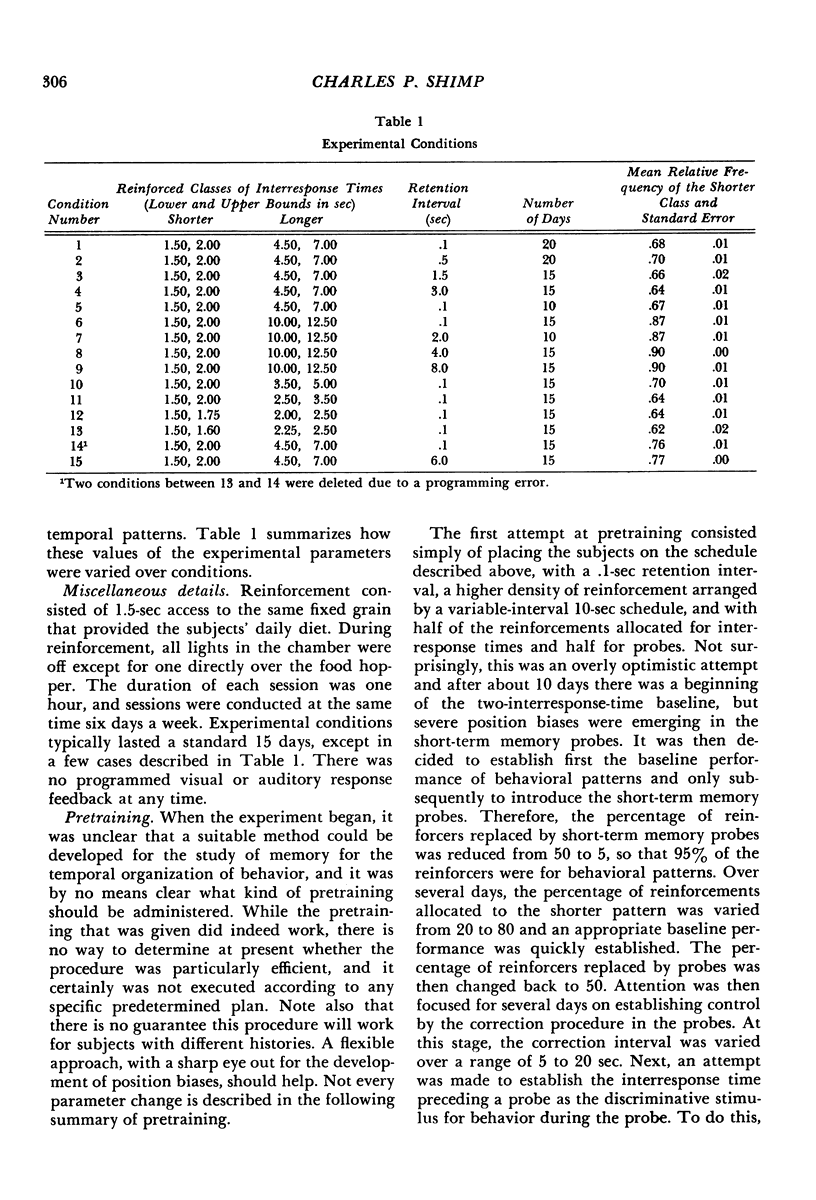
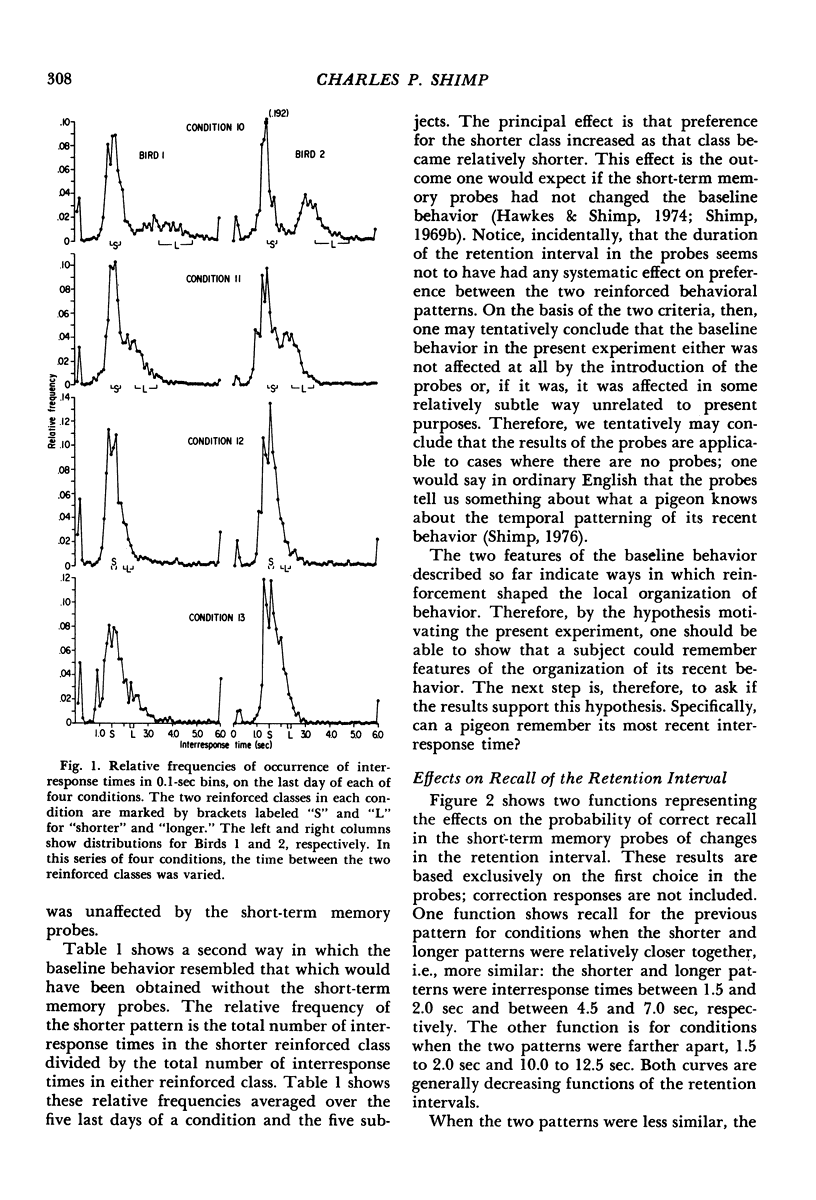
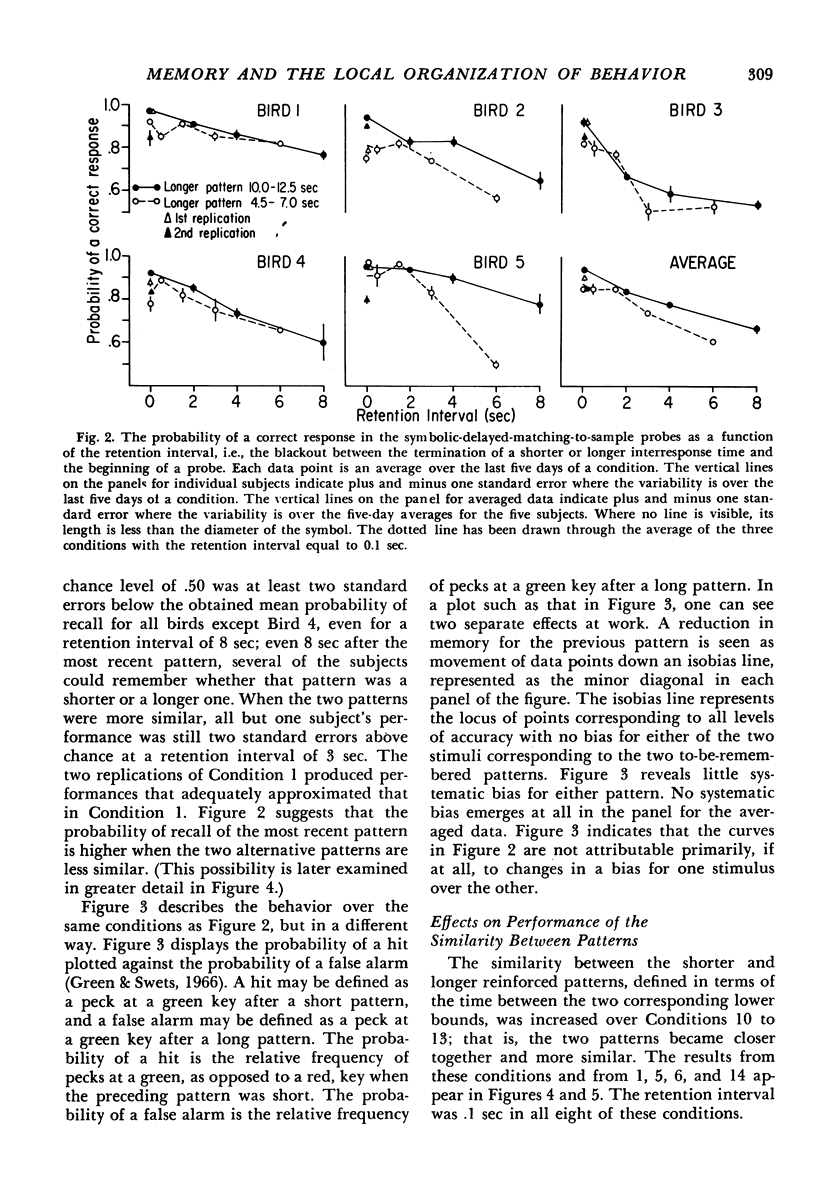
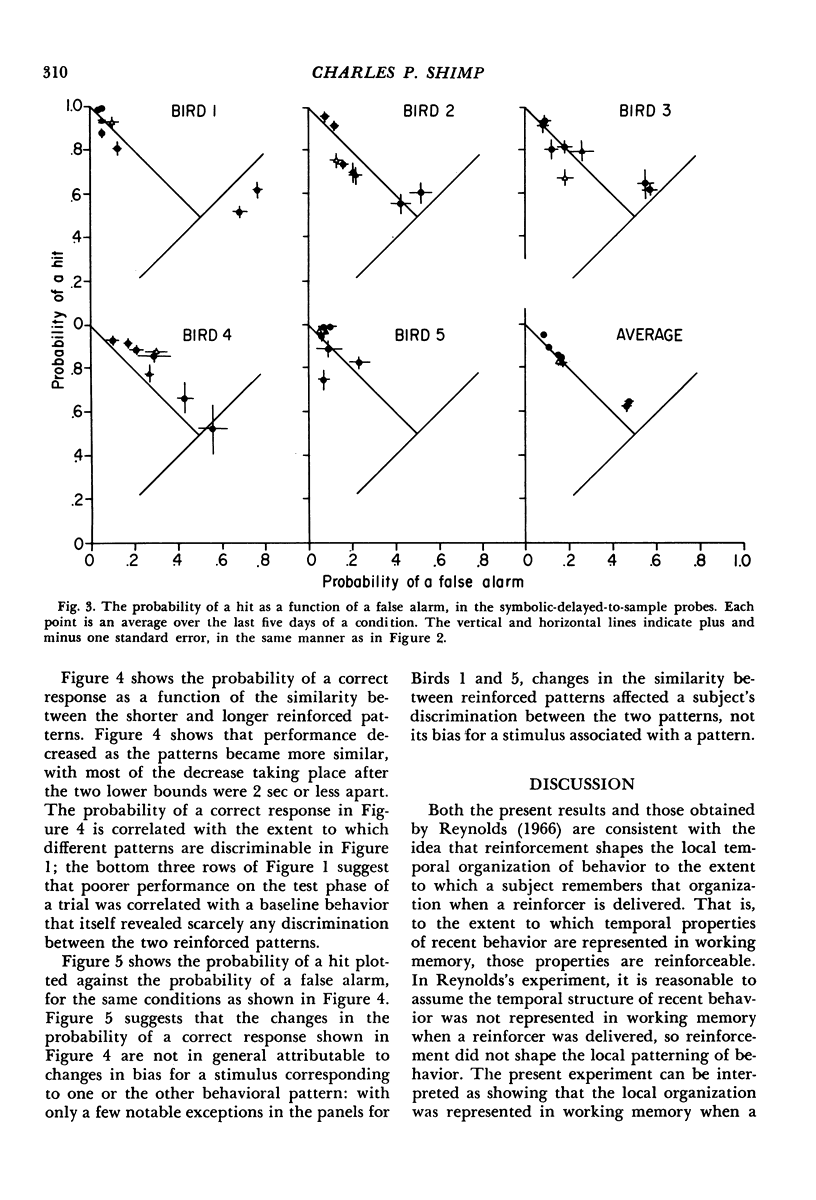
Abstract
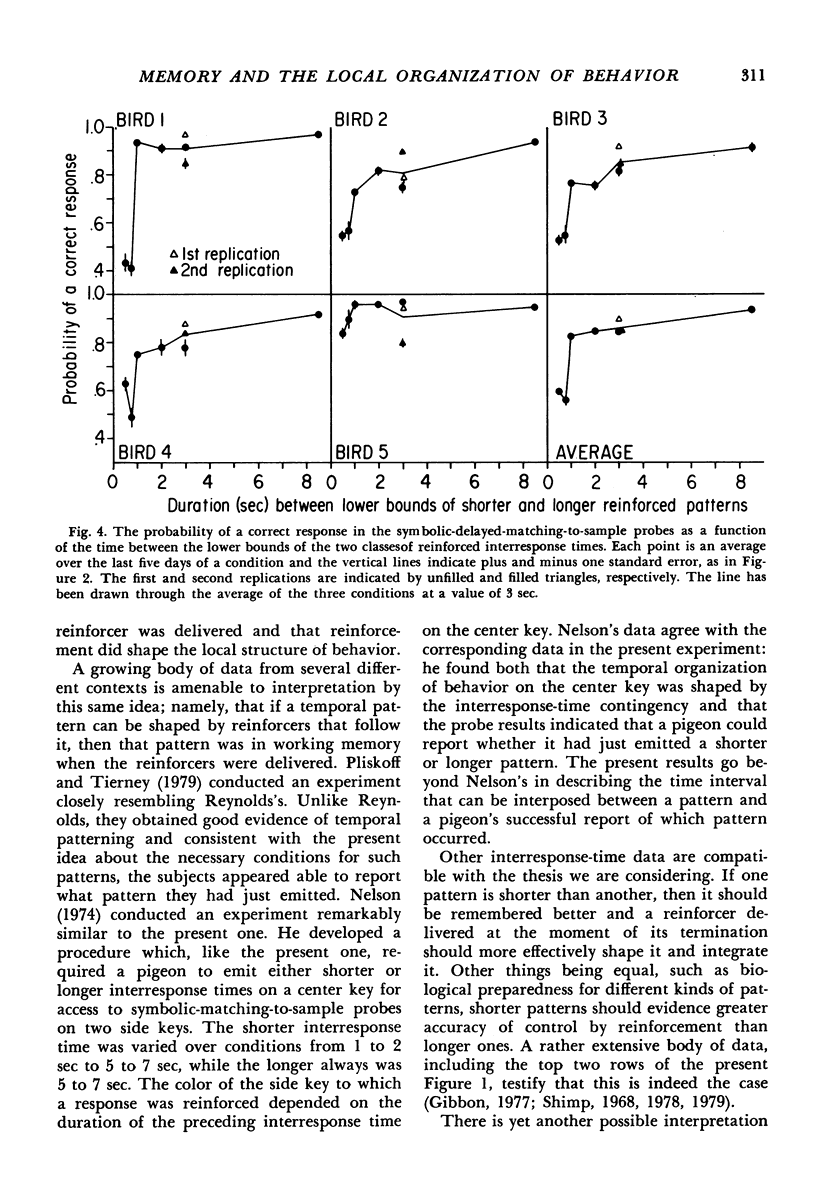
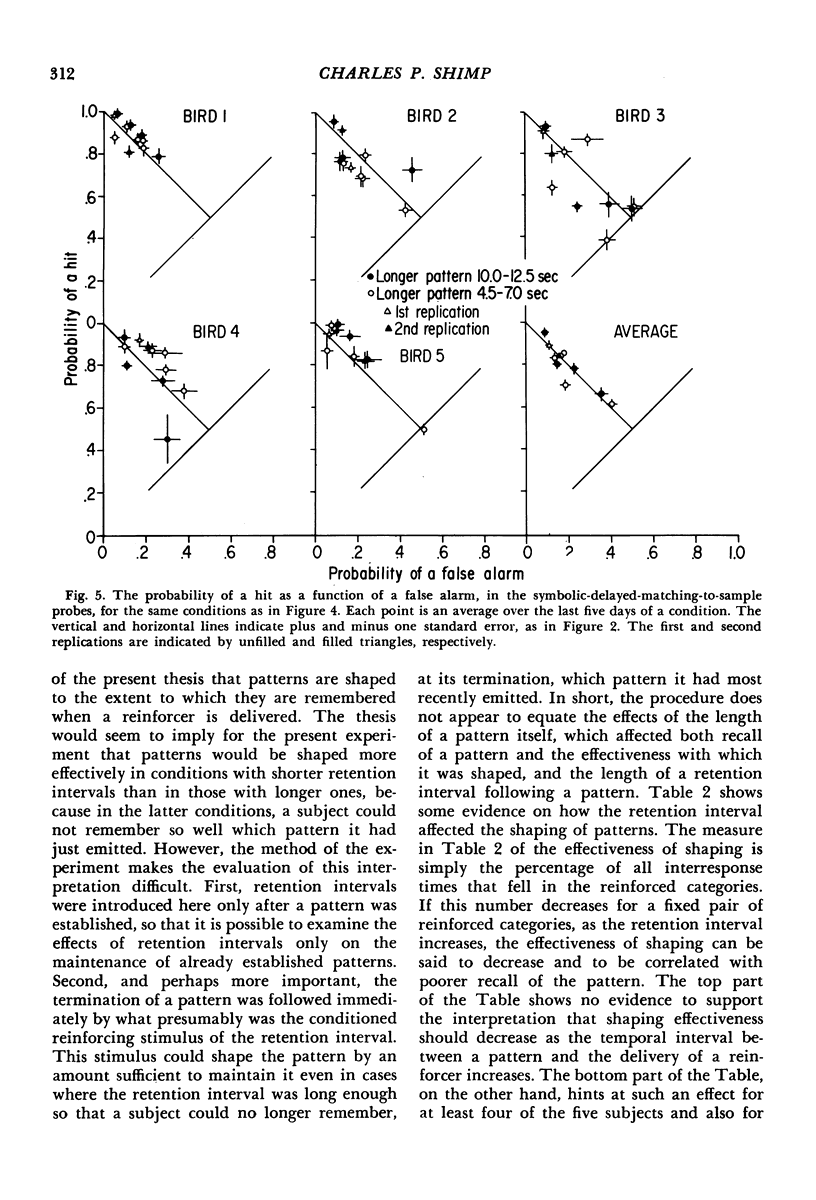
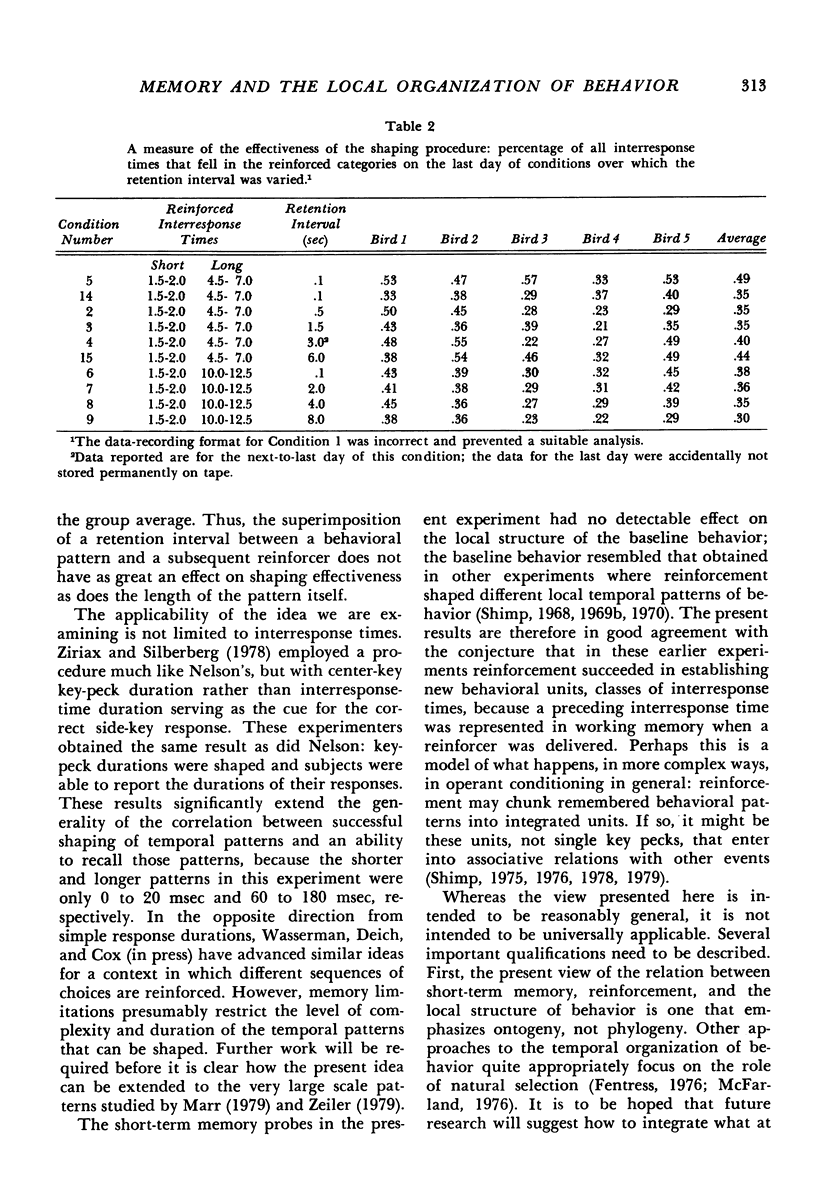
A procedure was developed to enable nonverbal organisms to report what they remember of the temporal organization of their recent behavior. A baseline behavior with known temporal structure was established by a concurrent variable-interval variable-interval schedule for two temporal patterns of behavior (two different classes of reinforced inter-response times). The five pigeon subjects emitted these two temporal patterns on a center key and were occasionally given a short-term memory probe for their most-recently-emitted pattern. The probes consisted of symbolic delayed matching-to-sample tests, in which a response on a green side key was reinforced if the most recent pattern belonged to the shorter reinforced class, and a response to a red side key was reinforced if the most recent pattern belonged to the longer reinforced class. All subjects could report with over ninety percent accuracy what their most recently emitted behavioral pattern was when a retention interval separating the pattern from the memory probe was only .1 seconds. The retention interval was then manipulated, and it was found that recall for a pattern was frequently above chance after a delay of as much as eight seconds. Thus, pigeons can remember their most recent interresponse time not only right after it is emitted, but for several seconds thereafter. In other conditions, the patterns themselves were manipulated. It was found that as the patterns became more similar, discrimination became poorer. These results agree with the view that reinforcement tends to organize and integrate the local structure of behavior to the extent to which that structure is remembered.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hawkes L., Shimp C. P. Choice between response rates. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jan;21(1):109–115. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. S. Discrimination and emission of temporal intervals by pigeons. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Jan;9(1):65–68. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimp C. P. Magnitude and frequency of reinforcement and frequencies of interresponse times. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Sep;11(5):525–535. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimp C. P. Organization in memory and behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Jul;26(1):113–130. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.26-113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimp C. P. Sequential dependencies in free-responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 May;19(3):491–497. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimp C. P. The concurrent reinforcement of two interresponse times: absolute rate of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Jan;13(1):1–8. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimp C. P. The concurrent reinforcement of two interresponse times: the relative frequency of an interresponse time equals its relative harmonic length. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 May;12(3):403–411. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



