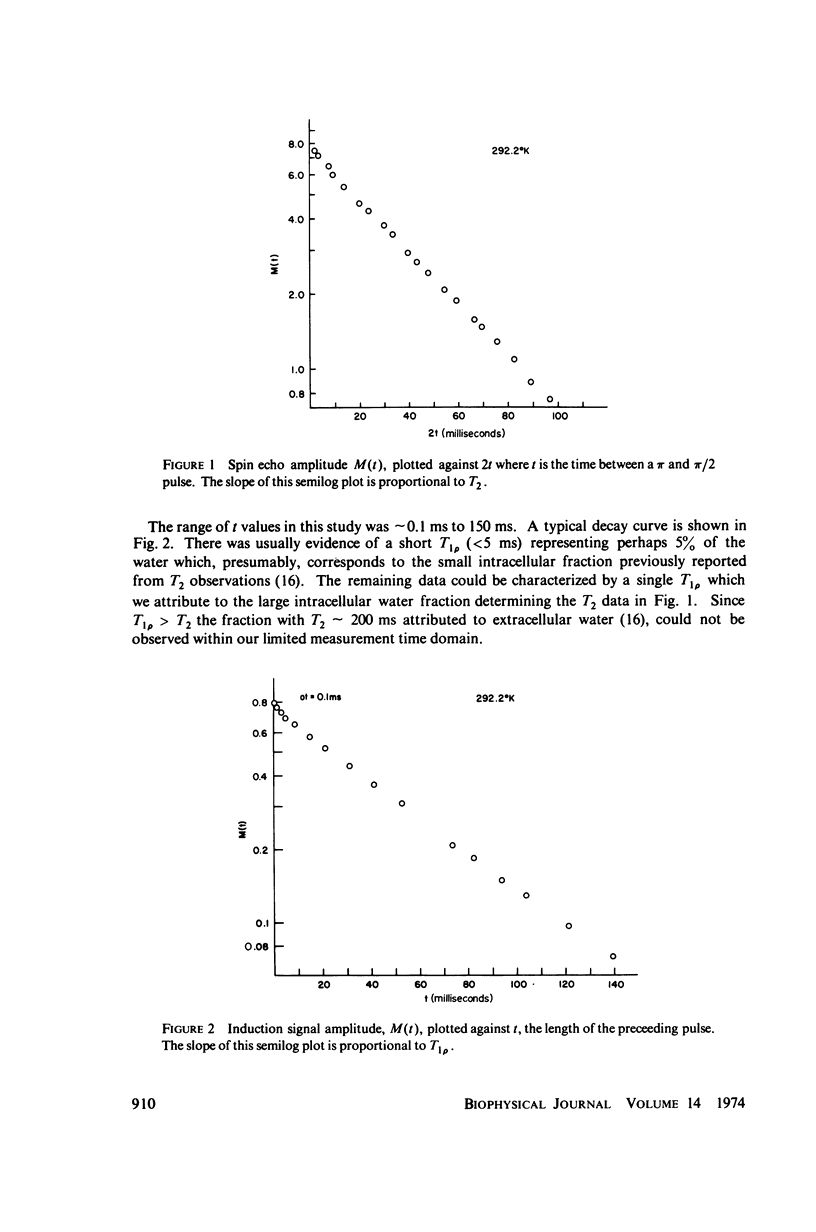
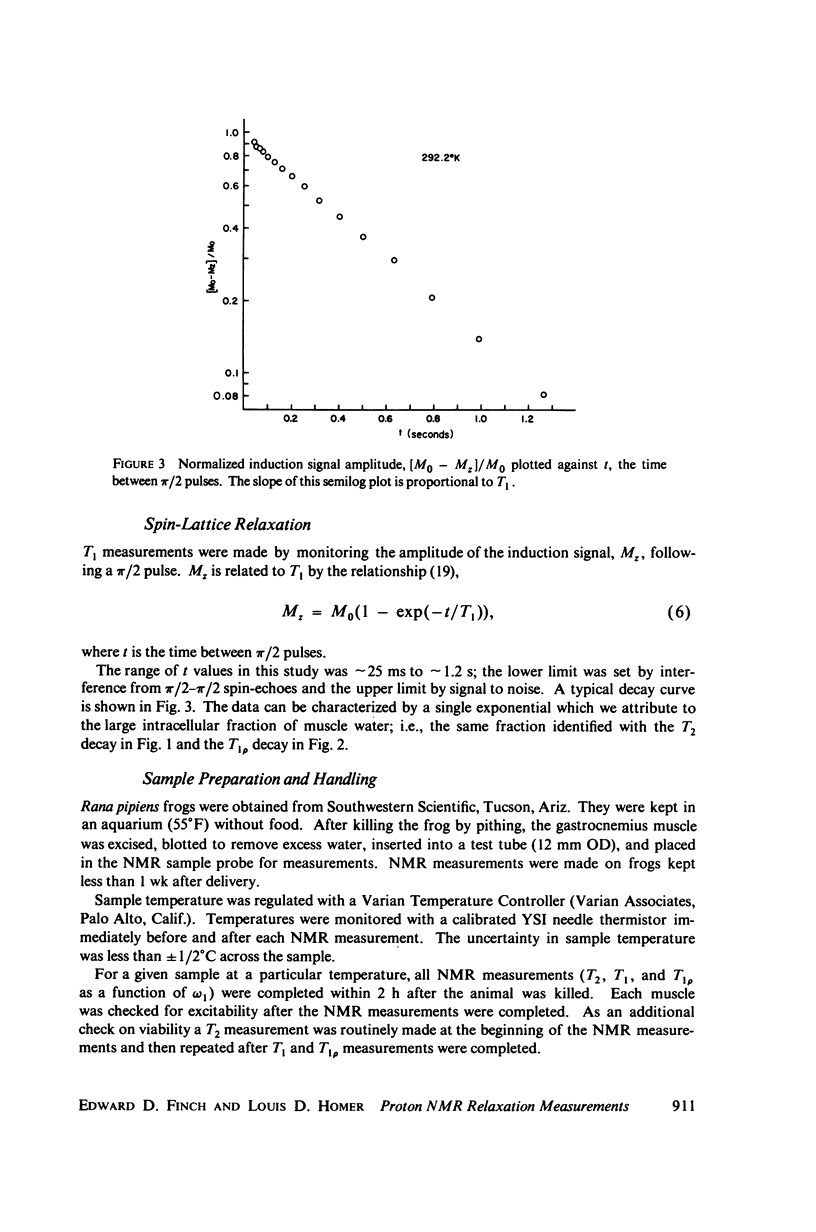
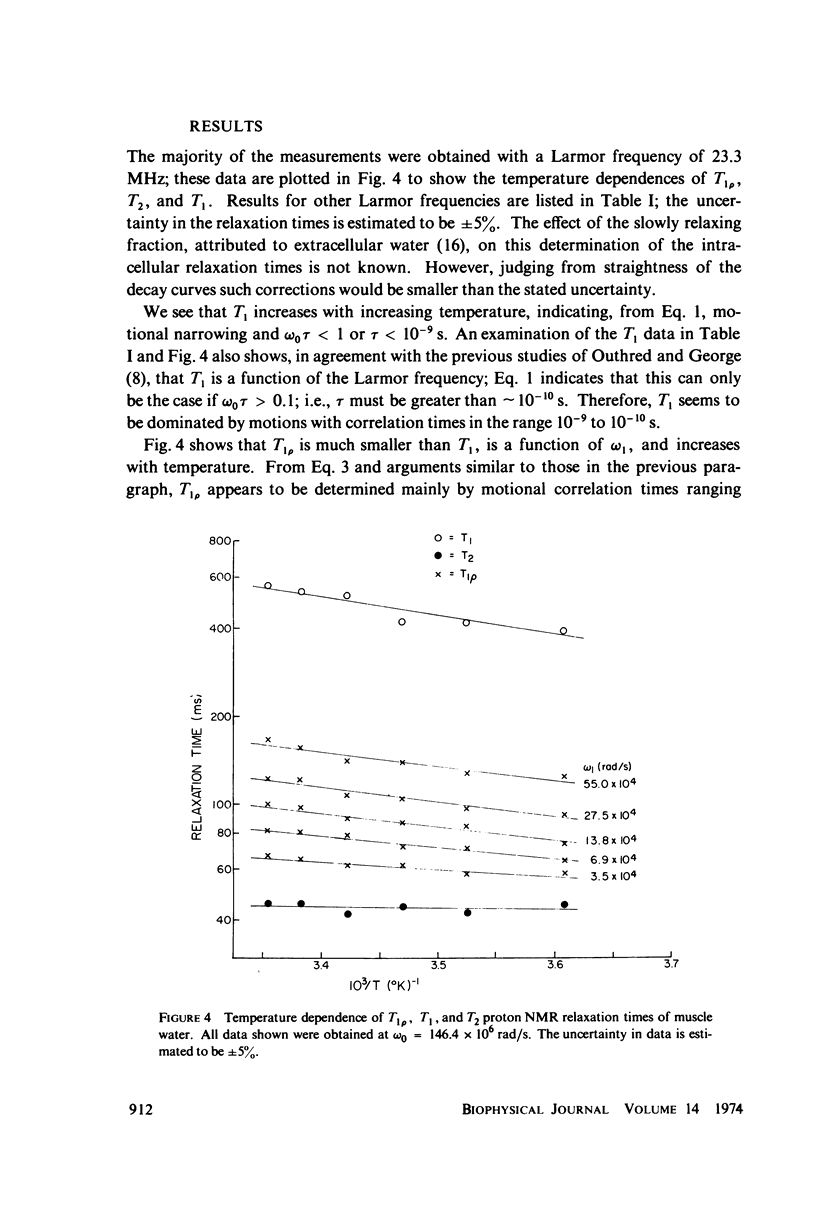
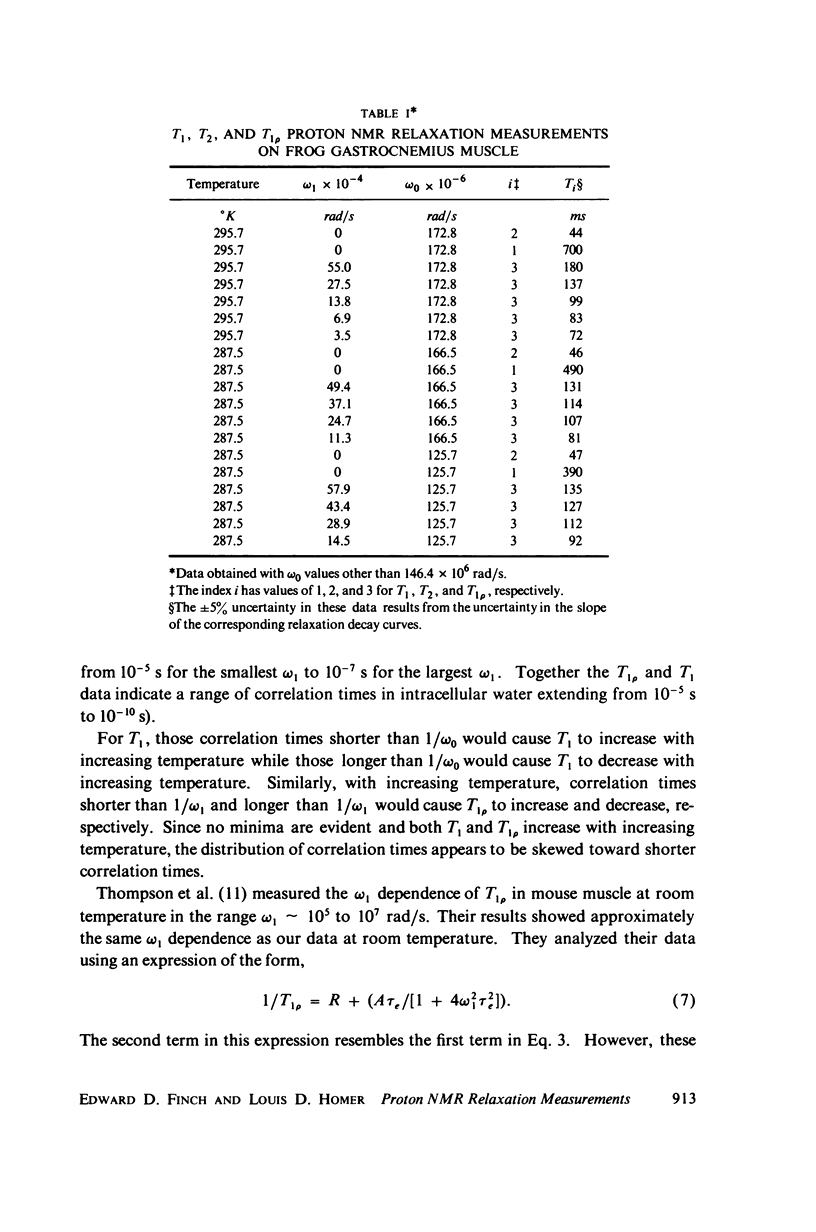
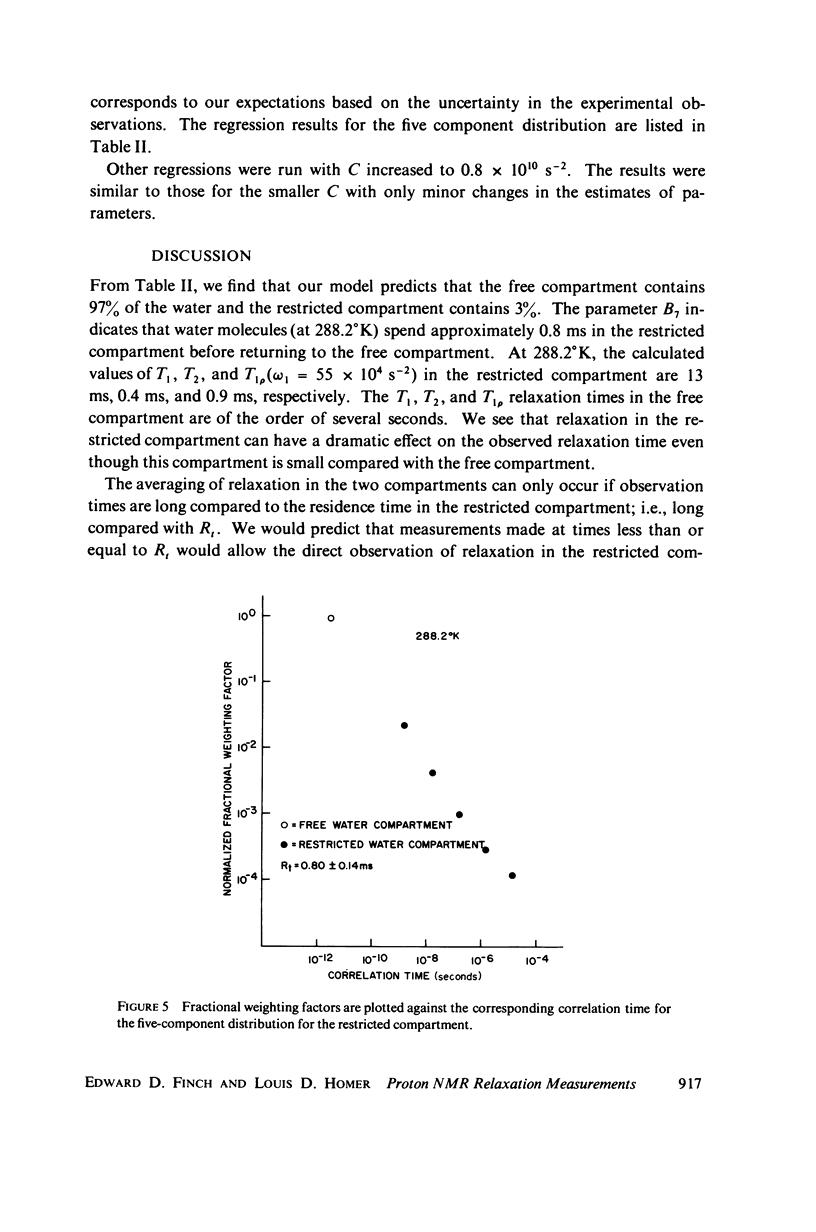
Abstract
Proton nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) relaxation measurements are reported for frog muscle as a function of temperature and Larmor frequency. Each T1ρ, T2, and T1 measurement covered a time domain sufficient to identify the average relaxation time for most intracellular water. Using regression analysis the data were fit with a model where intracellular water molecules are exchanging between a large compartment in which mobility is similar to ordinary water and a small compartment in which motion is restricted. The regression results suggest that: the restricted compartment exhibits a distribution of motions skewed toward that of free water; the residence time of water molecules in the restricted compartment is approximately 1 ms; and, the activation entropy for some water molecules in the restricted compartment is negative.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abetsedarskaia L. A., Miftakhutdinova F. G., Fedotov V. D. O sostoianii vody v zhivykh tkaniakh (rezul'taty issledovanii metodom IaMR-spinovoe ékho) Biofizika. 1968 Jul-Aug;13(4):630–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRATTON C. B., HOPKINS A. L., WEINBERG J. W. NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE STUDIES OF LIVING MUSCLE. Science. 1965 Feb 12;147(3659):738–739. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3659.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belton P. S., Jackson R. R., Packer K. J. Pulsed NMR studies of water in striated muscle. I. Transverse nuclear spin relaxation times and freezing effects. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 24;286(1):16–25. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. C., Rorschach H. E., Nichols B. L., Hazlewood C. F. Implications of diffusion coefficient measurements for the structure of cellular water. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Mar 30;204:434–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb30796.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R., Wien R. The state of water in muscle tissue as determined by proton nuclear magnetic resonance. Biophys J. 1971 Dec;11(12):1002–1017. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(71)86274-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope F. W. Nuclear magnetic resonance evidence using D2O for structured water in muscle and brain. Biophys J. 1969 Mar;9(3):303–319. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86388-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch E. D., Harmon J. F., Muller B. H. Pulsed NMR measurements of the diffusion constant of water in muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Nov;147(1):299–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90337-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good W. The role of water in the origin of life and its function in the primitive gene. J Theor Biol. 1973 May;39(2):249–276. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(73)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. R. Pulsed NMR study of water mobility in muscle and brain tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971;230(3):482–486. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S. C., Hoekstra P. Dielectric relaxation spectra of water adsorbed on lysozyme. J Phys Chem. 1972 Oct 12;76(21):2987–2994. doi: 10.1021/j100665a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazlewood C. F., Chang D. C., Nichols B. L., Woessner D. E. Nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation times of water protons in skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1974 Aug;14(8):583–606. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85937-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S. H., Schillinger W. E. Nuclear magnetic relaxation dispersion in protein solutions. I. Apotransferrin. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3283–3289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuntz I. D., Jr, Brassfield T. S. Hydration of macromolecules. II. Effects of urea on protein hydration. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Feb;142(2):660–664. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90532-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masszi G. Dielectric relaxation and water structure in gelatine solutions. Acta Biochim Biophys Acad Sci Hung. 1972;7(4):349–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Outhred R. K., George E. P. Water and ions in muscles and model systems. Biopolymers. 1973 Feb;13(2):97–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter J. A., Hope A. B. Proton magnetic resonance studies of water in slime mould plasmodia. Aust J Biol Sci. 1971 Jun;24(3):497–507. doi: 10.1071/bi9710497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner D. E., Snowden B. S., Jr A pulsed NMR study of dynamics and ordering of water molecules in interfacial systems. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Mar 30;204:113–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb30774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


