Abstract
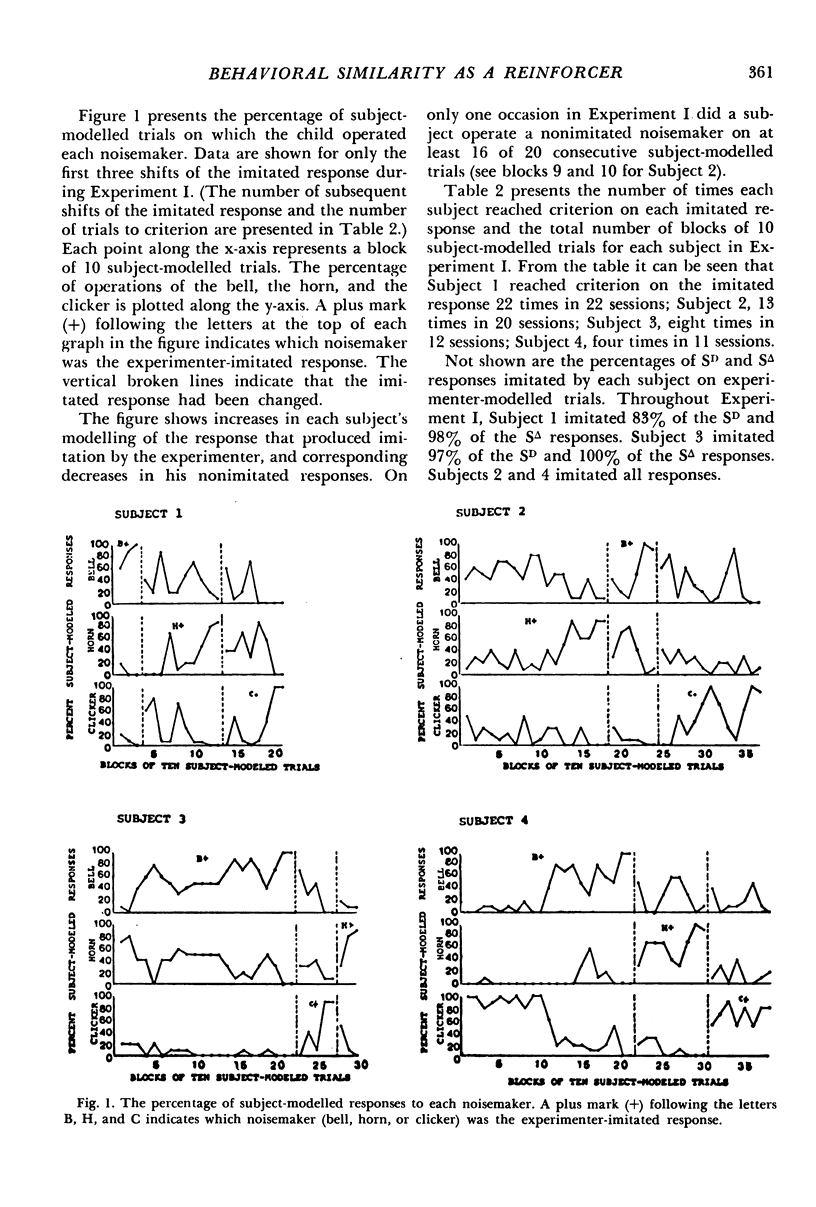
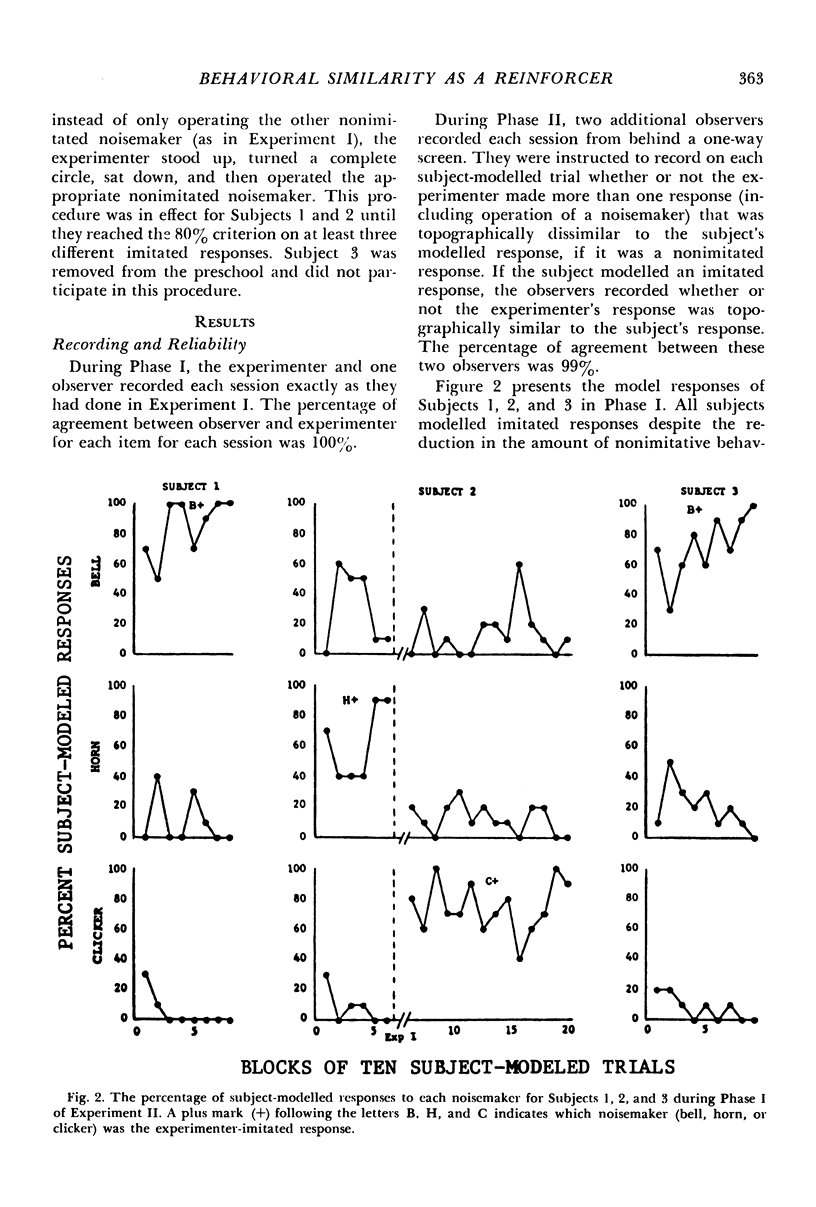
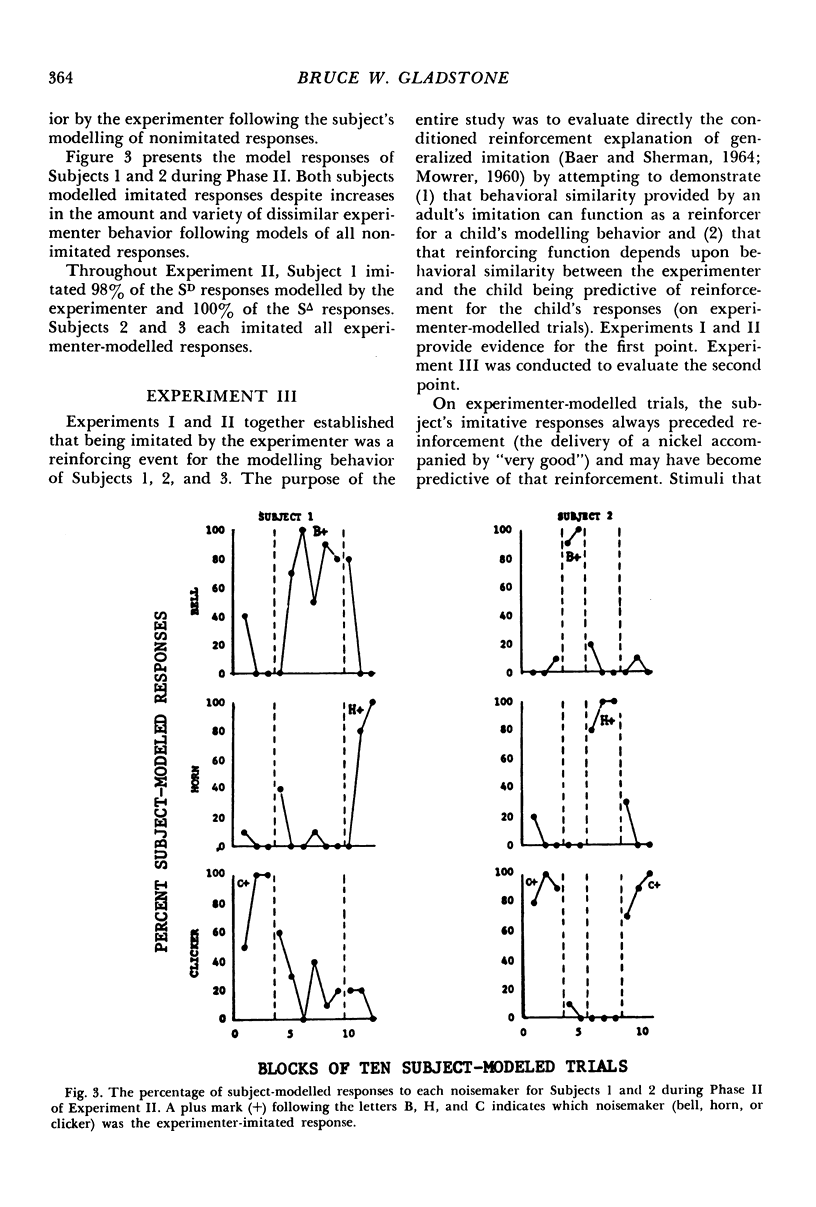
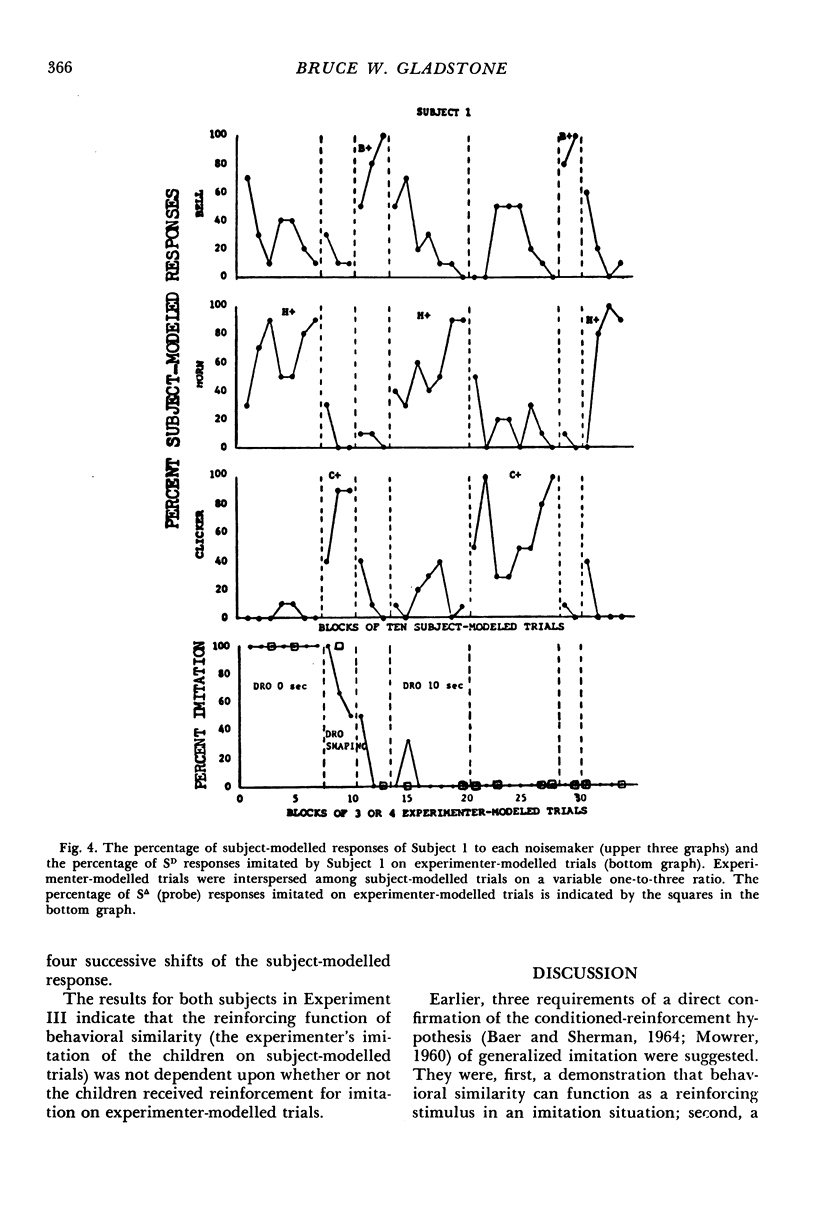
Three experiments evaluated whether behavioral similarity provided by an adult could serve as a reinforcer for the modelling behavior of four preschoolers. In each experiment, sessions consisted of two kinds of trials: (1) experimenter-modelled trials, when the child's imitation of modelled motor responses was reinforced with praise and tokens, and (2) child-modelled trials when experimenter imitation of child-modelled responses was contingent upon the child's modelling one of three alternative responses: operation of a ball, horn, or clicker. Experiment I showed that the children consistently modelled whichever responses the experimenter imitated. Experiment II determined whether that performance was due to differences in the amount of experimenter behavior following imitated versus nonimitated child models or to experimenter imitation. Neither reducing nor increasing the amount of experimenter behavior following the children's nonimitated models altered their modelling of imitated responses. Experiment III evaluated whether experimenter imitation of child models was a reinforcer because the child's imitative responses were reinforced on experimenter-modelled trials. In Experiment III, the children's nonimitation of experimenter-models was reinforced with praise and tokens on a schedule of differential reinforcement of other behavior, yet they continued to model experimenter-imitated responses on child-modelled trials. These results indicate behavioral similarity was reinforcing, though no conditioning history through which it acquired that function was demonstrated.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer D. M., Peterson R. F., Sherman J. A. The development of imitation by reinforcing behavioral similarity to a model. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Sep;10(5):405–416. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigham T. A., Sherman J. A. An experimental analysis of verbal imitation in preschool children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Summer;1(2):151–158. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. L., Burgess J. M., Esveldt K. C. An analysis of generalized imitation. J Appl Behav Anal. 1970 Spring;3(1):39–46. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1970.3-39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewirtz J. L., Stingle K. G. Learning of generalized imitation as the basis for identification. Psychol Rev. 1968 Sep;75(5):374–397. doi: 10.1037/h0026378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovaas O. I., Berberich J. P., Perloff B. F., Schaeffer B. Acquisition of imitative speech by schizophrenic children. Science. 1966 Feb 11;151(3711):705–707. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3711.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovaas O. I., Freitag G., Kinder M. I., Rubenstein B. D., Schaeffer B., Simmons J. Q. Establishment of social reinforcers in two schizophrenic children on the basis of food. J Exp Child Psychol. 1966 Oct;4(2):109–125. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(66)90011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



