Abstract
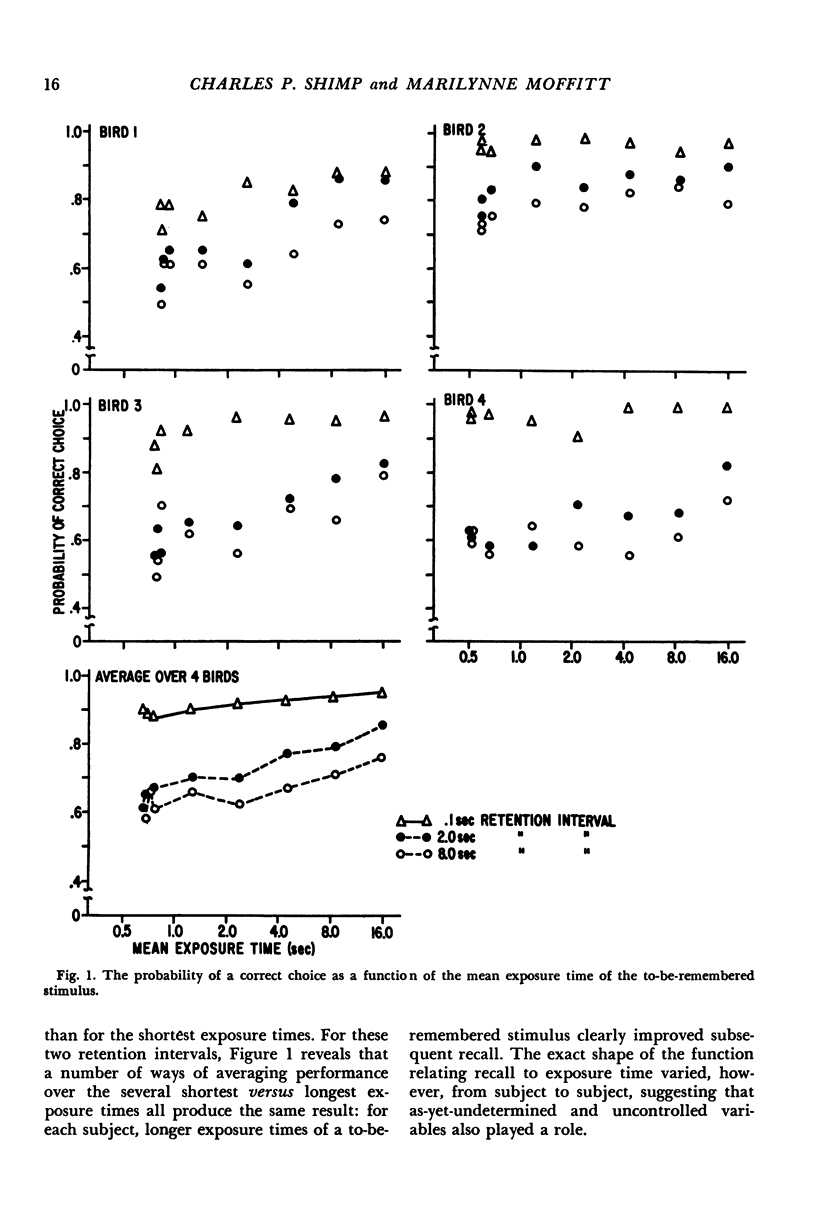
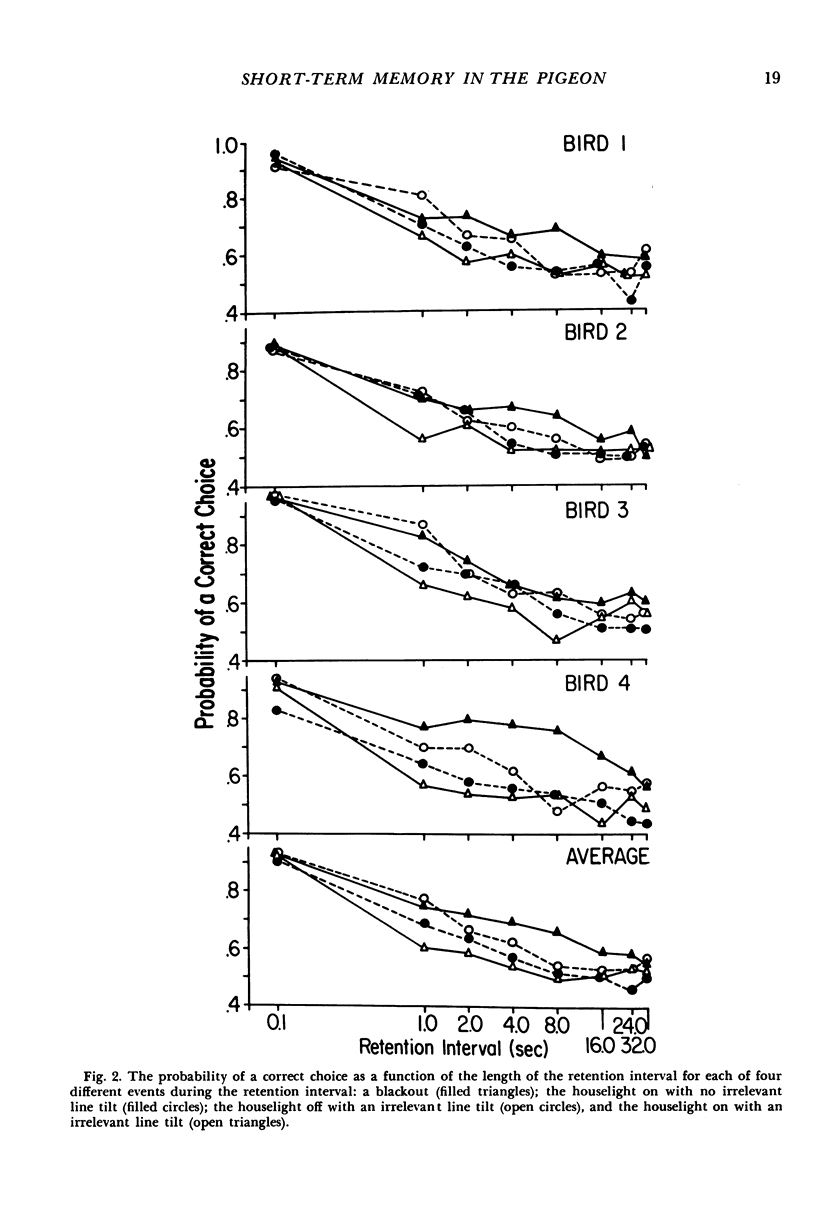
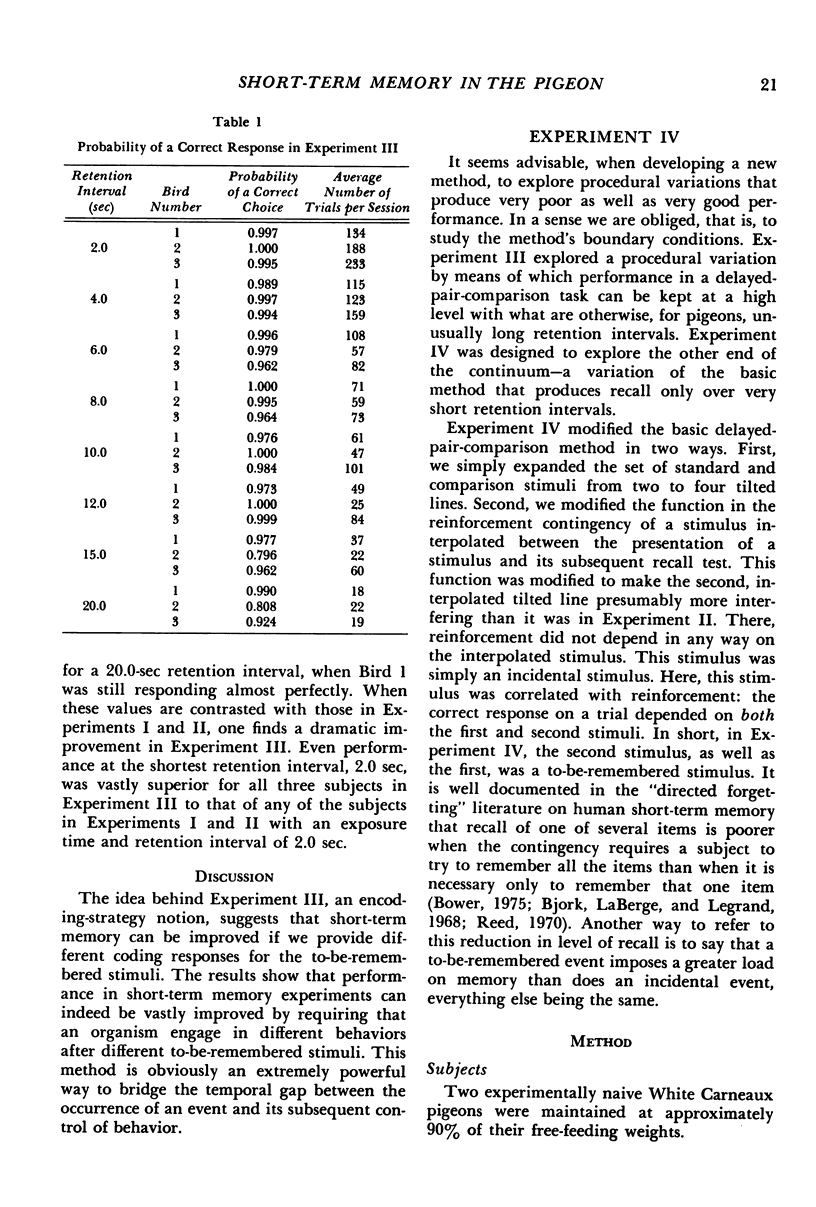
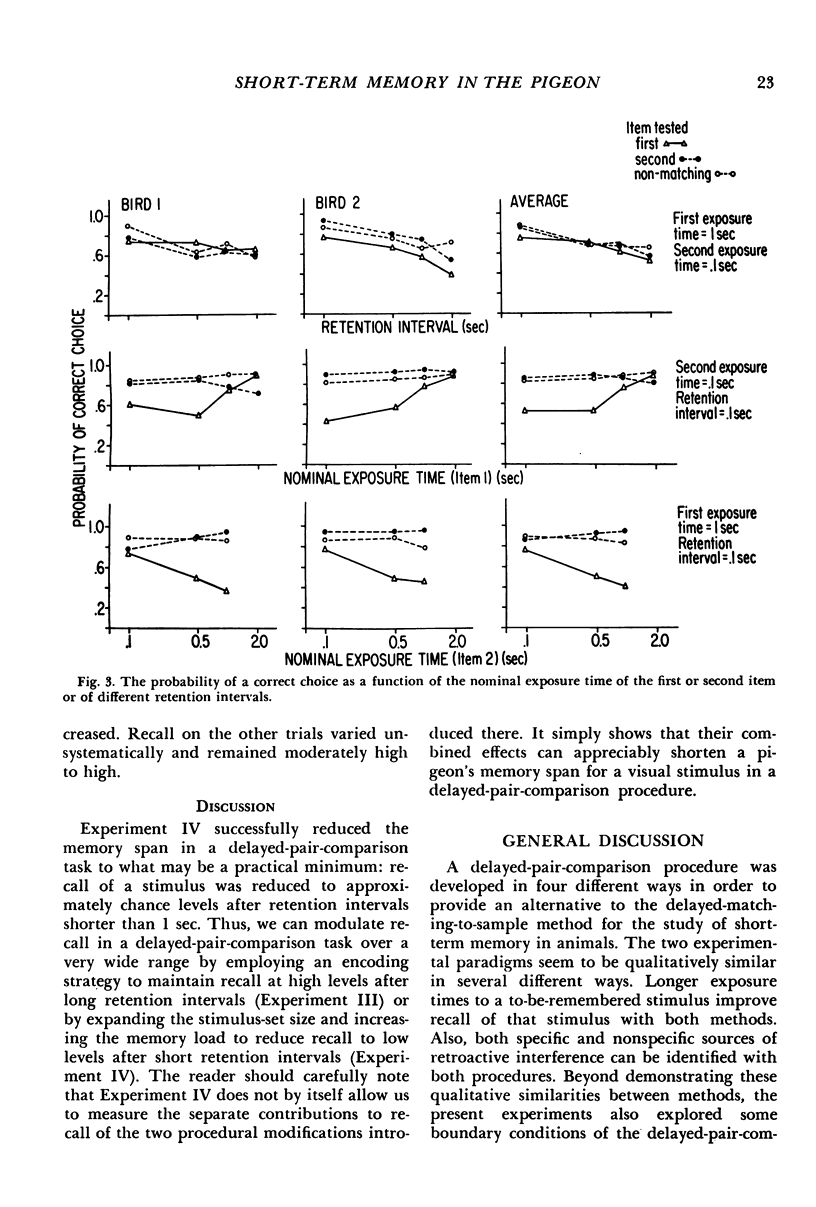
A discrete-trials, delayed-pair-comparison procedure was developed to study visual short-term memory for tilted lines. In four experiments, pigeons' responses on left or right keys were reinforced with food depending on whether a comparison stimulus was or was not the same as a standard stimulus presented earlier in the same trial. In Experimental I, recall was an increasing function of the exposure time of the to-be-remembered stimulus and was a decreasing function of the retention interval. In Experiment II, retroactive interference was investigated: recall was poorer after a retention interval during which was presented either a tilted line or contextual stimuli in the form of the illuminated experimental chamber. In Experiment III, a subject was required to engage, throughout the retention interval, in one or the other of two different behaviors, depending on which of two stimuli a subject was to remember. This mnemonic strategy vastly improved recall after 15- and 20-second retention intervals. In Experiment IV, the opposite end of the performance continuum was studied: by combining the effects of a larger stimulus set and the effects of what presumably was an increased memory load, performance was reduced to approximately chance levels after retention intervals shorter than 1 second.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOUGH D. S. Delayed matching in the pigeon. J Exp Anal Behav. 1959 Apr;2:151–160. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1959.2-151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C. Self-inhibiting effects of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 May;19(3):517–526. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumming W. W., Berryman R., Cohen L. R. Acquisition and transfer of zero-delay matching. Psychol Rep. 1965 Oct;17(2):435–445. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1965.17.2.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amato M. R., O'neill W. Effect of delay-interval illumination on matching behavior in the capuchin monkey. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 May;15(3):327–333. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckerman D. A. Generalization and response mediation of a conditional discrimination. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 May;13(3):301–316. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farthing G. W., Opuda M. J. Transfer of matching-to-sample in pigeons. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Mar;21(2):199–213. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes L., Shimp C. P. Reinforcement of behavioral patterns: shaping a scallop. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Jan;23(1):3–16. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.23-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lydersen T., Perkins D. Effects of response-produced stimuli upon conditional discrimination performance. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Mar;21(2):307–314. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER G. A. The magical number seven plus or minus two: some limits on our capacity for processing information. Psychol Rev. 1956 Mar;63(2):81–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massaro D. W. Retroactive interference in short-term recognition memory for pitch. J Exp Psychol. 1970 Jan;83(1):32–39. doi: 10.1037/h0028566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimp C. P., Moffitt M. Short-term memory in the pigeon: stimulus-response associations. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Nov;22(3):507–512. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimp C. P. Short-term memory in the pigeon: the previously reinforced response. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Nov;26(3):487–493. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.26-487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickelgren W. A. Consolidation and retroactive interference in short-term recognition memory for pitch. J Exp Psychol. 1966 Aug;72(2):250–259. doi: 10.1037/h0023438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. A. Probability learning as a function of momentary reinforcement probability. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 May;17(3):363–368. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


