Abstract
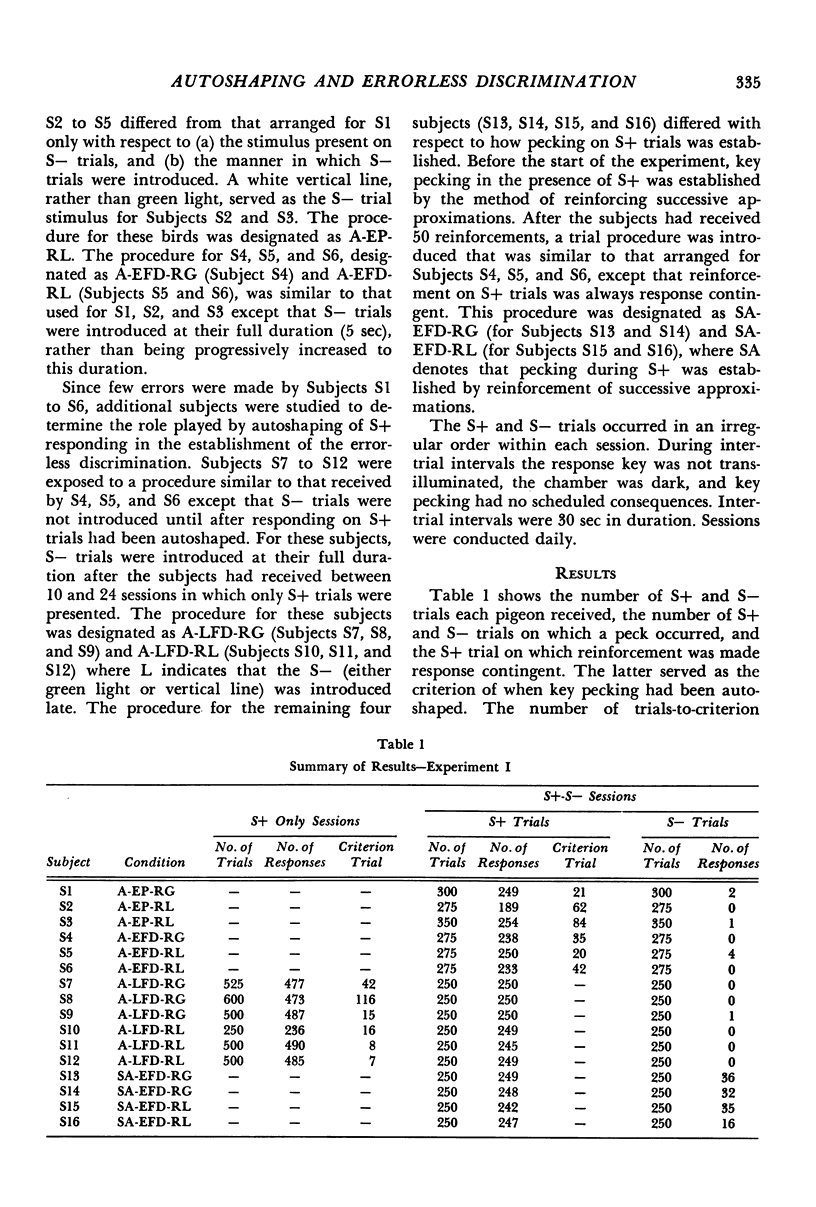
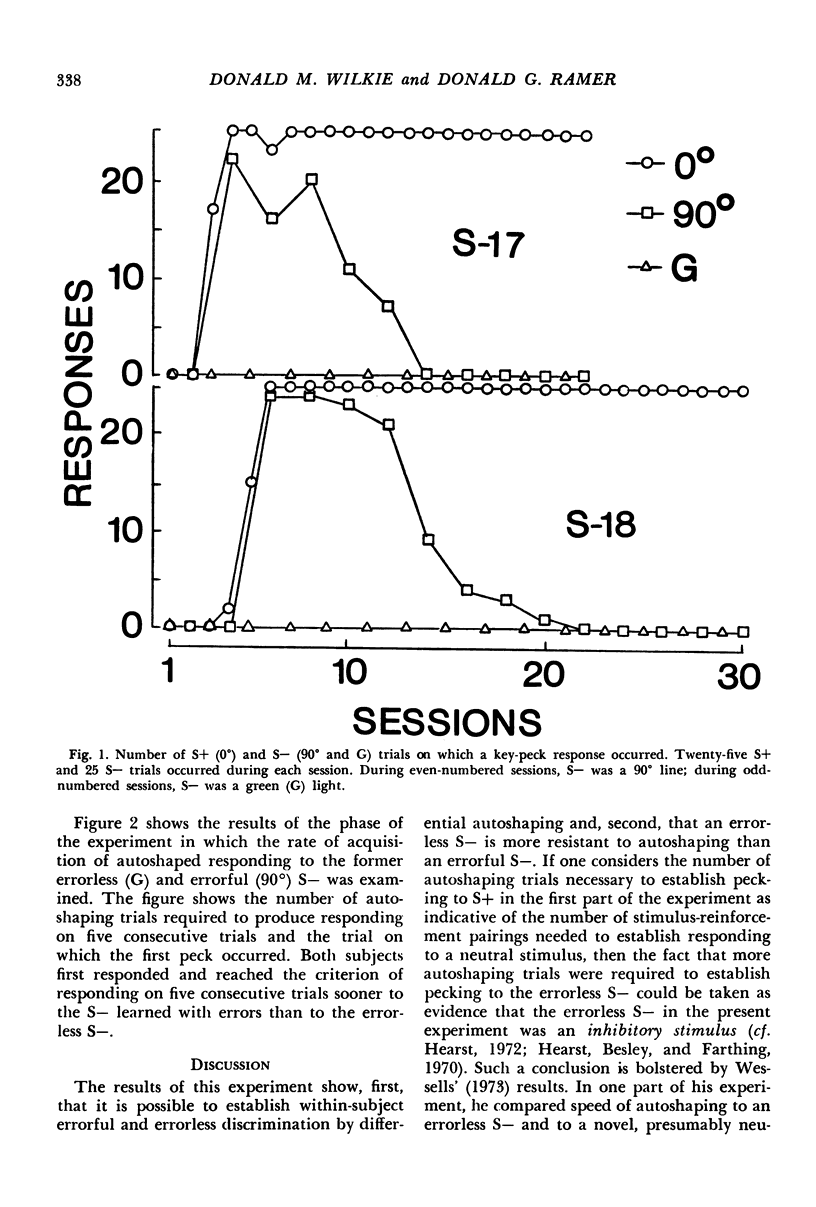
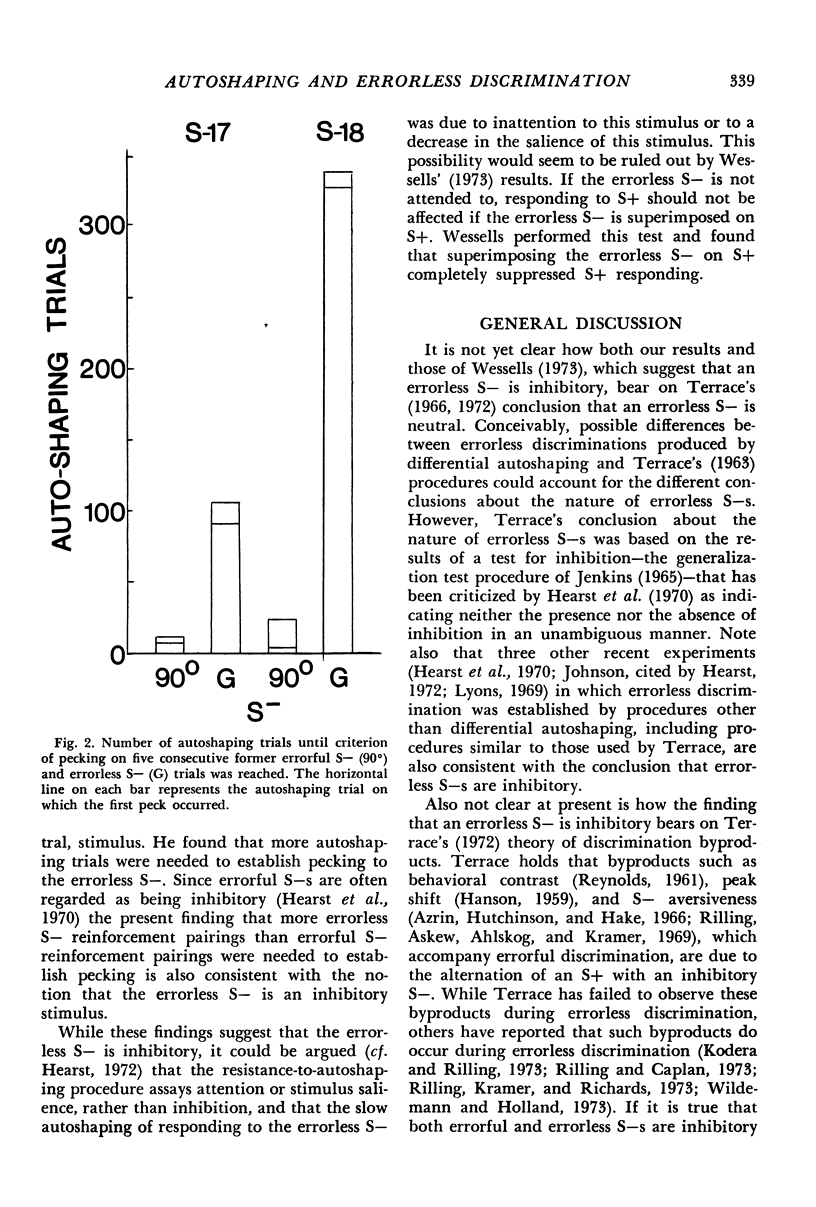
In Experiment I, pigeons exposed to a differential autoshaping procedure pecked a key in the presence of the stimulus associated with reinforcement but did not peck, or pecked infrequently, in the presence of the stimulus associated with nonreinforcement. In Experiment II, pigeons were exposed to a differential autoshaping procedure in which one stimulus was associated with reinforcement and two stimuli were associated with nonreinforcement. The birds initially responded in the presence of one stimulus associated with nonreinforcement but never responded in the presence of the second stimulus associated with nonreinforcement. They were subsequently exposed to an autoshaping procedure in which reinforcement followed both these stimuli. The number of stimulus-reinforcement pairings required to establish pecking in the presence of the stimulus during which responses had not previously occurred suggested that such stimuli are inhibitory. These findings have implications for autoshaping, errorless discrimination, inhibition, and theories of discrimination byproducts.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azrin N. H., Hutchinson R. R., Hake D. F. Extinction-induced aggression. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 May;9(3):191–204. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. L., Jenkins H. M. Auto-shaping of the pigeon's key-peck. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Jan;11(1):1–8. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamzu E., Schwartz B. The maintenance of key pecking by stimulus-contingent and response-independent food presentation. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Jan;19(1):65–72. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSON H. M. Effects of discrimination training on stimulus generalization. J Exp Psychol. 1959 Nov;58:321–334. doi: 10.1037/h0042606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearst E., Besley S., Farthing G. W. Inhibition and the stimulus control of operant behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Nov;14(3 Pt 2 Suppl):373–409. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.14-s373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINS H. M., HARRISON R. H. Effect of discrimination training on auditory generalization. J Exp Psychol. 1960 Apr;59:246–253. doi: 10.1037/h0041661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins H. M., Moore B. R. The form of the auto-shaped response with food or water reinforcers. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Sep;20(2):163–181. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons J. Stimulus generalization as a function of discrimination learning with and without errors. Science. 1969 Jan 31;163(3866):490–491. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3866.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S. Behavioral contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jan;4:57–71. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rilling M., Askew H. R., Ahlskog J. E., Kramer T. J. Aversive properties of the negative stimulus in a successive discrimination. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):917–932. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rilling M., Caplan H. J. Extinction-induced aggression during errorless discrimination learning. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Jul;20(1):85–92. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. Maintenance of key pecking by response-independent food presentation: the role of the modality of the signal for food. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Jul;20(1):17–22. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRACE H. S. Discrimination learning with and without "errors". J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jan;6:1–27. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrace H. S. Discrimination learning and inhibition. Science. 1966 Dec 30;154(3757):1677–1680. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3757.1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessells M. G. Errorless discrimination, autoshaping, and conditioned inhibition. Science. 1973 Nov 30;182(4115):941–943. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4115.941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildemann D. G., Holland J. G. The effect of the blackout method on acquisition and generalization. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Jan;19(1):73–80. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


