Abstract
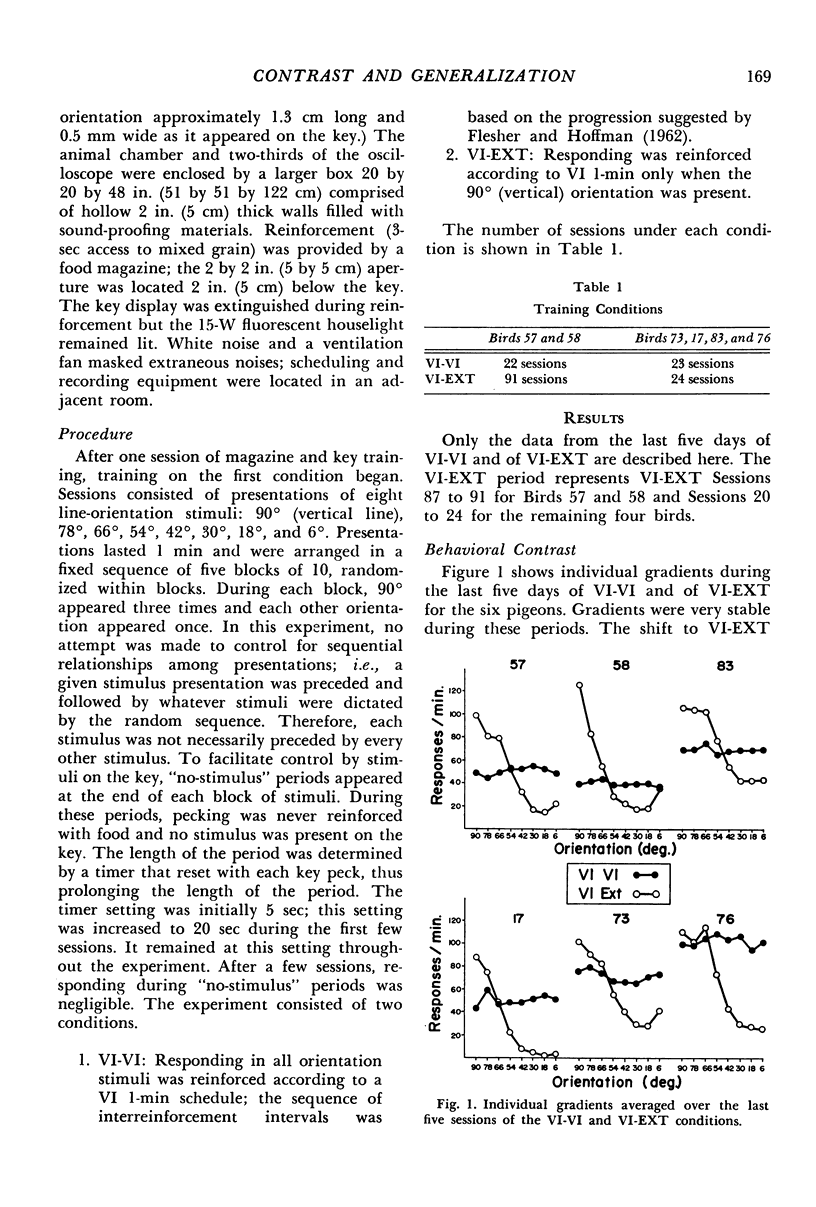
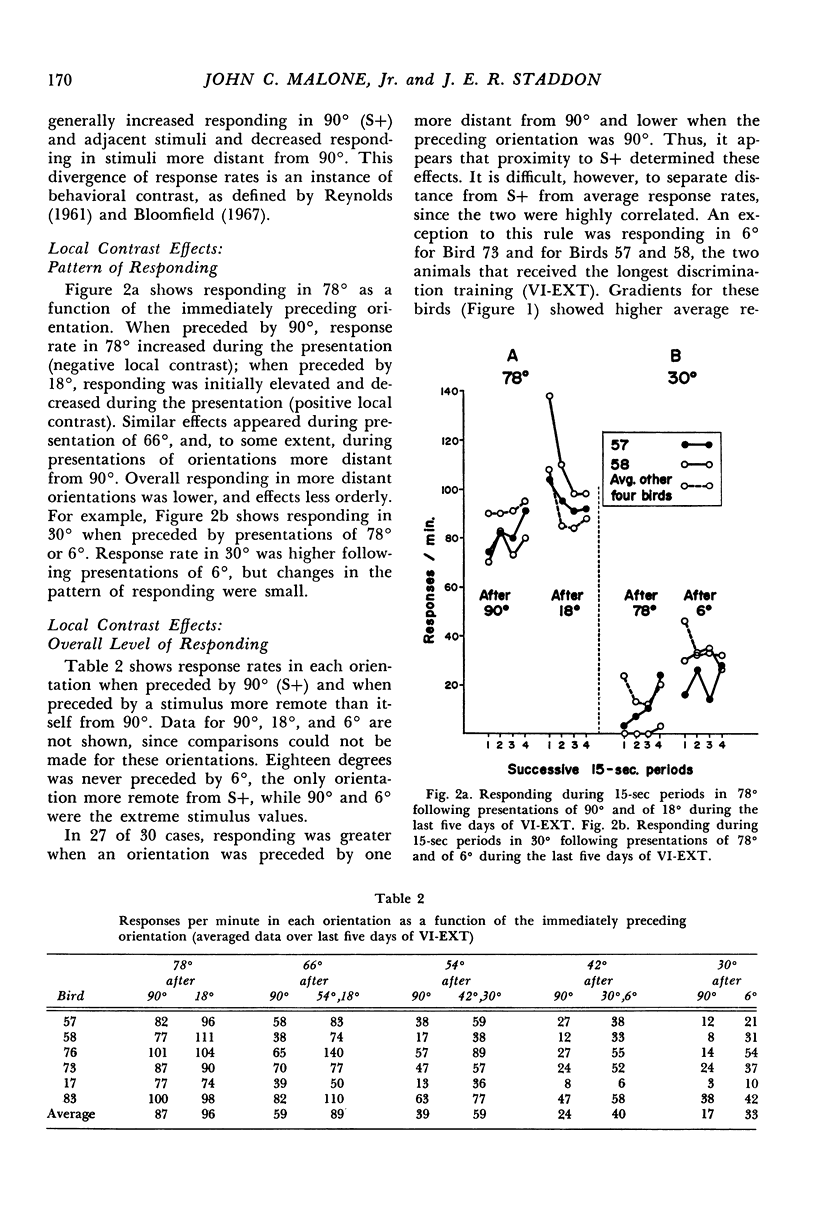
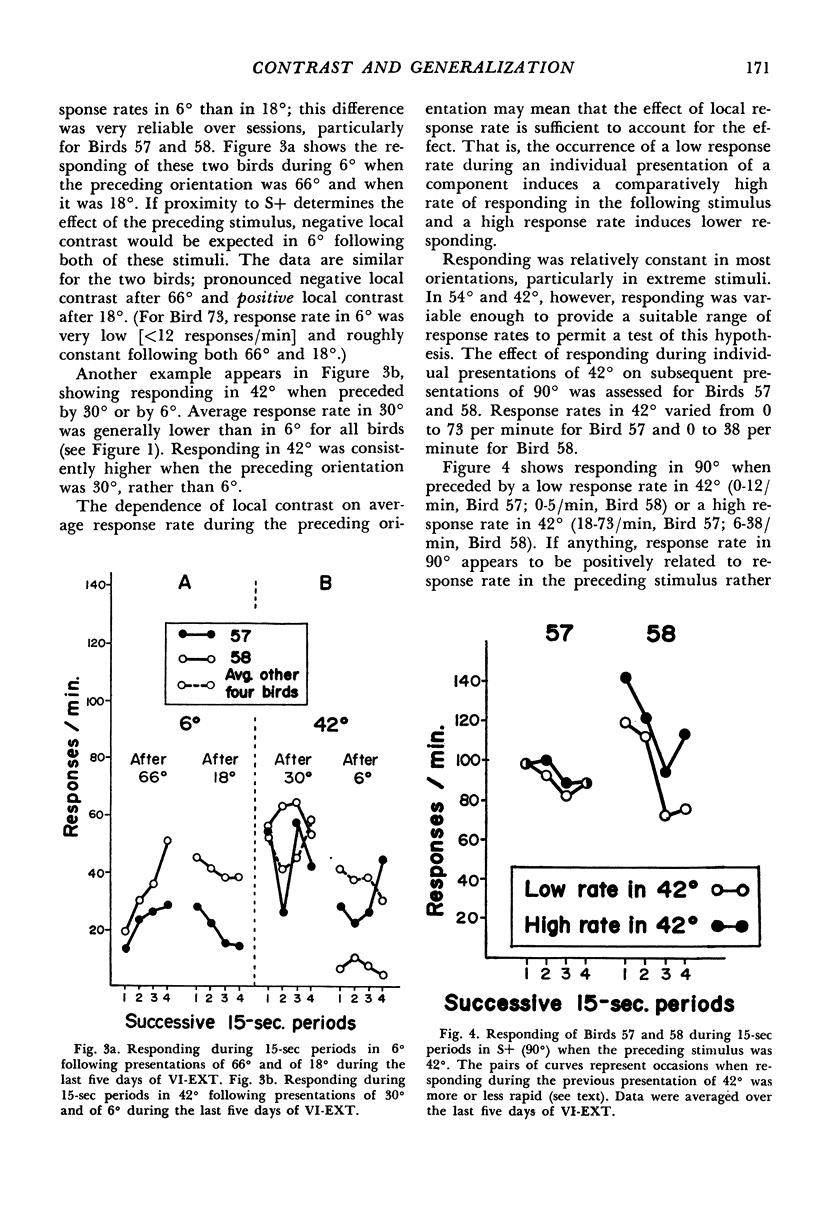
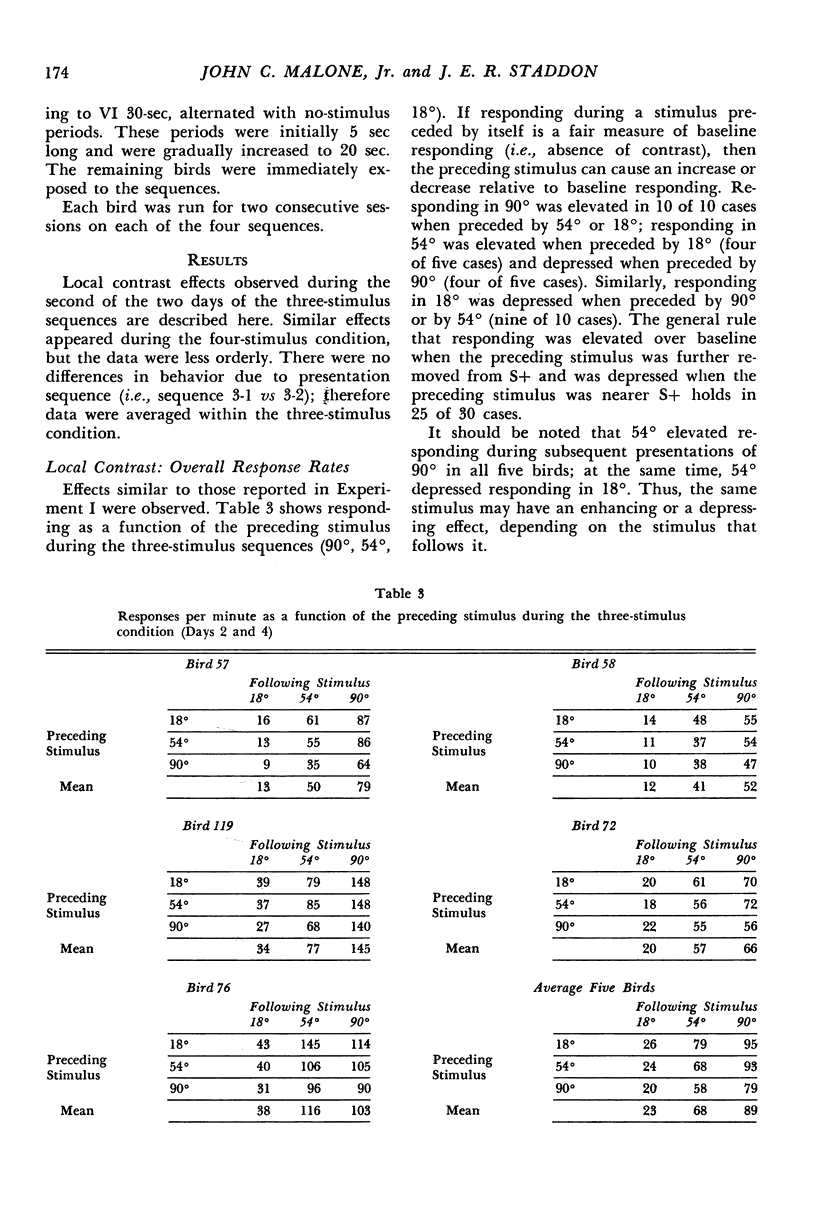
In Experiment I, pigeons were given equal reinforcement (variable-interval 1-min) for responding during randomized presentations of eight line-orientation stimuli. Then, only responding in the vertical orientation was reinforced. Stable generalization gradients soon formed and persistent behavioral and local (transient) contrast effects appeared. Local contrast effects were not a function of relative reinforcement frequency or of any other variable known to produce contrast. Instead, they were related to average response rates associated with each stimulus. Experiment II showed that local contrast effects represent increases and decreases in response rates relative to baseline responding, and that these effects are relative; a given stimulus might enhance responding during a subsequent presentation of one stimulus, but depress responding when followed by another. These data indicate that discrimination learning is not adequately described as the acquisition of excitatory properties by some stimuli and inhibitory properties by others. A more adequate account implies that stimuli exert both excitatory and inhibitory effects related to their value.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BONEAU C. A., AXELROD S. Work decrement and reminiscence in pigeon operant responding. J Exp Psychol. 1962 Oct;64:352–354. doi: 10.1037/h0047944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield T. M. Behavioral contrast and relative reinforcement frequency in two multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Mar;10(2):151–158. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLESHLER M., HOFFMAN H. S. A progression for generating variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:529–530. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearst E., Besley S., Farthing G. W. Inhibition and the stimulus control of operant behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Nov;14(3 Pt 2 Suppl):373–409. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.14-s373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A., Shettleworth S. J. An analysis of contrast effects in multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Jul;9(4):305–315. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S. Behavioral contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jan;4:57–71. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. S., Limpo A. J. On some causes of behavioral contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Sep;11(5):543–547. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staddon J. E. Multiple fixed-interval schedules: transient contrast and temporal inhibition. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Jul;12(4):583–590. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRACE H. S. Errorless transfer of a discrimination across two continua. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:223–232. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrace H. S. Discrimination learning, the peak shift, and behavioral contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):727–741. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


