Abstract
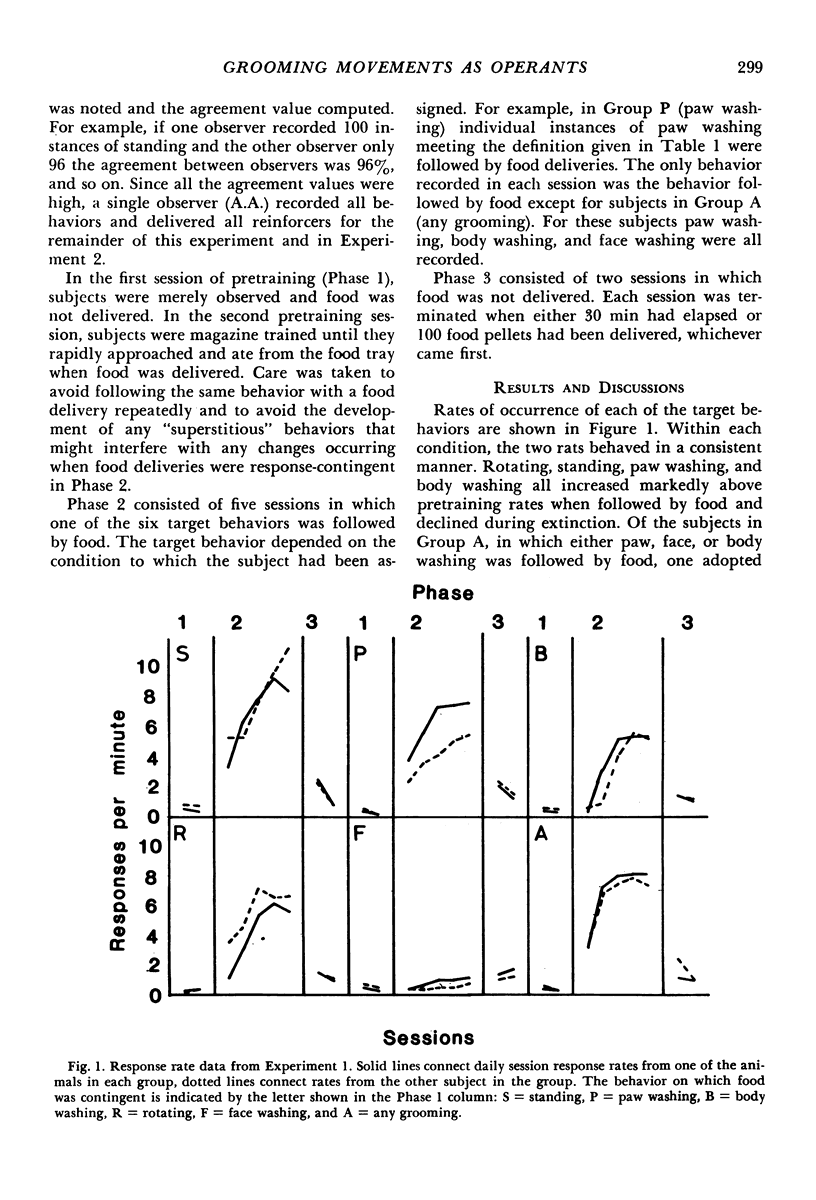
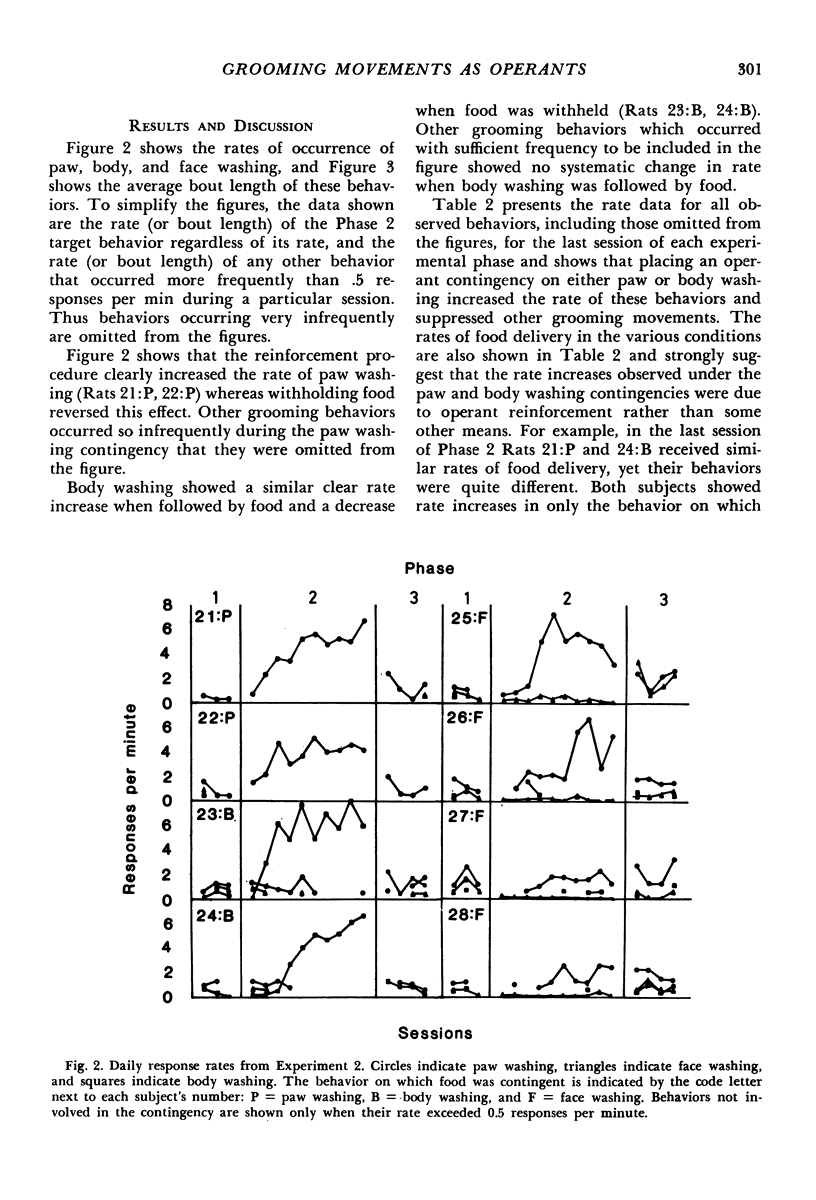
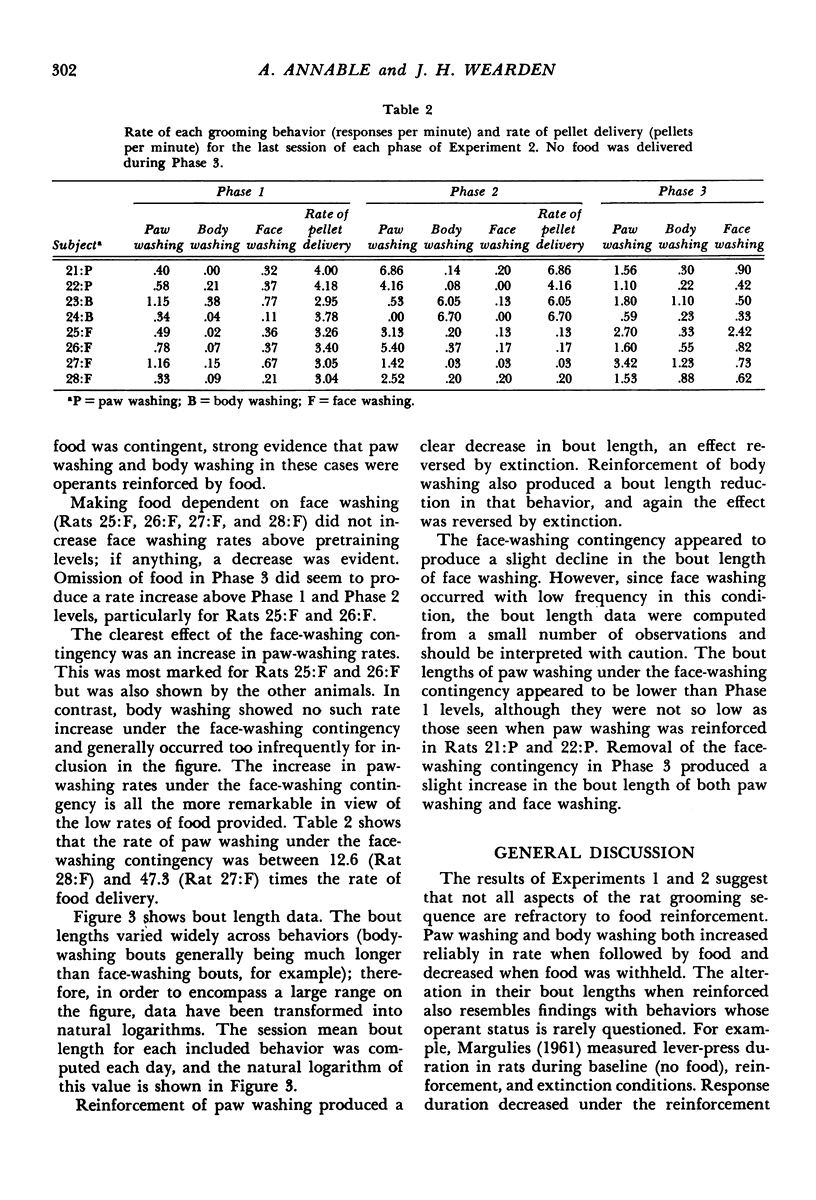
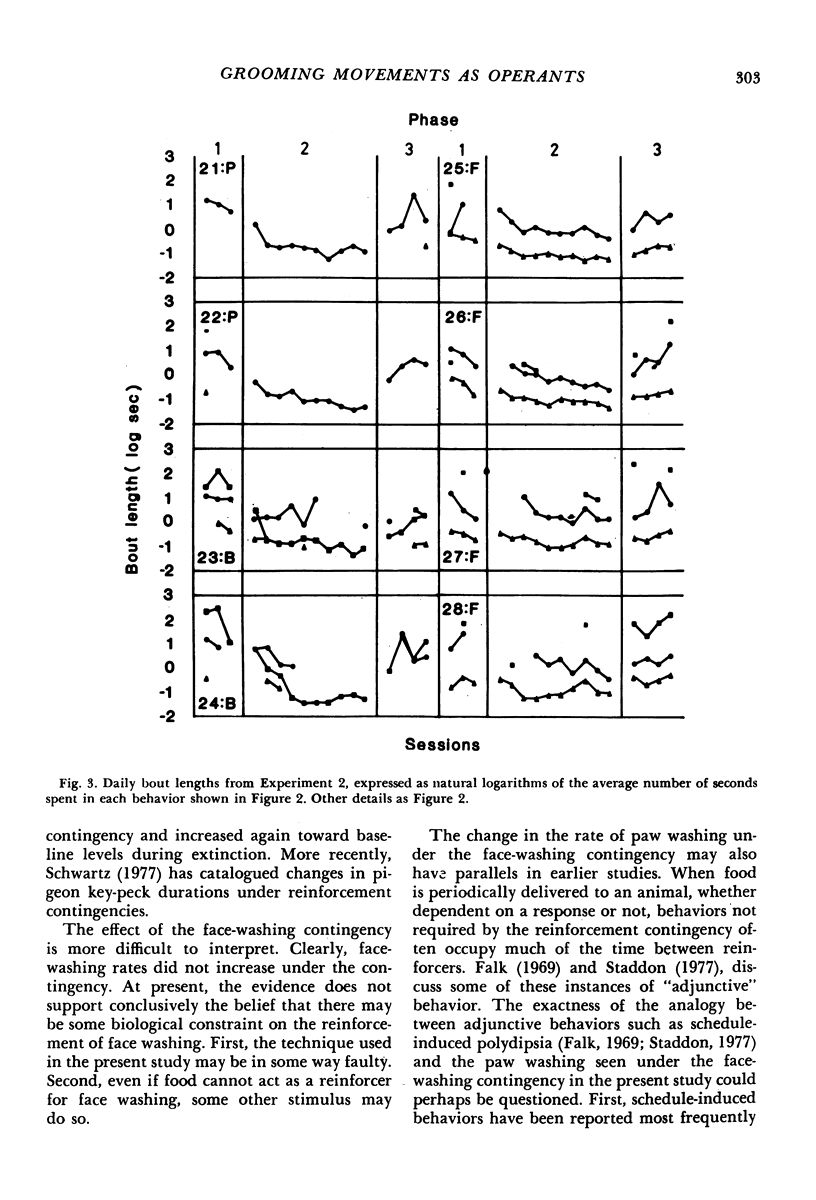
Two experiments investigated the effect of contingent food deliveries on grooming movements in rats. The grooming sequence was divided into three topographically distinct behaviors: paw washing, face washing, and body washing. The first experiment found that rates of paw washing and body washing increased reliably under a food contingency, but face washing did not. A second experiment replicated these findings, and, in addition, showed that the average duration of paw washing and body washing decreased in length when followed by food. Placing a contingency on face washing, however, produced an increase in the rate of paw washing but no increase in face washing. It was concluded that, on the one hand, paw washing and body washing may be influenced by operant contingencies in the same way as behaviors such as lever pressing. On the other hand, increases in paw washing under the face washing contingency suggested that increases in the rate of grooming movements may occur by means other than operant relations.
Keywords: constraints on learning, grooming movements, adjunctive behavior, rats
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Falk J. L. Conditions producing psychogenic polydipsia in animals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 May 15;157(2):569–593. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb12908.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGULIES S. Response duration in operant level, regular reinforcement, and extinction. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Oct;4:317–321. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. Studies of operant and reflexive key pecks in the pigeon. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 Mar;27(2):301–313. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.27-301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


