Abstract
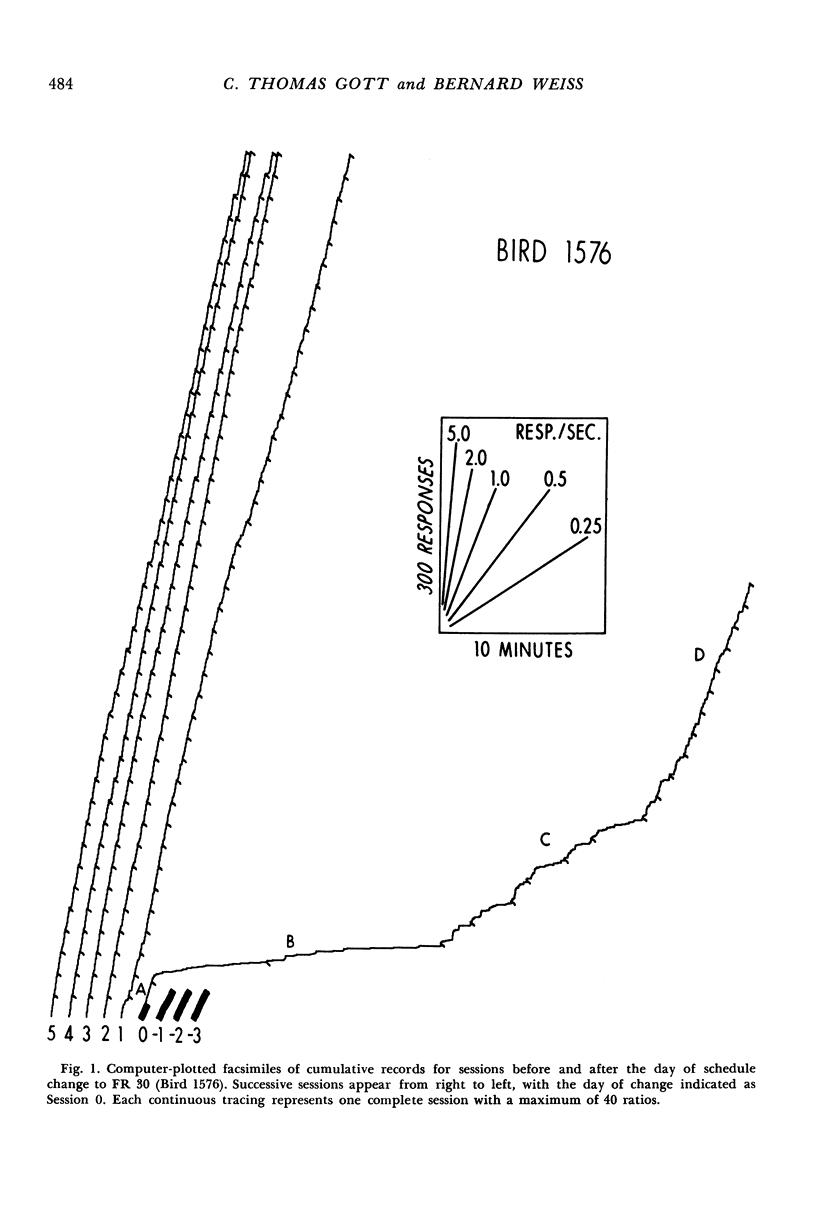
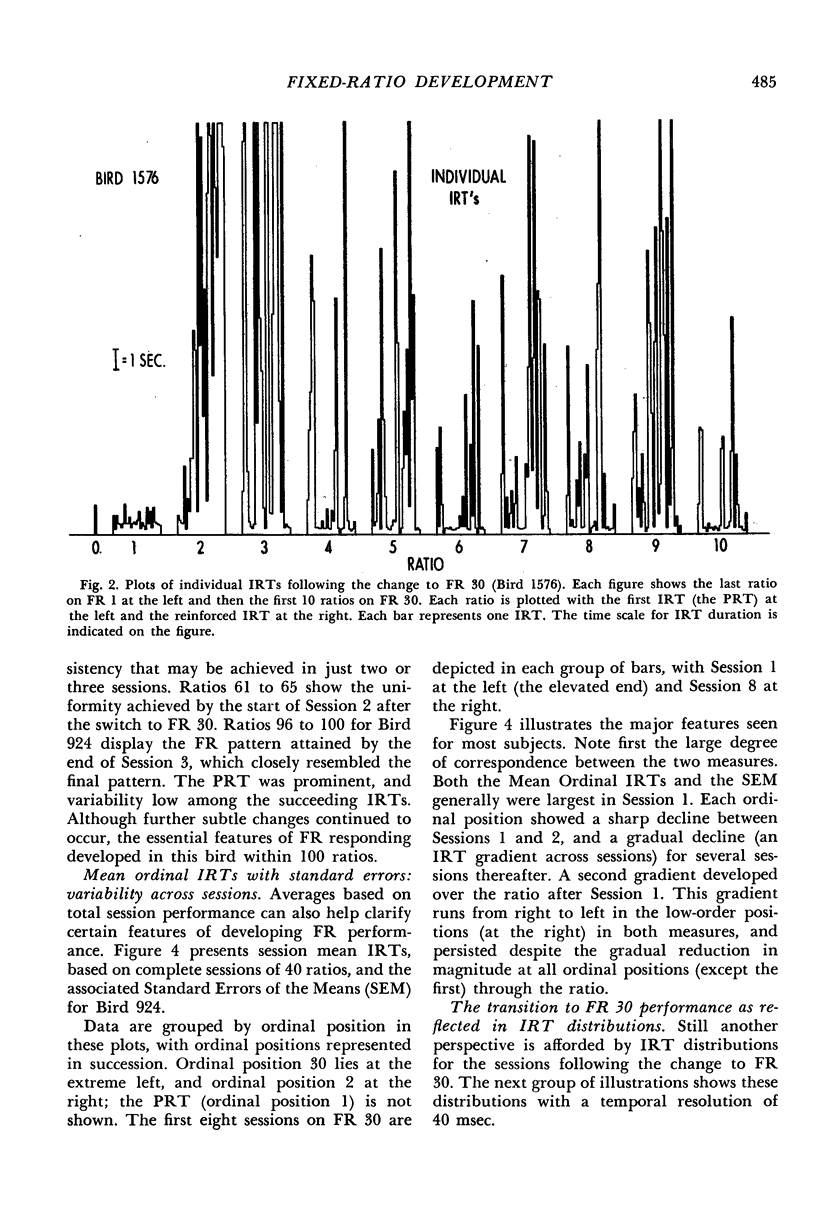
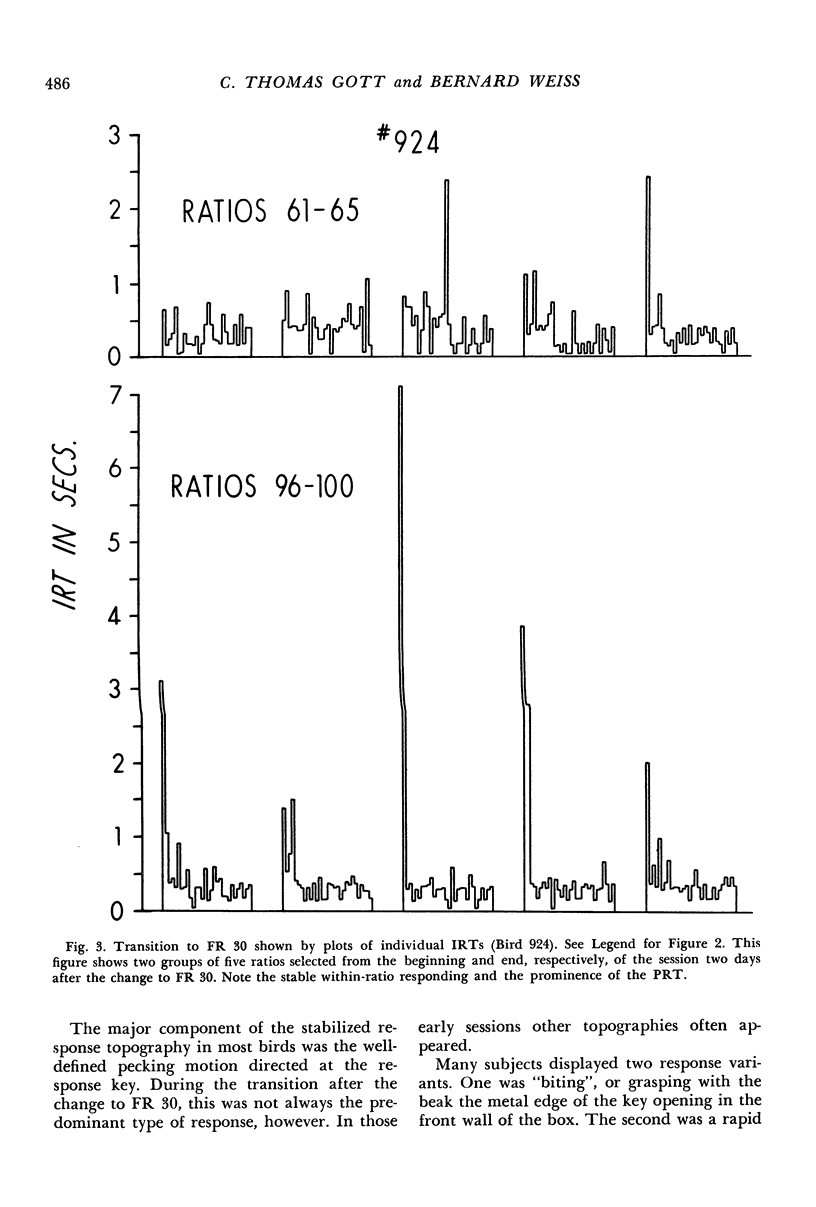
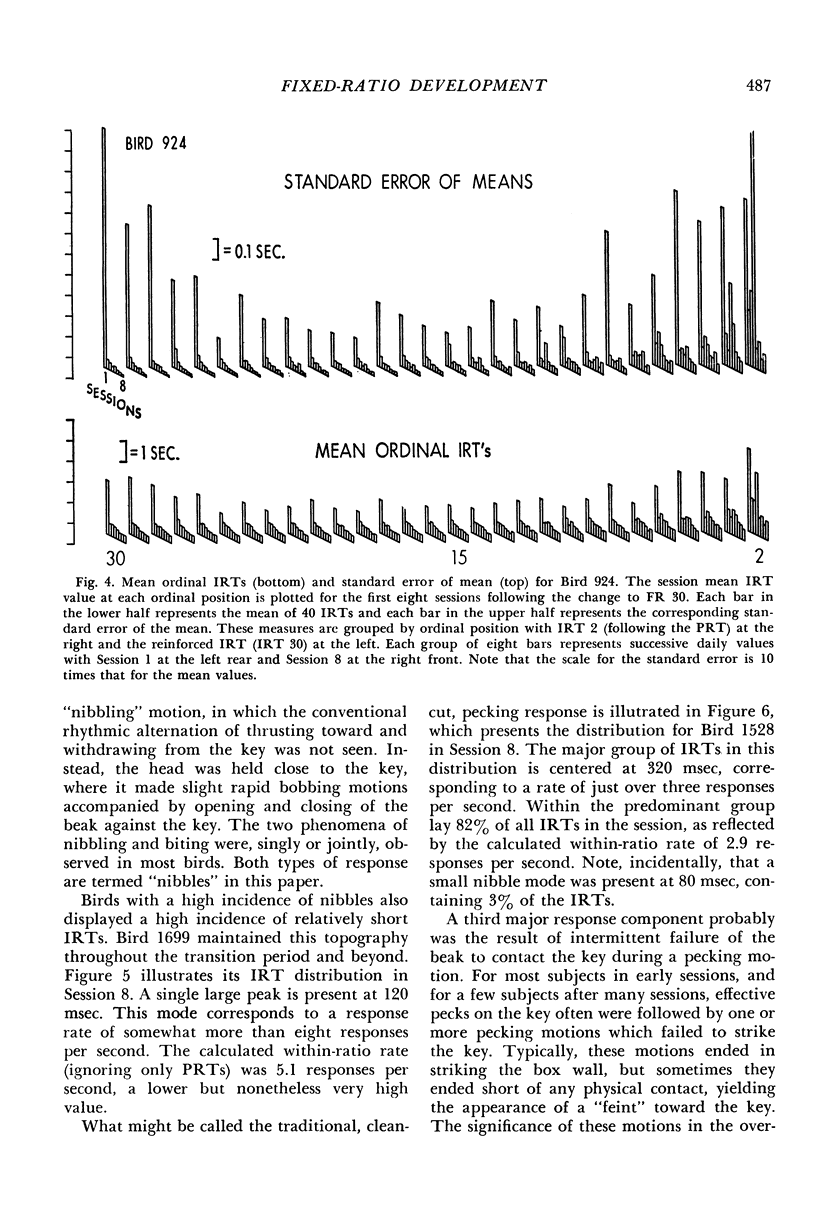
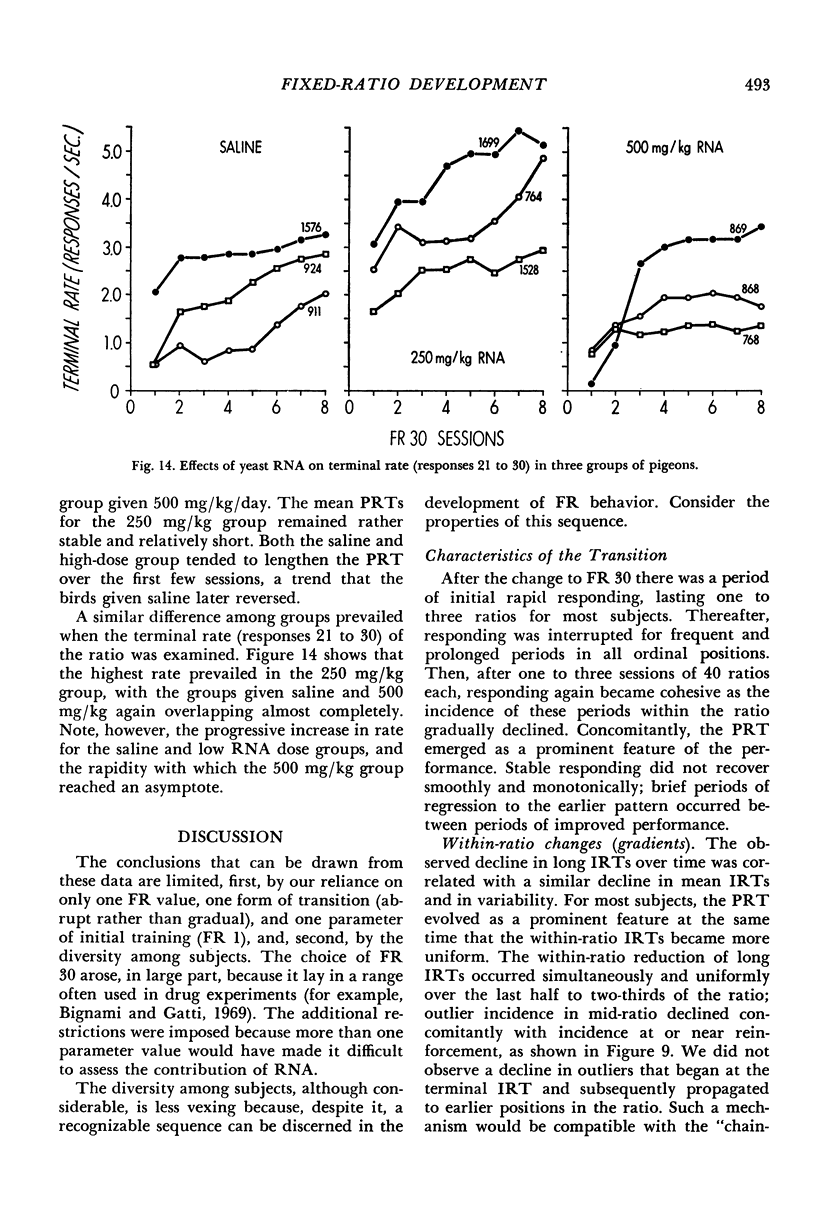
The transition from fixed-ratio 1 performance (every response reinforced) to fixed-ratio 30 performance (every thirtieth response reinforced) was studied in nine pigeons. These were divided into three treatment groups given daily oral doses of saline, or 250 mg/kg/day or 500 mg/kg/day of yeast ribonucleic acid. Detailed computer-assisted analyses of how fixed-ratio behavior develops revealed the following typical sequence. After the transition, the first few ratios typically were emitted without long interresponse times within the ratio. Steady responding then ceased, and numerous long interresponse times occurred, with no systematic relationship to ordinal position within the ratio. Gradually, a new pattern evolved, characterized by a consistently long post-reinforcement time, a border region of the next few interresponse times within which the mean interresponse time monotonically decreased, and short interresponse times within the last 80% of the ratio. Long interresponse times were eliminated from this last section of the ratio without regard to proximity to reinforcement. Various analytical procedures suggested that the final pattern can be conceived, in part, as the shaping of a reliable response topography. The group of three pigeons given 250 mg/kg/day of yeast ribonucleic acid responded at higher rates than the saline and 500 mg/kg/day groups. The latter group, in contrast to the saline and lower dose groups, which continued to increase their rates, reached a rate asymptote very early.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachrach A. J. A simple method of obtaining a scatter distribution of off-key pigeon pecking. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Mar;9(2):152–152. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignami G., Gatti G. L. Analysis of drug effects on multiple fixed ratio 33-fixed interval 5 min in pigeons. Psychopharmacologia. 1969;15(4):310–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00401686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blough D. S. Interresponse time as a function of continuous variables: a new method and some data. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6(2):237–246. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. L., Jenkins H. M. Auto-shaping of the pigeon's key-peck. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Jan;11(1):1–8. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEWS P. B. The effect of multiple S delta periods on responding on a fixed-interval schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Jul;5:369–374. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham P. J., Mariner A., Adams H. Enhancement of off-key pecking by on-key punishment. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):789–797. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felton M., Lyon D. O. The post-reinforcement pause. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Mar;9(2):131–134. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLEHER R. T., FRY W., COOK L. ADJUSTING FIXED-RATIO SCHEDULES IN THE SQUIRREL MONKEY. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Jan;7:69–77. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINTSCH W. FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION OF INTERRESPONSE TIMES DURING VI AND VR REINFORCEMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Sep;8:347–352. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen P. Reinforcement frequency and contingency as factors in fixed-ratio behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 May;12(3):391–395. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J., Schneider B. A. Separating the effects of interreinforcement time and number of interreinforcement responses. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):661–667. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POGGIO G. F., VIERNSTEIN L. J. TIME SERIES ANALYSIS OF IMPULSE SEQUENCES OF THALAMIC SOMATIC SENSORY NEURONS. J Neurophysiol. 1964 Jul;27:517–545. doi: 10.1152/jn.1964.27.4.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell R. W. The effect of small sequential changes in fixed-ratio size upon the post-reinforcement pause. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Sep;11(5):589–593. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rilling M., Kramer T. J., Askew H. R. A preliminary analysis of the dynamics of the pecking response in pigeons. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):267–278. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider B. A. A two-state analysis of fixed-interval responding in the pigeon. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):677–687. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull R. L., Brownstein A. J. Interresponse time duration in fixed-interval schedules of reinforcement: control by ordinal position and time since reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Jul;14(1):49–53. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.14-49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISS B., LATIES V. G. REINFORCEMENT SCHEDULE GENERATED BY AN ON-LINE DIGITAL COMPUTER. Science. 1965 Apr 30;148(3670):658–661. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3670.658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Gott C. T. A microanalysis of drug effects on fixed-ratio performance in pigeons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Feb;180(2):189–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler M. D. Time limits for completing fixed ratios. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Nov;14(3):275–286. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.14-275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



