Abstract
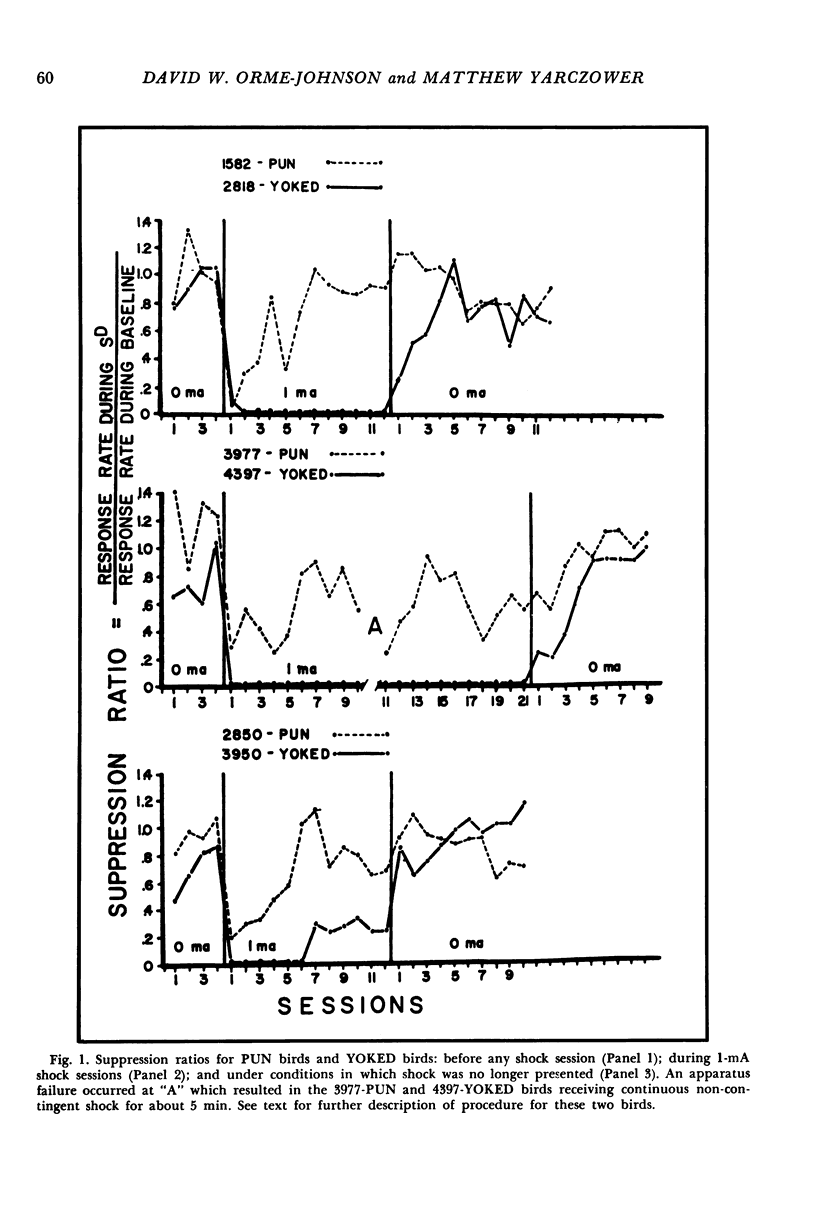
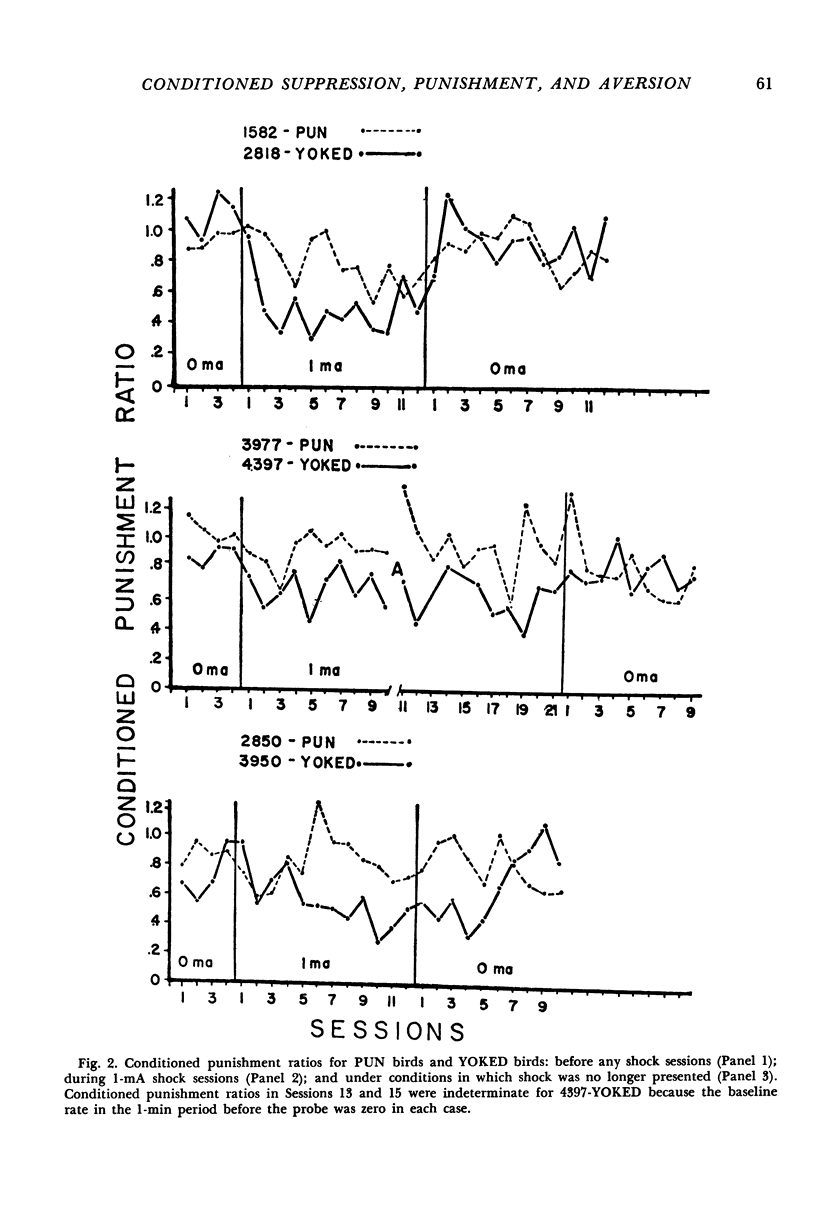
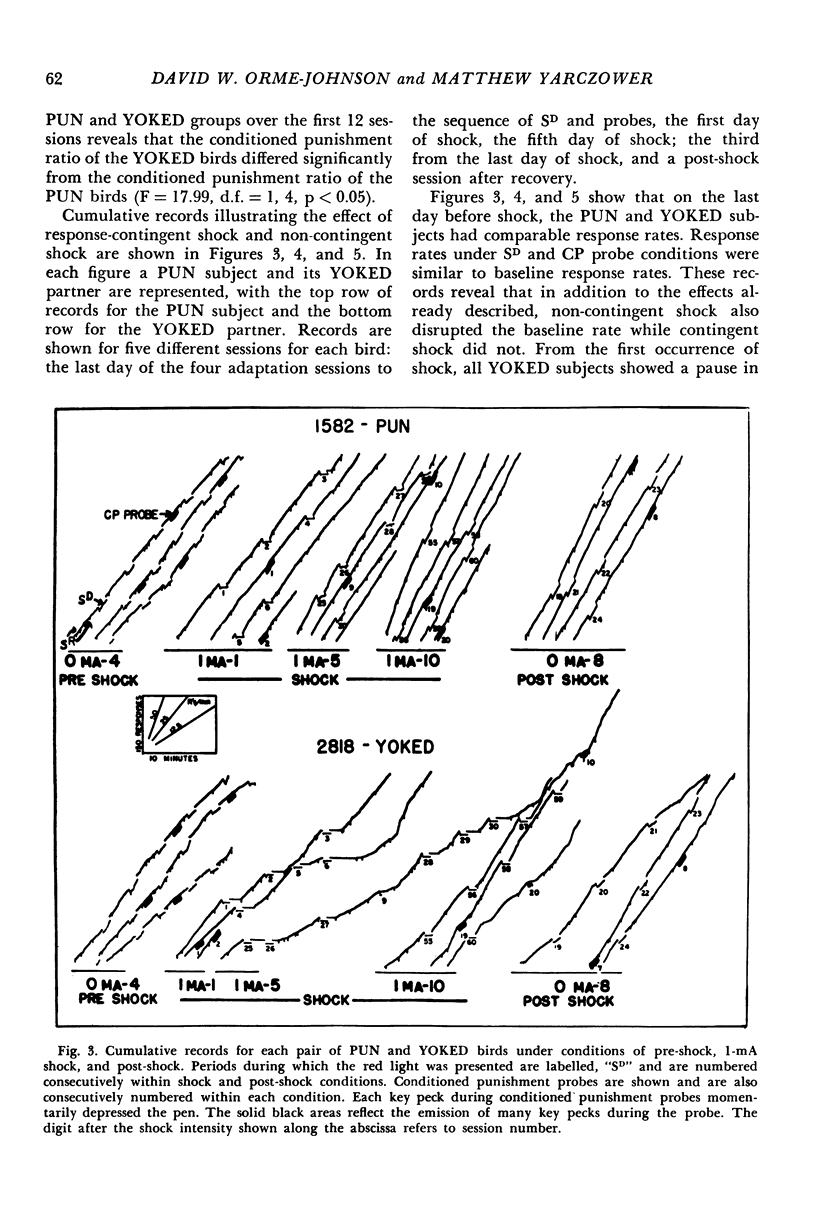
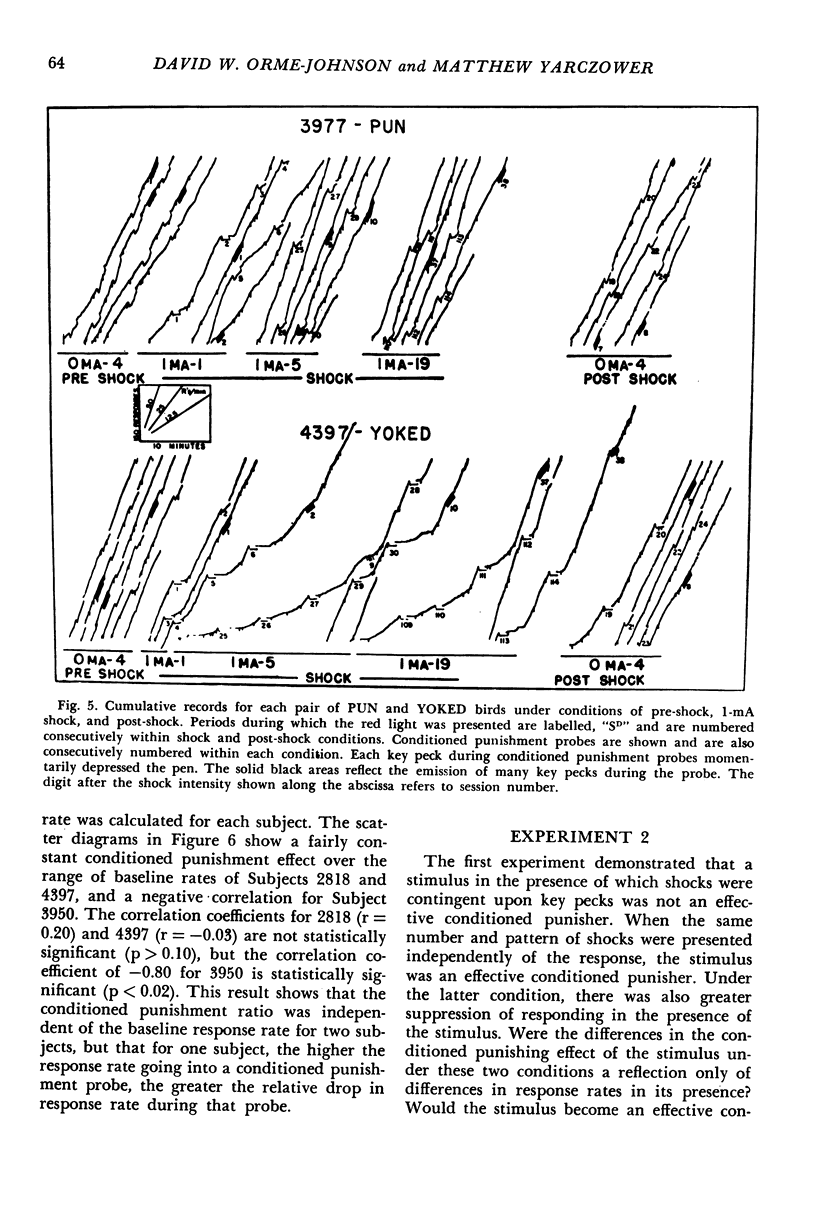
Three experiments were conducted to assess the aversive properties of a visual stimulus in the presence of which one group of birds received response-contingent shock (discriminated punishment) while a yoked group of birds received non-contingent shocks (conditioned suppression). In Experiment 1, presentation of the visual stimulus contingent on key pecking reduced the response rate (conditioned punishment effect) for birds under the conditioned suppression procedure but did not reduce the response rate of birds under the discriminative punishment procedure. Non-contingent shocks also produced greater suppression of responding maintained by positive reinforcement in the presence of a visual stimulus than did response-contingent shocks. In Experiment 2, a greater shock intensity (2 mA) was used. All the differences between the two groups found in Experiment 1 were also found in Experiment 2. Experiment 3 demonstrated that response-contingent shock did not result in a conditioned punishment effect even when positive reinforcers were unavailable during the discriminative punishment schedule. The exteroceptive stimulus that was paired with shock in the conditioned suppression procedure acquired the ability to punish behavior. The exteroceptive stimulus in the discriminative punishment schedule did not acquire this ability.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AZRIN N. H. A technique for delivering shock to pigeons. J Exp Anal Behav. 1959 Apr;2:161–163. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1959.2-161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boe E. E., Church R. M. Permanent effects of punishment during extinction. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1967 Jun;63(3):486–492. doi: 10.1037/h0024632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINSMOOR J. A. Punishment. I. The avoidance hypothesis. Psychol Rev. 1954 Jan;61(1):34–46. doi: 10.1037/h0062725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINSMOOR J. A. Punishment. II. An interpretation of empirical findings. Psychol Rev. 1955 Mar;62(2):96–105. doi: 10.1037/h0041258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLESHLER M., HOFFMAN H. S. A progression for generating variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:529–530. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKE D. F., AZRIN N. H. CONDITIONED PUNISHMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Sep;8:279–293. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMAN H. S., FLESHLER M. STIMULUS ASPECTS OF AVERSIVE CONTROLS: THE EFFECTS OF RESPONSE CONTINGENT SHOCK. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Mar;8:89–96. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT H. F., BRADY J. V. Some effects of punishment and intercurrent anxiety on a simple operant. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1955 Aug;48(4):305–310. doi: 10.1037/h0042529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hake D. F., Azrin N. H., Oxford R. The effects of punishment intensity on squirrel monkeys. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jan;10(1):95–107. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman H. S., Barrett J. Overt activity during conditioned suppression: a search for punishment artifacts. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Nov;16(3):343–348. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.16-343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster R., Rachlin H. Indifference between punishment and free shock: evidence for the negative law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):777–786. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


