Abstract
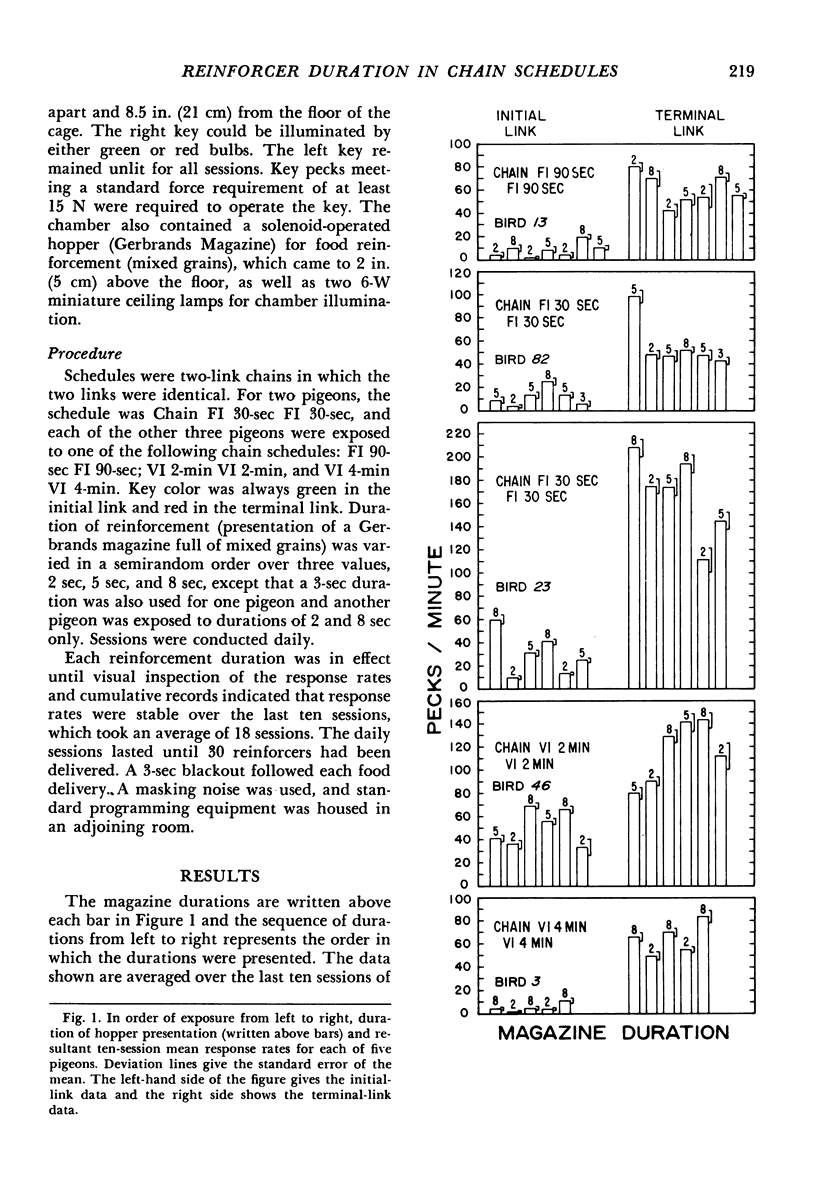
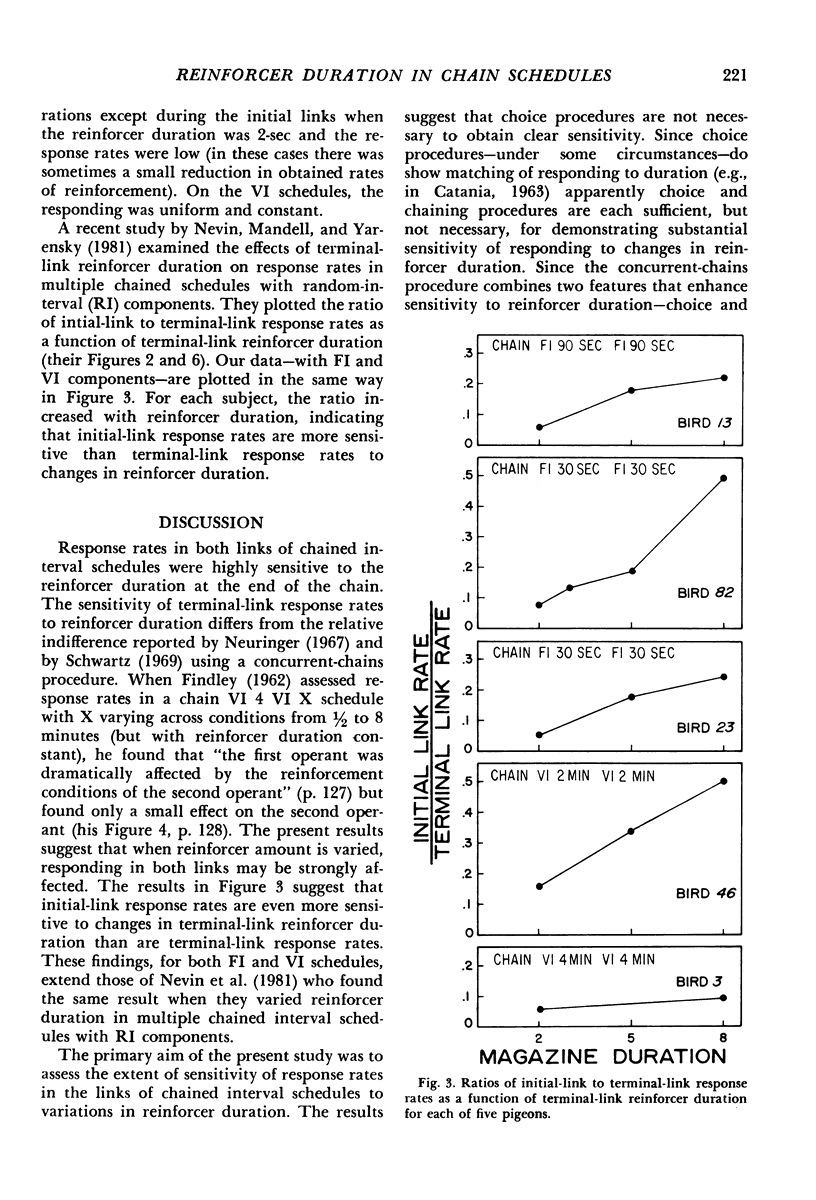
Each of five pigeons was exposed to two or more durations of access to mixed grains on two-link, chained, interval schedules in which both links were identical fixed-interval or variable-interval schedules. Response rates were an increasing function of reinforcer duration for both initial and terminal links. For both types of interval schedules, initial-link response rates were more sensitive to reinforcer duration than were terminal-link response rates. The present results, together with prior ones, suggest that chaining and choice procedures are each sufficient for demonstrating substantial sensitivity of responding to changes in reinforcer duration.
Keywords: reinforcer duration, chain schedules, variable-interval schedules, fixed-interval schedules, key peck, pigeons
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: a baseline for the study of reinforcement magnitude. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:299–300. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLIER G., SISKEL M., Jr Performance as a joint function of amount of reinforcement and inter-reinforcement interval. J Exp Psychol. 1959 Feb;57(2):115–120. doi: 10.1037/h0040857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINDLEY J. D. An experimental outline for building and exploring multi-operant behavior repertoires. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Jan;5(Suppl):113–166. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-s113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E., Squires N., Delbrück N., Peterson C. Choice behavior and the accessibility of the reinforcer. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jul;18(1):35–43. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTTMAN N. Operant conditioning, extinction, and periodic reinforcement in relation to concentration of sucrose used as reinforcing agent. J Exp Psychol. 1953 Oct;46(4):213–224. doi: 10.1037/h0061893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen C., Fallon D. Behavioral aftereffects of reinforcement and its omission as a function of reinforcement magnitude. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 May;19(3):459–468. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEESEY R. E., KLING J. W. Amount of reinforcement and free-operant responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Apr;4:125–132. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe C. F., Davey G. C., Harzem P. Effects of reinforcement magnitude on interval and ratio schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Nov;22(3):553–560. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merigan W. H., Miller J. S., Gollub L. R. Short-component multiple schedules: effects of relative reinforcement duration. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Sep;24(2):183–189. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.24-183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J. Effects of reinforcement magnitude on choice and rate of responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Sep;10(5):417–424. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHETTLEWORTH S., NEVIN J. A. RELATIVE RATE OF RESPONSE AND RELATIVE MAGNITUDE OF REINFORCEMENT IN MULTIPLE SCHEDULES. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Jul;8:199–202. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEBBINS W. C., MEAD P. B., MARTIN J. M. The relation of amount of reinforcement to performance under a fixed-in-terval schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1959 Oct;2:351–355. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1959.2-351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider B. A. A two-state analysis of fixed-interval responding in the pigeon. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):677–687. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. W. Reinforcer effectiveness as a function of reinforcer rate and magnitude: a comparison of concurrent performances. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Nov;20(3):461–471. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. Effects of reinforcement magnitude on pigeons' preference for different fixed-ratio schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Mar;12(2):253–259. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staddon J. E. Effect of reinforcement duration on fixed-interval responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Jan;13(1):9–11. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


