Abstract
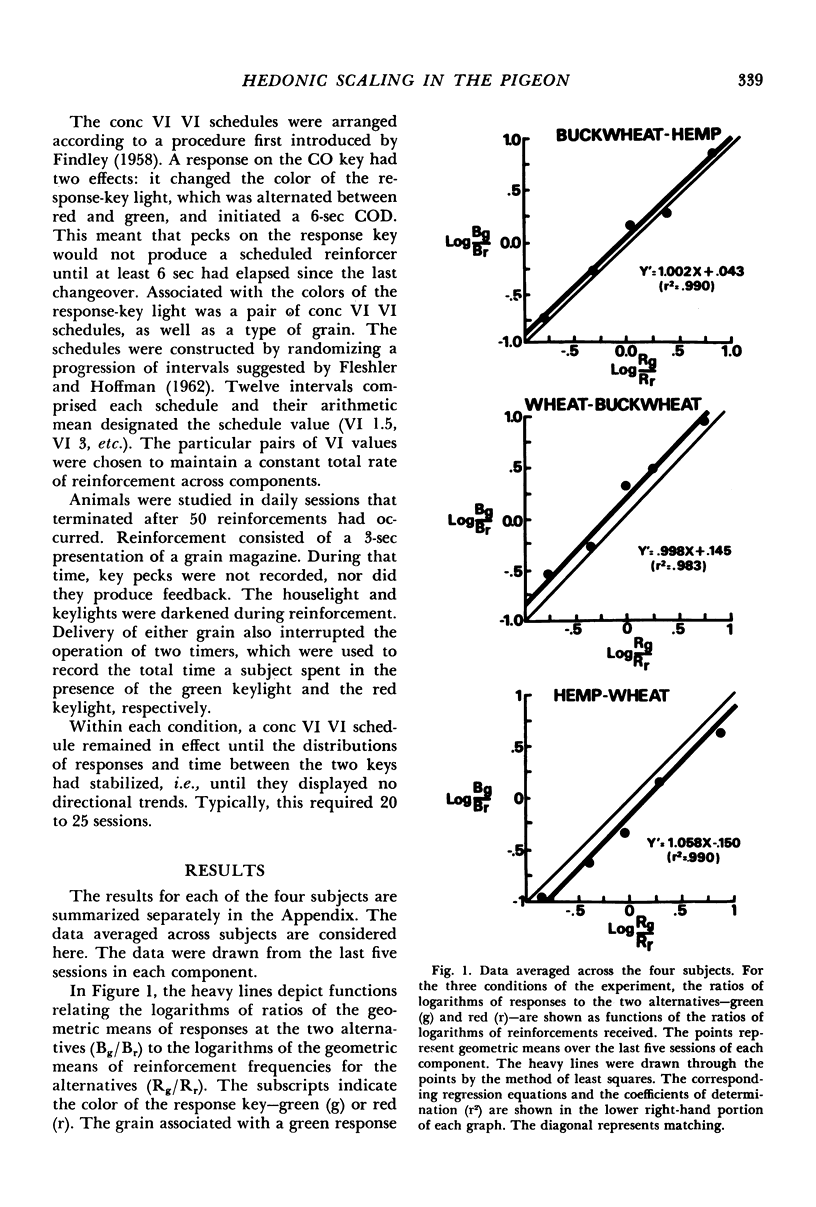
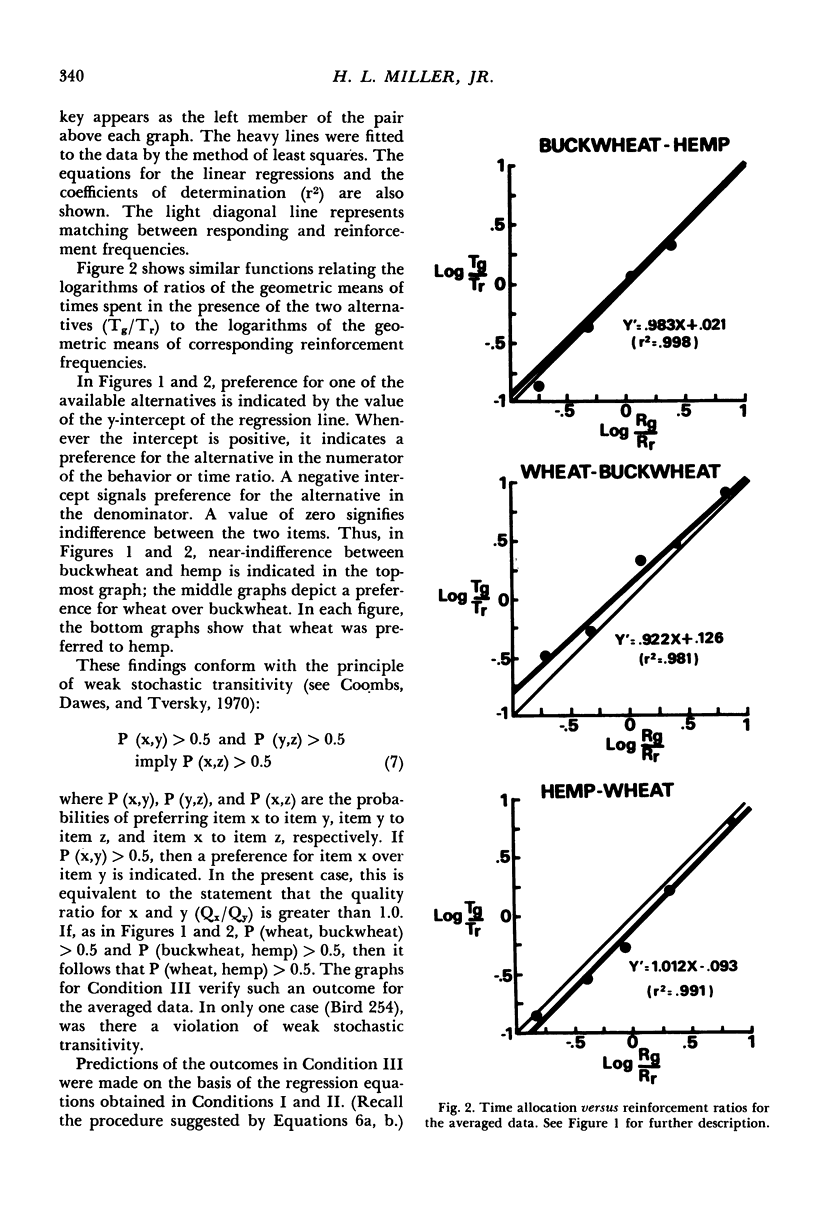
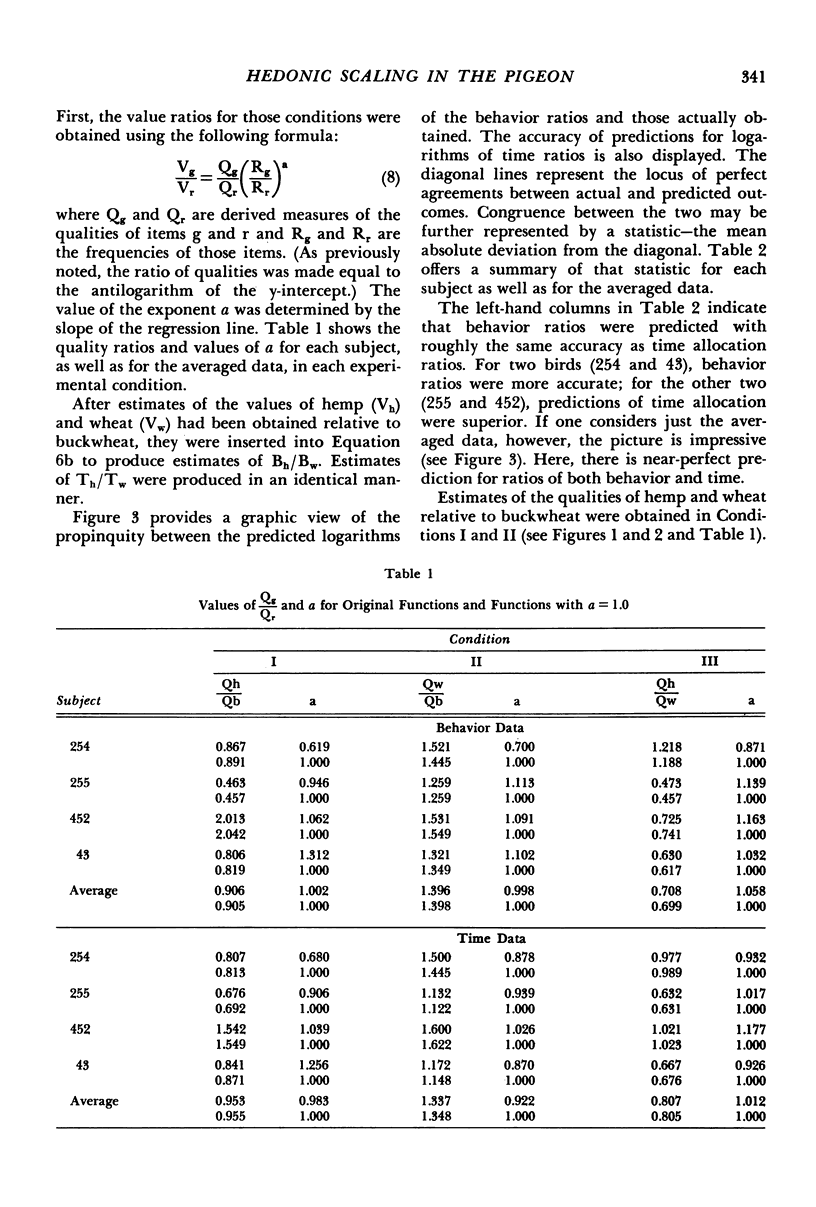
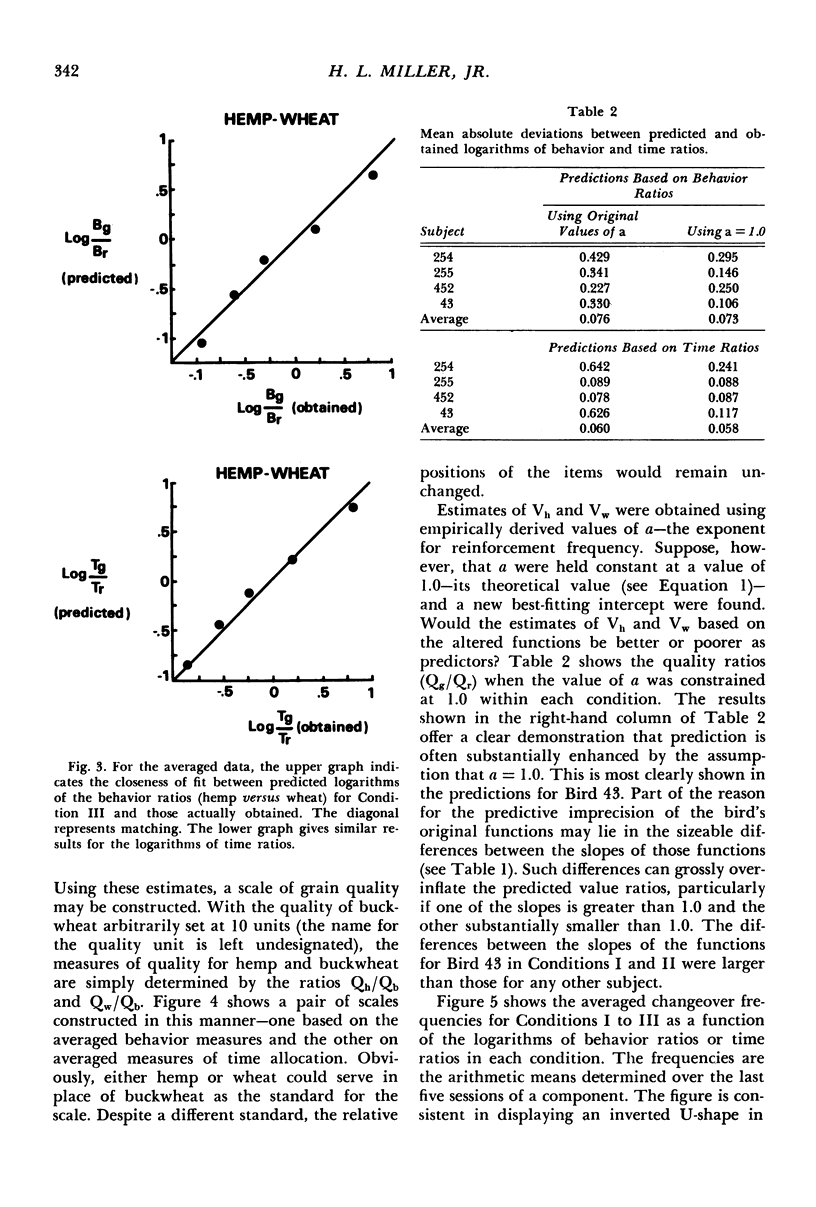
Four slightly hungry pigeons chose between pairs of grains in a Findley concurrent choice procedure. For Condition I, choice involved hemp versus buckwheat; for Condition II, wheat versus buckwheat; and for Condition III, hemp versus wheat. In all conditions, frequency of reinforcement was arranged according to concurrent variable-interval variable-interval schedules. On the assumption that subjects matched their behavior and time distributions to those of reinforcer value, the choice functions obtained in Conditions I and II were transformed to yield estimates of values of hemp and wheat relative to buckwheat. These, in turn, provided predictions about behavior and time allocation in Condition III. In general, the predicted outcomes were close to those actually obtained. The results evidence the effectiveness of matching-based hedonic scales in the prediction of choice between qualitatively different reinforcers.
Keywords: matching law, food preference, reinforcer quality, concurrent variable-interval schedules, pigeons
Full text
PDF



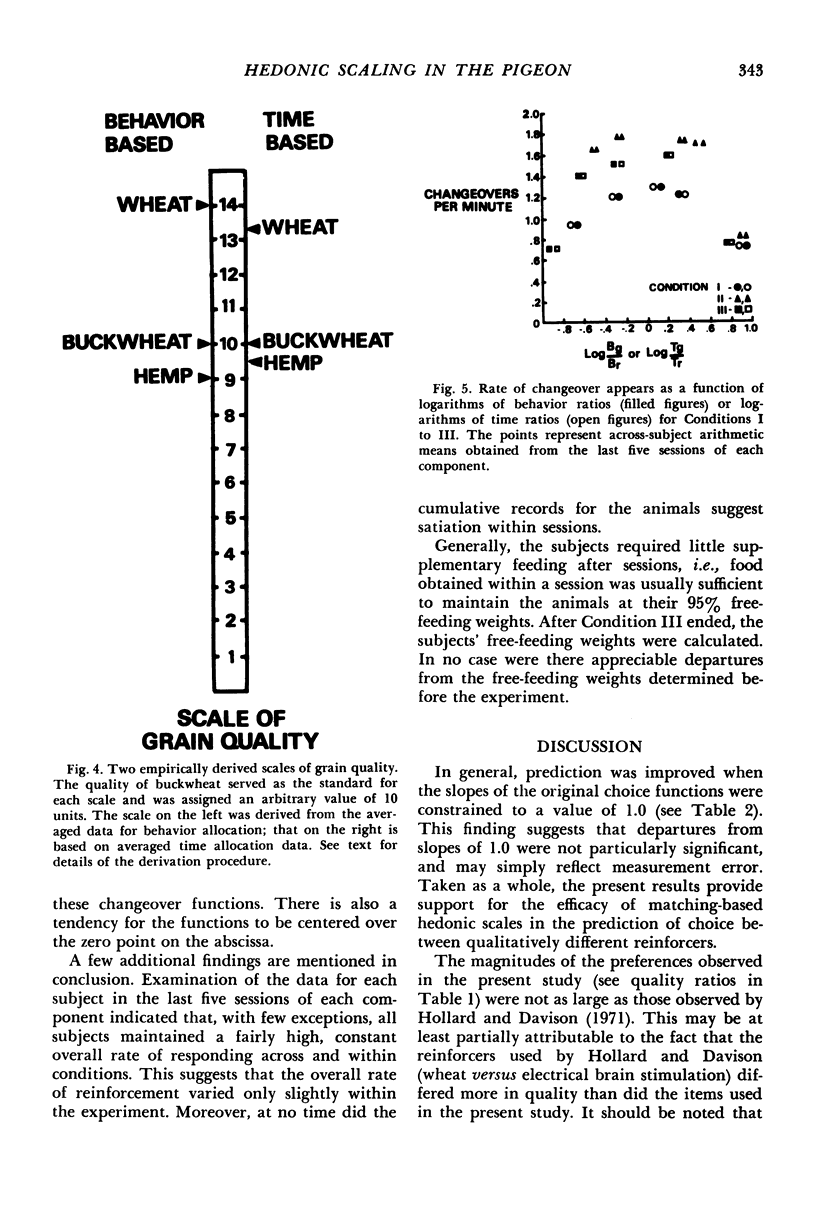


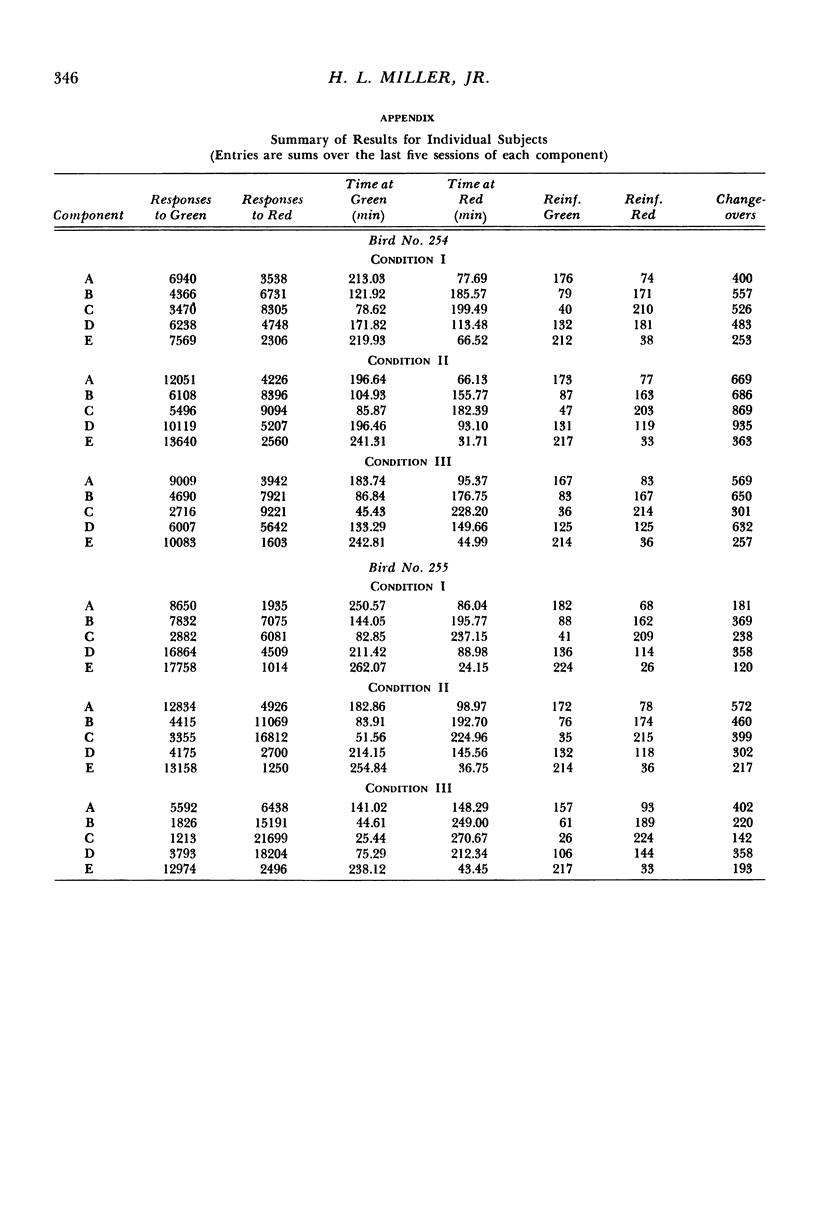
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum W. M. Choice in free-ranging wild pigeons. Science. 1974 Jul 5;185(4145):78–79. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4145.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M., Rachlin H. C. Choice as time allocation. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):861–874. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M. Time allocation in human vigilance. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Jan;23(1):45–53. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.23-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E., Squires N., Delbrück N., Peterson C. Choice behavior and the accessibility of the reinforcer. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jul;18(1):35–43. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findley J. D. Preference and Switching under Concurrent Scheduling. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Apr;1(2):123–144. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. Formal properties of the matching law. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jan;21(1):159–164. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. Quantitative hedonism. J Psychiatr Res. 1971 Aug;8(3):399–412. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(71)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollard V., Davison M. C. Preference for qualitatively different reinforcers. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Nov;16(3):375–380. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.16-375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen P. The matching law. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 May;17(3):489–495. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander D. G., Irwin R. J. Multiple schedules: effects of the distribution of reinforcements between component on the distribution of responses between conponents. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Sep;11(5):517–524. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSweeney F. K. Matching and contrast on several concurrent treadle-press schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Mar;23(2):193–198. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.23-193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A. Rates and patterns of responding with concurrent fixed-interval and variable-interval reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Sep;16(2):241–247. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.16-241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pliskoff S. S., Brown T. G. Matching with a trio of concurrent variable-interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Jan;25(1):69–73. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.25-69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachlin H. On the tautology of the matching law. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Mar;15(2):249–251. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKINNER B. F. Are theories of learning necessary? Psychol Rev. 1950 Jul;57(4):193–216. doi: 10.1037/h0054367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. W. Reinforcer effectiveness as a function of reinforcer rate and magnitude: a comparison of concurrent performances. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Nov;20(3):461–471. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder S. R., Holland J. G. Reinforcement of eye movement with concurrent schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):897–903. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staddon J. E. Spaced responding and choice: a preliminary analysis. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):669–682. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todorov J. C. Interaction of frequency and magnitude of reinforcement on concurrent performances. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 May;19(3):451–458. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevett A. J., Davison M. C., Williams R. J. Performance in concurrent interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 May;17(3):369–374. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


