Abstract
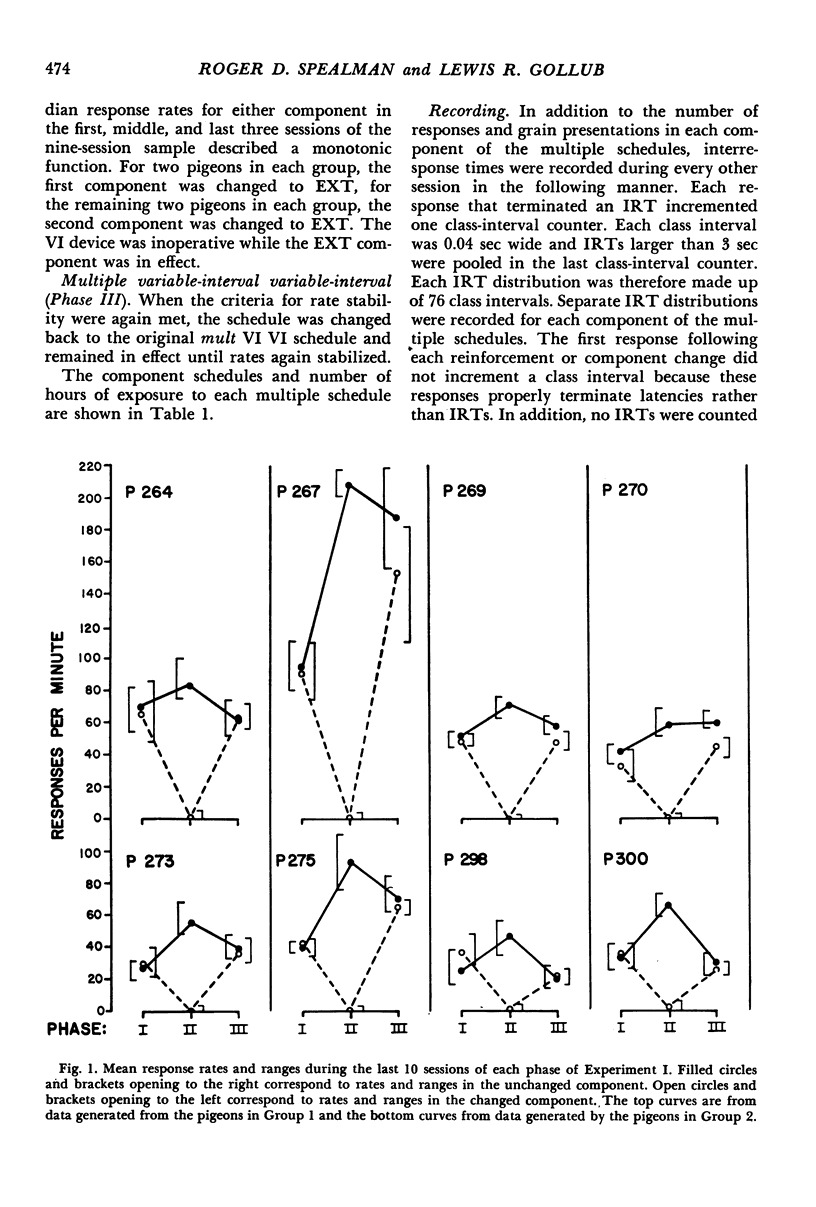
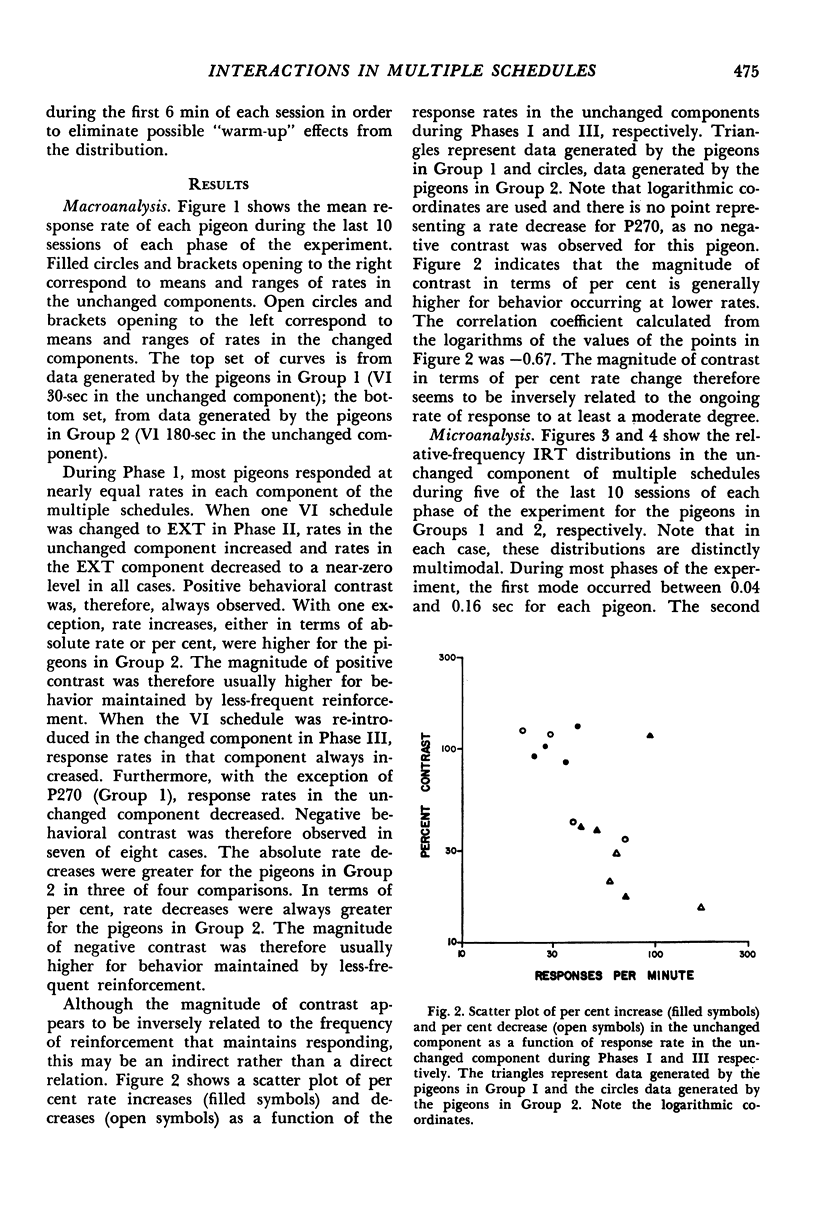
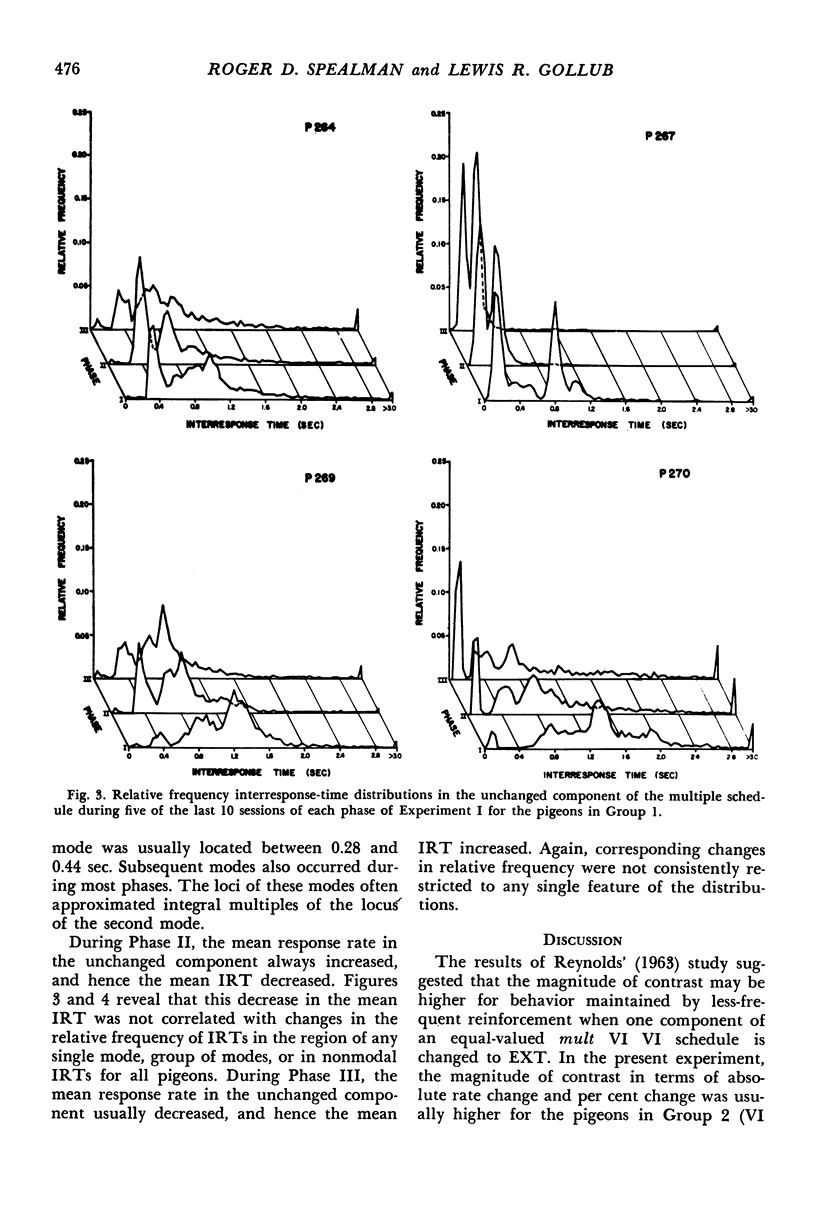
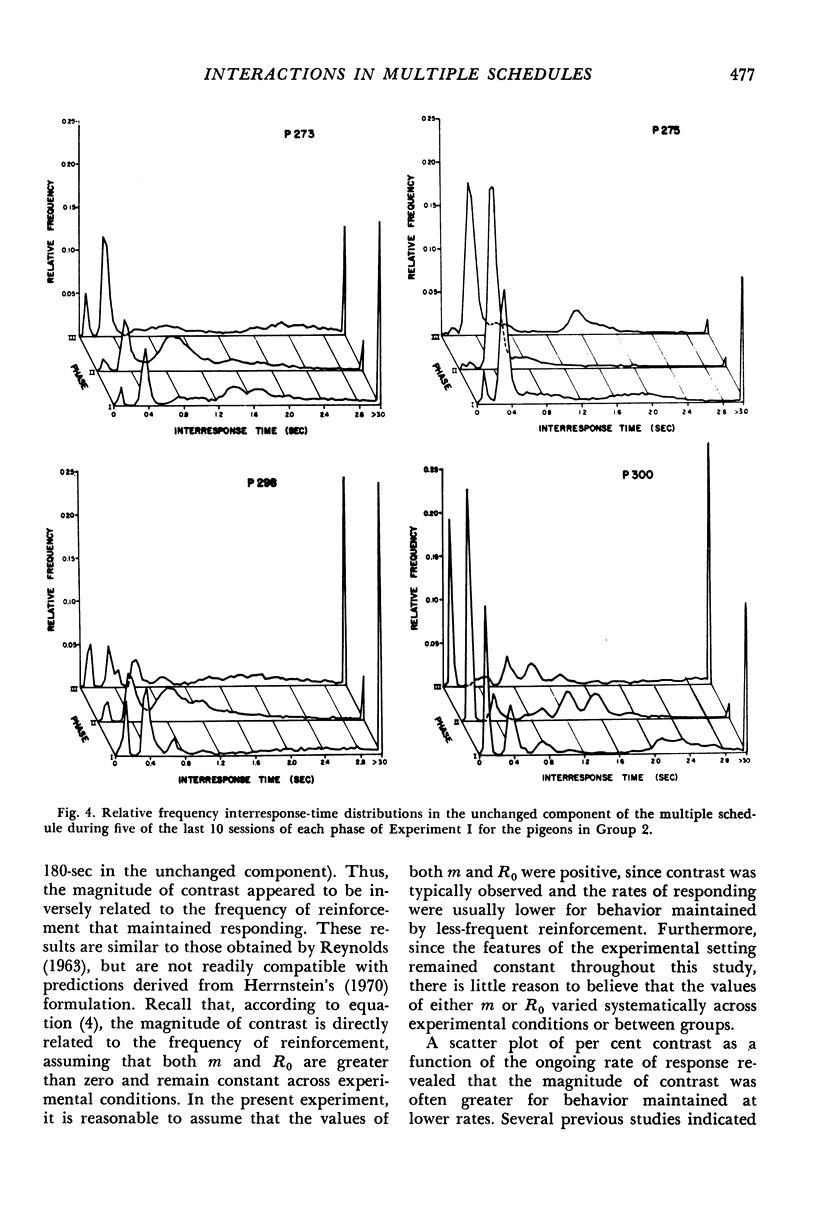
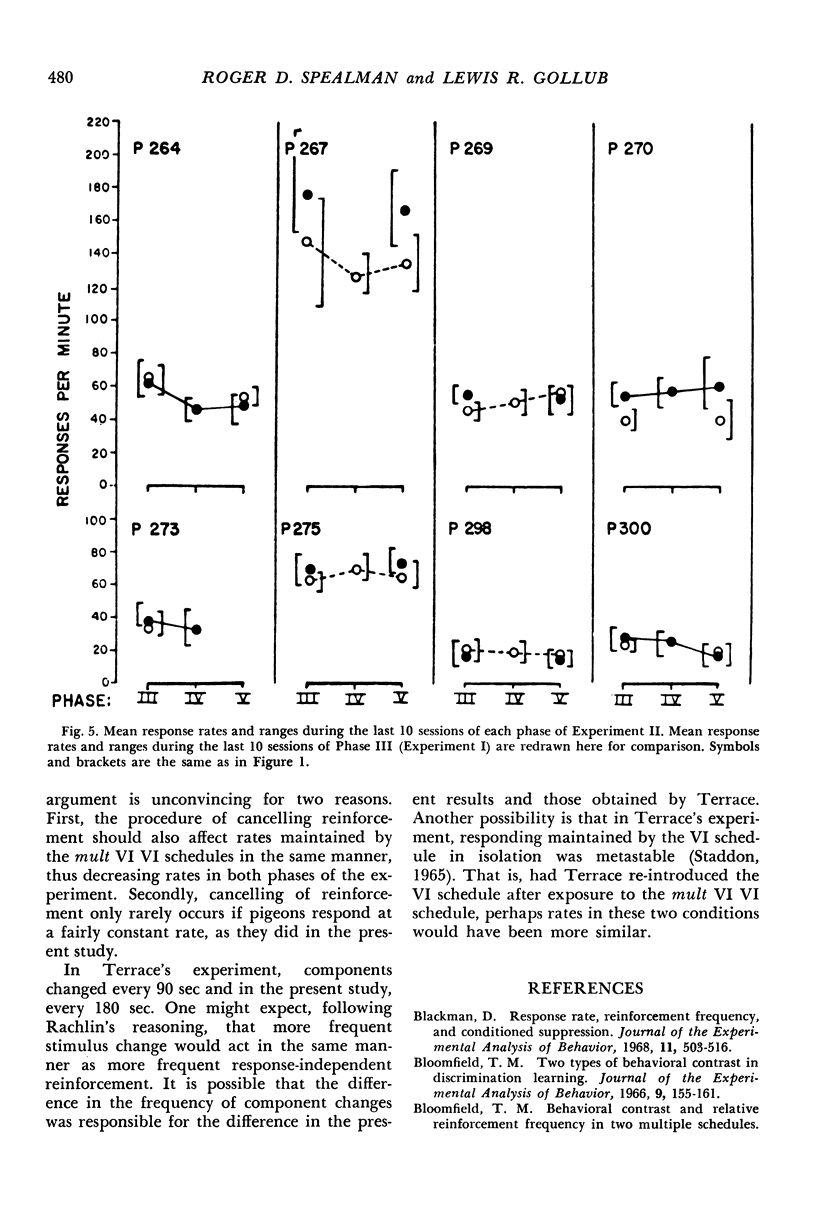
In Experiment I, two groups of four pigeons each were exposed to multiple schedules in which one component was always a variable-interval schedule with a mean interreinforcement interval of 30 or 180 seconds. The other component was either an equal variable-interval schedule or extinction. Response rates in the unchanged component always increased when reinforcement was no longer scheduled in the changed component, and decreased in seven of eight cases when the variable-interval schedule was re-introduced. The per cent rate change in the unchanged component was inversely related to the frequency of reinforcement and to the ongoing response rate in the unchanged component. Rate changes in the unchanged component were not consistently correlated with changes in any single feature of the relative-frequency interresponse-time distributions. In Experiment II, the same pigeons were exposed to variable-interval schedules and multiple variable-interval variable-interval schedules with equal mean interreinforcement intervals. Response rates were similar under both conditions.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackman D. Response rate, reinforcement frequency, and conditioned suppression. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Sep;11(5):503–516. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield T. M. Two types of behavioral contrast in discrimination learning. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Mar;9(2):155–161. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARMER J. PROPERTIES OF BEHAVIOR UNDER RANDOM INTERVAL REINFORCEMENT SCHEDULES. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Oct;6:607–616. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmes N. S., Eckerman D. A. Positive interaction (induction) in multiple variable-interval, differential-reinforcement-of-high-rate schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jan;17(1):51–57. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. On the law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):243–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher R. T., Morse W. H. Determinants of the specificity of behavioral effects of drugs. Ergeb Physiol. 1968;60:1–56. doi: 10.1007/BFb0107250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A. Differential reinforcement and stimulus control of not responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):715–726. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S. Behavioral contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jan;4:57–71. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S., CATANIA A. C. Behavioral contrast with fixed interval and low-rate reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Oct;4:387–391. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S. Some limitations on behavioral contrast and induction during successive discrimination. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jan;6:131–139. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADDON J. E. SOME PROPERTIES OF SPACED RESPONDING IN PIGEONS. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Jan;8:19–27. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F. Topography of the food-reinforced key peck and the source of 30-millisecond interresponse times. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 May;21(3):541–551. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrace H. S. Discrimination learning, the peak shift, and behavioral contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):727–741. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman R. G. Factors influencing inhibitory stimulus control: differential reinforcement of other behavior during discrimination training. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Jul;14(1):87–91. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.14-87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Gott C. T. A microanalysis of drug effects on fixed-ratio performance in pigeons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Feb;180(2):189–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


