Abstract
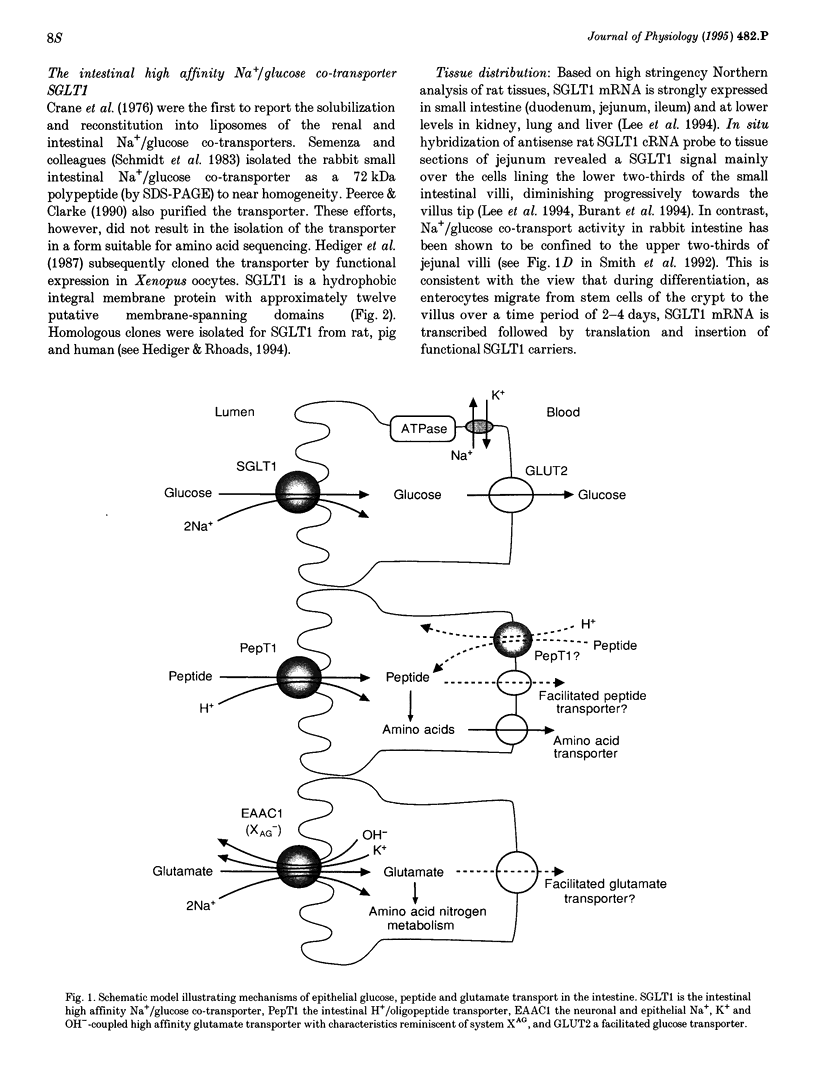
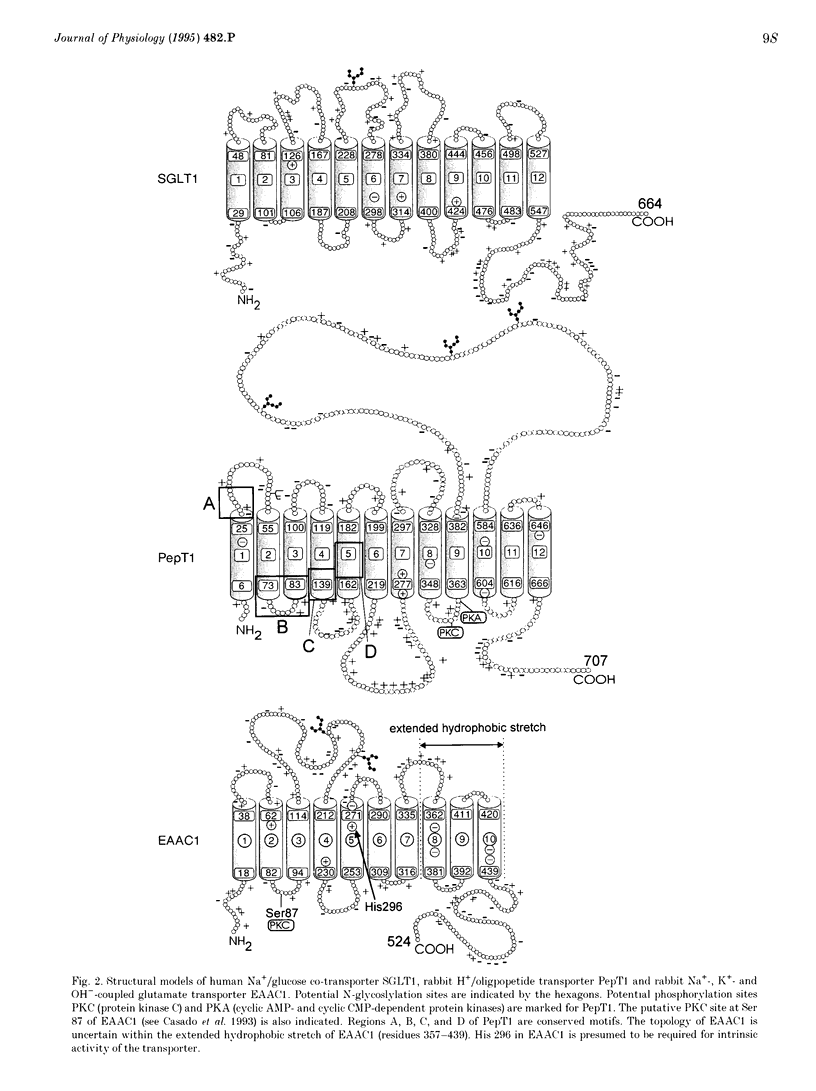
Active transport of solutes into and out of cells proceeds via specialized transporters that utilize diverse energy-coupling mechanisms. Ion-coupled transporters link uphill solute transport to downhill electrochemical ion gradients. In mammals, these transporters are coupled to the co-transport of H+, Na+, Cl- and/or to the countertransport of K+ or OH-. By contrast, ATP-dependent transporters are directly energized by the hydrolysis of ATP. The development of expression cloning approaches to select cDNA clones solely based on their capacity to induce transport function in Xenopus oocytes has led to the cloning of several ion-coupled transporter cDNAs and revealed new insights into structural designs, energy-coupling mechanisms and physiological relevance of the transporter proteins. Different types of mammalian ion-coupled transporters are illustrated by discussing transporters isolated in our own laboratory such as the Na+/glucose co-transporters SGLT1 and SGLT2, the H(+)-coupled oligopeptide transporters PepT1 and PepT2, and the Na(+)- and K(+)-dependent neuronal and epithelial high affinity glutamate transporter EAAC1. Most mammalian ion-coupled organic solute transporters studied so far can be grouped into the following transporter families: (1) the predominantly Na(+)-coupled transporter family which includes the Na+/glucose co-transporters SGLT1, SGLT2, SGLT3 (SAAT-pSGLT2) and the inositol transporter SMIT, (2) the Na(+)- and Cl(-)-coupled transporter family which includes the neurotransmitter transporters of gamma-amino-butyric acid (GABA), serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, glycine and proline as well as transporters of beta-amino acids, (3) the Na(+)- and K(+)-dependent glutamate/neurotransmitter family which includes the high affinity glutamate transporters EAAC1, GLT-1, GLAST, EAAT4 and the neutral amino acid transporters ASCT1 and SATT1 reminiscent of system ASC and (4) the H(+)-coupled oligopeptide transporter family which includes the intestinal H(+)-dependent oligopeptide transporter PepT1.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arriza J. L., Fairman W. A., Wadiche J. I., Murdoch G. H., Kavanaugh M. P., Amara S. G. Functional comparisons of three glutamate transporter subtypes cloned from human motor cortex. J Neurosci. 1994 Sep;14(9):5559–5569. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-09-05559.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arriza J. L., Kavanaugh M. P., Fairman W. A., Wu Y. N., Murdoch G. H., North R. A., Amara S. G. Cloning and expression of a human neutral amino acid transporter with structural similarity to the glutamate transporter gene family. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15329–15332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barfuss D. W., Schafer J. A. Differences in active and passive glucose transport along the proximal nephron. Am J Physiol. 1981 Sep;241(3):F322–F332. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.3.F322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett E., Kimmich G. A. Na+ binding to the Na(+)-glucose cotransporter is potential dependent. Am J Physiol. 1992 Feb;262(2 Pt 1):C510–C516. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.2.C510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier M., Szatkowski M., Amato A., Attwell D. The glial cell glutamate uptake carrier countertransports pH-changing anions. Nature. 1992 Dec 3;360(6403):471–474. doi: 10.1038/360471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandsch M., Miyamoto Y., Ganapathy V., Leibach F. H. Expression and protein kinase C-dependent regulation of peptide/H+ co-transport system in the Caco-2 human colon carcinoma cell line. Biochem J. 1994 Apr 1;299(Pt 1):253–260. doi: 10.1042/bj2990253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burant C. F., Flink S., DePaoli A. M., Chen J., Lee W. S., Hediger M. A., Buse J. B., Chang E. B. Small intestine hexose transport in experimental diabetes. Increased transporter mRNA and protein expression in enterocytes. J Clin Invest. 1994 Feb;93(2):578–585. doi: 10.1172/JCI117010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casado M., Bendahan A., Zafra F., Danbolt N. C., Aragón C., Giménez C., Kanner B. I. Phosphorylation and modulation of brain glutamate transporters by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 25;268(36):27313–27317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane R. K., Malathi P., Preiser H. Reconstitution of specific Na+-dependent D-glucose transport in liposomes by Triton X-100-extracted proteins from purified brush border membranes of rabbit kidney cortex. FEBS Lett. 1976 Aug 15;67(2):214–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80369-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantzig A. H., Hoskins J. A., Tabas L. B., Bright S., Shepard R. L., Jenkins I. L., Duckworth D. C., Sportsman J. R., Mackensen D., Rosteck P. R., Jr Association of intestinal peptide transport with a protein related to the cadherin superfamily. Science. 1994 Apr 15;264(5157):430–433. doi: 10.1126/science.8153632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fei Y. J., Kanai Y., Nussberger S., Ganapathy V., Leibach F. H., Romero M. F., Singh S. K., Boron W. F., Hediger M. A. Expression cloning of a mammalian proton-coupled oligopeptide transporter. Nature. 1994 Apr 7;368(6471):563–566. doi: 10.1038/368563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A., Coady M. J., Ikeda T. S., Wright E. M. Expression cloning and cDNA sequencing of the Na+/glucose co-transporter. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):379–381. doi: 10.1038/330379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A., Rhoads D. B. Molecular physiology of sodium-glucose cotransporters. Physiol Rev. 1994 Oct;74(4):993–1026. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1994.74.4.993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz E., Sommerfeld D. L., Kinne R. K. Electrogenicity of sodium/L-glutamate cotransport in rabbit renal brush-border membranes: a reevaluation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 22;937(2):300–308. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori R., Tomita Y., Katsura T., Yasuhara M., Inui K., Takano M. Transport of bestatin in rat renal brush-border membrane vesicles. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 May 5;45(9):1763–1768. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90431-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda T. S., Hwang E. S., Coady M. J., Hirayama B. A., Hediger M. A., Wright E. M. Characterization of a Na+/glucose cotransporter cloned from rabbit small intestine. J Membr Biol. 1989 Aug;110(1):87–95. doi: 10.1007/BF01870995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai Y., Hediger M. A. Primary structure and functional characterization of a high-affinity glutamate transporter. Nature. 1992 Dec 3;360(6403):467–471. doi: 10.1038/360467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai Y., Lee W. S., You G., Brown D., Hediger M. A. The human kidney low affinity Na+/glucose cotransporter SGLT2. Delineation of the major renal reabsorptive mechanism for D-glucose. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jan;93(1):397–404. doi: 10.1172/JCI116972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai Y., Smith C. P., Hediger M. A. A new family of neurotransmitter transporters: the high-affinity glutamate transporters. FASEB J. 1993 Dec;7(15):1450–1459. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.15.7903261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai Y., Stelzner M., Nussberger S., Khawaja S., Hebert S. C., Smith C. P., Hediger M. A. The neuronal and epithelial human high affinity glutamate transporter. Insights into structure and mechanism of transport. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 12;269(32):20599–20606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner B. I., Schuldiner S. Mechanism of transport and storage of neurotransmitters. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1987;22(1):1–38. doi: 10.3109/10409238709082546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner B. I. Structure and function of sodium-coupled neurotransmitter transporters. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1993;48:243–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong C. T., Yet S. F., Lever J. E. Cloning and expression of a mammalian Na+/amino acid cotransporter with sequence similarity to Na+/glucose cotransporters. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1509–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Girbig F., Gutjahr U., Kowalewski S., Adam F., Schiebler W. Intestinal absorption of beta-lactam antibiotics and oligopeptides. Functional and stereospecific reconstitution of the oligopeptide transport system from rabbit small intestine. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Mar 1;204(2):923–930. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. S., Kanai Y., Wells R. G., Hediger M. A. The high affinity Na+/glucose cotransporter. Re-evaluation of function and distribution of expression. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 22;269(16):12032–12039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden D. J., Routtenberg A. The role of protein kinase C in long-term potentiation: a testable model. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1989 Jul-Sep;14(3):279–296. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(89)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas M. Determination of acid surface pH in vivo in rat proximal jejunum. Gut. 1983 Aug;24(8):734–739. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.8.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie B., Panayotova-Heiermann M., Loo D. D., Lever J. E., Wright E. M. SAAT1 is a low affinity Na+/glucose cotransporter and not an amino acid transporter. A reinterpretation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 9;269(36):22488–22491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto S., Saito H., Inui K. Transcellular transport of oral cephalosporins in human intestinal epithelial cells, Caco-2: interaction with dipeptide transport systems in apical and basolateral membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Aug;270(2):498–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momburg F., Roelse J., Howard J. C., Butcher G. W., Hämmerling G. J., Neefjes J. J. Selectivity of MHC-encoded peptide transporters from human, mouse and rat. Nature. 1994 Feb 17;367(6464):648–651. doi: 10.1038/367648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pajor A. M., Wright E. M. Cloning and functional expression of a mammalian Na+/nucleoside cotransporter. A member of the SGLT family. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3557–3560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent L., Supplisson S., Loo D. D., Wright E. M. Electrogenic properties of the cloned Na+/glucose cotransporter: I. Voltage-clamp studies. J Membr Biol. 1992 Jan;125(1):49–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00235797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen I. T., Skurray R. A. The POT family of transport proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Oct;19(10):404–404. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerce B. E., Clarke R. D. Isolation and reconstitution of the intestinal Na+/glucose cotransporter. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1731–1736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry J. R., Basrai M. A., Steiner H. Y., Naider F., Becker J. M. Isolation and characterization of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae peptide transport gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):104–115. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines G., Danbolt N. C., Bjørås M., Zhang Y., Bendahan A., Eide L., Koepsell H., Storm-Mathisen J., Seeberg E., Kanner B. I. Cloning and expression of a rat brain L-glutamate transporter. Nature. 1992 Dec 3;360(6403):464–467. doi: 10.1038/360464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein J. D., Martin L., Levey A. I., Dykes-Hoberg M., Jin L., Wu D., Nash N., Kuncl R. W. Localization of neuronal and glial glutamate transporters. Neuron. 1994 Sep;13(3):713–725. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Inui K. Dipeptide transporters in apical and basolateral membranes of the human intestinal cell line Caco-2. Am J Physiol. 1993 Aug;265(2 Pt 1):G289–G294. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1993.265.2.G289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt U. M., Eddy B., Fraser C. M., Venter J. C., Semenza G. Isolation of (a subunit of) the Na+/D-glucose cotransporter(s) of rabbit intestinal brush border membranes using monoclonal antibodies. FEBS Lett. 1983 Sep 19;161(2):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafqat S., Tamarappoo B. K., Kilberg M. S., Puranam R. S., McNamara J. O., Guadaño-Ferraz A., Fremeau R. T., Jr Cloning and expression of a novel Na(+)-dependent neutral amino acid transporter structurally related to mammalian Na+/glutamate cotransporters. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15351–15355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. W., Turvey A., Freeman T. C. Appearance of phloridzin-sensitive glucose transport is not controlled at mRNA level in rabbit jejunal enterocytes. Exp Physiol. 1992 May;77(3):525–528. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1992.sp003616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storck T., Schulte S., Hofmann K., Stoffel W. Structure, expression, and functional analysis of a Na(+)-dependent glutamate/aspartate transporter from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10955–10959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacnet F., Lauthier F., Ripoche P. Mechanisms of zinc transport into pig small intestine brush-border membrane vesicles. J Physiol. 1993 Jun;465:57–72. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thwaites D. T., McEwan G. T., Hirst B. H., Simmons N. L. Transepithelial dipeptide (glycylsarcosine) transport across epithelial monolayers of human Caco-2 cells is rheogenic. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Oct;425(1-2):178–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00374520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsay Y. F., Schroeder J. I., Feldmann K. A., Crawford N. M. The herbicide sensitivity gene CHL1 of Arabidopsis encodes a nitrate-inducible nitrate transporter. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):705–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90399-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. J., Moran A. Stoichiometric studies of the renal outer cortical brush border membrane D-glucose transporter. J Membr Biol. 1982;67(1):73–80. doi: 10.1007/BF01868649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. G., Hediger M. A. Cloning of a rat kidney cDNA that stimulates dibasic and neutral amino acid transport and has sequence similarity to glucosidases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5596–5600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Pines G., Kanner B. I. Histidine 326 is critical for the function of GLT-1, a (Na+ + K+)-coupled glutamate transporter from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 29;269(30):19573–19577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]