Abstract
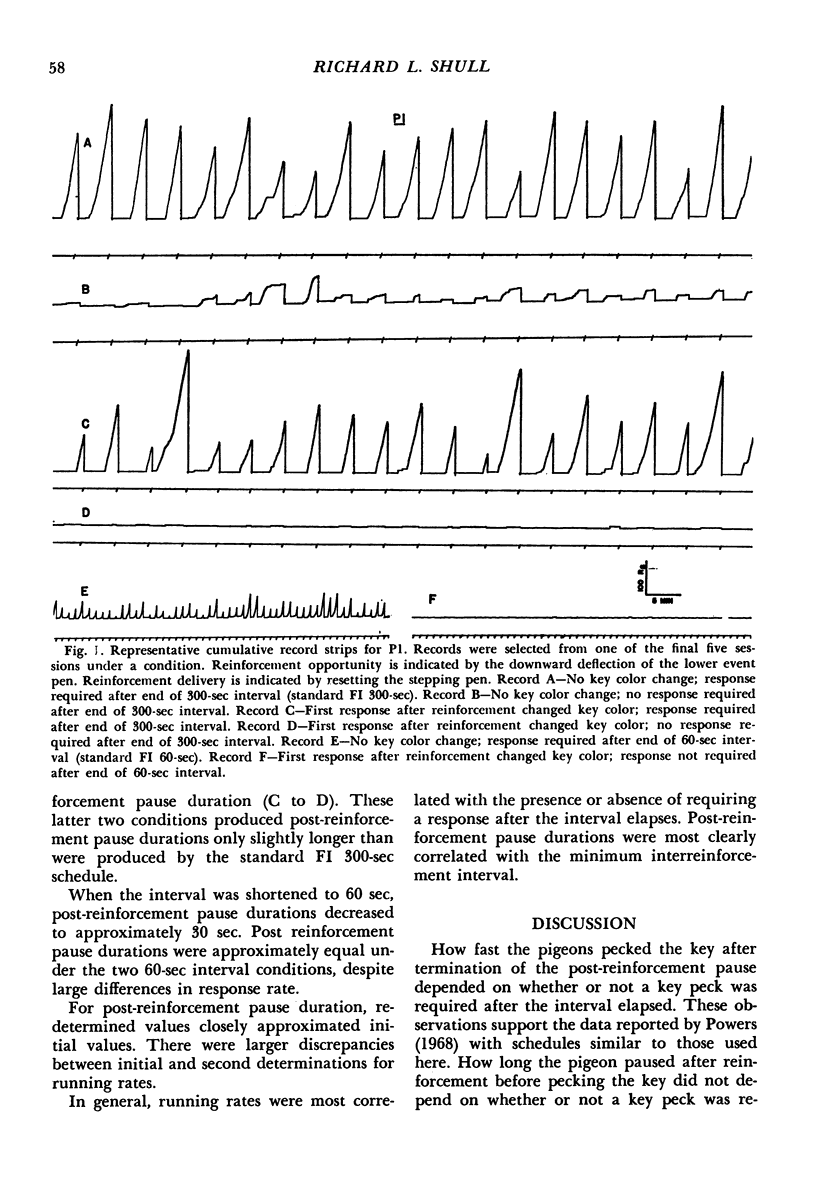
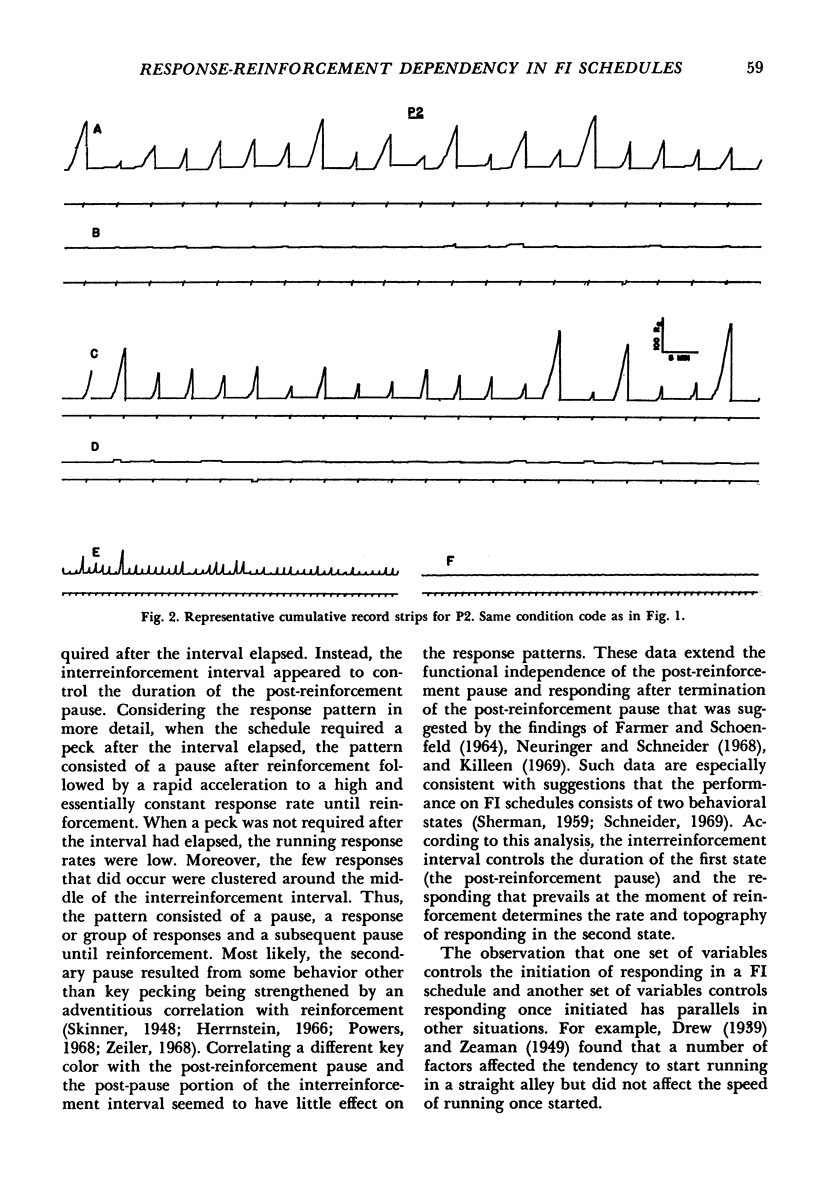
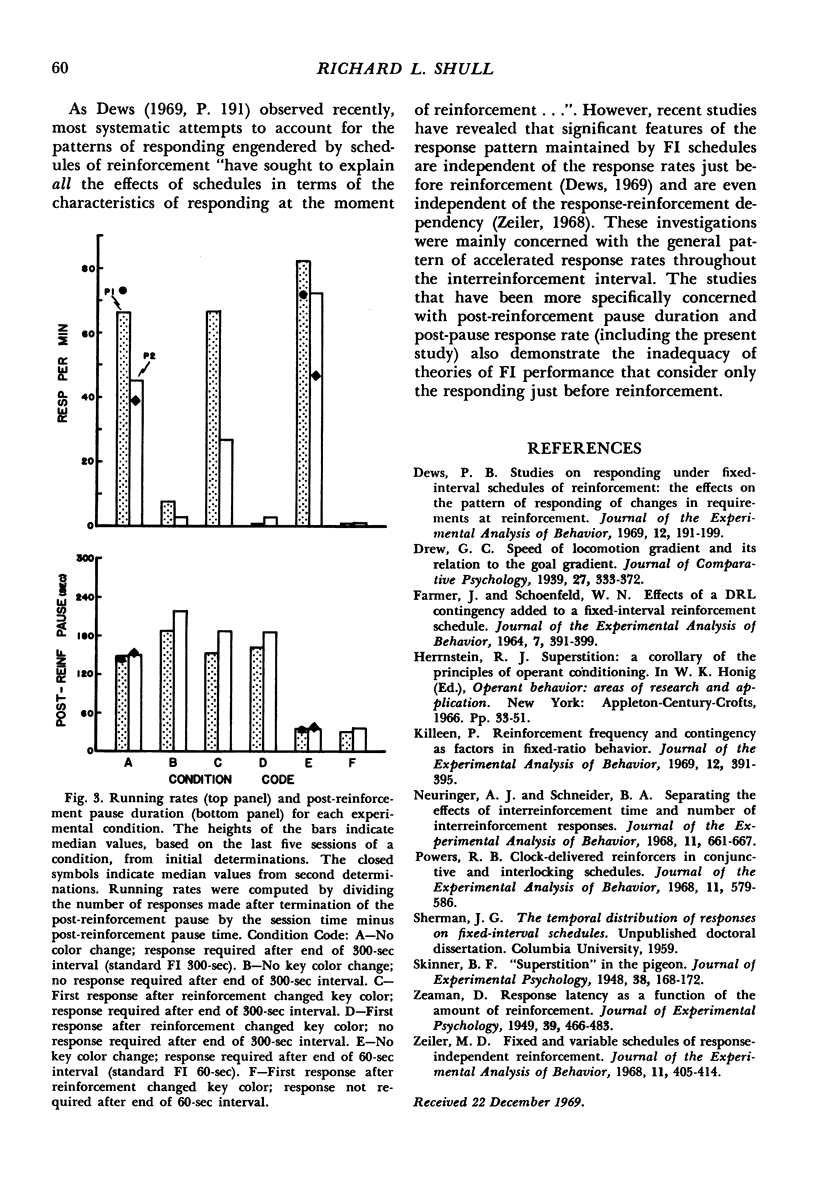
Pigeons were exposed to four different schedules of food reinforcement that arranged a fixed minimum time interval between reinforcements (60 sec or 300 sec). The first was a standard fixed-interval schedule. The second was a schedule in which food was presented automatically at the end of the fixed time interval as long as a response had occurred earlier. The third and fourth schedules were identical to the first two except that the first response after reinforcement changed the color on the key. When the schedule required a peck after the interval elapsed, the response pattern consisted of a pause after reinforcement followed by responding at a high rate until reinforcement. When a response was not required after the termination of the interval, the pattern consisted of a pause after reinforcement, followed by responses and then by a subsequent pause until reinforcement. Having the first response after reinforcement change the color on the key had little effect on performance. Post-reinforcement pause duration varied with the minimum interreinforcement interval but was unaffected by whether or not a response was required after the interval elapsed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dews P. B. Studies on responding under fixed-interval schedules of reinforcement: the effects on the pattern of responding of changes in requirements at reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Mar;12(2):191–199. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARMER J., SCHOENFELD W. N. EFFECTS OF A DRL CONTINGENCY ADDED TO A FIXED-INTERVAL REINFORCEMENT SCHEDULE. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Nov;7:391–399. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen P. Reinforcement frequency and contingency as factors in fixed-ratio behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 May;12(3):391–395. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J., Schneider B. A. Separating the effects of interreinforcement time and number of interreinforcement responses. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):661–667. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers R. B. Clock-delivered reinforcers in conjunctive and interlocking schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Sep;11(5):579–586. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler M. D. Fixed and variable schedules of response-independent reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Jul;11(4):405–414. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


