Abstract
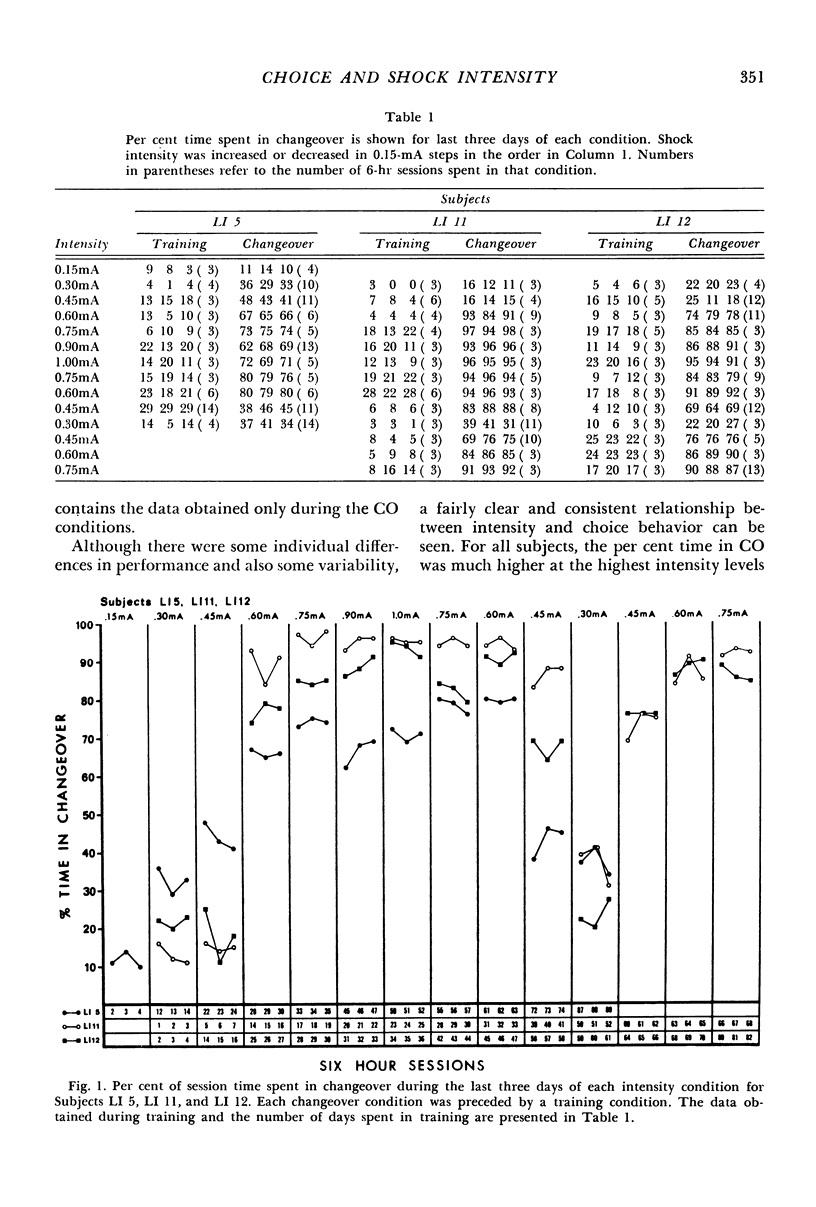
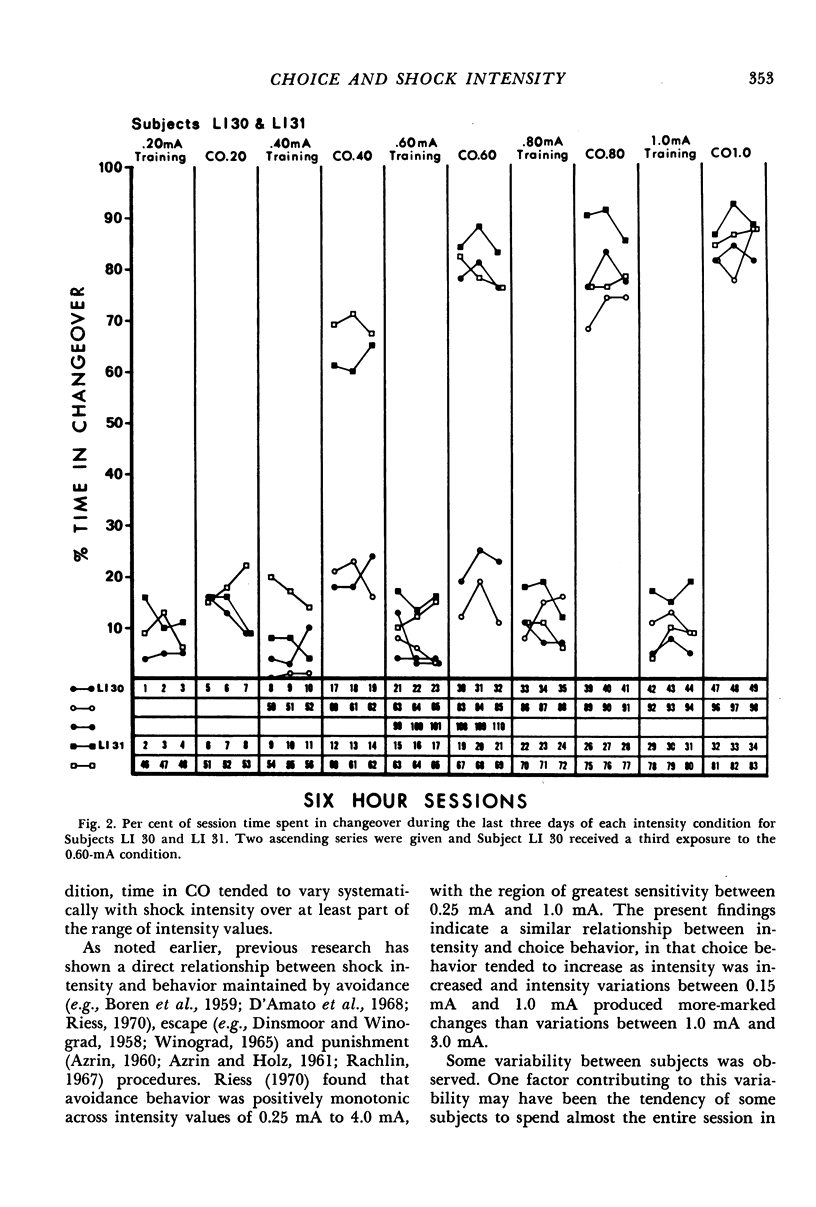
Choice between a signalled shock schedule and an unsignalled one was examined at various shock intensities. Three rats were given the opportunity to change from the unsignalled schedule to the signalled one at intensity values between 0.15 mA and 1.0 mA. Steps were usually 0.15 mA and both ascending and descending series were given. For two other rats, shock intensity increased from 0.20 mA to 1.0 mA in 0.20-mA increments; for two additional rats, shock intensity was first 3.0 mA and was then reduced to 1.0 mA. Subjects tended to remain in the unsignalled schedule at the lower shock intensities, but spent most of each session under the signalled schedule at the higher intensities (1.0 mA and 3.0 mA). In addition, the time spent in the signalled schedule tended to vary systematically with shock intensity over at least part of the range of intensity values. It was concluded that the relationship between shock intensity and choice behavior is similar to the relationship between intensity and behavior in procedures involving avoidance, escape, and punishment.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANNAU Z., KAMIN L. J. The conditioned emotional response as a function of intensity of the US. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1961 Aug;54:428–432. doi: 10.1037/h0042199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AZRIN N. H. Effects of punishment intensity during variable-interval reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Apr;3:123–142. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AZRIN N. H., HOLZ W. C. Punishment during fixed-interval reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Oct;4:343–347. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOREN J. J., SIDMAN M., HERRNSTEIN R. J. Avoidance, escape, and extinction as functions of shock intensity. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1959 Aug;52:420–426. doi: 10.1037/h0042727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badia P., Coker C., Harsh J. Choice of higher density signalled shock over lower density unsignalled shock. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Jul;20(1):47–55. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badia P., Culbertson S., Harsh J. Choice of longer or stronger signalled shock over shorter or weaker unsignalled shock. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Jan;19(1):25–32. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badia P., Culbertson S., Lewis P. The relative aversiveness of signalled vs unsignalled avoidance. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Jul;16(1):113–121. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.16-113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badia P., Culbertson S. The relative aversiveness of signalled vs unsignalled escapable and inescapable shock. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 May;17(3):463–471. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amato M. R., Fazzaro J., Etkin M. Anticipatory responding and avoidance discrimination as factors in avoidance conditioning. J Exp Psychol. 1968 May;77(1):41–47. doi: 10.1037/h0025763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinsmoor J. A., Winograd E. Shock Intensity in Variable-interval Escape Schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Apr;1(2):145–148. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hake D. F., Azrin N. H., Oxford R. The effects of punishment intensity on squirrel monkeys. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jan;10(1):95–107. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOCKARD J. S. Choice of a warning signal or no warning signal in an unavoidable shock situation. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1963 Jun;56:526–530. doi: 10.1037/h0041552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER N. E. Learning resistance to pain and fear: effects of overlearning, exposure, and rewarded expsure in context. J Exp Psychol. 1960 Sep;60:137–145. doi: 10.1037/h0043321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins C. C., Jr An analysis of the concept of reinforcement. Psychol Rev. 1968 Mar;75(2):155–172. doi: 10.1037/h0025509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins C. C., Jr, Seymann R. G., Levis D. J., Spencer R., Jr Factors affecting preference for signal-shock over shock-signal. J Exp Psychol. 1966 Aug;72(2):190–196. doi: 10.1037/h0023491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachlin H. The effect of shock intensity on concurrent and single-key responding in concurrent-chain schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jan;10(1):87–93. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rescorla R. A. Conditioned inhibition of fear resulting from negative CS-US contingencies. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1969 Apr;67(4):504–509. doi: 10.1037/h0027313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riess D. Sidman avoidance in rats as a function of shock intensity and duration. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1970 Dec;73(3):481–485. doi: 10.1037/h0030235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERHAVE T. The functional properties of a time out from an avoidance schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:391–422. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINOGRAD E. ESCAPE BEHAVIOR UNDER DIFFERENT FIXED RATIOS AND SHOCK INTENSITIES. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Mar;8:117–124. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman R. G., Litner J. S. Role of the intertrial interval in Pavlovian differential conditioning of fear in rats. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1971 Feb;74(2):211–218. doi: 10.1037/h0030347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman R. G., Litner J. S. The course of Pavlovian excitation and inhibition of fear in rats. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1969 Dec;69(4):667–672. doi: 10.1037/h0028213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



