Abstract
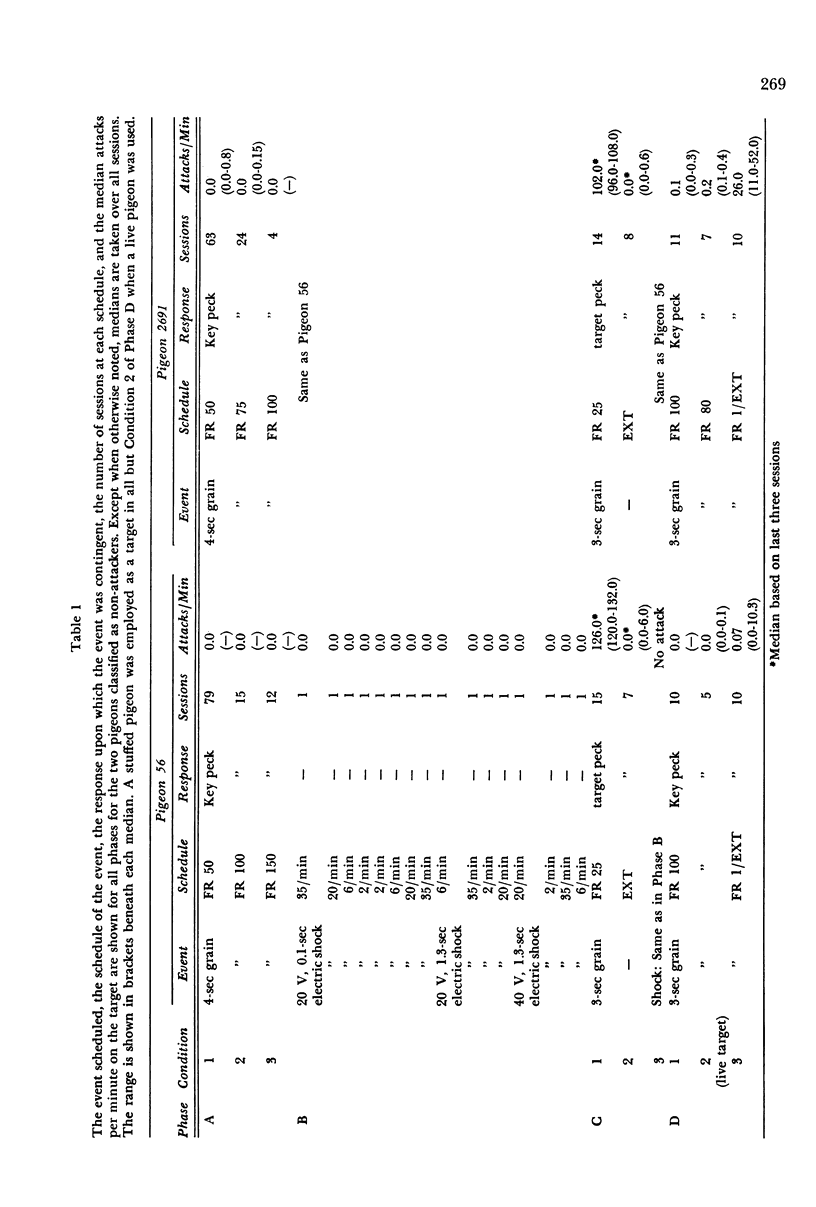
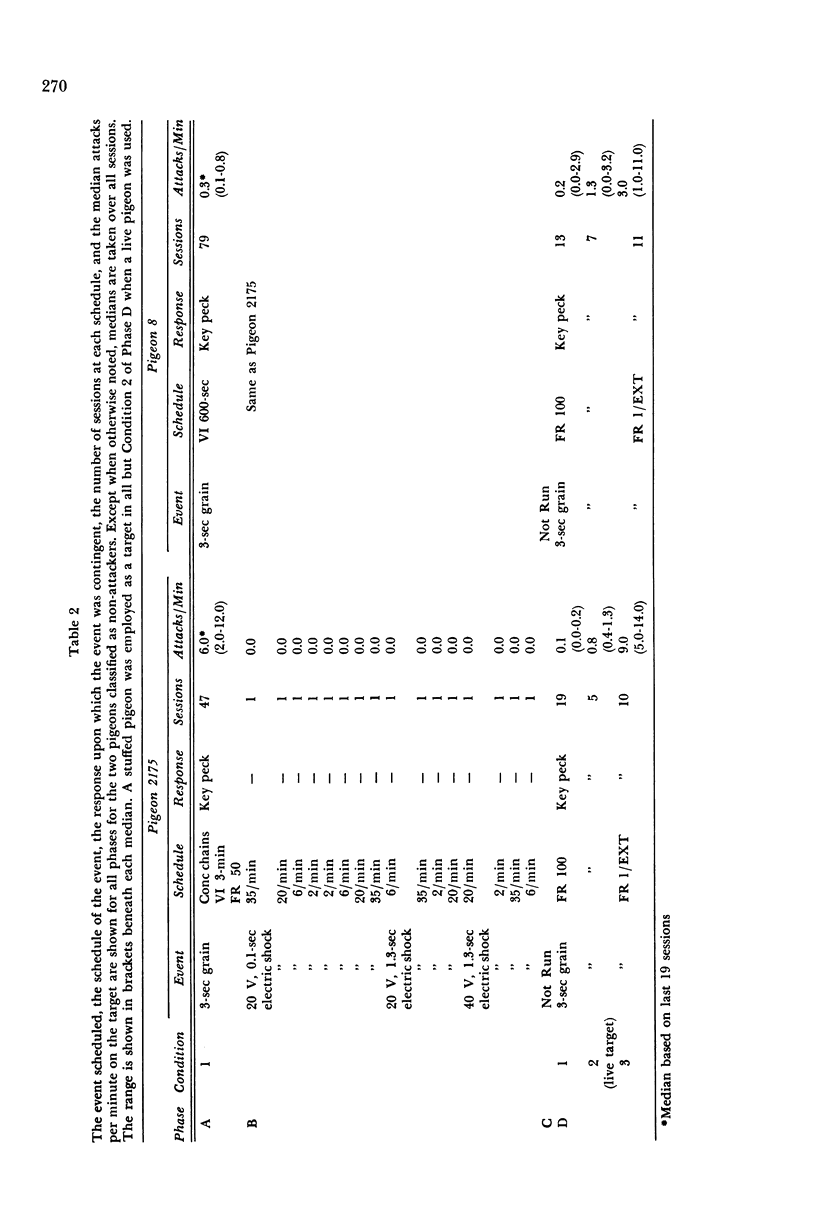
Two pigeons that attacked a taxidermically prepared target pigeon during a schedule of positive reinforcement for key pecking, and two that did not, were shocked through implanted electrodes in the presence of the target. Shock intensities of 2 and 4 mA, durations of 0.1 and 1.3 sec, and frequencies of 2, 6, 20, and 35 per minute were delivered across 16 sessions with 180 shocks per session. No pigeon attacked the target; one pecked the shockplug on its back. The two pigeons that had not attacked during the positive reinforcement schedules were conditioned to peck the target for food reinforcement before another 16 sessions of shock. No attack was observed in these shock sessions. During subsequent positive reinforcement of key pecking, the target was attacked by the two pigeons that had originally attacked and by one that had not. Absence of shock-elicited attack in these pigeons may be related to the parameters of the experiment or may be yet another instance of the absence of shock-elicited attack in the class Aves. At least under the present conditions, it was not possible to predict the level of attack during electric shock from the level of attack during schedules of positive reinforcement for key pecking.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AZRIN N. H., HAKE D. F., HOLZ W. C., HUTCHINSON R. R. MOTIVATIONAL ASPECTS OF ESCAPE FROM PUNISHMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Jan;8:31–44. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AZRIN N. H., ULRICH R. E., HUTCHINSON R. R., NORMAN D. G. EFFECT OF SHOCK DURATION ON SHOCK-INDUCED FIGHTING. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Jan;7:9–11. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akerman B. Behavioural effects of electrical stimulation in the forebrain of the pigeon. II. Protective behaviour. Behaviour. 1966;26(3):339–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azrin N. H., Hutchinson R. R., Hake D. F. Extinction-induced aggression. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 May;9(3):191–204. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flory R. Attack behavior as a function of minimum inter-food interval. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):825–828. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry W. D. Fixed-ratio schedule-induced aggression. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):813–817. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKE D. F., AZRIN N. H. CONDITIONED PUNISHMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Sep;8:279–293. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMAN H. S. A flexible connector for delivering shock to pigeons. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Oct;3:330–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumia A. R. The relationships among testosterone, conditioned aggression, and dominance in male pigeons. Horm Behav. 1972 Sep;3(3):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0018-506x(72)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murton R. K., Thearle R. J., Lofts B. The endocrine basis of breeding behaviour in the feral pigeon (Columba livia). I. Effects of exogenous hormones on the pre-incubation behaviour of intact males. Anim Behav. 1969 May;17(2):286–306. doi: 10.1016/0003-3472(69)90014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S., CATANIA A. C., SKINNER B. F. Conditioned and unconditioned aggression in pigeons. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jan;6:73–74. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F., Gustavson C. R., Gregor G. L. Incompatability between the pigeons' unconditioned response to shock and the conditioned key-peck response. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jul;18(1):147–153. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ULRICH R. E., AZRIN N. H. Reflexive fighting in response to aversive stimulation. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:511–520. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


