Abstract
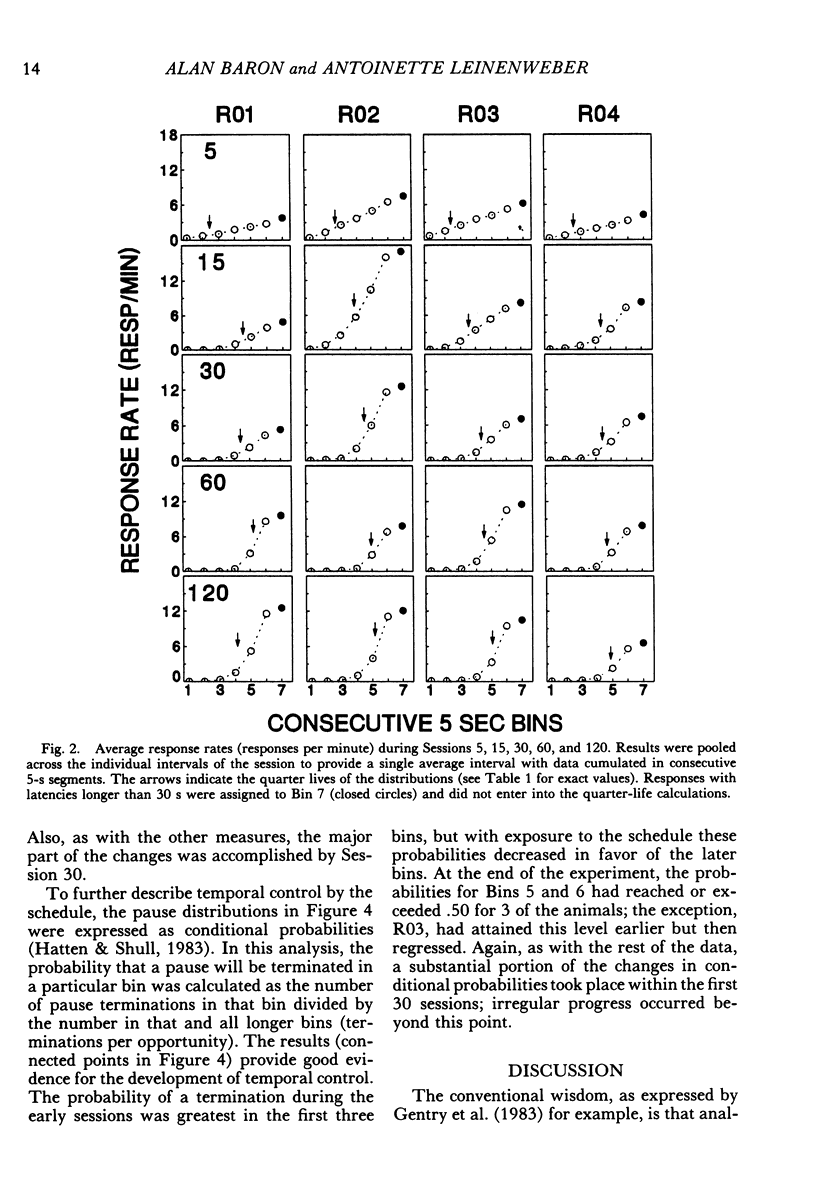
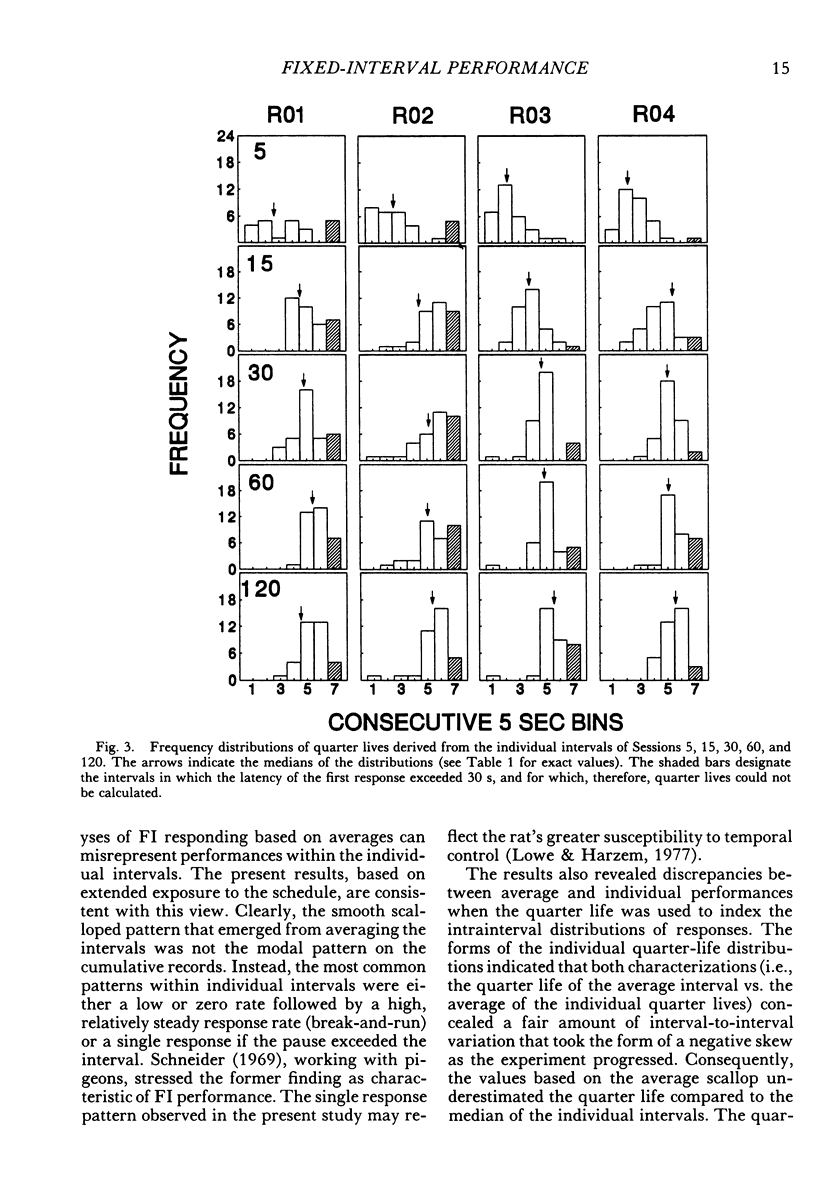
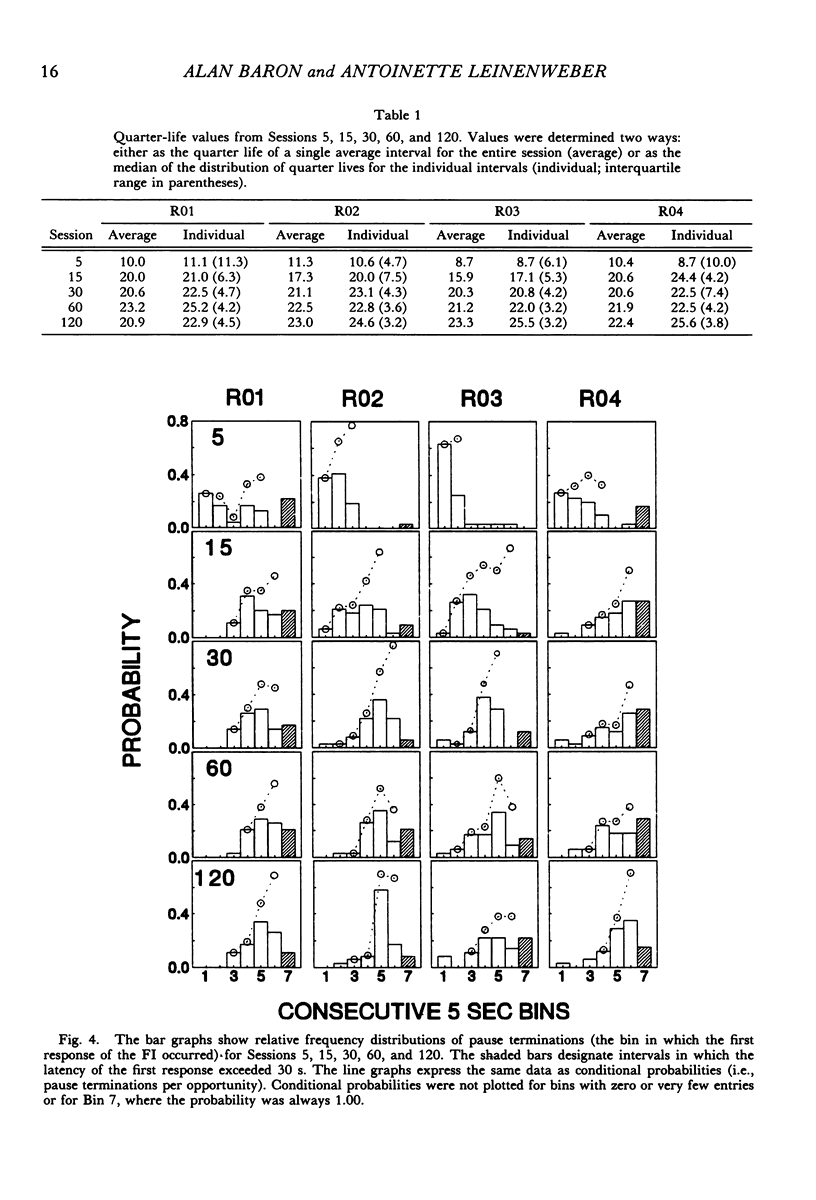
Fixed-interval performances of rats were described either in terms of the individual intervals of the session or in terms of a single average interval constructed for the entire session. Responding in the individual intervals usually followed break-and-run and single response patterns rather than the scalloped pattern that emerged when the results were averaged. There was, however, a reasonable correspondence between the quarter-life values calculated from individual intervals and those calculated from the averages. According to the pattern exhibited by the average interval, the probability of a response increased as the interval elapsed. The same conclusion was indicated by more molecular analyses of the conditional probabilities of pause terminations. The results showed that descriptions of fixed-interval data in terms of overall averages reveal aspects of performance that are not immediately apparent within individual intervals.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Branch M. N., Gollub L. R. A detailed analysis of the effects of d-amphetamine on behavior under fixed-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 May;21(3):519–539. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch M. N. Rate dependency, behavioral mechanisms, and behavioral pharmacology. J Exp Anal Behav. 1984 Nov;42(3):511–522. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1984.42-511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumming W. W., Schoenfeld W. N. Behavior under extended exposure to a high-value fixed interval reinforcement schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Aug;1(3):245–263. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dukich T. D., Lee A. E. A comparison of measures of responding under fixed-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Sep;20(2):281–290. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman T. J., Lattal K. A. Stimulus control of behavioral history. J Exp Anal Behav. 1992 Jan;57(1):5–15. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1992.57-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLLUB L. R. THE RELATIONS AMONG MEASURES OF PERFORMANCE ON FIXED-INTERVAL SCHEDULES. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Sep;7:337–343. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry G. D., Weiss B., Laties V. G. The microanalysis of fixed-interval responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 Mar;39(2):327–343. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.39-327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe C. F., Harzem P. Species differences in temporal control of behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 Nov;28(3):189–201. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.28-189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAuley F., Leslie J. C. Molecular analyses of the effects of d-amphetamine on fixed-interval schedule performances of rats. J Exp Anal Behav. 1986 Mar;45(2):207–219. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1986.45-207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider B. A. A two-state analysis of fixed-interval responding in the pigeon. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):677–687. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanchisen B. A., Tatham T. A., Mooney S. E. Variable-ratio conditioning history produces high- and low-rate fixed-interval performance in rats. J Exp Anal Behav. 1989 Sep;52(2):167–179. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1989.52-167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


