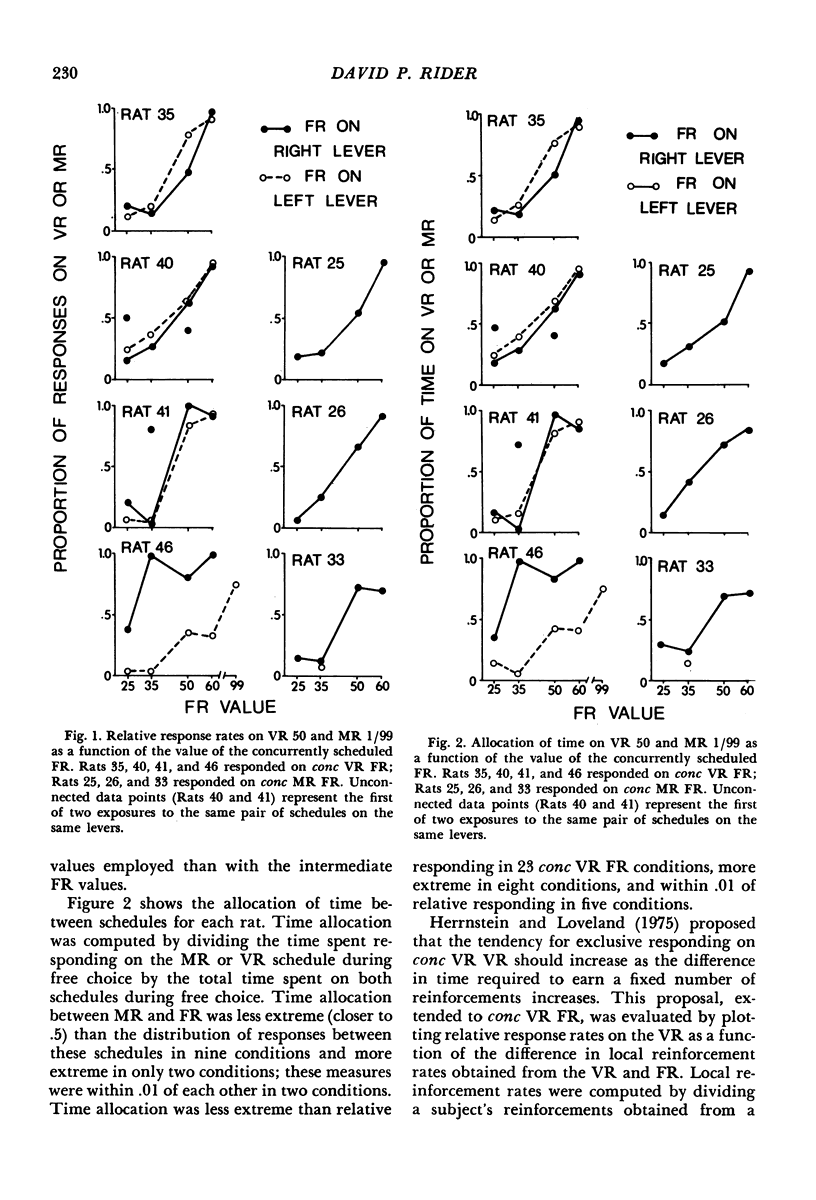
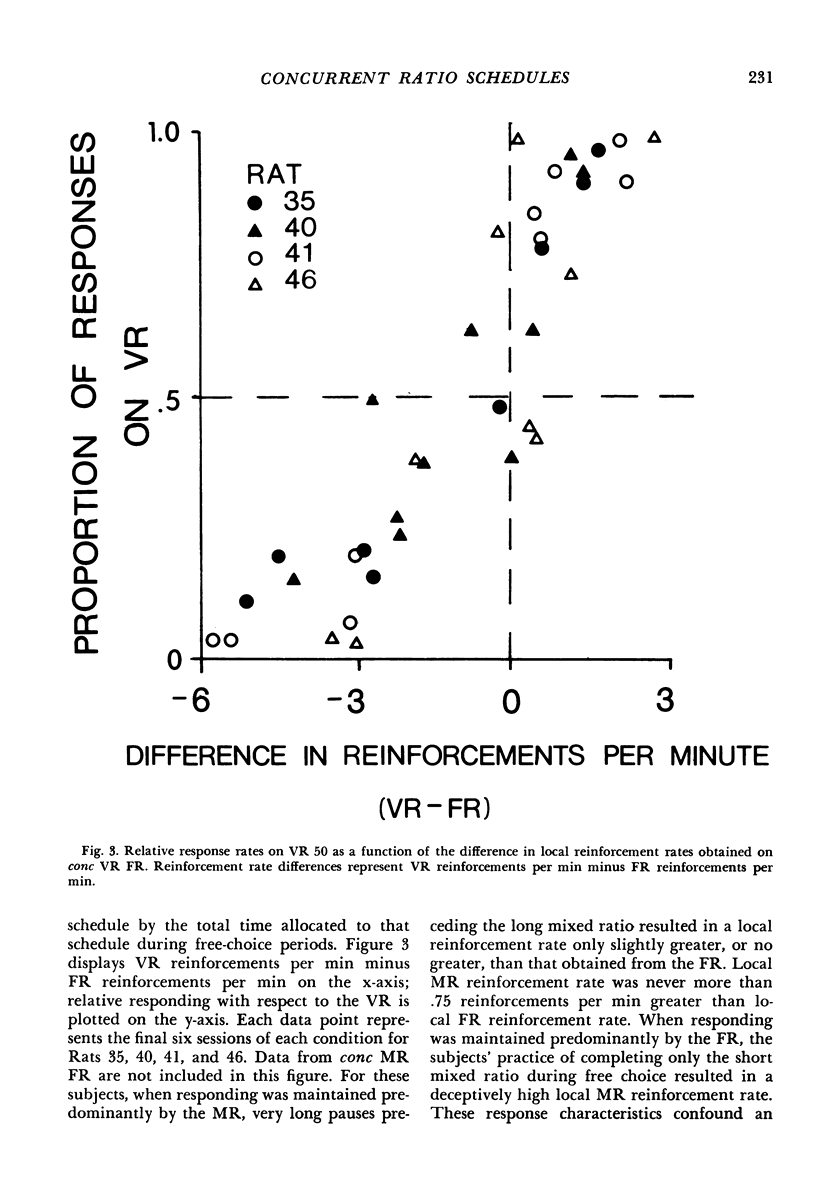
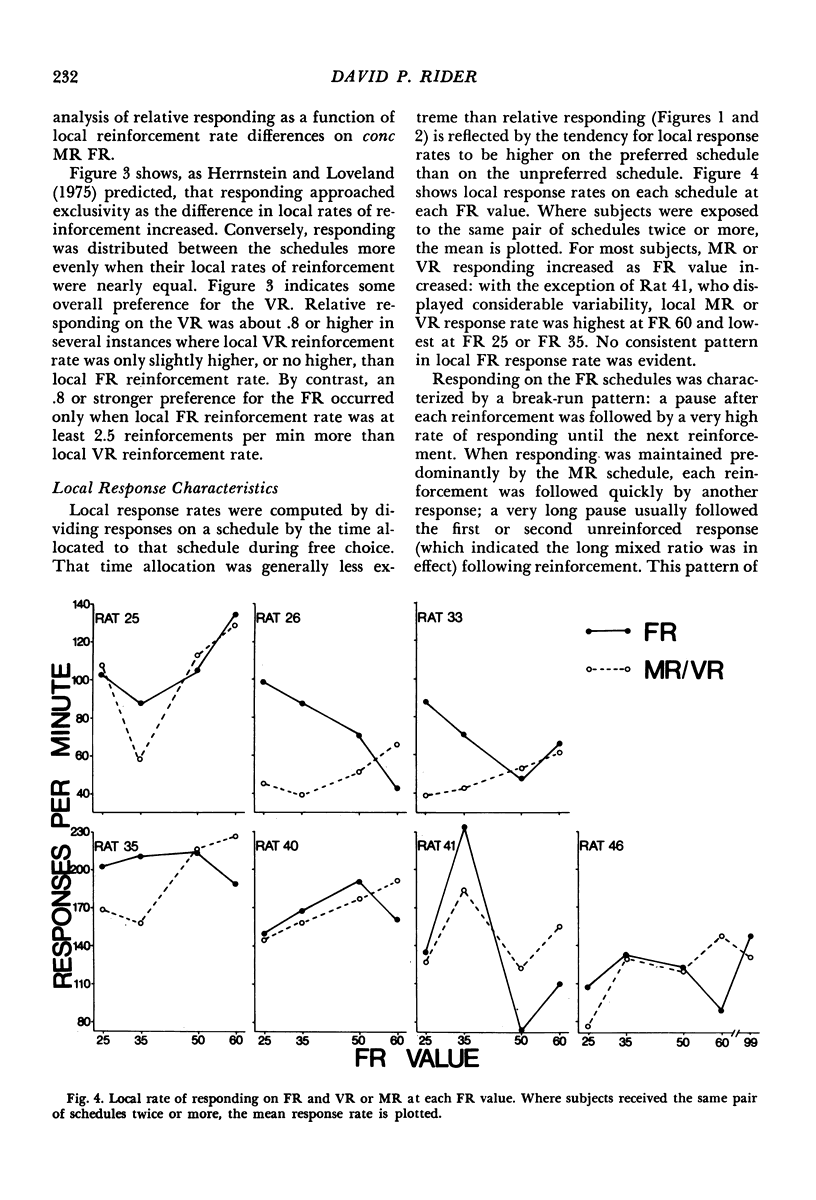
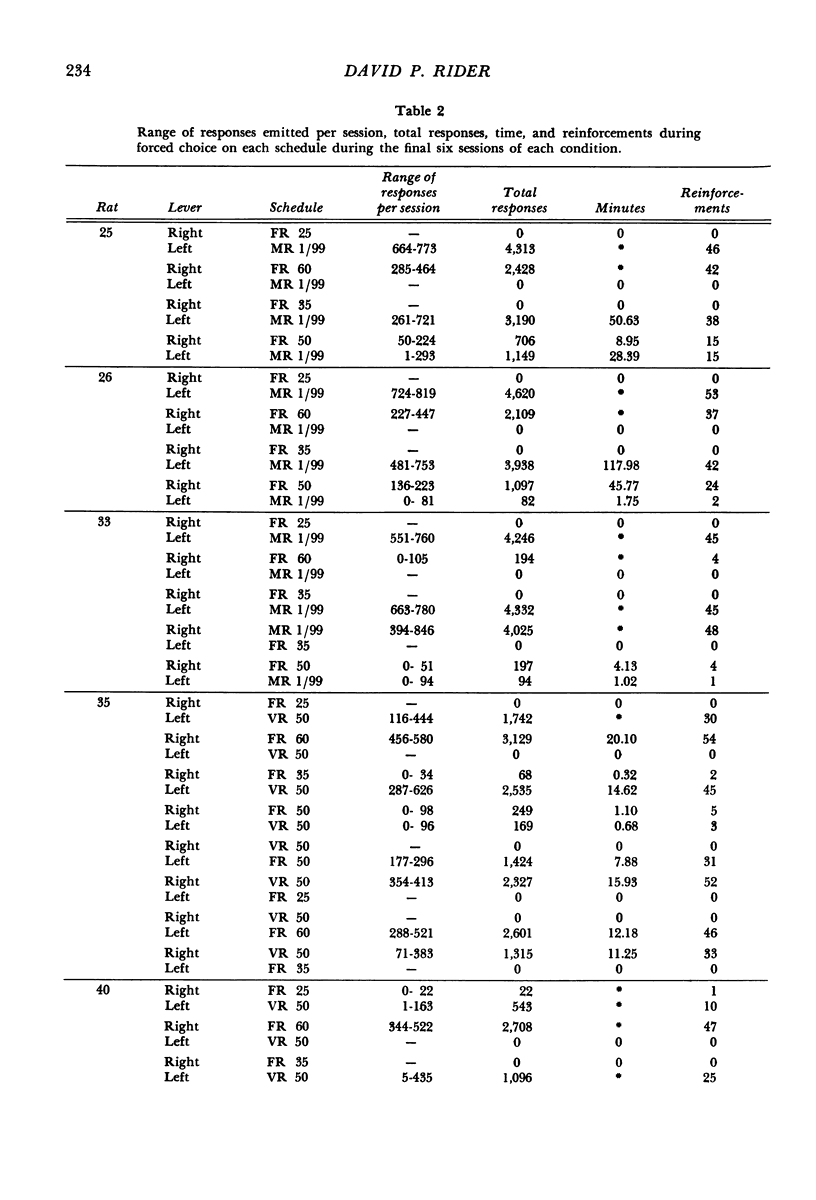
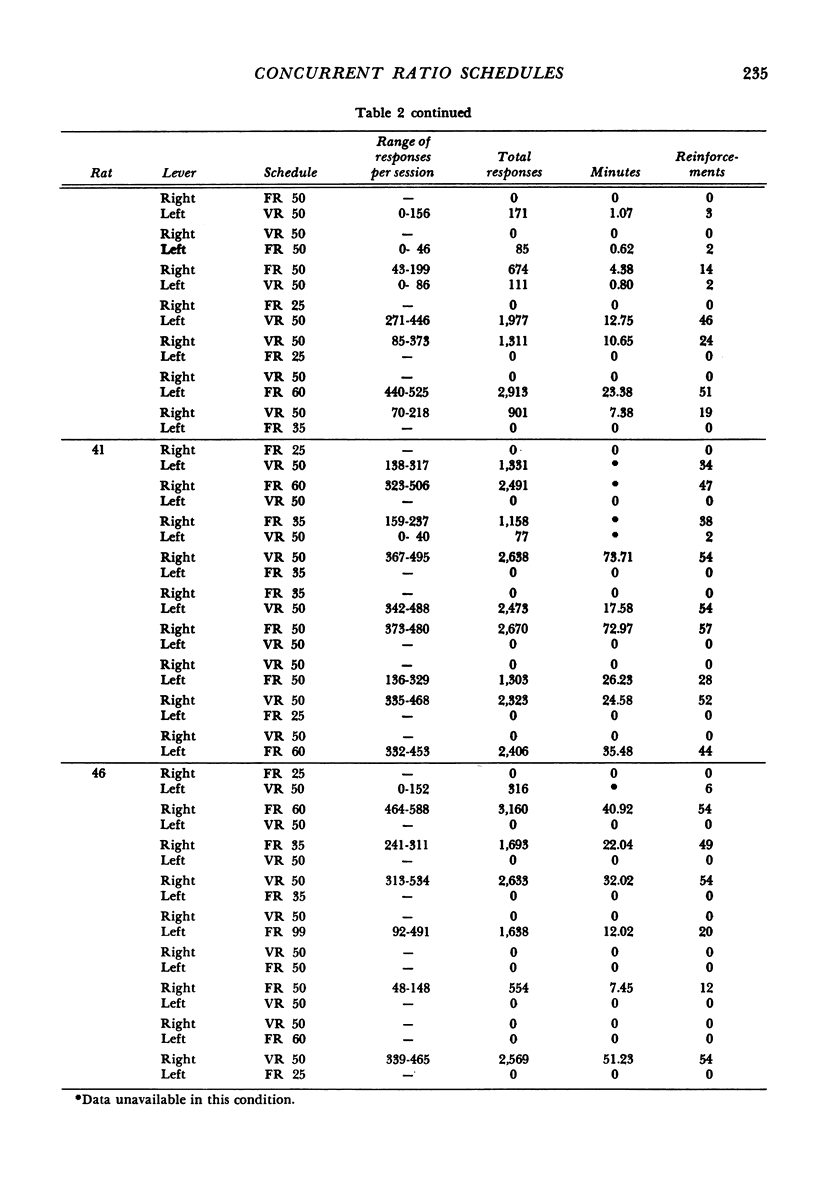
Rats were trained on concurrent fixed-ratio variable-ratio or concurrent fixed-ratio mixed-ratio schedules of food reinforcement. The variable-ratio schedule was composed of an arithmetic sequence of 11 ratios that averaged 50; the mixed-ratio schedule consisted of equiprobable ratios of 1 and 99. Fixed-ratio values, varied over experimental conditions, included 25, 35, 50, 60, and 99. The proportion of responses and time allocated to the variable- or mixed-ratio schedule increased as the size of the fixed ratio increased. For most subjects, higher proportions of responses and time were maintained on the fixed-ratio schedule at fixed-ratio values of 25 and 35; higher proportions of responses and time were maintained on the variable- or mixed-ratio schedule at fixed-ratio values of 50 or higher. On concurrent variable-ratio fixed-ratio schedules, the tendency for responding to be maintained exclusively by one schedule was related to the difference in local reinforcement rates obtained from those schedules. Exclusive responding was approximated when the difference in local reinforcement rates obtained from those schedules was large; responding was more evenly distributed between the schedules as the difference in the rates at which reinforcement was obtained from each decreased.
Keywords: concurrent schedules, fixed ratio, variable ratio, mixed ratio, preference, local reinforcement rate, lever press, rats
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crossman E. K., Silverman L. T. Altering the proportion of components in a mixed fixed-ratio schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Sep;20(2):273–279. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. Relative and absolute strength of response as a function of frequency of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jul;4:267–272. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. SECONDARY REINFORCEMENT AND RATE OF PRIMARY REINFORCEMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Jan;7:27–36. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J., Loveland D. H. Maximizing and matching on concurrent ratio schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Jul;24(1):107–116. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.24-107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. On the law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):243–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman J. A., Thomas J. R. Some factors controlling preference between fixed-ratio and variable-ratio schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):689–702. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


