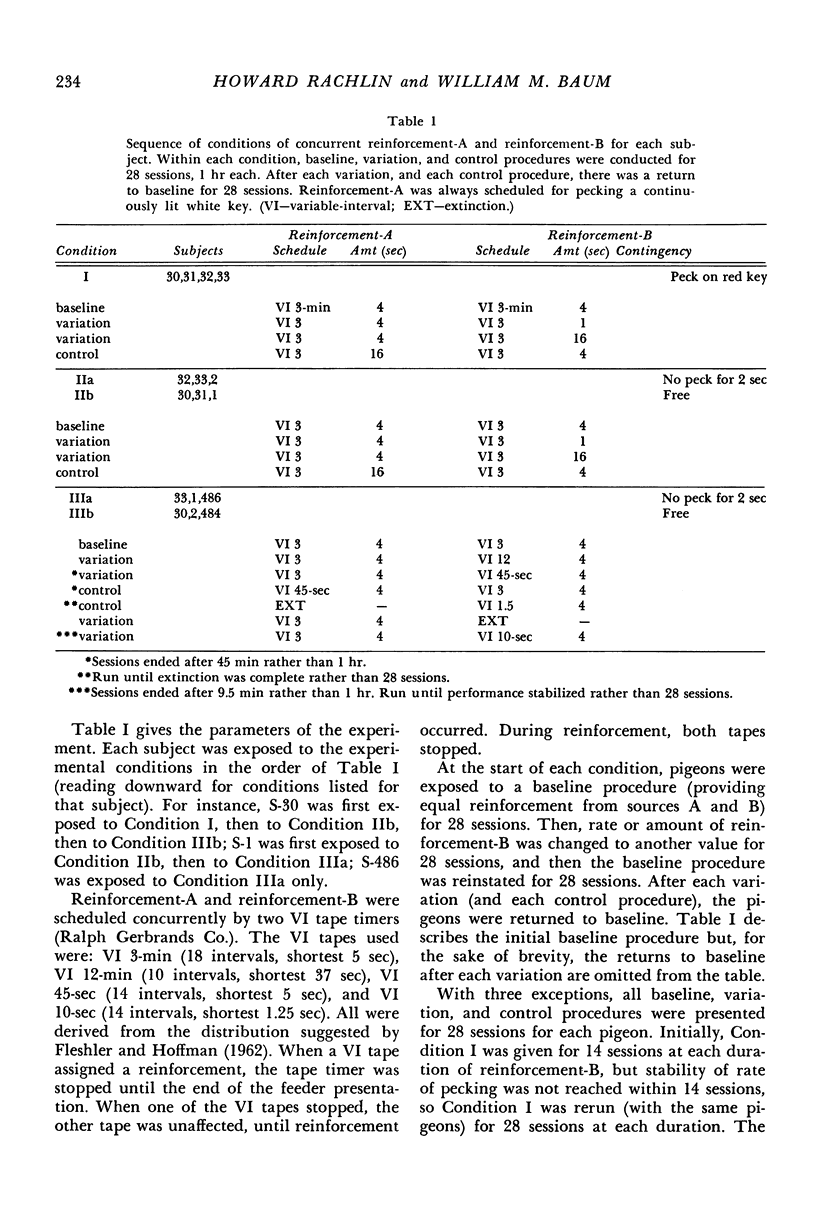
Abstract
In a chamber with a single response key, pigeon's key pecks were reinforced with food according to a variable-interval schedule. In addition, extra reinforcements occurred concurrently according to an independent schedule. In one condition, availability of the extra reinforcements was signalled by a change in key color from white to red. The extra reinforcements occurred after a peck on the red key. In a second condition, the extra reinforcements were unsignalled and occurred only after a 2-sec pause in pecking for one group of subjects and were unsignalled and occurred freely as scheduled for another group of subjects. In the first two conditions, duration of reinforcement was varied. A third condition duplicated the second but varied rate rather than duration of reinforcement. The rate of pecking varied inversely with the amount of extra reinforcement per unit time according to the same function, regardless of the condition regulating occurrence of the extra reinforcements, and regardless of whether or not a 2-sec pause was required for their occurrence. The shape of this function was predicted by Herrnstein's (1970) matching law.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum W. M., Rachlin H. C. Choice as time allocation. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):861–874. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield T. M. Some temporal properties of behavioral contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Mar;10(2):159–164. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. L., Jenkins H. M. Auto-shaping of the pigeon's key-peck. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Jan;11(1):1–8. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: a baseline for the study of reinforcement magnitude. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:299–300. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: reinforcement interaction and response independence. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:253–263. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C. Concurrent performances: inhibition of one response by reinforcement of another. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):731–744. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C., Reynolds G. S. A quantitative analysis of the responding maintained by interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 May;11(3 Suppl):327–383. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-s327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLESHLER M., HOFFMAN H. S. A progression for generating variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:529–530. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. Relative and absolute strength of response as a function of frequency of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jul;4:267–272. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliday M. S., Boakes R. A. Behavioral contrast and response independent reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Nov;16(3):429–434. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.16-429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. On the law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):243–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander D. G., Irwin R. J. Multiple schedules: effects of the distribution of reinforcements between component on the distribution of responses between conponents. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Sep;11(5):517–524. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J. Animals respond for food in the presence of free food. Science. 1969 Oct 17;166(3903):399–401. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3903.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A. Differential reinforcement and stimulus control of not responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):715–726. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S. Behavioral contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jan;4:57–71. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachlin H., Baum W. M. Response rate as a function of amount of reinforcement for a signalled concurrent response. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Jan;12(1):11–16. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimp C. P., Wheatley K. L. Matching to relative reinforcement frequency in multiple schedules with a short component duration. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Mar;15(2):205–210. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todorov J. C. Component duration and relative response rates in multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jan;17(1):45–49. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todorov J. C. Concurrent performances: effect of punishment contingent on the switching response. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Jul;16(1):51–62. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.16-51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


