Abstract
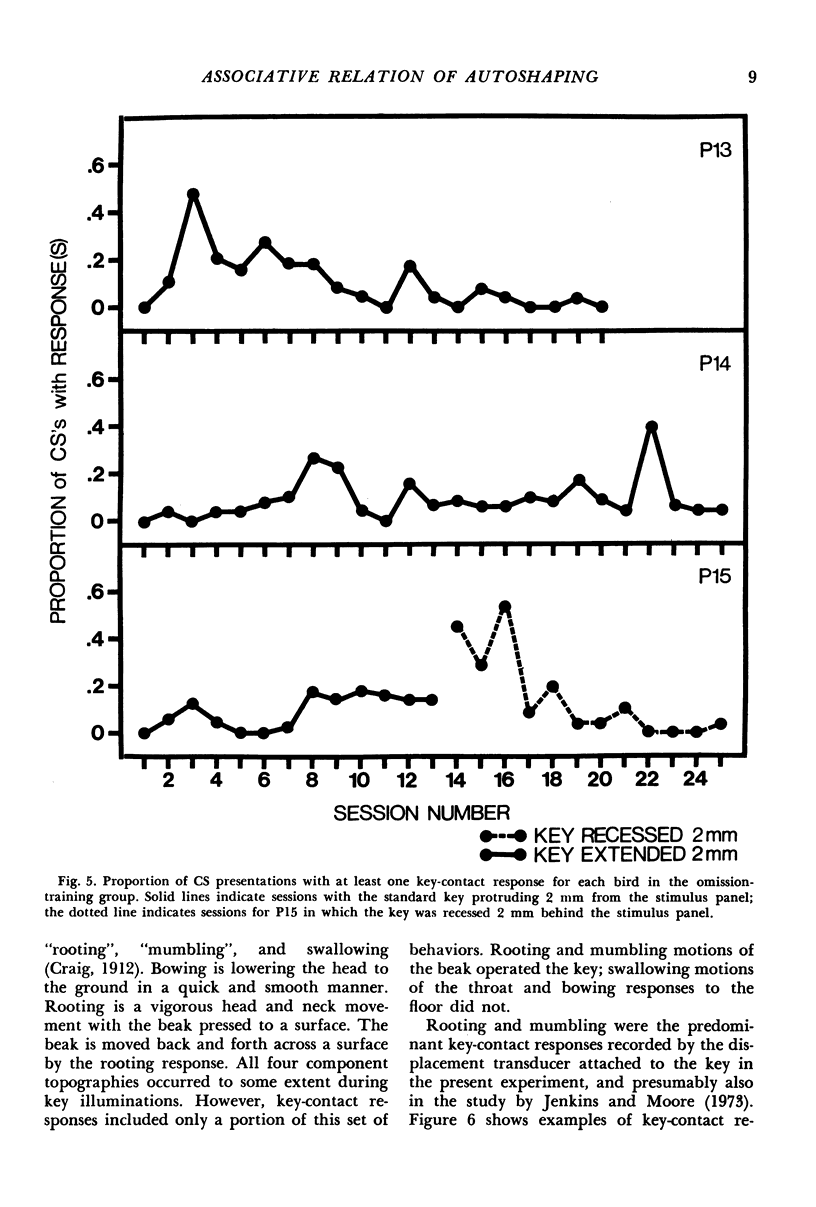
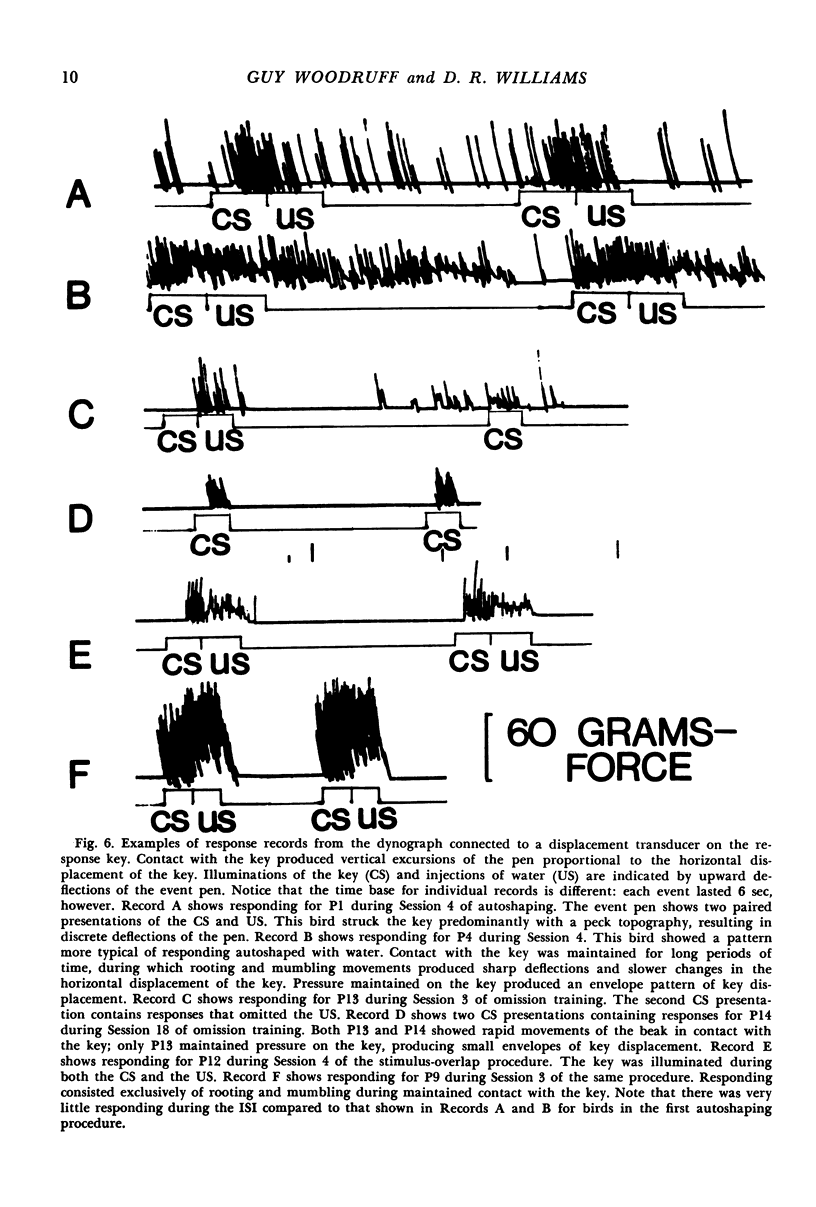
Fifteen pigeons were exposed to either response-independent or response-dependent schedules of water reinforcement, whereby water was injected directly into the unrestrained pigeons' mandibles. Key-contact responses were released by a lighted key correlated with water, but not by a lighted key uncorrelated with water. A negative response-reinforcer contingency suppressed autoshaped key-contact responses, resulting in responding directed away from the lighted key. In all pigeons, water injected directly into the mandibles elicited a consummatory fixed-action pattern of “mumbling” and swallowing. The lighted key correlated with water released a broader set of both appetitive and consummatory responses: approach to the lighted key, “bowing”, “rooting”, “mumbling”, and swallowing. Key-contact responses were “rooting” and “mumbling” motions of the beak on the surface of the key. Views of autoshaping based on stimulus substitution or stimulus surrogation do not fully explain the origin of autoshaped responses not previously elicited by the reinforcer. The present findings are consonant with views of conditioning that emphasize the large degree of biological pre-organization in conditioned response patterns, and the importance of associative factors in the control of such patterns.
Keywords: autoshaping, respondent conditioning, stimulus substitution, stimulus surrogation, “learned release”, water reinforcer, species-specific behavior, key peck, pigeon
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrera F. J. Centrifugal selection of signal-directed pecking. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Sep;22(2):341–355. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. L., Jenkins H. M. Auto-shaping of the pigeon's key-peck. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Jan;11(1):1–8. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamzu E. R., Williams D. R. Associative factors underlying the pigeon's key pecking in auto-shaping procedures. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Mar;19(2):225–232. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamzu E., Schwartz B. The maintenance of key pecking by stimulus-contingent and response-independent food presentation. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Jan;19(1):65–72. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamzu E., Williams D. R. Classical conditioning of a complex skeletal response. Science. 1971 Mar 5;171(3974):923–925. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3974.923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins H. M., Moore B. R. The form of the auto-shaped response with food or water reinforcers. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Sep;20(2):163–181. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins C. C., Beavers W. O., Hancock R. A., Hemmendinger P. C., Hemmendinger D., Ricci J. A. Some variables affecting rate of key pecking during response-independent procedures (autoshaping). J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Jul;24(1):59–72. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.24-59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rescorla R. A., Solomon R. L. Two-process learning theory: Relationships between Pavlovian conditioning and instrumental learning. Psychol Rev. 1967 May;74(3):151–182. doi: 10.1037/h0024475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. R., Williams H. Auto-maintenance in the pigeon: sustained pecking despite contingent non-reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Jul;12(4):511–520. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


