Abstract
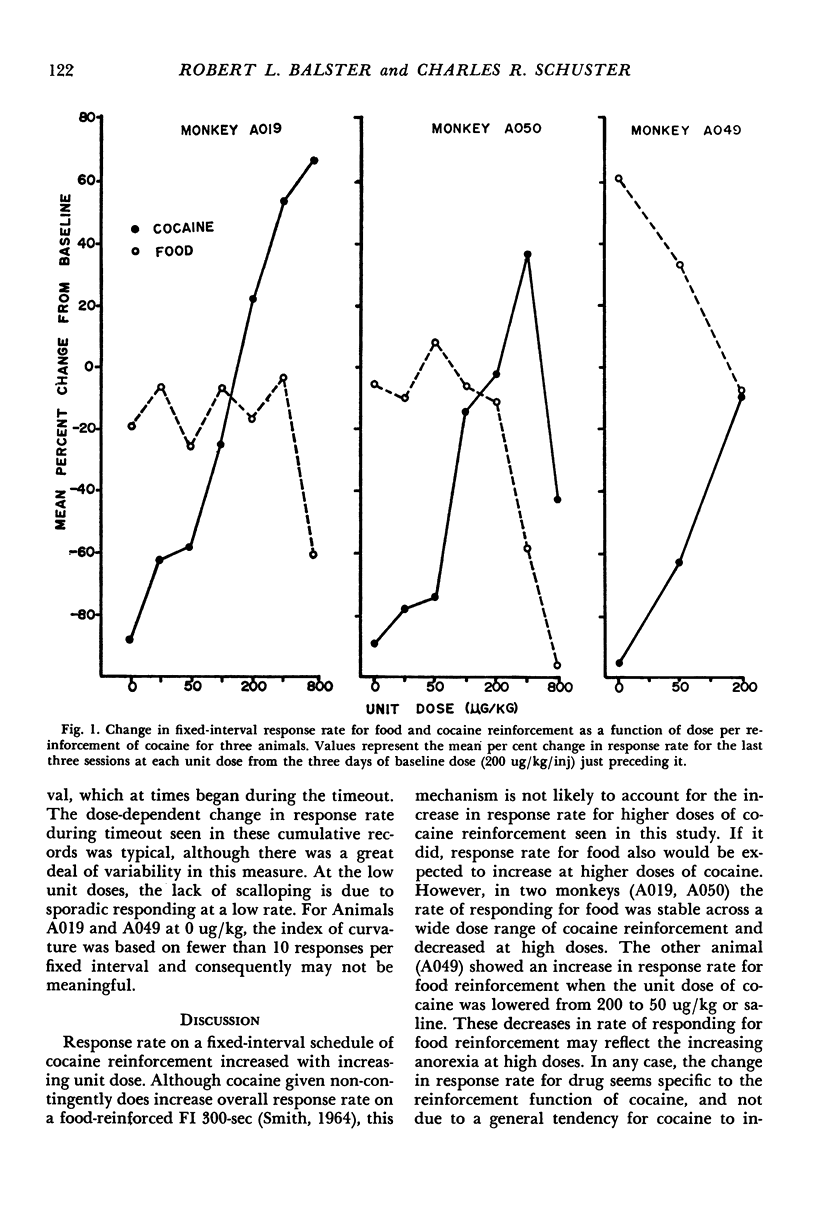
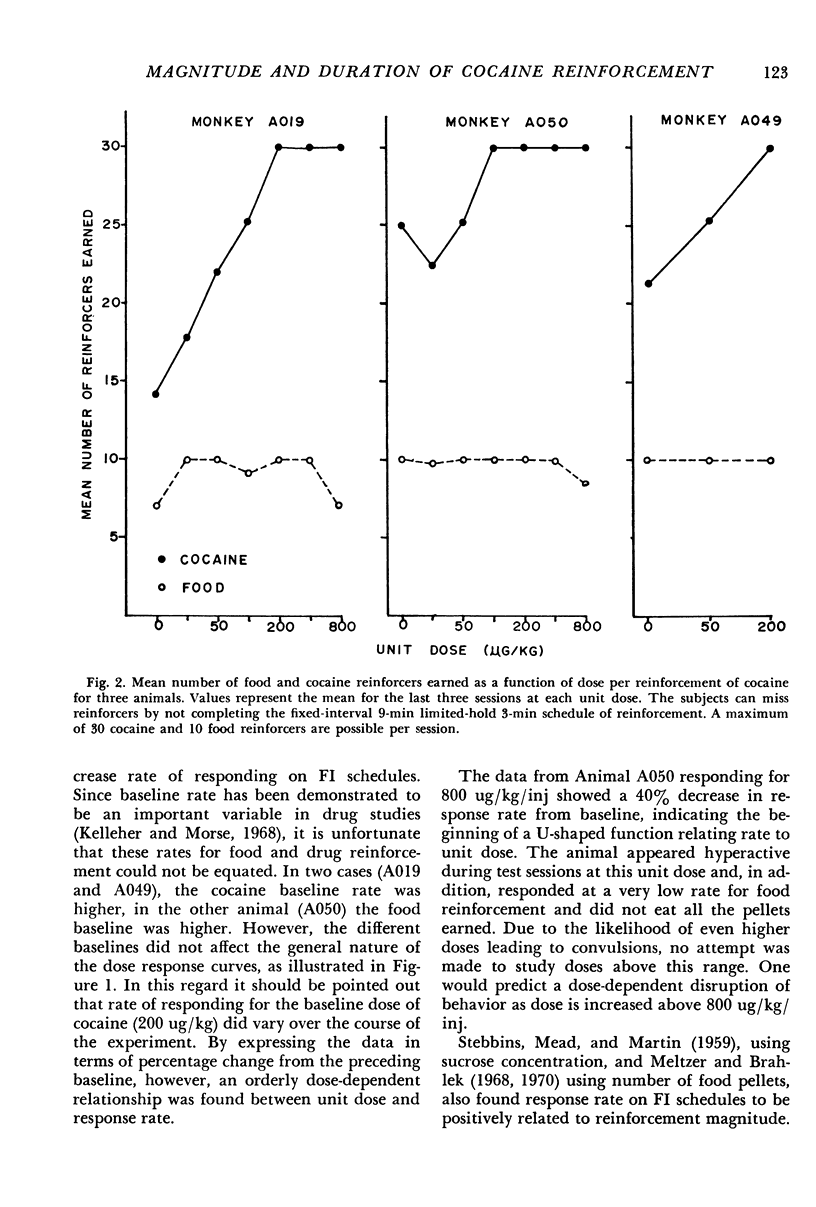
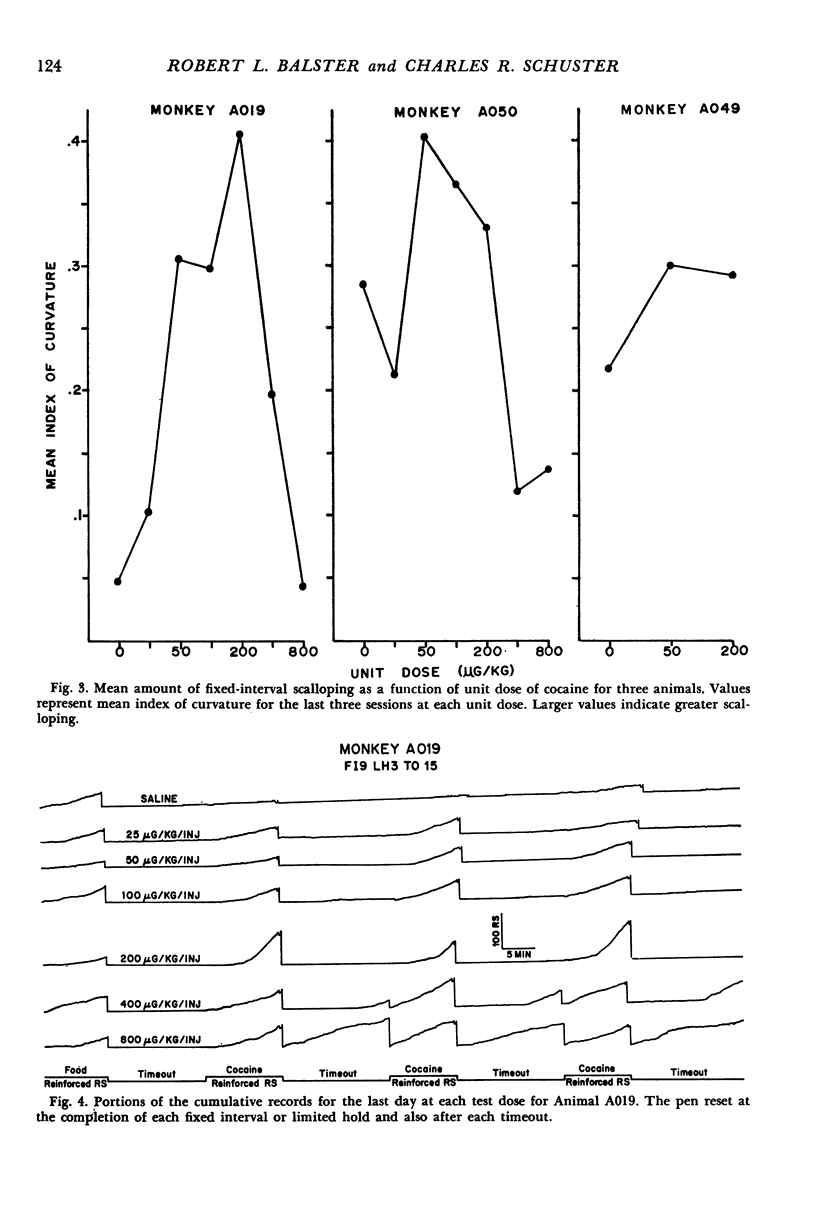
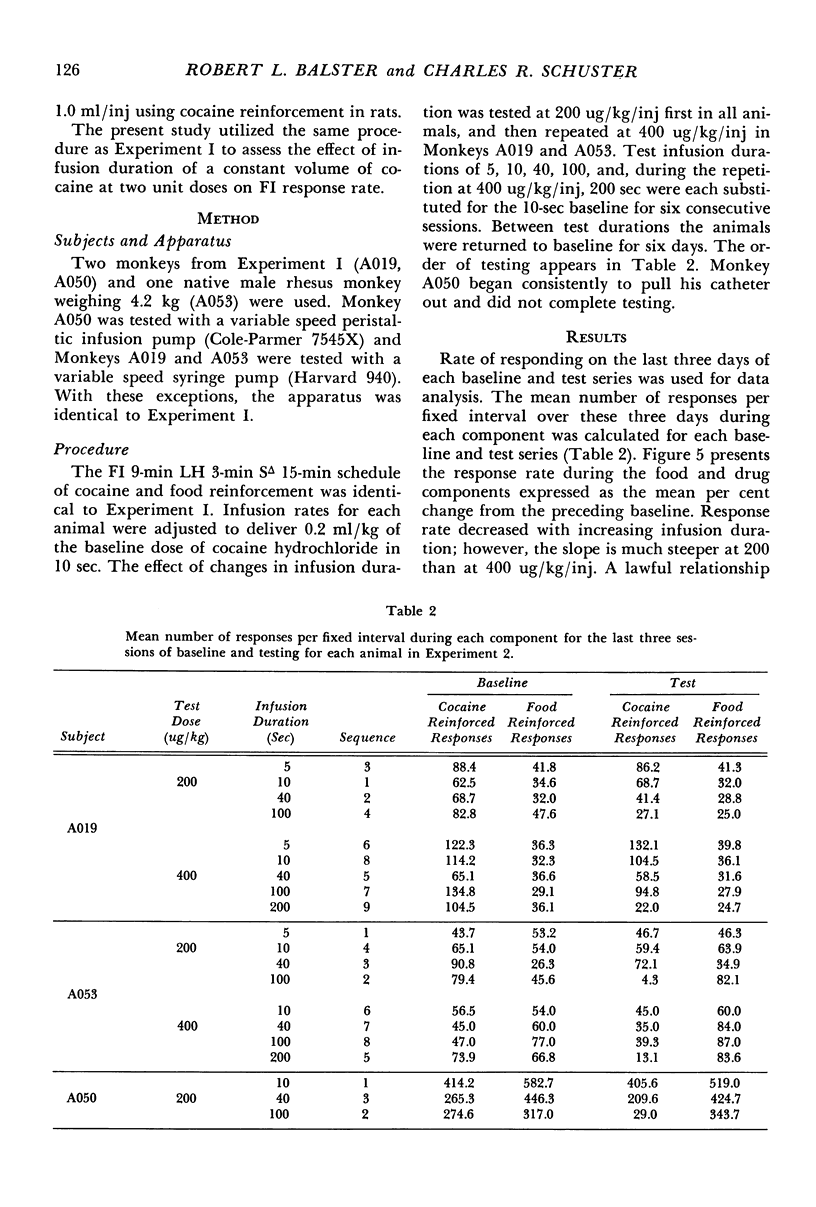
Rhesus monkeys were trained on a fixed-interval 9-min limited-hold 3-min schedule of intravenous cocaine reinforcement. A 15-min timeout followed each reinforcement or limited-hold expiration. An identical schedule of food reinforcement was interspersed in the session to assess rate-modifying effects of the drug infusions not specific to drug reinforcement. In one experiment, response rate for cocaine reinforcement was shown to be a positive function of reinforcement magnitude for a dose range from 0 to 800 ug/kg/inj. At these doses, there was little effect on food reinforced responding except at the highest dose, where responding decreased. Results of the second experiment indicated that increasing the duration of the cocaine infusion produced a change in response rate similar to decreasing unit dose. The response rate change for a given increase in infustion duration was less at a unit dose of 400 ug/kg than at 200 ug/kg.
Full text
PDF



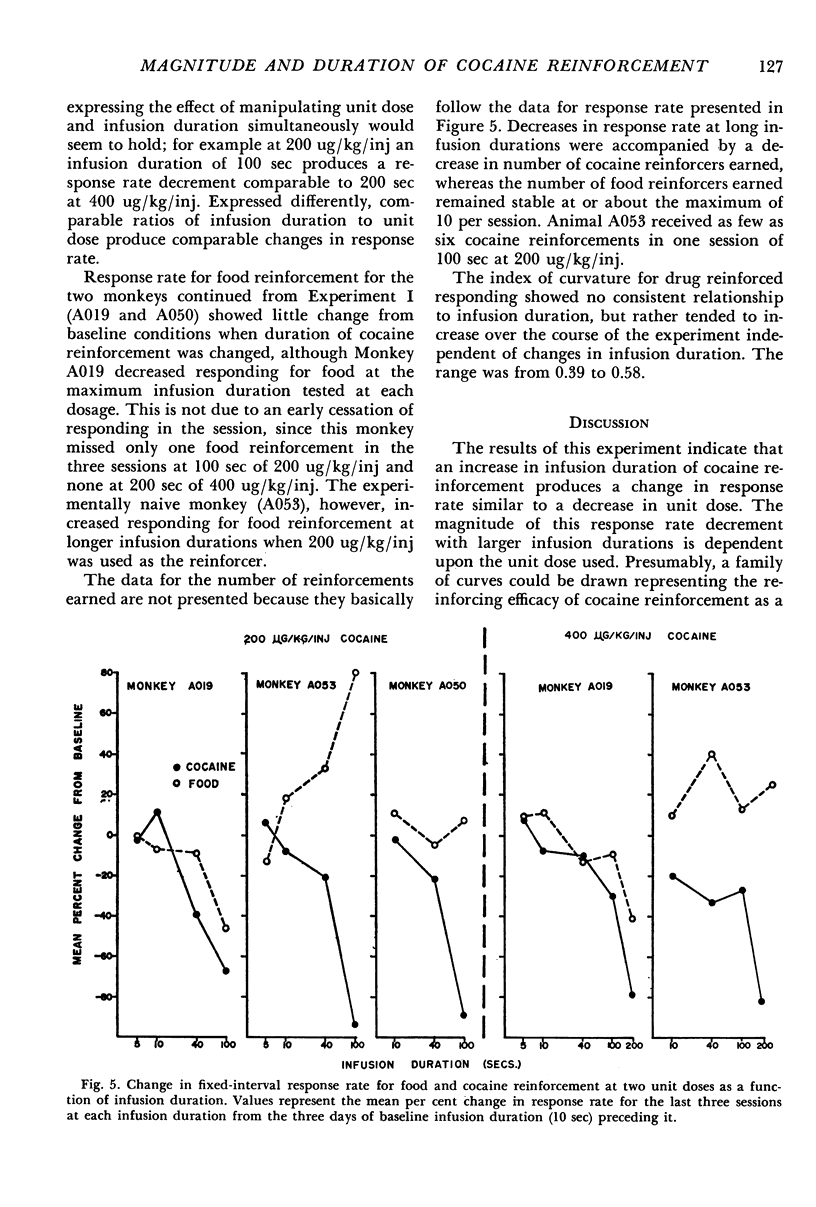

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deneau G., Yanagita T., Seevers M. H. Self-administration of psychoactive substances by the monkey. Psychopharmacologia. 1969;16(1):30–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00405254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRY W., KELLEHER R. T., COOK L. A mathematical index of performance on fixed-interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Jul;3:193–199. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findley J. D., Robinson W. W., Peregrino L. Addiction to secobarbital and chlordiazepoxide in the rhesus monkey by means of a self-infusion preference procedure. Psychopharmacologia. 1972;26(2):93–114. doi: 10.1007/BF00422097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg S. R., Hoffmeister F., Schlichting U. U., Wuttke W. A comparison of pentobarbital and cocaine self-administration in rhesus monkeys: effects of dose and fixed-ratio parameter. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Nov;179(2):277–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher R. T., Morse W. H. Determinants of the specificity of behavioral effects of drugs. Ergeb Physiol. 1968;60:1–56. doi: 10.1007/BFb0107250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickens R., Harris W. C. Self-administration of d-amphetamine by rats. Psychopharmacologia. 1968;12(2):158–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00401545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
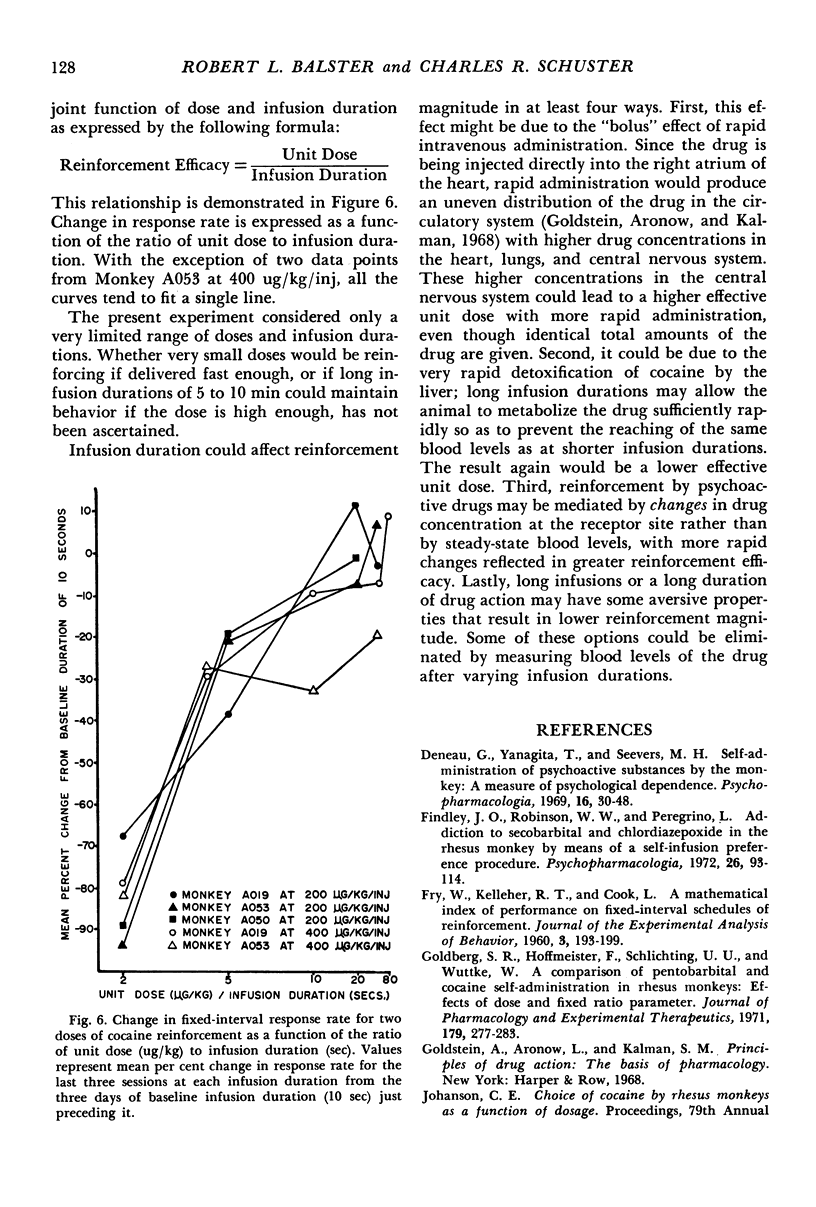
- Pickens R., Thompson T. Cocaine-reinforced behavior in rats: effects of reinforcement magnitude and fixed-ratio size. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 May;161(1):122–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS R. W. The relationship between stimulation voltage and rate of hypothalamic self-stimulation in the rat. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1958 Apr;51(2):193–198. doi: 10.1037/h0048362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C. B. EFFECTS OF D-AMPHETAMINE UPON OPERANT BEHAVIOR OF PIGEONS: ENHANCEMENT BY RESERPINE. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 Nov;146:167–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEBBINS W. C., MEAD P. B., MARTIN J. M. The relation of amount of reinforcement to performance under a fixed-in-terval schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1959 Oct;2:351–355. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1959.2-351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENSTEIN E. S. PROBLEMS OF MEASUREMENT AND INTERPRETATION WITH REINFORCING BRAIN STIMULATION. Psychol Rev. 1964 Nov;71:415–437. doi: 10.1037/h0040694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. C., Hitomi M., Schuster C. R. Psychomotor stimulant self administration as a function of dosage per injection in the rhesus monkey. Psychopharmacologia. 1971;22(3):271–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00401789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


