Abstract
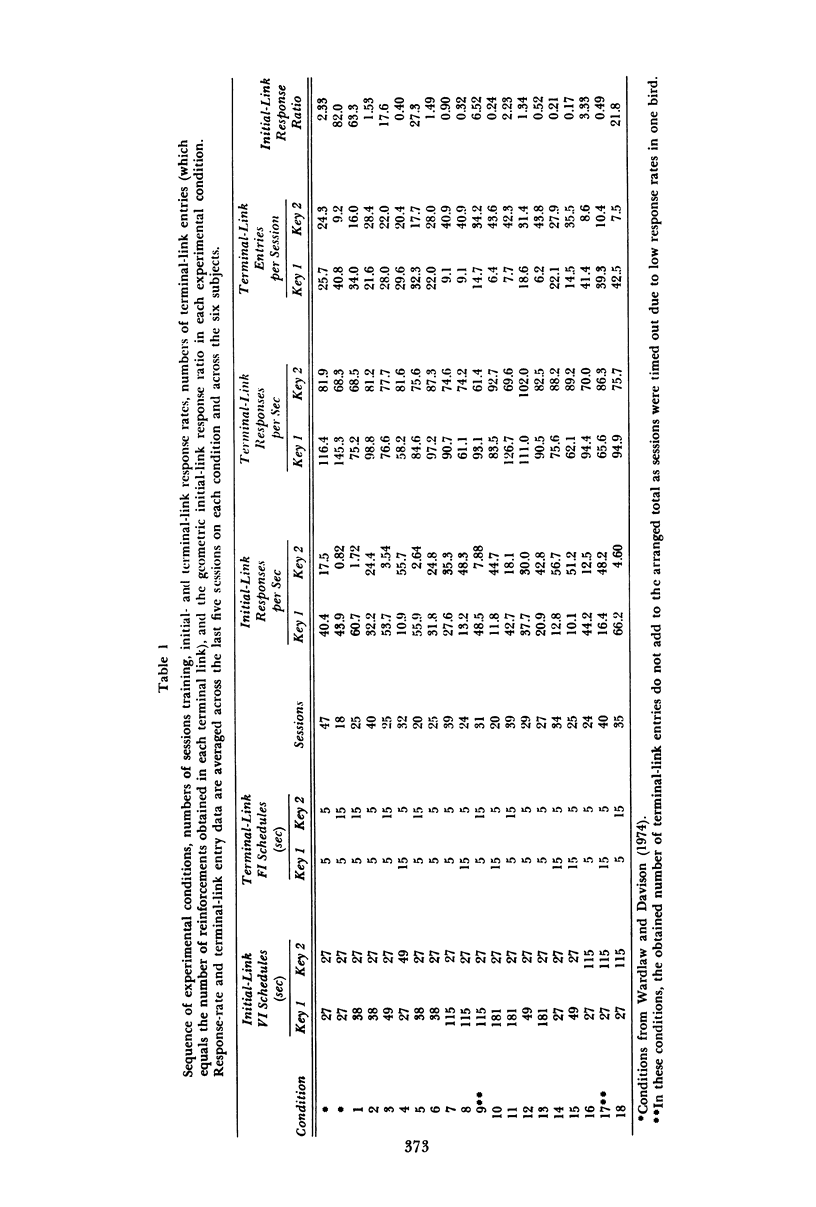
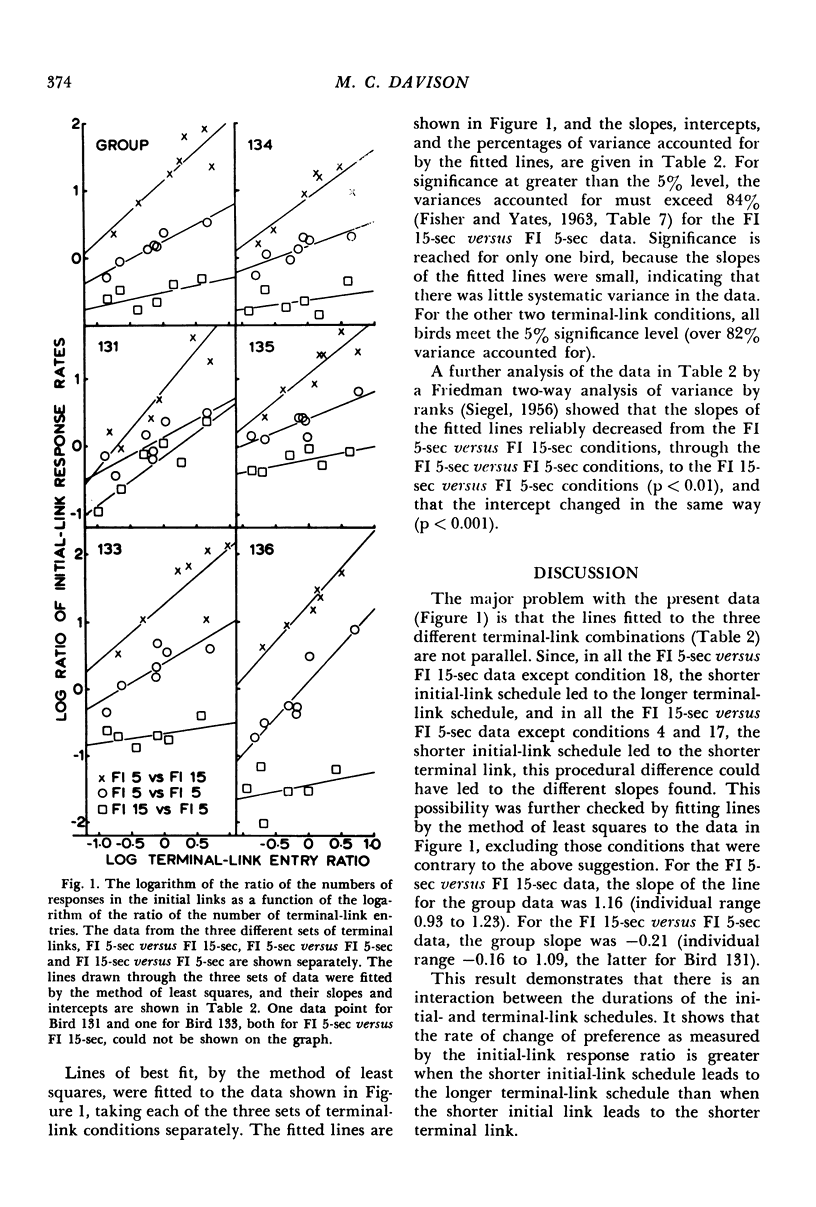
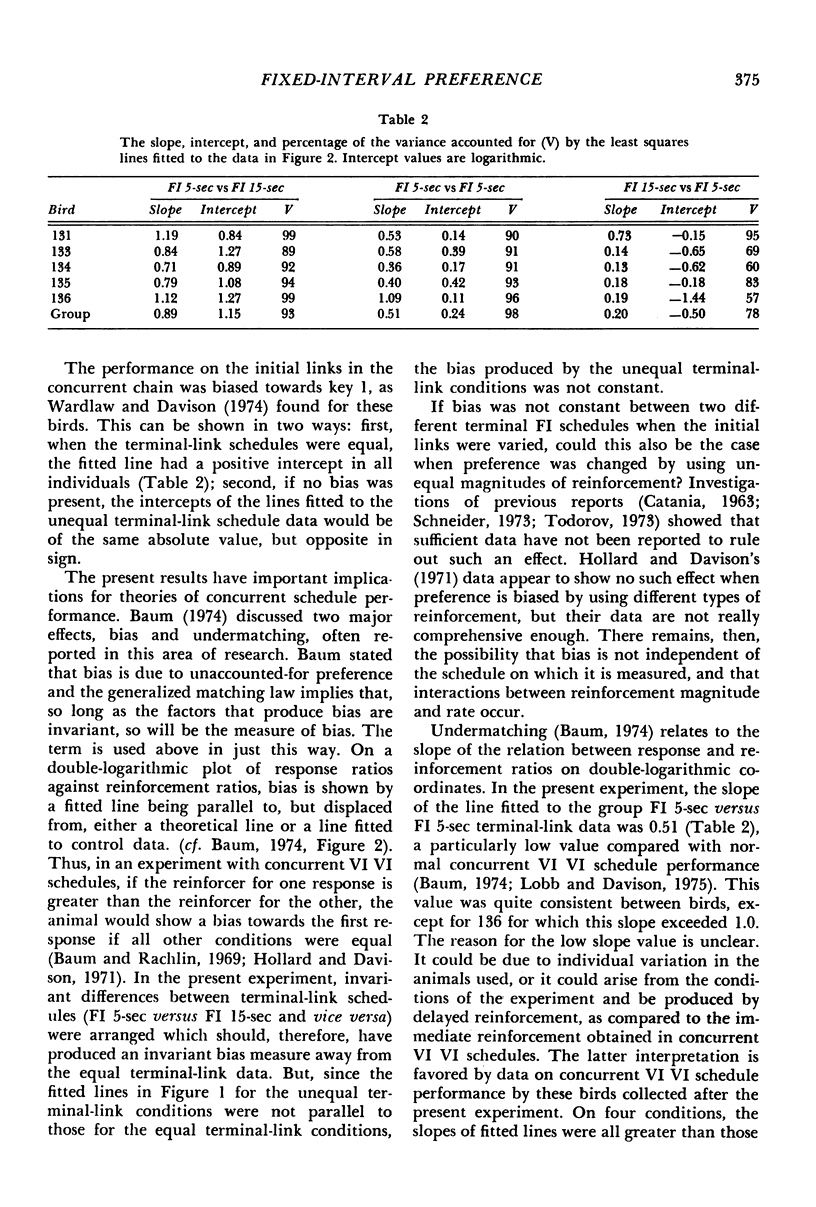
Six homing pigeons were trained on concurrent chain schedules in which the terminal links were fixed-interval schedules of 5 sec or 15 sec. One initial-link schedule was always VI 27-sec; the other was varied over conditions from VI 27-sec to VI 181-sec. Preference measured in the initial links varied as a joint function of the initial- and terminal-link schedules. When the initial links were varied with constant, but unequal, terminal links, the slope of the function relating the logarithm of the initial-link response ratio to the logarithm of the terminal-link entry ratio differed from that obtained with equal terminal links. This result indicates that biases attributable to the terminal-link schedules were not constant. The rate of change of preference, or degree of undermatching, in the initial links depended on whether the shorter initial link led to the shorter or the longer terminal link. These results raise the question of whether bias and undermatching in concurrent schedule performance are independent measures.
Keywords: concurrent chain schedules, variable-interval schedules, fixed-interval schedules, preference, bias, pecking, pigeons
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum W. M. On two types of deviation from the matching law: bias and undermatching. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jul;22(1):231–242. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M., Rachlin H. C. Choice as time allocation. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):861–874. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: a baseline for the study of reinforcement magnitude. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:299–300. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison M. C. Preference for mixed-interval versus fixed-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Mar;12(2):247–252. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison M. C. Preference for mixed-interval versus fixed-interval schedules: number of component intervals. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Mar;17(2):169–176. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison M. C., Temple W. Preference for fixed-interval schedules: an alternative model. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Nov;20(3):393–403. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison M. C., Temple W. Preference for fixed-interval terminal links in a three-key concurrent chain schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jul;22(1):11–19. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan B., Fantino E. Choice for periodic schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Jul;14(1):73–86. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.14-73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E. Choice and rate of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):723–730. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E. Preference for mixed- versus fixed-ratio schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jan;10(1):35–43. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. SECONDARY REINFORCEMENT AND RATE OF PRIMARY REINFORCEMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Jan;7:27–36. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollard V., Davison M. C. Preference for qualitatively different reinforcers. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Nov;16(3):375–380. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.16-375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen P. On the measurement of reinforcement frequency in the study of preference. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 May;11(3):263–269. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen P. Preference for fixed-interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Sep;14(2):127–131. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.14-127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb B., Davison M. C. Performance in concurrent interval schedules: a systematic replication. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Sep;24(2):191–197. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.24-191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. W. Reinforcer effectiveness as a function of reinforcer rate and magnitude: a comparison of concurrent performances. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Nov;20(3):461–471. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires N., Fantino E. A model for choice in simple concurrent and concurrent-chains schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Jan;15(1):27–38. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todorov J. C. Interaction of frequency and magnitude of reinforcement on concurrent performances. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 May;19(3):451–458. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw G. R., Davison M. C. Preference for fixed-interval schedules: effects of initial-link length. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Mar;21(2):331–340. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


