Abstract
Pigeons were trained to discriminate without errors between a green light and a dark key. The key-pecking response was reinforced in the presence of green, and extinction was in effect in the presence of the dark key. The duration of the dark key was gradually increased during the first few sessions of conditioning. The opportunity to attack a restrained target pigeon was also present. During discrimination training, the rate of attack in the presence of the dark key was higher for each animal than the operant level, even though most of the animals acquired the discrimination without errors. Furthermore, the rate of attack did not decrease during 45 sessions of discrimination training. Attack also occurred in the presence of the green stimulus, although to a lesser extent than during extinction. Reinforcement during green is a determinant of attack during extinction because removal of reinforcement virtually eliminated attack during extinction.
Full text
PDF


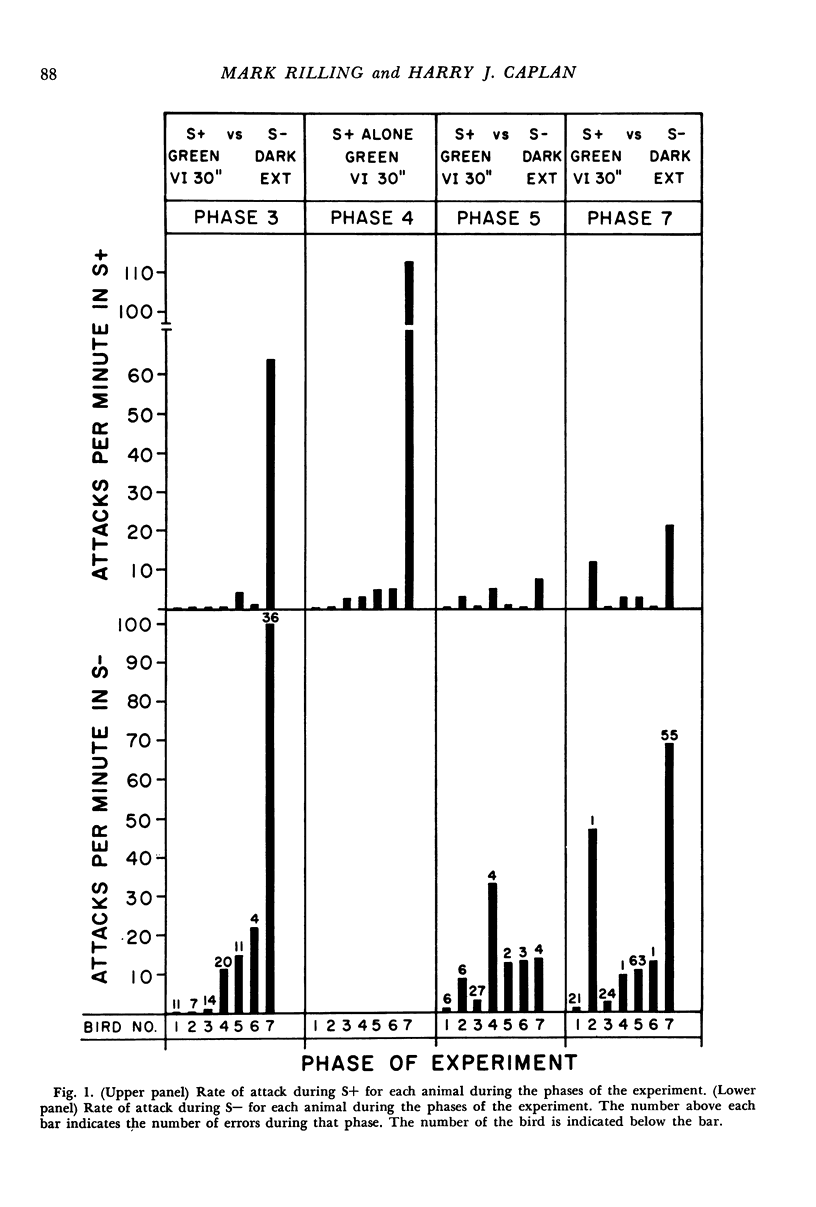
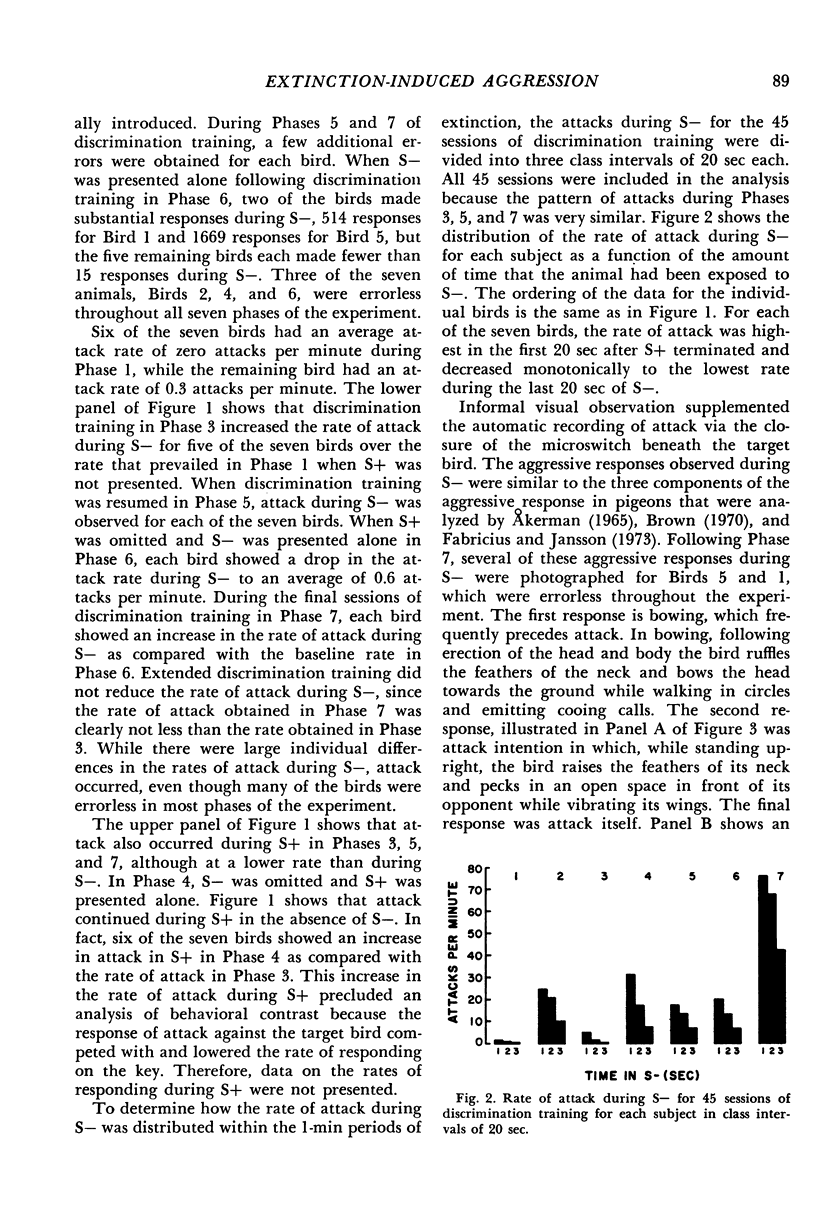
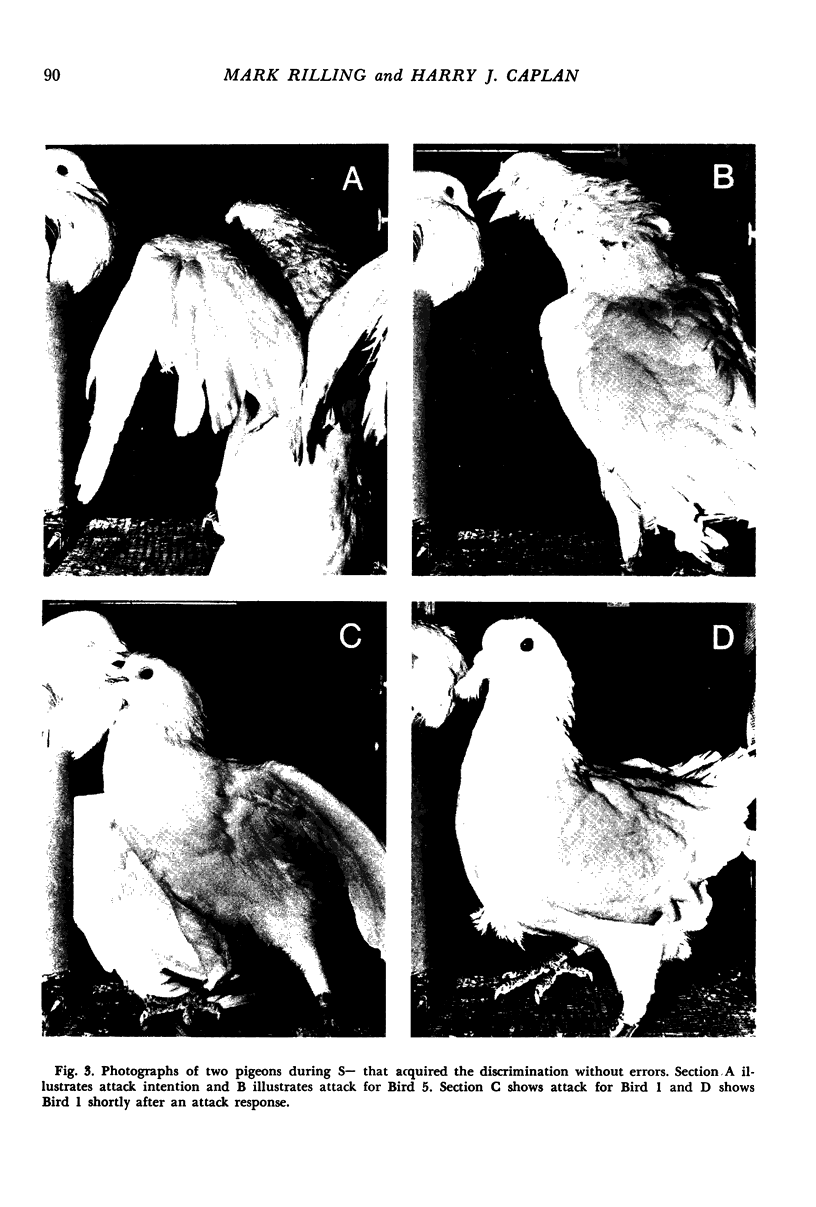


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azrin N. H., Hutchinson R. R., Hake D. F. Extinction-induced aggression. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 May;9(3):191–204. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. G., Flory R. K. Schedule-induced escape from fixed-interval reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 May;17(3):395–403. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk J. L. The nature and determinants of adjunctive behavior. Physiol Behav. 1971 May;6(5):577–588. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(71)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. W., Rilling M. Aversive aspects of a fixed-interval schedule of food reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 May;17(3):405–411. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rilling M., Askew H. R., Ahlskog J. E., Kramer T. J. Aversive properties of the negative stimulus in a successive discrimination. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):917–932. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRACE H. S. Errorless discrimination learning inthe pigeon: effects of chlorpromazine and impiramine. Science. 1963 Apr 19;140(3564):318–319. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3564.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRACE H. S. WAVELENGTH GENERALIZATION AFTER DISCRIMINATION LEARNING WITH AND WITHOUT ERRORS. Science. 1964 Apr 3;144(3614):78–80. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3614.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]