Abstract
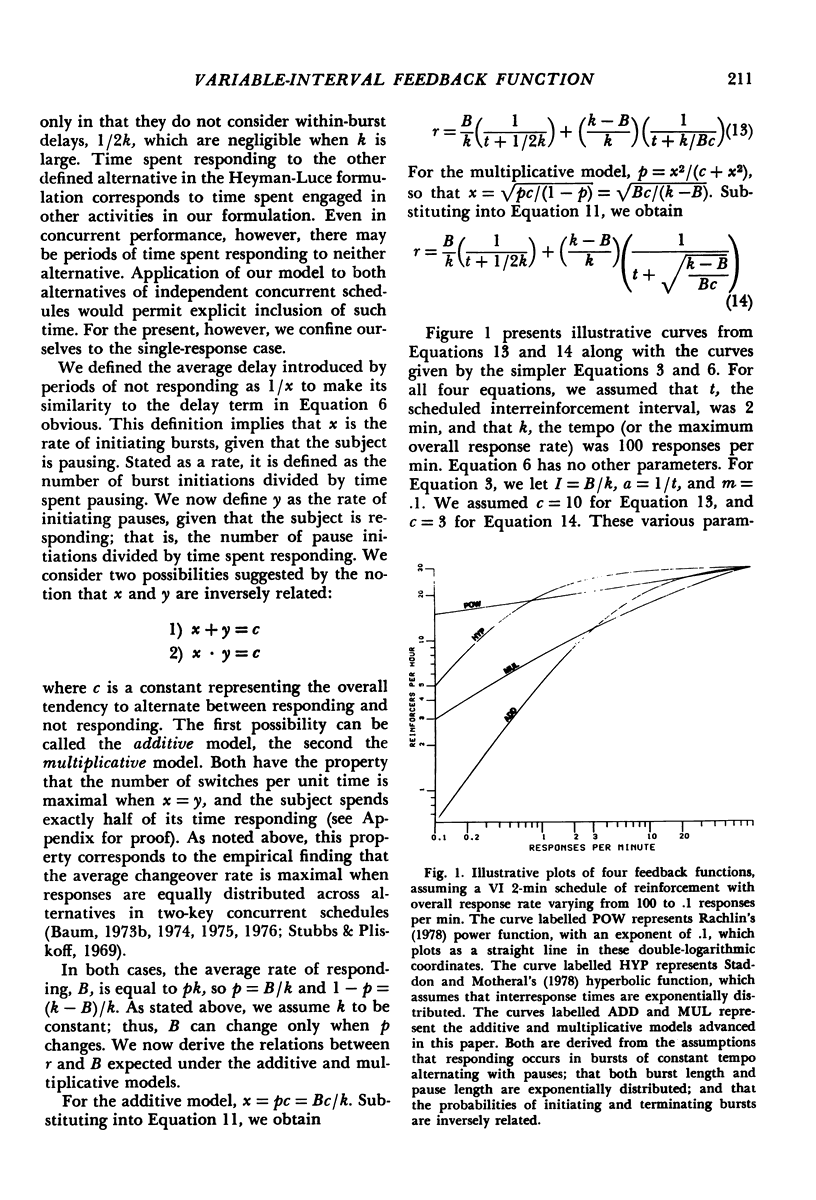
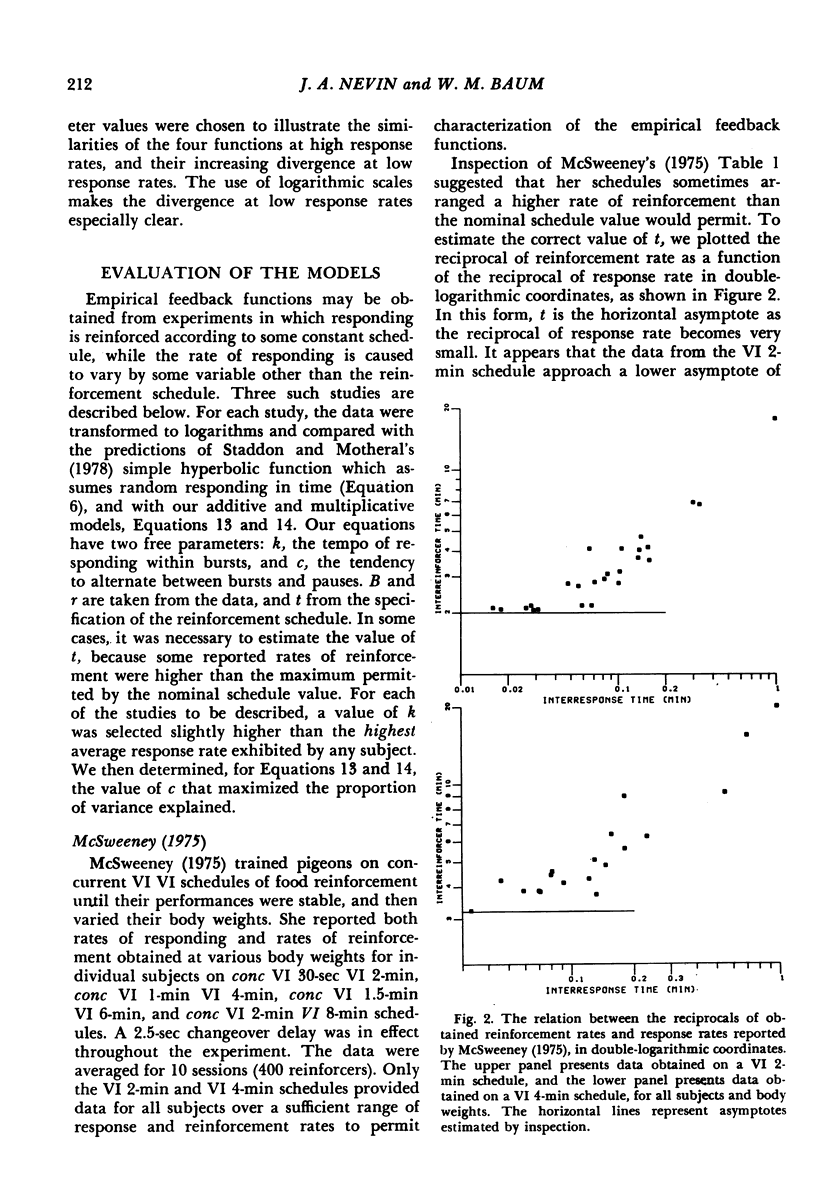
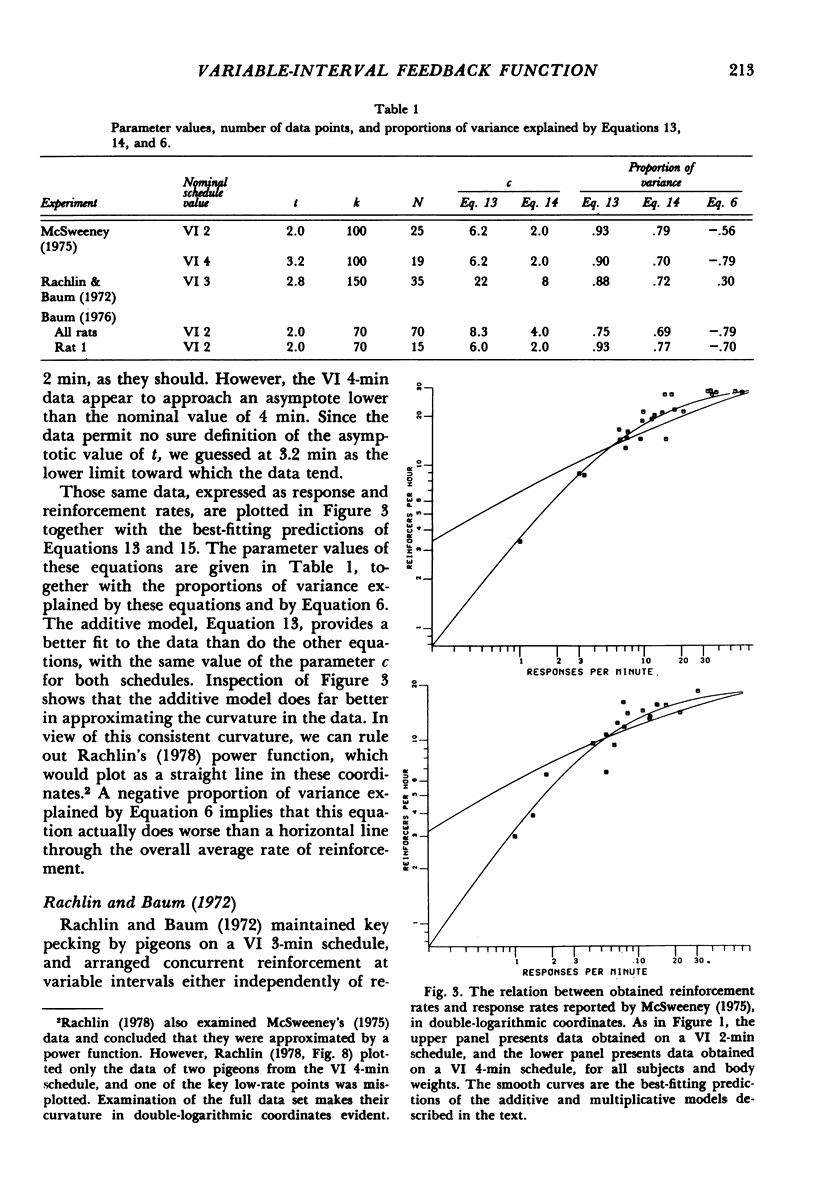
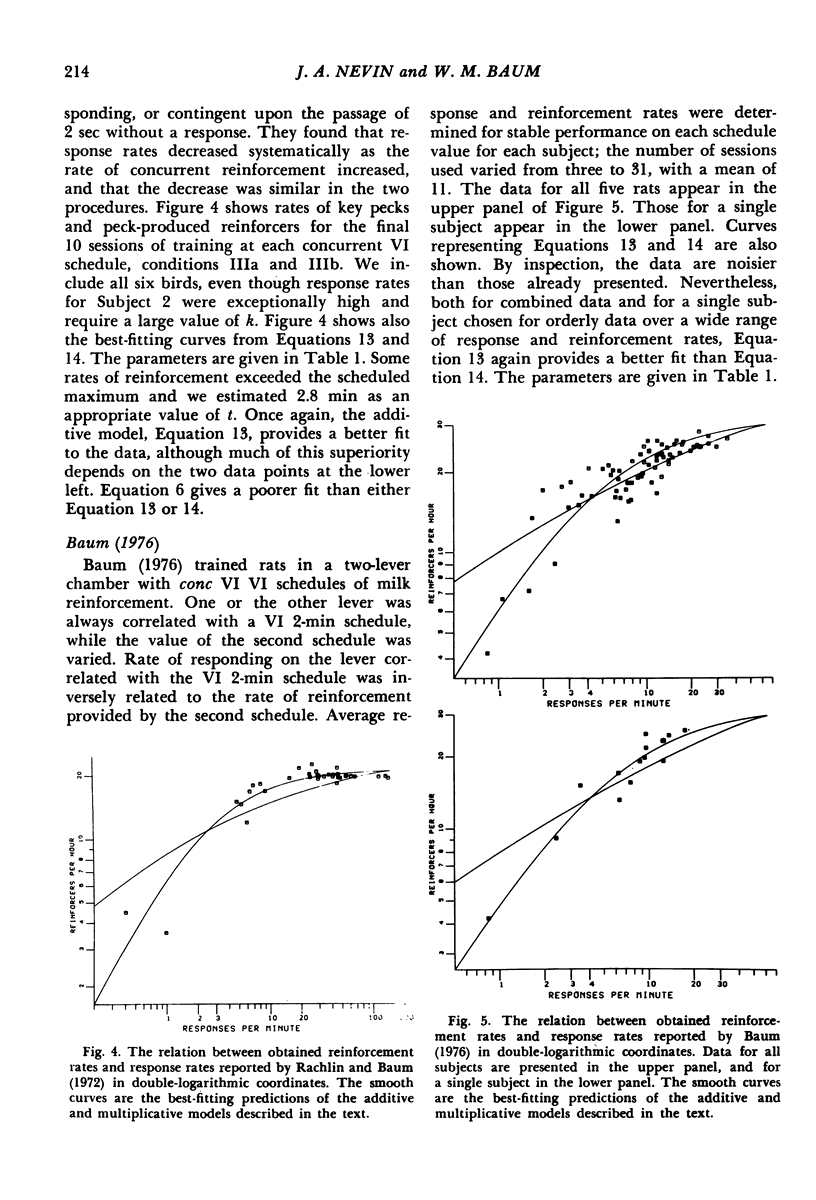
On a given variable-interval schedule, the average obtained rate of reinforcement depends on the average rate of responding. An expression for this feedback effect is derived from the assumptions that free-operant responding occurs in bursts with a constant tempo, alternating with periods of engagement in other activities; that the durations of bursts and other activities are exponentially distributed; and that the rates of initiating and terminating bursts are inversely related. The expression provides a satisfactory account of the data of three experiments.
Keywords: variable interval, feedback function, correlation, contingency, molar analysis, reinforcement
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum W. M. Chained concurrent schedules: reinforcement as situation transition. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jul;22(1):91–101. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M. Time-based and count-based measurement of preference. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Jul;26(1):27–35. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.26-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blough D. S. Interresponse time as a function of continuous variables: a new method and some data. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6(2):237–246. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILBERT T. F. Fundamental dimensional properties of the operant. Psychol Rev. 1958 Sep;65(5):272–282. doi: 10.1037/h0044071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. Formal properties of the matching law. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jan;21(1):159–164. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. On the law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):243–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman G. M. A Markov model description of changeover probabilities on concurrent variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1979 Jan;31(1):41–51. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1979.31-41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcucella H., Macdonall J. S. A molecular analysis of multiple schedule interactions: negative contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 Jul;28(1):71–82. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.28-71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PREMACK D., SCHAEFFER R. W. Distributional properties of operant-level locomotion in the rat. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Jan;5:89–95. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pear J. J., Rector B. L. Constituents of response rates. J Exp Anal Behav. 1979 Nov;32(3):341–362. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1979.32-341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachlin H. A molar theory of reinforcement schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Nov;30(3):345–360. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.30-345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachlin H., Baum W. M. Effects of alternative reinforcement: does the source matter? J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Sep;18(2):231–241. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spealman R. D., Gollub L. R. Behavioral interactions in multiple variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Nov;22(3):471–481. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs D. A., Pliskoff S. S. Concurrent responding with fixed relative rate of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):887–895. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


