Abstract
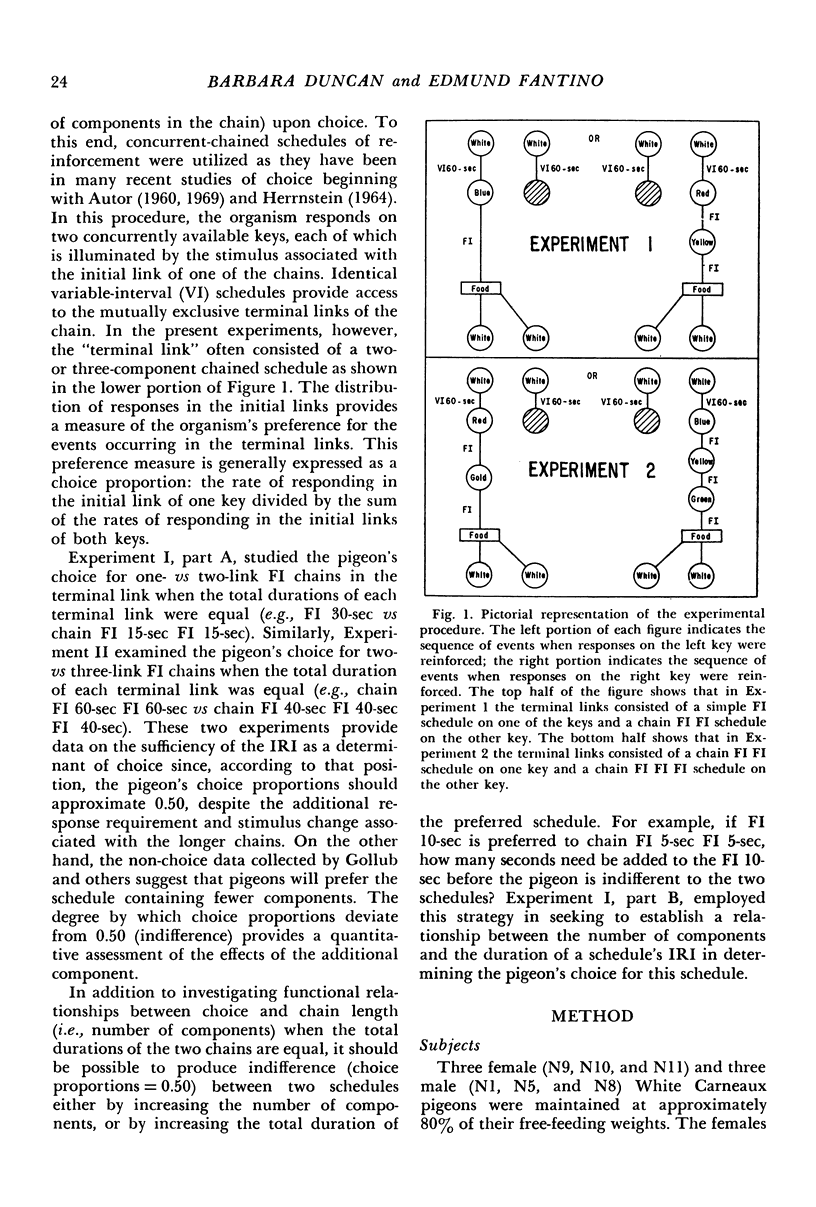
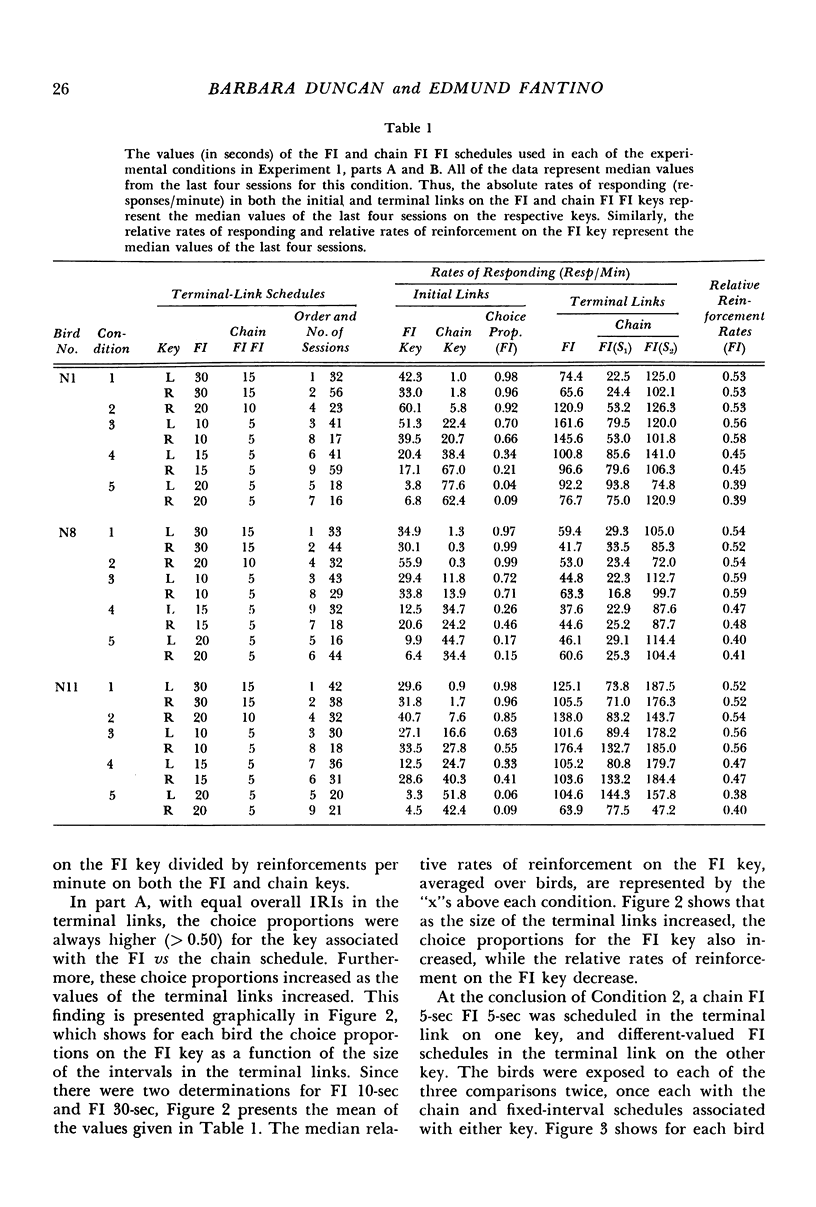
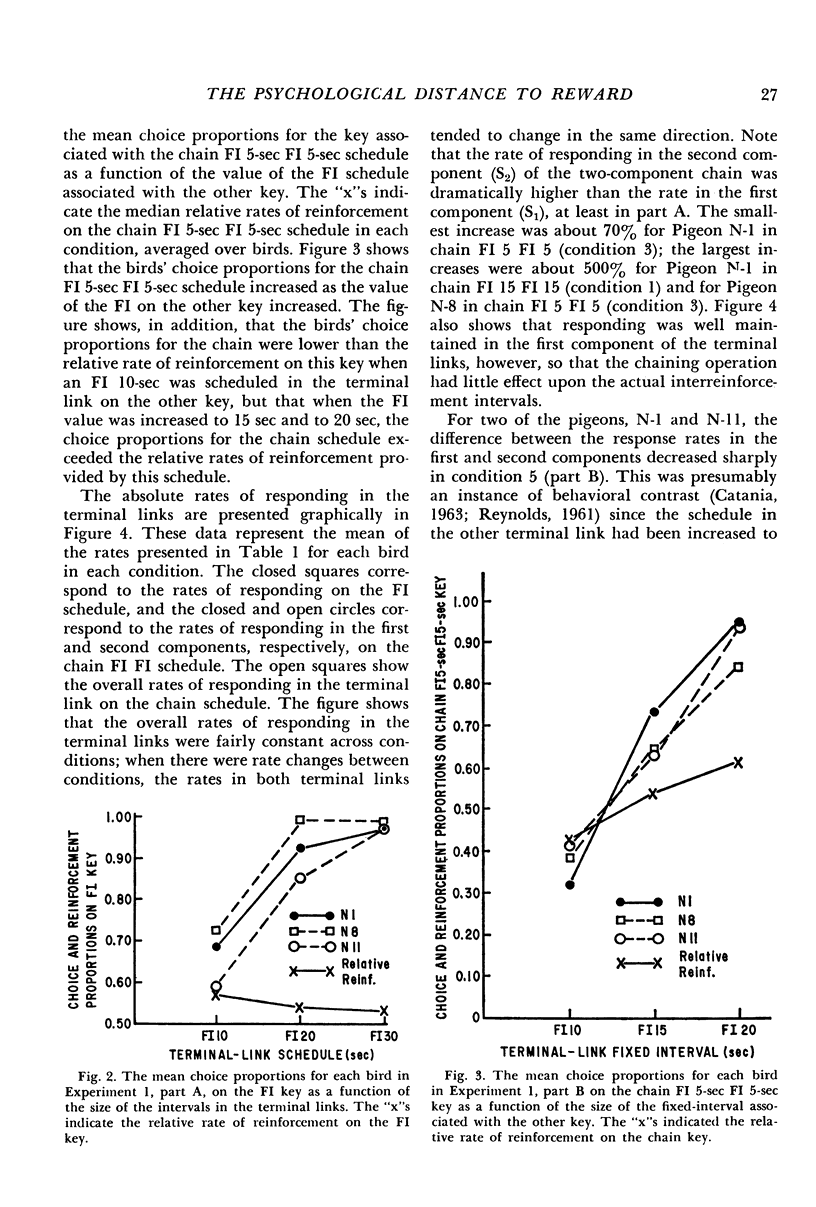
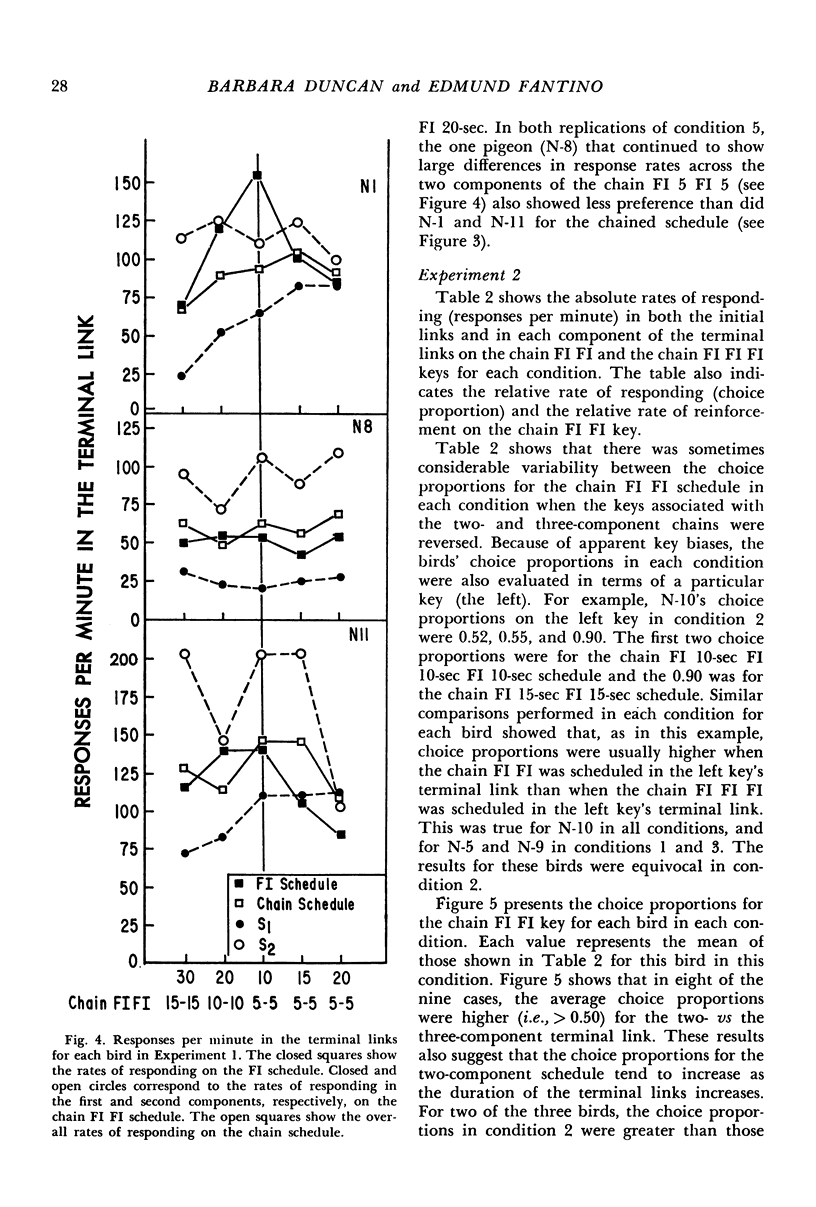
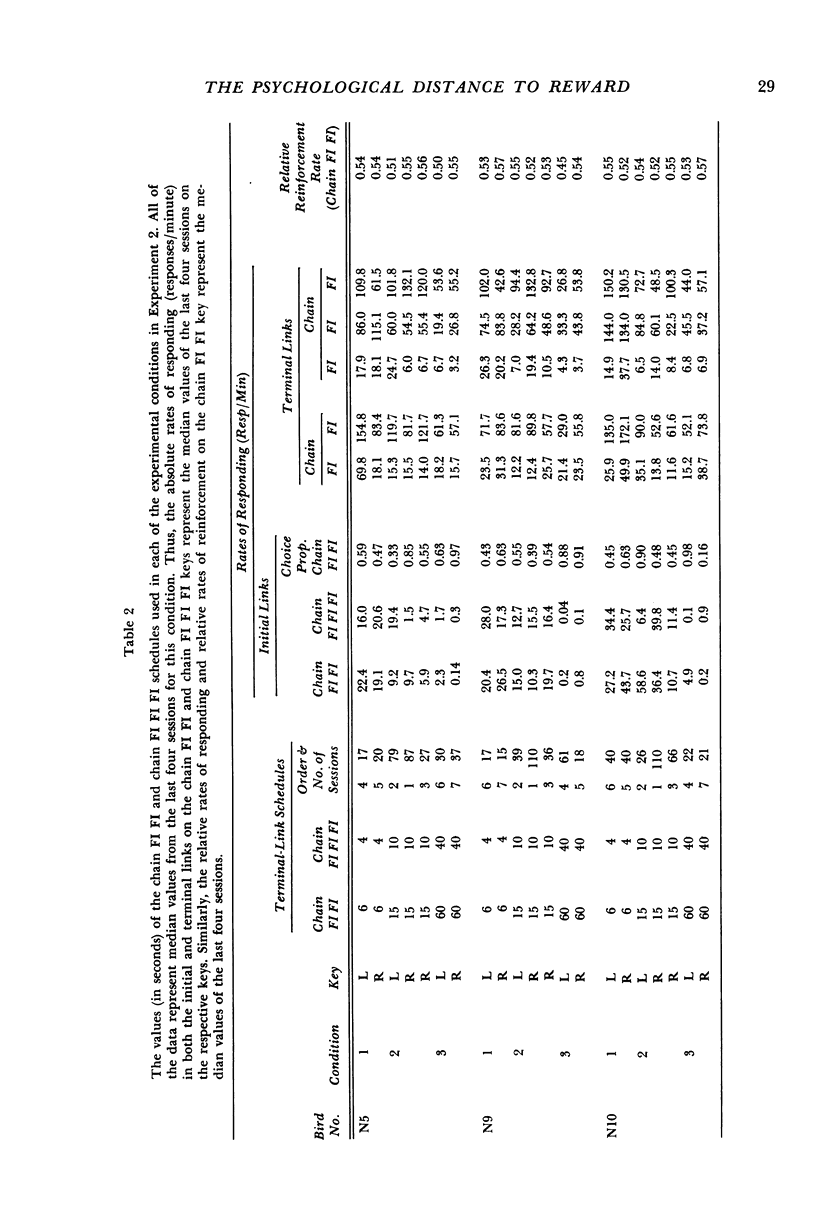
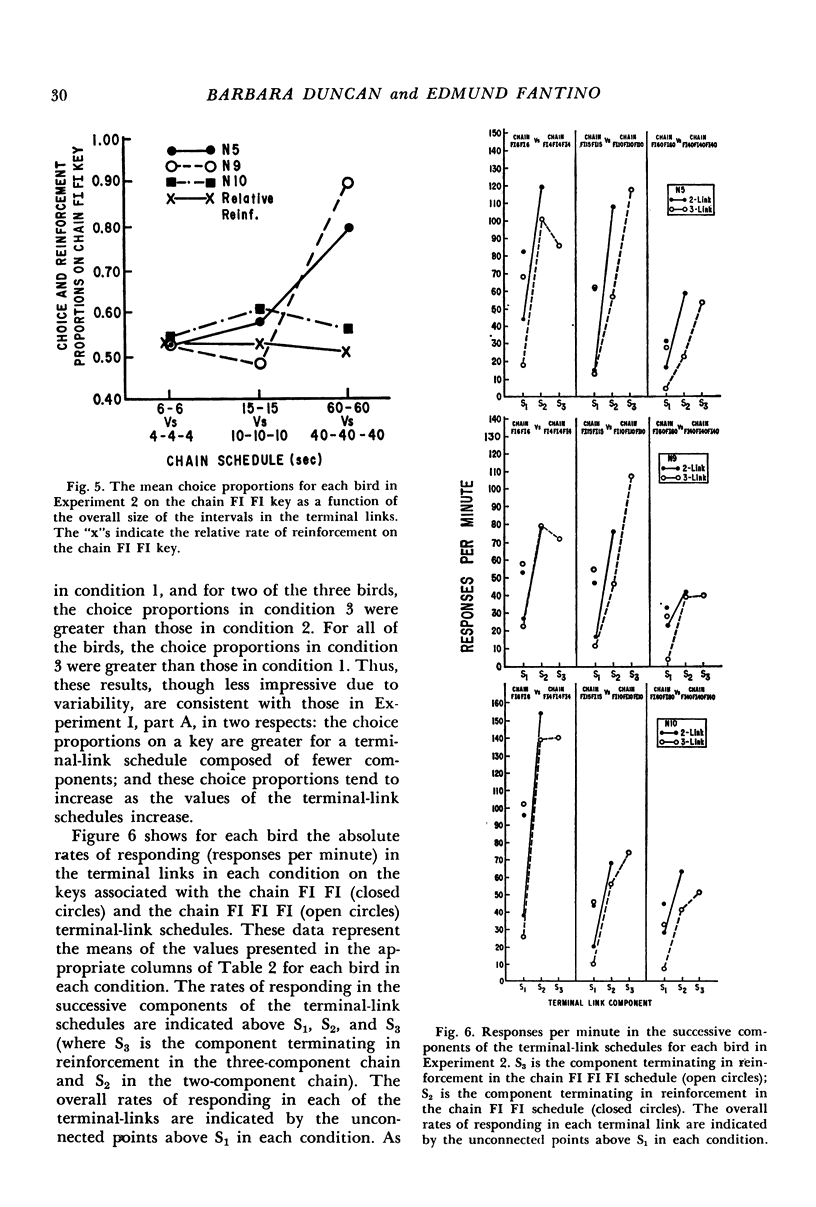
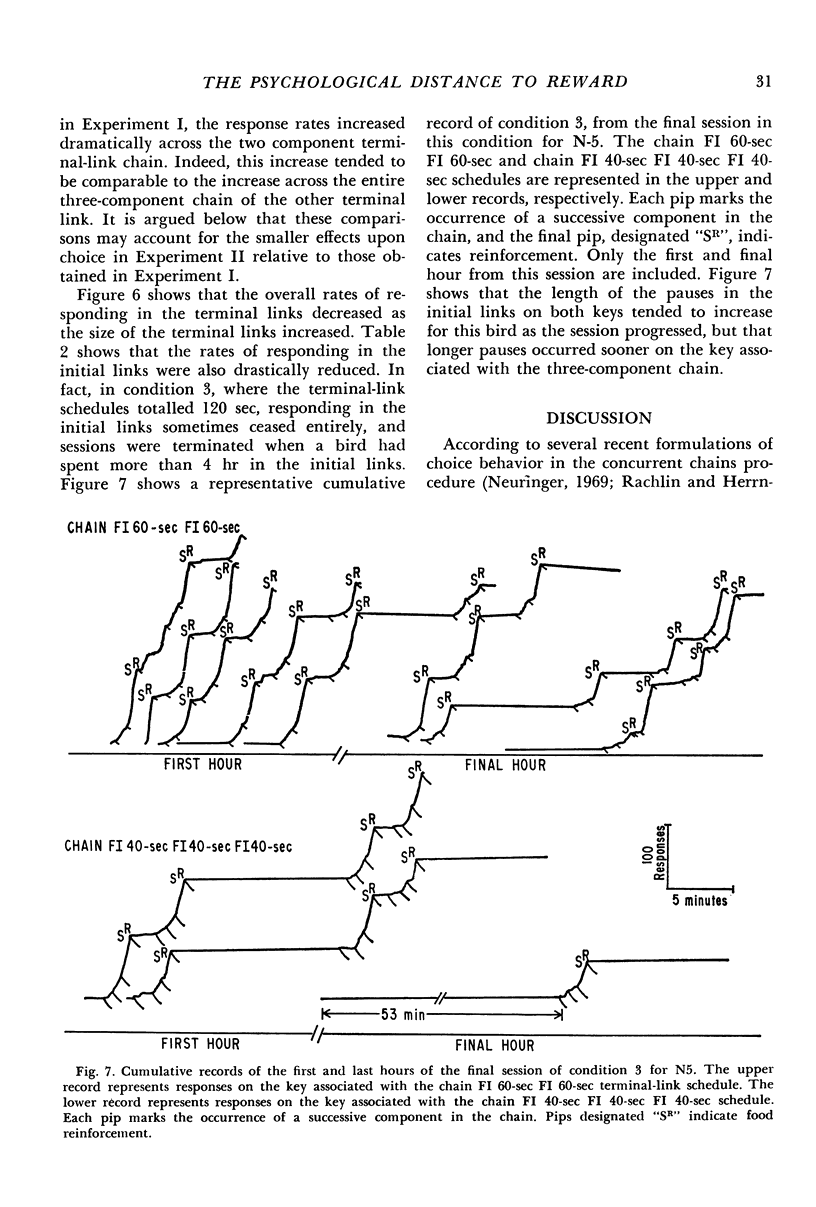
Pigeons' responses in the presence of two concurrently available (initial-link) stimuli produced entry into one of two different and mutually exclusive terminal link stimuli according to identical but independent variable-interval schedules. In one experiment, a two-component chained fixed-interval schedule produced food in one terminal link while a simple fixed-interval schedule produced food in the other terminal link. When the interreinforcement intervals were equal in the two terminal links (i.e., the simple fixed-interval was twice the size of each of the components in the chained schedule) pigeons preferred the simple fixed-interval as measured by their relative rates of responding in the concurrently available initial links. This preference increased as the duration of the terminal links increased. The preference could be reversed by making the simple fixed-interval schedule sufficiently longer than the chained schedule. In the second experiment, the terminal links consisted of two- vs three-component chained fixed-intervals, again with equal interreinforcement intervals. Pigeons preferred the two-component chain to the three-component chain, although these results were less consistent and less dramatic than those in the first experiment. Again, preference increased as the duration of the terminal links increased. The results show that an organism's choice for a schedule will be substantially lowered by the chaining operation even when the interreinforcement interval remains constant.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Byrd L. D., Marr M. J. Relations between patterns of responding and the presentation of stimuli under second-order schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):713–722. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: reinforcement interaction and response independence. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:253–263. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lorge J. Fixed-interval behavior maintained by conditioned reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 May;10(3):271–276. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan B., Fantino E. Choice for periodic schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Jul;14(1):73–86. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.14-73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINDLEY J. D. An experimental outline for building and exploring multi-operant behavior repertoires. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Jan;5(Suppl):113–166. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-s113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E. Choice and rate of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):723–730. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E. Effects of required rates of responding upon choice. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Jan;11(1):15–22. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. SECONDARY REINFORCEMENT AND RATE OF PRIMARY REINFORCEMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Jan;7:27–36. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLEHER R. T., FRY W. T. Stimulus functions in chained fixed-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Apr;5:167–173. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen P. Preference for fixed-interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Sep;14(2):127–131. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.14-127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. K., Gollub L. R. Second-order schedules with fixed-ratio components: variation of component size. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 May;15(3):303–310. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J. Delayed reinforcement versus reinforcement after a fixed interval. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 May;12(3):375–383. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S. Behavioral contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jan;4:57–71. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires N., Fantino E. A model for choice in simple concurrent and concurrent-chains schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Jan;15(1):27–38. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


