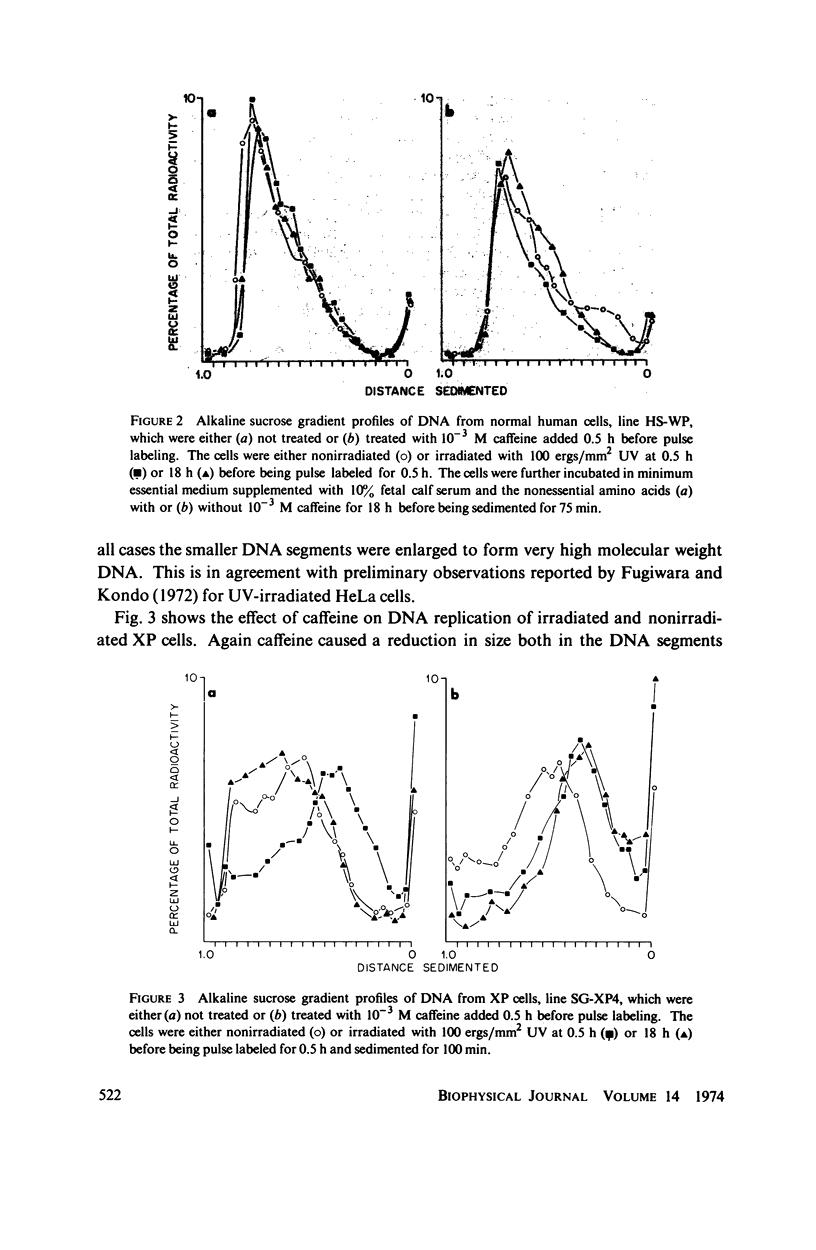
Abstract
DNA synthesized shortly after ultraviolet (UV) irradiation of human cells is made in segments that are smaller than normal, but at long times after irradiation the segments made are normal in size. Upon incubation, both the shorter and the normal segments are elongated and joined by the insertion of exogenous nucleotides to form high molecular weight DNA as in nonirradiated cells. These processes occur in normal human cells, where UV-induced pyrimidine dimers are excised, as well as in xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) cells, where dimers are not excised. The effect of caffeine on these processes was determined for both normal human and XP cells. Caffeine, which binds to denatured regions of DNA, inhibited DNA chain elongation and joining in irradiated XP cells but not in irradiated normal human or nonirradiated cells. Caffeine also caused an alteration in the ability to recover synthesis of DNA of normal size at long times after irradiation in XP cells but not in normal cells.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buhl S. N., Setlow R. B., Regan J. D. Recovery of the ability to synthesize DNA in segments of normal size at long times after ultraviolet irradiation of human cells. Biophys J. 1973 Dec;13(12):1265–1275. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)86061-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhl S. N., Setlow R. B., Regan J. D. Steps in DNA chain elongation and joining after ultra-violet irradiation of human cells. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1972 Nov;22(5):417–424. doi: 10.1080/09553007214551301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhl S. N., Stillman R. M., Setlow R. B., Regan J. D. DNA chain elongation and joining in normal human and xeroderma pigmentosum cells after ultraviolet irradiation. Biophys J. 1972 Sep;12(9):1183–1191. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(72)86154-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrier W. L., Setlow R. B. Endonuclease from Micrococcus luteus which has activity toward ultraviolet-irradiated deoxyribonucleic acid: purification and properties. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):178–186. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.178-186.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrier W. L., Setlow R. B. Paper strip method for assaying gradient fractions containing radioactive macromolecules. Anal Biochem. 1971 Oct;43(2):427–432. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E. Defective repair replication of DNA in xeroderma pigmentosum. Nature. 1968 May 18;218(5142):652–656. doi: 10.1038/218652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E. Repair replication of mammalian cell DNA: effects of compounds that inhibit DNA synthesis or dark repair. Radiat Res. 1969 Feb;37(2):334–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E., Thomas G. H. Single strand interruptions in DNA and the effects of caffeine in Chinese hamster cells irradiated with ultraviolet light. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jul 23;36(2):203–208. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90315-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domon M., Rauth A. M. Effects of caffeine on ultraviolet-irradiated mouse L cells. Radiat Res. 1969 Jul;39(1):207–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freifelder D. Molecular weights of coliphages and coliphage DNA. IV. Molecular weights of DNA from bacteriophages T4, T5 and T7 and the general problem of determination of M. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 28;54(3):567–577. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara Y., Kondo T. Caffeine-sensitive repair of ultraviolet light-damaged DNA of mouse L cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 12;47(3):557–564. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90915-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlmann W., Fromme H. G., Heege E. M., Ostertag W. The mutagenic action of caffeine in higher organisms. Cancer Res. 1968 Nov;28(11):2375–2389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann A. R., Ormerod M. G. The replication of DNA in murine lymphoma cells (L5178Y). I. Rate of replication. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 19;204(1):128–143. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90496-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyn R. E., Humphrey R. M. Deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in ultraviolet-light-irradiated Chinese hamster cells. Biophys J. 1971 Mar;11(3):295–301. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(71)86215-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. D., Trosko J. E., Carrier W. L. Evidence for excision of ultraviolet-induced pyrimidine dimers from the DNA of human cells in vitro. Biophys J. 1968 Mar;8(3):319–325. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(68)86490-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow R. B., Regan J. D., German J., Carrier W. L. Evidence that xeroderma pigmentosum cells do not perform the first step in the repair of ultraviolet damage to their DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):1035–1041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson R., Kiefer J., Nias A. H. Effects of post-treatment with caffeine on the sensitivity to ultraviolet light irradiation of two lines of HeLa cells. Mutat Res. 1970 Jul;10(1):67–72. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(70)90147-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


