Abstract
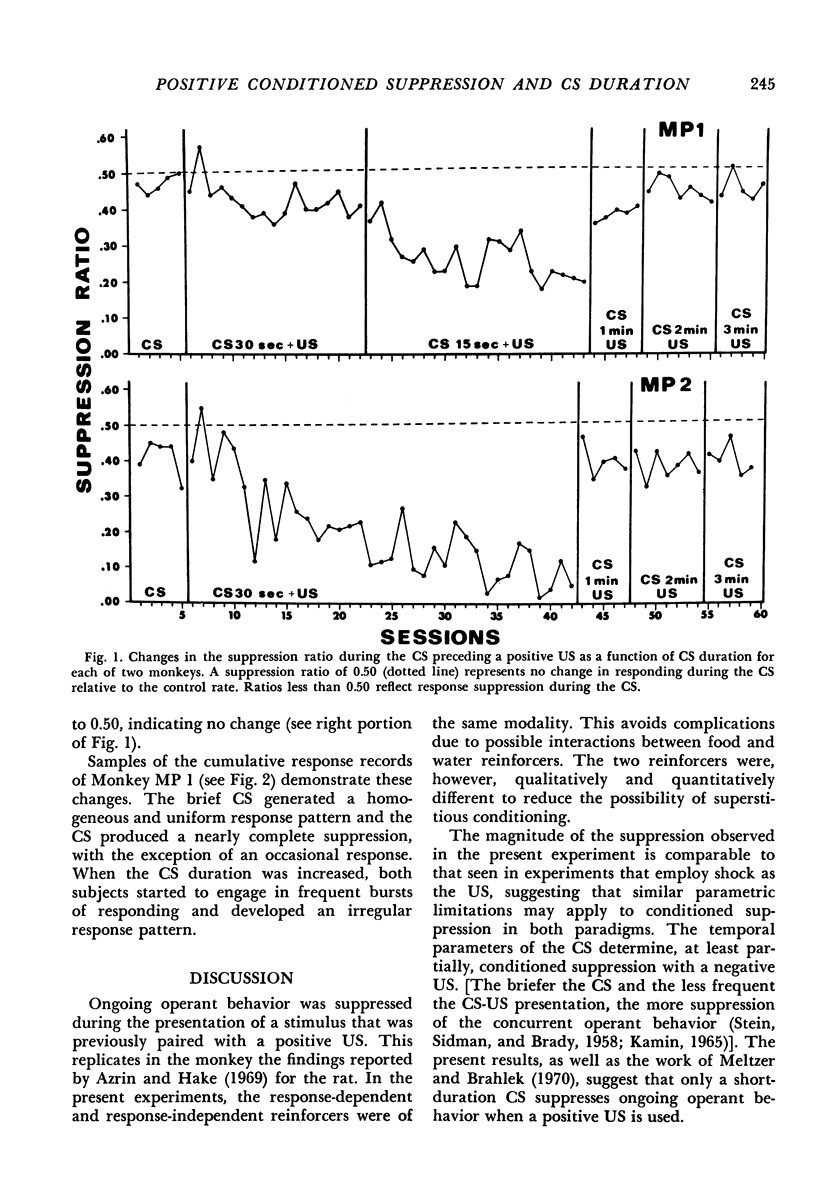
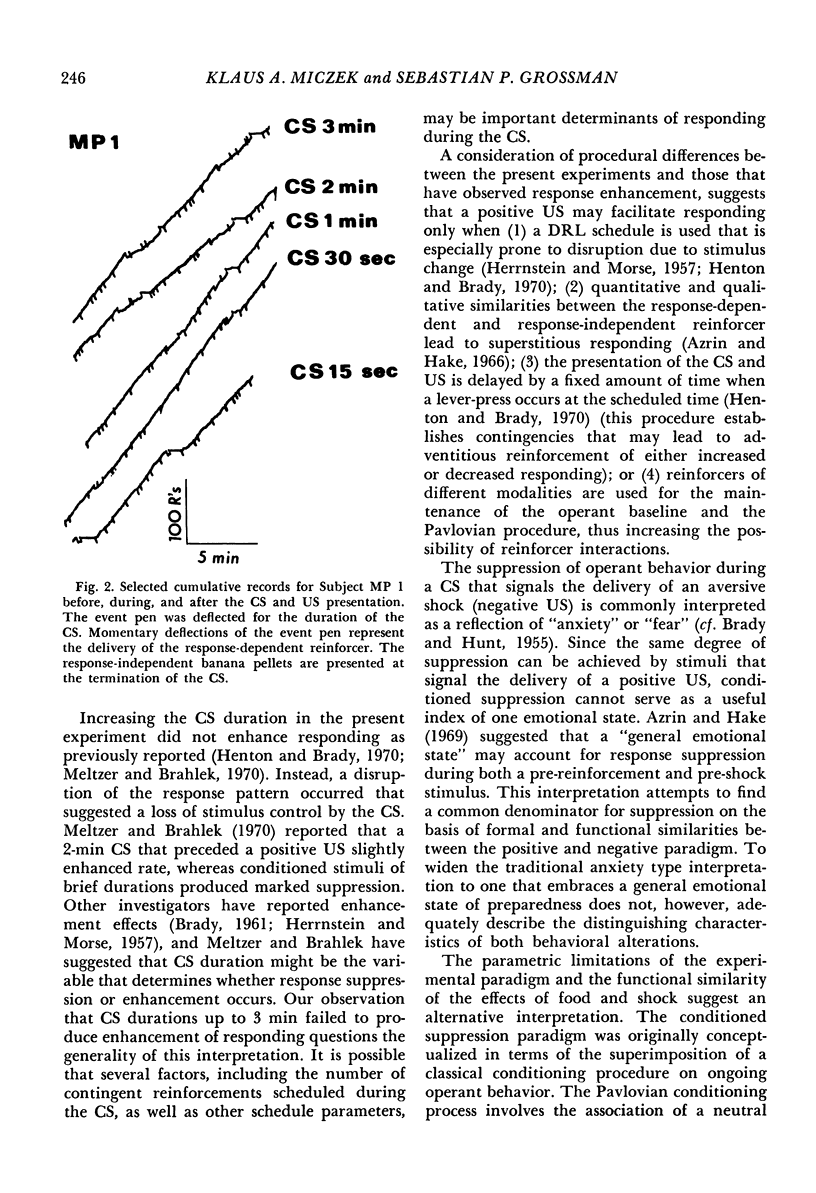
During a brief conditioned stimulus (15 or 30 sec) that terminated with the response-independent delivery of banana pellets, operant responding reinforced by other food pellets according to a variable-interval schedule of reinforcement was suppressed in the squirrel monkey. Conditioned stimuli of longer duration (1, 2, and 3 min) did not reliably affect the rate of operant performance. Brief conditioned stimuli generated homogeneous response patterns of nearly complete suppression. Increasing the CS duration did not enhance responding, as previously reported, but led to alternate bursting and pausing, which suggested a loss of control by the conditioned stimulus. The results suggest that the magnitude of “positive” or “negative” conditioned suppression reflects the strength of the classical conditioning process.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANNAU Z., KAMIN L. J. The conditioned emotional response as a function of intensity of the US. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1961 Aug;54:428–432. doi: 10.1037/h0042199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azrin N. H., Hake D. F. Positive conditioned suppression: conditioned suppression using positive reinforcers as the unconditioned stimuli. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Jan;12(1):167–173. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKE D. F., AZRIN N. H. An apparatus for delivering pain shock to monkevs. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:297–298. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J., MORSE W. H. Some effects of response-independent positive reinforcement on maintained operant behavior. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1957 Oct;50(5):461–467. doi: 10.1037/h0041506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henton W. W., Brady J. V. Operant acceleration during a pre-reward stimulus. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):205–209. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer D., Brahlek J. A. Conditioned suppression and conditioned enhancement with the same positive UCS: an effect of CS duration. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Jan;13(1):67–73. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenfeld W. N., Cumming W. W., Hearst E. ON THE CLASSIFICATION OF REINFORCEMENT SCHEDULES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Aug;42(8):563–570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.8.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein L., Sidman M., Brady J. V. Some effects of Two Temporal Variables on Conditioned Suppression. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Apr;1(2):153–162. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



