Abstract
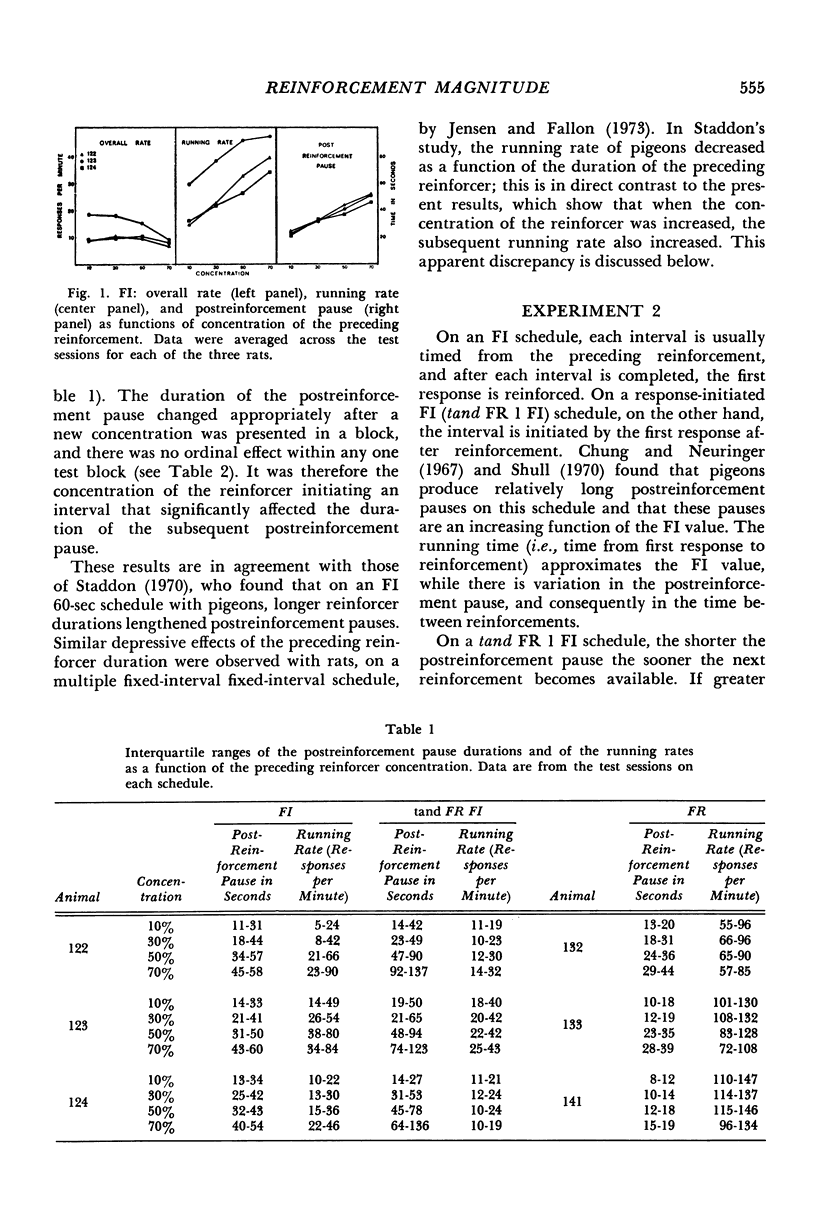
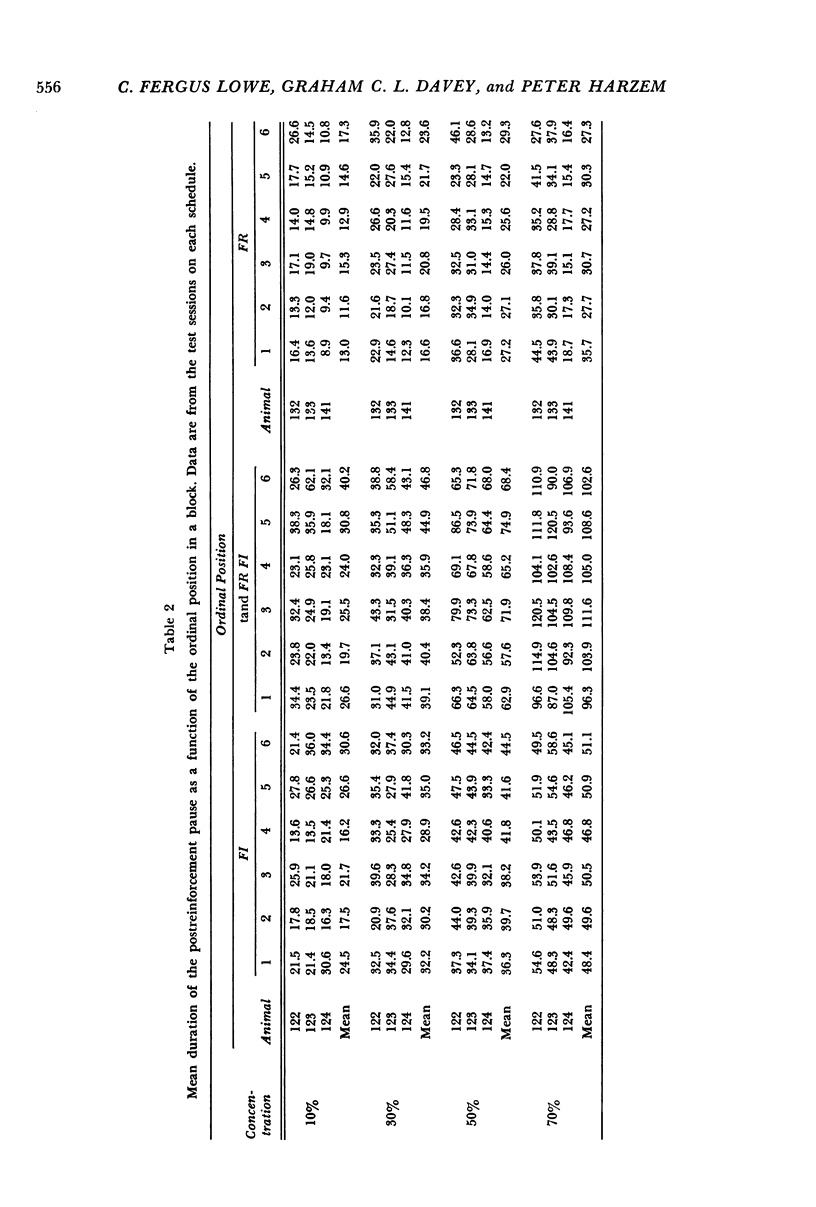
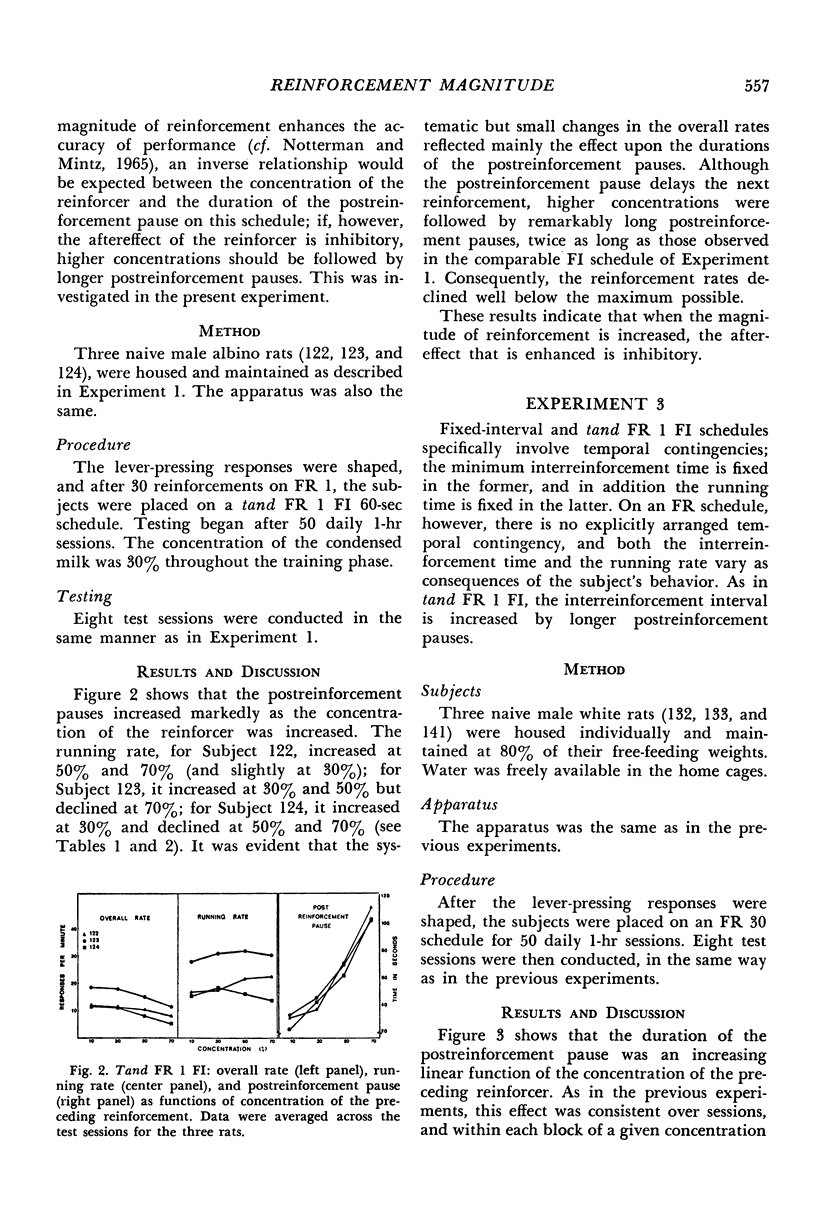
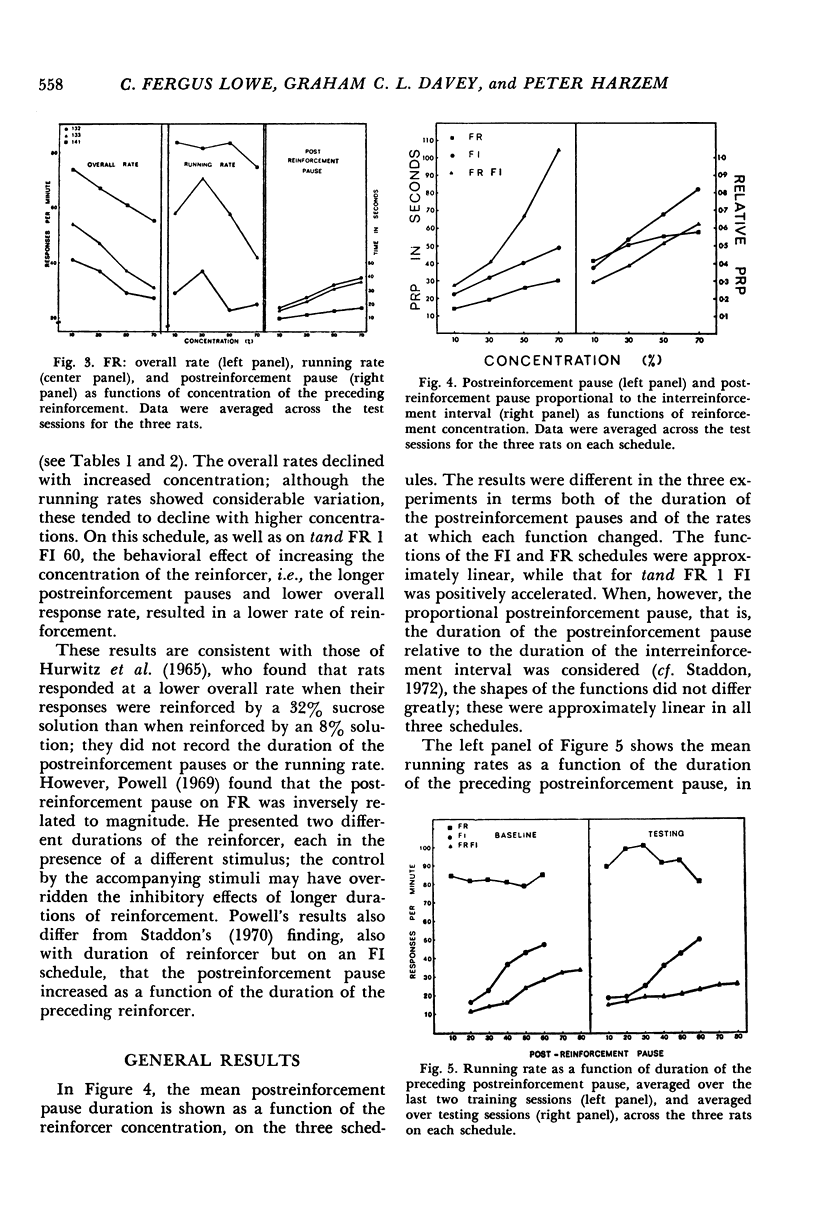
Rats' lever pressing was studied on three schedules of reinforcement: fixed interval, response-initiated fixed interval, and fixed ratio. In testing, concentration of the milk reinforcer was varied within each session. On all schedules, duration of the postreinforcement pause was an increasing function of the concentration of the preceding reinforcer. The running rate (response rate calculated by excluding the postreinforcement pauses) increased linearly as a function of the preceding magnitude of reinforcement on fixed interval, showed slight increases for two of the three animals on response-initiated fixed interval, and did not change systematically on fixed ratio. In all cases, the overall response rate either declined or showed no effect of concentration. The major effect of increasing the reinforcement magnitude was in determining the duration of the following postreinforcement pause, and changes in the response rate reflected this main effect.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COLLIER G., MYERS L. The loci of reinforcement. J Exp Psychol. 1961 Jan;61:57–66. doi: 10.1037/h0048851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLIER G., WILLIS F. N. Deprivation and reinforcement. J Exp Psychol. 1961 Oct;62:377–384. doi: 10.1037/h0047144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DILOLLO V., ENSMINGER W. D., NOTTERMAN J. M. RESPONSE FORCE AS A FUNCTION OF AMOUNT OF REINFORCEMENT. J Exp Psychol. 1965 Jul;70:27–31. doi: 10.1037/h0022062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTTMAN N. Operant conditioning, extinction, and periodic reinforcement in relation to concentration of sucrose used as reinforcing agent. J Exp Psychol. 1953 Oct;46(4):213–224. doi: 10.1037/h0061893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTT P. J. Rate of bar pressing as a function of quality and quantity of food reward. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1954 Jun;47(3):235–239. doi: 10.1037/h0059855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen C., Fallon D. Behavioral aftereffects of reinforcement and its omission as a function of reinforcement magnitude. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 May;19(3):459–468. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEESEY R. E., KLING J. W. Amount of reinforcement and free-operant responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Apr;4:125–132. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen P. Reinforcement frequency and contingency as factors in fixed-ratio behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 May;12(3):391–395. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J. Effects of reinforcement magnitude on choice and rate of responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Sep;10(5):417–424. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J., Schneider B. A. Separating the effects of interreinforcement time and number of interreinforcement responses. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):661–667. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEBBINS W. C., MEAD P. B., MARTIN J. M. The relation of amount of reinforcement to performance under a fixed-in-terval schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1959 Oct;2:351–355. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1959.2-351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scull J. W. The Amsel frustration effect: interpretations and research. Psychol Bull. 1973 Jun;79(6):352–361. doi: 10.1037/h0034430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull R. L. A response-initiated fixed-interval schedule of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Jan;13(1):13–15. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staddon J. E. Effect of reinforcement duration on fixed-interval responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Jan;13(1):9–11. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


