Abstract
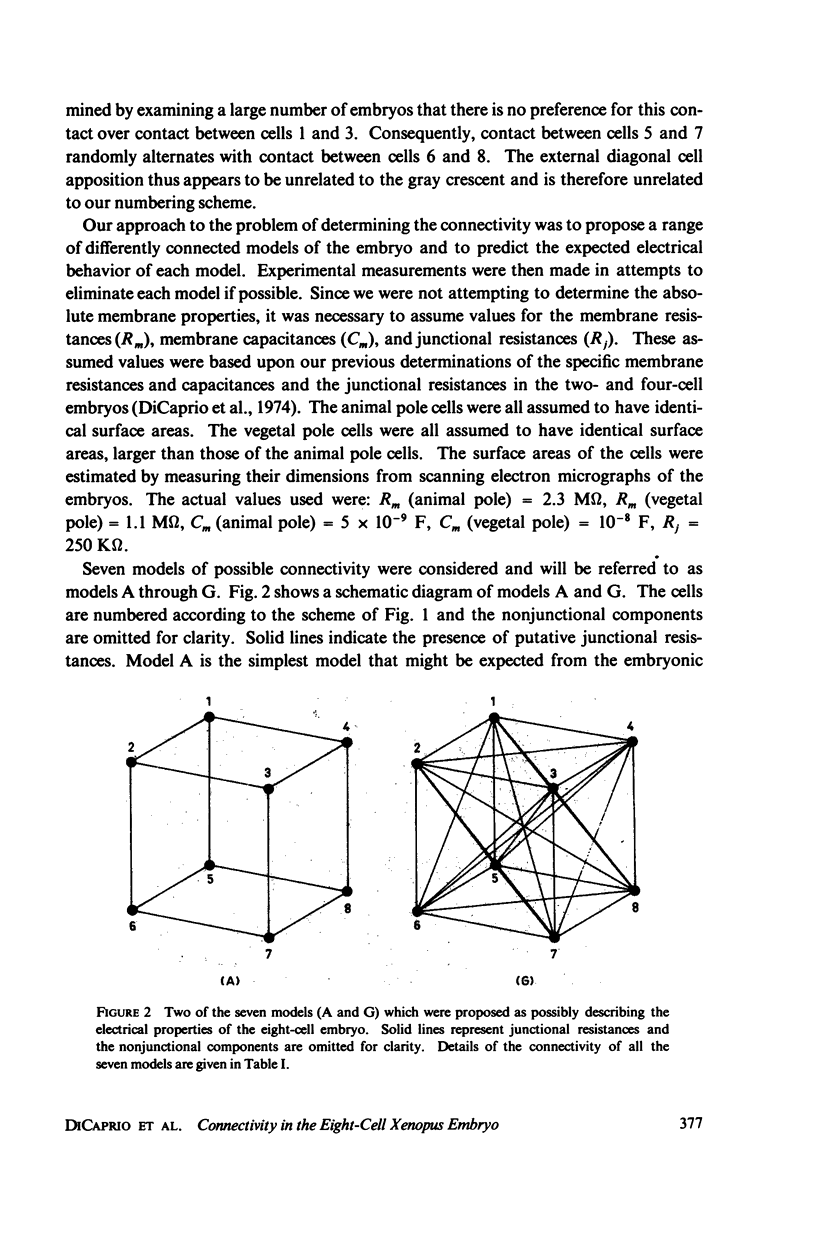
The distribution of individual intercellular electrical junctions has been examined in eight-cell Xenopus embryos using linear systems analysis. Morphological evidence for corresponding intercellular contacts has been sought by light microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. The electrical investigation indicated that each cell is directly coupled to each of the other seven cells by identical resistive junctions. Scanning electron microscopy of the cell surfaces of cleaved embryos revealed protrusions from the surfaces of the cells which could mediate such intercellular connections. Light microscopy of serial sections through the embryos also showed fine processes of the cell surfaces which come into contact with several other cells. The complete intercellular connectivity suggested by these results appears to be an extension of similarly close connectivity in the two- and four-cell embryos. The possible significance of this high connectivity to morphogenesis is discussed.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azarnia R., Larsen W. J., Loewenstein W. R. The membrane junctions in communicating and noncommunicating cells, their hybrids, and segregants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):880–884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. V., Spira M. E., Pappas G. D. Properties of electrotonic junctions between embryonic cells of Fundulus. Dev Biol. 1972 Dec;29(4):419–435. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90082-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. V., Trinkaus J. P. Electrical coupling between embryonic cells by way of extracellular space and specialized junctions. J Cell Biol. 1970 Mar;44(3):592–610. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.3.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawid I. B. Deoxyribonucleic acid in amphibian eggs. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):581–599. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80313-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicaprio R. A., French A. S., Sanders E. J. Dynamic Properties of Electrotonic Coupling between Cells of Early Xenopus Embryos. Biophys J. 1974 May;14(5):387–411. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85923-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French A. S. Automated spectral analysis of neurophysiological data using intermediate magnetic tape storage. Comput Programs Biomed. 1973 Mar;3(1):45–57. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(73)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furshpan E. J., Potter D. D. Low-resistance junctions between cells in embryos and tissue culture. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1968;3:95–127. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60352-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROBSTEIN C. Cell contact in relation to embryonic induction. Exp Cell Res. 1961;Suppl 8:234–245. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90352-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUSTAFSON T. CELLULAR MECHANISMS IN THE MORPHOGENESIS OF THE SEA URCHIN EMBRYO. CELL CONTACTS WITHIN THE ECTODERM AND BETWEEN MESENCHYME AND ECTODERM CELLS. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Dec;32:570–589. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilula N. B., Reeves O. R., Steinbach A. Metabolic coupling, ionic coupling and cell contacts. Nature. 1972 Feb 4;235(5336):262–265. doi: 10.1038/235262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Hori N. Electrical characteristics of Triturus egg cells during cleavage. J Gen Physiol. 1966 May;49(5):1019–1027. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.5.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Loewenstein W. R. Ionic communication between early embryonic cells. Dev Biol. 1969 Mar;19(3):228–243. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(69)90062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalt M. R., Tandler B. A study of fixation of early amphibian embryos for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Sep;36(5):633–645. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. On the genesis of cellular communication. Dev Biol. 1967 Jun;15(6):503–520. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(67)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Permeability of membrane junctions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):441–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordling S., Miettinen H., Wartiovaara J., Saxén L. Transmission and spread of embryonic induction. I. Temporal relationships in transfilter induction of kidney tubules in vitro. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1971 Oct;26(2):231–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. F., Slack C. Some bio-electric parameters of early Xenopus embryos. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1970 Nov;24(3):535–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payton B. W., Bennett M. V., Pappas G. D. Permeability and structure of junctional membranes at an electrotonic synapse. Science. 1969 Dec 26;166(3913):1641–1643. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3913.1641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter K. R., Todaro G. J., Fonte V. A scanning electron microscope study of surface features of viral and spontaneous transformants of mouse Balb-3T3 cells. J Cell Biol. 1973 Dec;59(3):633–642. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan J. D. Dye movement and low-resistance junctions between reaggregated embryonic cells. Dev Biol. 1971 Dec;26(4):627–636. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singal P. K., Sanders E. J. An ultrastructural study of the first cleavage of Xenopus embryos. J Ultrastruct Res. 1974 Jun;47(3):433–451. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(74)90019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack C., Palmer J. F. The permeability of intercellular junctions in the early embryo of Xenopus laevis, studied with a fluorescent tracer. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Jun;55(3):416–419. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90577-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack C., Warner A. E. Intracellular and intercellular potentials in the early amphibian embryo. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(2):313–330. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Laat W. S., Bluemink J. G. New membrane formation during cytokinesis in normal and cytochalasin B-treated eggs of Xenopus laevis. II. Electrophysiological observations. J Cell Biol. 1974 Mar;60(3):529–540. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.3.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







